Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group8 110807043046 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
gkalr54Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group8 110807043046 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
gkalr54Copyright:
Available Formats
Group
Addresses decisions on
Acquisition Utilization Allocation
of limited production resources Resources include the production facilities, labor and materials. Constraints include the availability of resources, delivery times for the products and management policies. Oct-12
Main objective is to take appropriate decisions. Typical decisions
Work force level Production lot sizes Assignment of overtime Sequencing of production runs
Oct-12
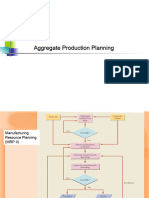
Process Planning
Re-planning
Scheduling
Corrective Action
Functions of PPC
Loading
Follow up Dispatching
Combining Functions
Oct-12
Objective
To predict demand for planning purposes
Laws of Forecasting
Forecasts are always wrong Forecasts always change The further into the future, the less reliable the
forecast will be
Oct-12
5
Qualitative Demand Forecasting
Prediction Market Delphi Technique Game Theory Intentions and Expectations Surveys Conjoint Analysis
Oct-12
Quantitative Demand Forecasting
Discrete Event Simulation Quantitative Analogies Neural Networks Data Mining Causal Models Segmentation
Oct-12
Concerned with timetable of production
Scheduling arranges the different manufacturing operations in order of priority, fixing the time & date for the commencement & completion of each operation. Types of scheduling
Forward scheduling Backward scheduling
Oct-12
8
The pattern of scheduling differs from one job to another which is explained as below.
Master Schedule Production Schedule Manufacturing Schedule Scheduling of Job Order Manufacturing
Oct-12
To find out and direct
Right people Right place Right time Right price
Oct-12
10
Issues
Basic Staffing Calculations and labor hours Working Environment Flexibility/Agility Quality
Oct-12
11
Oct-12
12
The process of determining the production
capacity needed to meet changing demands
Maximum amount of work that an organization is
capable of completing in a given period of time
Oct-12
13
Wrong Capacity
Oct-12
14
Classes of capacity planning
Lead strategy Lag strategy Match strategy
Oct-12
15
Issues
Stand-alone capacities and congestion effects Capacity Strategy Make-or-Buy Flexibility Scalability and learning curves
Oct-12
16
JIT is the technique for reducing inventories and elimination of waste in the production system. Objectives
To eliminate waste To improve quality To minimize lead time To reduce costs To improve productivity
Oct-12
17
Pull production and kanban JIT is associated with pull systems. Toyota was the first developer of kanban system. Examples
McDonalds' Office Xerox Paper
Oct-12
18
Issues
JIT Interdependencies Implementing Issues JIT purchasing Expected Outcomes
Oct-12
19
You might also like
- Chap012.ppt Facilities and Aggregate PlanningDocument25 pagesChap012.ppt Facilities and Aggregate PlanningSaad Khadur EilyesNo ratings yet
- Case study on launch of new credit card using PERT and CPMDocument34 pagesCase study on launch of new credit card using PERT and CPMMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- PPCDocument87 pagesPPCPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Resource Allocation Process (Crashing and Crunching)Document36 pagesResource Allocation Process (Crashing and Crunching)LokamNo ratings yet
- SCHEDULINGDocument29 pagesSCHEDULINGkishoreNo ratings yet
- ERP - The Way Forward by Habit ConsultingDocument41 pagesERP - The Way Forward by Habit Consultingtheglobalist2003No ratings yet
- Implementing Demantra As A Replacement To A Legacy Forecasting Tool: A TI Success StoryDocument73 pagesImplementing Demantra As A Replacement To A Legacy Forecasting Tool: A TI Success StoryRai Prashant Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Resource Allocation and Crashing TechniquesDocument34 pagesResource Allocation and Crashing TechniquesShekhar Singh100% (1)
- TPS, ERP & Enterprise AppsDocument30 pagesTPS, ERP & Enterprise AppsSahil WadhwaNo ratings yet
- AggPlanning - PKBDocument47 pagesAggPlanning - PKBAugust LewisNo ratings yet
- Bhatt Tang Dong Wang WhitepaperDocument8 pagesBhatt Tang Dong Wang Whitepaperapi-247208605No ratings yet
- Production PlanningDocument17 pagesProduction Planningswapnarao12No ratings yet
