Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knight Ch14
Uploaded by
aaljuhani123Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knight Ch14
Uploaded by
aaljuhani123Copyright:
Available Formats
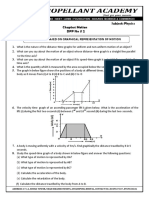
Chapter 14
An object moves with simple harmonic motion. If the amplitude and the period are both doubled, the objects maximum speed is
1. quartered. 2. halved. 3. quadrupled. 4. doubled. 5. unchanged.
An object moves with simple harmonic motion. If the amplitude and the period are both doubled, the objects maximum speed is
1. quartered. 2. halved. 3. quadrupled. 4. doubled. 5. unchanged.
The figure shows four oscillators at t = 0. Which one has the phase constant
1) a
2) b 3) c
4) d
The figure shows four oscillators at t = 0. Which one has the phase constant
1) a
2) b 3) c
4) d
Four springs have been compressed from their equilibrium position at x = 0 cm. When released, they will start to oscillate. Rank in order, from highest to lowest, the maximum speeds of the oscillators.
1. c > b > a = d
2. c > b > a > d
3. d > a > b > c 4. a = d > b > c 5. b > c > a = d
Four springs have been compressed from their equilibrium position at x = 0 cm. When released, they will start to oscillate. Rank in order, from highest to lowest, the maximum speeds of the oscillators.
1. c > b > a = d
2. c > b > a > d
3. d > a > b > c 4. a = d > b > c 5. b > c > a = d
This is the position graph of a mass on a spring. What can you say about the velocity and the force at the instant indicated by the dotted line?
1. Velocity is positive; force is to the right. 2. Velocity is negative; force is to the left. 3. Velocity is negative; force is to the right. 4. Velocity is zero; force is to the right. 5. Velocity is zero; force is to the left.
This is the position graph of a mass on a spring. What can you say about the velocity and the force at the instant indicated by the dotted line?
1. Velocity is positive; force is to the right. 2. Velocity is negative; force is to the left. 3. Velocity is negative; force is to the right. 4. Velocity is zero; force is to the right. 5. Velocity is zero; force is to the left.
One person swings on a swing and finds that the period is 3.0 s. Then a second person of equal mass joins him. With two people swinging, the period is
1. 1.5 s. 2. <3.0 s but not necessarily 1.5 s. 3. 3.0 s. 4. >3.0 s but not necessarily 6.0 s. 5. 6.0 s.
One person swings on a swing and finds that the period is 3.0 s. Then a second person of equal mass joins him. With two people swinging, the period is
1. 1.5 s. 2. <3.0 s but not necessarily 1.5 s. 3. 3.0 s. 4. >3.0 s but not necessarily 6.0 s. 5. 6.0 s.
Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the time constants of the decays shown in the figure. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the time constants of the decays shown in the figure. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Chapter 14 Reading Quiz
What is the name of the quantity represented by the symbol
1. Angular momentum 2. Angular frequency 3. Phase constant 4. Uniform circular motion 5. Centripetal acceleration
What is the name of the quantity represented by the symbol
1. Angular momentum 2. Angular frequency 3. Phase constant 4. Uniform circular motion 5. Centripetal acceleration
What term is used to describe an oscillator that runs down and eventually stops?
1. Tired oscillator 2. Out of shape oscillator 3. Damped Oscillator 4. Resonant oscillator 5. Driven oscillator
What term is used to describe an oscillator that runs down and eventually stops?
1. Tired oscillator 2. Out of shape oscillator 3. Damped Oscillator 4. Resonant oscillator 5. Driven oscillator
The starting conditions of an oscillator are characterized by
1. the initial acceleration. 2. the phase constant. 3. the phase angle. 4. the frequency.
The starting conditions of an oscillator are characterized by
1. the initial acceleration. 2. the phase constant. 3. the phase angle. 4. the frequency.
Wavelength is
1. the time in which an oscillation repeats itself. 2. the distance in which an oscillation repeats itself. 3. the distance from one end of an oscillation to the other. 4. the maximum displacement of an oscillator. 5. not discussed in Chapter 14.
Wavelength is
1. the time in which an oscillation repeats itself. 2. the distance in which an oscillation repeats itself. 3. the distance from one end of an oscillation to the other. 4. the maximum displacement of an oscillator. 5. not discussed in Chapter 14.
You might also like
- NAKED Singularities - PenroseDocument10 pagesNAKED Singularities - PenroseLeon FosiltNo ratings yet
- Margaret A. NewmanDocument7 pagesMargaret A. NewmanMarde Cabucos Phillip Bonachita100% (2)
- Wave Motion. But There Are Also Three Points On The Rope That Are Colored Red. When You ObserveDocument8 pagesWave Motion. But There Are Also Three Points On The Rope That Are Colored Red. When You ObserveG4 BARRERA, Francheska Denise N.No ratings yet
- FreeVibrationTutorial FromFreeStudy PDFDocument26 pagesFreeVibrationTutorial FromFreeStudy PDFJim HarrisNo ratings yet
- Regw PDFDocument66 pagesRegw PDFVikas TomarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE A2 Physics Unit 4 Oscillations Test 14 - 15 With Marks SchemeDocument27 pagesEdexcel GCE A2 Physics Unit 4 Oscillations Test 14 - 15 With Marks SchemePaul Burgess100% (1)
- Dynamics Tutorial 10-Natural Vibrations-One Degree of Freedom-27p PDFDocument31 pagesDynamics Tutorial 10-Natural Vibrations-One Degree of Freedom-27p PDFmanfredm6435No ratings yet
- Reg WDocument66 pagesReg WCeline ColeNo ratings yet
- A2 Oscillation PDFDocument29 pagesA2 Oscillation PDFhussainNo ratings yet
- 09 Rotational MotionDocument10 pages09 Rotational MotionBalaram MullapudiNo ratings yet
- OscillationDocument34 pagesOscillationApex Institute100% (2)
- 10SHM PDFDocument6 pages10SHM PDFAman BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Transverse PulsesDocument17 pagesTransverse PulsesMundu MustafaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th CH 10 PhysicsDocument3 pagesClass 10th CH 10 PhysicsIrteza khan100% (1)
- PhysicsLAB - Period of A PendulumDocument3 pagesPhysicsLAB - Period of A PendulumCitizen Kwadwo AnsongNo ratings yet
- Knight Ch13dDocument20 pagesKnight Ch13dAgam MittalNo ratings yet
- 1 TVgovindrajDocument10 pages1 TVgovindrajvijaynagathanNo ratings yet
- Free VibrationsDocument27 pagesFree Vibrationshelllooo00No ratings yet
- 17.1 17.3 Oscillations SHM and EnergyDocument26 pages17.1 17.3 Oscillations SHM and EnergyTruly SkunkedNo ratings yet
- Waves Sound HWDocument1 pageWaves Sound HWaxiang88No ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations Lecture NotesDocument133 pagesMechanical Vibrations Lecture NotesHarrison AdemuNo ratings yet
- I PU Viva QuestionsDocument4 pagesI PU Viva QuestionsPoornima M SNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics Halfyearly Important QuestionsDocument3 pages1st Year Physics Halfyearly Important QuestionsmohiuddinmanzoorsyedNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Time Period of A Simple PendulumDocument32 pagesFactors Affecting The Time Period of A Simple PendulumLow Ban HengNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lecture ppt-GOOLE CLASSDocument69 pagesUnit 1 Lecture ppt-GOOLE CLASSajay amuthaprianNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law and SHMDocument9 pagesHookes Law and SHMzahraNo ratings yet
- مختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumDocument6 pagesمختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumm9ngmnsxp4No ratings yet
- Free Damped and Forced OscillationsDocument4 pagesFree Damped and Forced OscillationsjcblackmoreNo ratings yet
- SCINCE NOTES Part IDocument16 pagesSCINCE NOTES Part ISANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Q2 - Module 3Document14 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Q2 - Module 3grizNo ratings yet
- TASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)Document3 pagesTASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)frank 101No ratings yet
- TASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)Document3 pagesTASK 1 Physics Class XI: (Do Always Any Five Numerical Problems Related To The Chapter)frank 101No ratings yet
- JR. Physics Important QsDocument10 pagesJR. Physics Important QsRocky WaterNo ratings yet
- Physics1styr 2marksDocument7 pagesPhysics1styr 2marksRP Sir QuizzesNo ratings yet
- Simple Pendulum (Hemn) SoundDocument9 pagesSimple Pendulum (Hemn) Soundhemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Physics QuizDocument17 pagesPhysics QuizReenNo ratings yet
- Walter Lewin Notes 5Document12 pagesWalter Lewin Notes 5Romesor ApolNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Circular MotionDocument13 pagesCH 3 - Circular MotionRabbitNo ratings yet
- Welcome To This Course Physics 1Document31 pagesWelcome To This Course Physics 1andrewsiby63No ratings yet
- IC Sol W13D1-3Document9 pagesIC Sol W13D1-3nzewd720gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Important Questions 2019 - 2020Document3 pages1st Year Important Questions 2019 - 2020Lohith CharyNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus: Quarter 2 - Module 5Document17 pagesPre-Calculus: Quarter 2 - Module 5Mark Allen LabasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 New-2Document37 pagesChapter 13 New-2BeirutmarathonNo ratings yet
- Web Dao Đ NG Và SóngDocument6 pagesWeb Dao Đ NG Và SóngdinhlynhndNo ratings yet