- Product Development Processes: Prof. Olivier de WeckDocument43 pagesProduct Development Processes: Prof. Olivier de Wecksamknight2009No ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning and SchedulingDocument7 pagesAggregate Planning and SchedulingTeerraNo ratings yet
- Pom Presentation - Group 6Document19 pagesPom Presentation - Group 6Neetu PandeyNo ratings yet
- My APICS CPIM MPR NotesDocument45 pagesMy APICS CPIM MPR NotesMarkusTruelove100% (1)
- JIT Production System Theory, Benefits & ImplementationDocument31 pagesJIT Production System Theory, Benefits & ImplementationHitesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Chap012 - Aggregate PlanningDocument29 pagesChap012 - Aggregate PlanningAgentSkySkyNo ratings yet
- DS412:IntroDocument15 pagesDS412:IntroDavid HuNo ratings yet
- Ch09 - Resource AllocationDocument36 pagesCh09 - Resource AllocationDjana AnhNo ratings yet
- A3 ThinkingDocument17 pagesA3 Thinkingfdsa01100% (5)
- Resource AllocationDocument44 pagesResource AllocationShekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Resource Allocation IIIDocument32 pagesResource Allocation IIIMCA DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Industrial Facilities Design: (7 Term, Batch 2009)Document32 pagesIndustrial Facilities Design: (7 Term, Batch 2009)SadiaAslamNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Production Planning and ControlDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Production Planning and Controlh03318kj100% (1)
- Production Planning and Control - I: Dr. Alok ChoudharyDocument39 pagesProduction Planning and Control - I: Dr. Alok ChoudharyJason LeeNo ratings yet
- Aggregate PlanningDocument134 pagesAggregate PlanningPriya Singh100% (1)
- Operations Management: - Aggregate PlanningDocument56 pagesOperations Management: - Aggregate PlanningWisena PercekaNo ratings yet
- SOP PresentationDocument49 pagesSOP PresentationMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- SOP Outline 2013-14Document3 pagesSOP Outline 2013-14Mohit KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning OPCDocument20 pagesAggregate Planning OPCMaithili PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Production PlanningDocument30 pagesAggregate Production PlanningViksit TripathiNo ratings yet
- Optimize IT Portfolio and Achieve Business ObjectivesDocument13 pagesOptimize IT Portfolio and Achieve Business Objectivesdhruv_agarwalNo ratings yet
- Project Time ManagementDocument26 pagesProject Time Managementshriramsridhar100% (1)
- Applications of Operations Research in The Field of EngineeringDocument12 pagesApplications of Operations Research in The Field of EngineeringMeghs KeshNo ratings yet
- What Is PlanningDocument33 pagesWhat Is PlanningkelazindagikaNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Production Planning and ControlDocument6 pagesThesis On Production Planning and Controldwtnpjyv100% (2)
- PPP CapacityPlanDocument23 pagesPPP CapacityPlanuddindjmNo ratings yet
- AgileDocument29 pagesAgileRohit Khurana100% (1)
- VIP For Capital ProjectsDocument24 pagesVIP For Capital ProjectsNoman Abu-FarhaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Demand To Plan OverviewDocument53 pagesOracle Demand To Plan Overviewaedsouza100% (1)
- Topic 5 - Aggregate PlanningDocument46 pagesTopic 5 - Aggregate PlanningWan ArifNo ratings yet
- 14 Midterm ExamDocument167 pages14 Midterm Examapi-2978344330% (1)
- Mb0044 Unit 13 SLMDocument22 pagesMb0044 Unit 13 SLMamit_idea1100% (2)
- Operation ManagementDocument7 pagesOperation ManagementrabiaumarNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning and MPS - Final 2009Document28 pagesAggregate Planning and MPS - Final 2009Savya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Production Planning By: DeepakDocument58 pagesAggregate Production Planning By: DeepakMadhuri ReddyNo ratings yet
- It and RetailDocument49 pagesIt and RetailchetnachhabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Allocating ResourcesDocument60 pagesChapter 6 - Allocating ResourcesAbdur RashidNo ratings yet
- BPC Tricks, TipsDocument134 pagesBPC Tricks, TipsTrivikram As100% (5)
- SD Part1Document71 pagesSD Part1Glen AndersonNo ratings yet
- 03 - Master DataDocument58 pages03 - Master DataAgnihotri VikasNo ratings yet
- Sales and Operations Planning: Taruna Nagpal Sean O'Donnell Anthony Stramecki Vivian YuDocument49 pagesSales and Operations Planning: Taruna Nagpal Sean O'Donnell Anthony Stramecki Vivian YuRockey MoseNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Project Time ManagementDocument24 pagesStudy Notes Project Time ManagementhumaidjafriNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Facilities Design & Material Handling: Sixth EditionFrom EverandManufacturing Facilities Design & Material Handling: Sixth EditionNo ratings yet