- Fizy LabDocument6 pagesFizy LabSafwan BakrmanyNo ratings yet
- SHM Notes CompleteDocument58 pagesSHM Notes CompleteTushar SinghNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of Forces Physics4Document15 pagesTurning Effect of Forces Physics4dddeeeezzzNo ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum Simple Harmonic OscillatorDocument4 pagesThe Simple Pendulum Simple Harmonic OscillatortpsoftxNo ratings yet
- SCINCE NOTES Part 1 OCT 1Document16 pagesSCINCE NOTES Part 1 OCT 1SANJAY GANGANNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument22 pagesWavesMawande WandarhNo ratings yet
- M.A Ch13 L13.1 Phy. GR 10Document10 pagesM.A Ch13 L13.1 Phy. GR 10هخه •No ratings yet
- WavesDocument31 pagesWavesShauna Prettygyol HamilNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document3 pagesWorksheet 2Anushka GandhiNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Lab - Basic VersionDocument6 pagesPendulum Lab - Basic VersionTeachLABScINo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers, 6e: Chapter 15 - Oscillatory MotionDocument19 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers, 6e: Chapter 15 - Oscillatory Motionaisyah syazwaniNo ratings yet
- Energy Oscillating Vibrating: Smsains Muzaffar SyahDocument11 pagesEnergy Oscillating Vibrating: Smsains Muzaffar Syahhasl arbNo ratings yet
- Online Phys12 Mid ExamDocument3 pagesOnline Phys12 Mid ExamJanisa SacariaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Motion. Equations, GraphsDocument12 pagesMotion. Equations, GraphsManash SinghaNo ratings yet
- Emilio Elizalde Et Al - Casimir Effect in de Sitter and Anti-De Sitter BraneworldsDocument36 pagesEmilio Elizalde Et Al - Casimir Effect in de Sitter and Anti-De Sitter BraneworldsTurmav12345No ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics All in One Notes-87-151Document65 pages1st Year Physics All in One Notes-87-151Zoya NaeemNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B Notes - Kinematics in One DimensionDocument8 pagesAP Physics B Notes - Kinematics in One DimensionAndy He100% (1)
- The Collected Essays of Dewey B LarsonDocument148 pagesThe Collected Essays of Dewey B LarsonDavid WaycasterNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument6 pagesCircular Motion, Kinetics, Mechanics Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (1)
- Blau. Lectures Notes On GR PDFDocument550 pagesBlau. Lectures Notes On GR PDFDavid PrietoNo ratings yet
- Kinematic of Linear Motion Matriculation STPMDocument79 pagesKinematic of Linear Motion Matriculation STPMJue Saadiah100% (9)
- General Relativity Solved ProblemsDocument81 pagesGeneral Relativity Solved ProblemsGag PafNo ratings yet
- Free Fall Lab ReportDocument9 pagesFree Fall Lab Reportapi-410426030No ratings yet
- Graphical Representation of MotionDocument23 pagesGraphical Representation of Motionkumargaurav0391No ratings yet
- Free Fall: Lab ReportDocument20 pagesFree Fall: Lab Reportapi-514272917No ratings yet
- Concept QuizDocument55 pagesConcept QuizhaloNo ratings yet
- HW04 - EnergyDocument6 pagesHW04 - EnergyBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 106: Uniform Circular MotionDocument7 pagesExperiment 106: Uniform Circular MotionJasmin DionisioNo ratings yet
- Commands of SQLDocument4 pagesCommands of SQLMayur GawadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 09 Multiple Choice Questions With Answersvikrampunia3100% (1)
- Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: D D D DDocument1 pageSynopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: D D D DAishwarya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Some Properties of The Schwarzschild de Sitter and Schwarzschild Anti-De Sitter SpacetimesDocument15 pagesSome Properties of The Schwarzschild de Sitter and Schwarzschild Anti-De Sitter SpacetimesFrancisco Tello OrtizNo ratings yet
- Newtons Second Law of Motion 9 5-9 6 Independent TasksDocument5 pagesNewtons Second Law of Motion 9 5-9 6 Independent Tasksapi-372548146No ratings yet
- Class: 9 Subject: Physics Chapter: Motion DPP No # 2: Questions Based On Graphical Representation of MotionDocument3 pagesClass: 9 Subject: Physics Chapter: Motion DPP No # 2: Questions Based On Graphical Representation of MotionshashwatNo ratings yet
- Using Mathcad For Statics and DynamicsDocument104 pagesUsing Mathcad For Statics and Dynamicskurishi88% (8)
- Cosmology AND Astrophysics: An Elementary IntroductionDocument76 pagesCosmology AND Astrophysics: An Elementary Introductionuhraman100% (1)
- Self Test - Answers: 1. GravitationDocument4 pagesSelf Test - Answers: 1. GravitationAvishkar Patil100% (1)
- MOTIONDocument6 pagesMOTIONAnthropophobe NyctophileNo ratings yet
- Problems On DynamicsDocument3 pagesProblems On DynamicsPablo AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Assignment 01Document2 pagesUnit 2 Assignment 01Jeff BrownNo ratings yet
- Theory Notes of Newton's Laws of Motion For NEET & IIT 2017Document18 pagesTheory Notes of Newton's Laws of Motion For NEET & IIT 2017umved singh yadav90% (10)