- Master Scheduling: A Practical Guide to Competitive ManufacturingFrom EverandMaster Scheduling: A Practical Guide to Competitive ManufacturingNo ratings yet
- Plan Do Check Act: Lean Six Sigma Project Execution Essentials, #1From EverandPlan Do Check Act: Lean Six Sigma Project Execution Essentials, #1No ratings yet
- Agile by Design: An Implementation Guide to Analytic Lifecycle ManagementFrom EverandAgile by Design: An Implementation Guide to Analytic Lifecycle ManagementNo ratings yet
- WWW Vskills in Practice Lean Manufacturing Mock TestDocument34 pagesWWW Vskills in Practice Lean Manufacturing Mock TestRoopesh KesavarajuNo ratings yet
- OM3 CH 17 Lean Operating SystemsDocument11 pagesOM3 CH 17 Lean Operating SystemsGanessa Roland100% (1)
- Operations Management - Theory and Practice - B. MahadevanDocument1,195 pagesOperations Management - Theory and Practice - B. MahadevanBhavya Gupta94% (127)
- Lect12 - Kanban SystemsDocument37 pagesLect12 - Kanban Systemsmaniea1990100% (1)
- Bajaj Auto's Lean Manufacturing TransformationDocument16 pagesBajaj Auto's Lean Manufacturing TransformationArjun K BhagatNo ratings yet
- 086 - ME8094, ME6703 Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems - Question BankDocument6 pages086 - ME8094, ME6703 Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems - Question BankJeganNo ratings yet
- Resume For Marclyn Paige - 2019Document2 pagesResume For Marclyn Paige - 2019api-355608555No ratings yet
- Software Project ManagementDocument55 pagesSoftware Project ManagementSuyog Nepal100% (1)
- Pazek K. Lean Manufacturing 2021Document223 pagesPazek K. Lean Manufacturing 2021Mourad Ben OthmaneNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument8 pagesCase StudiesGowtham RasamsettyNo ratings yet
- SCM Project - Final ReportDocument10 pagesSCM Project - Final Reportmuwadit AhmedNo ratings yet
- Apple Computer's Suppliers Hubs: A Tale of Three CitiesDocument23 pagesApple Computer's Suppliers Hubs: A Tale of Three CitiesSudha VungaralaNo ratings yet
- Lean Logistics Case Study SpotlightDocument1 pageLean Logistics Case Study SpotlightPiyush PatelNo ratings yet
- TPS Basics TRG Material (Supplier)Document185 pagesTPS Basics TRG Material (Supplier)Jai Veer Singh100% (1)
- Kanban Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageKanban Cheat Sheet PDFstewatiaNo ratings yet
- Important supply chain concepts handbookDocument65 pagesImportant supply chain concepts handbookAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Boeing's Lean Manufacturing Strategies for Waste Elimination and Continuous ImprovementDocument40 pagesBoeing's Lean Manufacturing Strategies for Waste Elimination and Continuous ImprovementTina Vaz0% (1)
- Toyota Production System (TPS)Document20 pagesToyota Production System (TPS)Loxman ZahariNo ratings yet
- OM Quiz MergedDocument12 pagesOM Quiz MergedMba ForLife100% (1)
- The State of The Art of Agile Kanban Method ChalleDocument16 pagesThe State of The Art of Agile Kanban Method Challe21P113 - MOHAMMED FAHAD ANo ratings yet
- Shriram PistonsDocument91 pagesShriram PistonsAmarAulakh0% (1)
- DENSO's Relationship with Toyota and Global Supplier StrategyDocument4 pagesDENSO's Relationship with Toyota and Global Supplier StrategySingye S Samdrup100% (2)
- Chapter 16 - JIT and Lean OperationsDocument62 pagesChapter 16 - JIT and Lean OperationsGennia Mae MartinezNo ratings yet
- PPC Materials MRPDocument33 pagesPPC Materials MRPHarshwardhan PhatakNo ratings yet
- JIT Mod 5Document11 pagesJIT Mod 5hetsagarNo ratings yet
- MCQ DivyaDocument6 pagesMCQ DivyaEng-Ahmed BaasaayNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps to Achieving Lean ProductionDocument14 pages10 Steps to Achieving Lean ProductionTuğrul BesciNo ratings yet
- Toyota Production SystemDocument37 pagesToyota Production Systemjaiswalswatin87100% (1)
- Kanban System Analysis and Improvement of The Supply Carset in BMW Logistics at Jakarta Plant Using Just in Time (JIT) MethodDocument9 pagesKanban System Analysis and Improvement of The Supply Carset in BMW Logistics at Jakarta Plant Using Just in Time (JIT) MethodInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Overview of Six SigmaDocument51 pagesOverview of Six SigmastefanhenryNo ratings yet