Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Retailing
Uploaded by
Divyang PatelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Retailing
Uploaded by
Divyang PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Retailing?
Retail comes from the French word retaillier, which refers to "cutting off, clip and divide" in terms of tailoring (1365). It first was recorded as a noun with the meaning of a "sale in small quantities" in 1433 (French) Retailing involves selling products and services to consumers for their personal or family use As the final link between consumers and manufacturers, retailers are a vital part of the business world. Retailers add value to products by making it easier for manufactures to sell and consumers to buy.
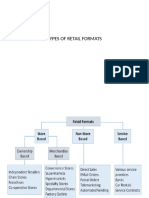
Store Formats by Location
a) Chain store Multi-locational Operates multiple outlets under common ownership Engages in some level of centralized or coordinated purchasing and decision making b) High street format: A retail chain that seeks to locate itself in busy shopping areas (generally less than 2,000 sft, with no parking facilities and focused merchandise categories) c) Destination format: Independent retail stores located specifically in an area with alluring propositions (usually large in size, with ample concessions, huge parking space, wide merchandise categories) d) Convenience store format: Accessible carrying wide array of consumable goods (less than 5,000 sft, extended hours, parking for few vehicles, convenience merchandise)
Store Formats by Ownership
a) Independent Generally higher level of independent retailers exists 50% of these are run by owners and their families Why so many? Ease of entry b) Franchise: A contractual agreement between a franchisor and a retail franchisee, which allows the franchisee to conduct business under an established name and according to a given under an established name and according to a given pattern of business Franchisee pays an initial fee and a monthly percentage of gross sales in exchange for the exclusive rights to sell goods and services in an area
Store Formats by Merchandise Category
a) Family store Store dealing in all categories of related item (For e.g. apparel store offering merchandise to suit the wardrobe of a family) b) Specialty format: Narrow product lines with good depth. Specializing in a given type of merchandise, offering attentive customer services. c) Department store format: Large in size having several departments working as SBUs d) Super market format: Departmentalized, specializing in foodstuff, grocery and limited non-food categories, free access displays so that customers can pick from shelves. e) Emporium: Selling a variety of a particular group of merchandise (sari emporium).
Store Formats by Size
a) Superstore format Single-level large store, twice the size of a supermarket, offers nontraditional goods and services like pharmacy, flower shop, bookstore, salad bar, bakery etc. b) Shopping Mall: Spread over a large area, arrangement of retail stores and places for leisure activities. c) Shopping Center: Plaza combining five or more tenant spaces developed under one building. d) Hypermarket: Wide variety, offering in large quantities in each category selling huge volumes at low margins.
Store Formats by Price
a) Discount format Bazaar format, believing in discounts more often. b) EDLP format: Specialize in a particular merchandise line, assuring consistently low prices. c) Category killer format: Large specialty store having enormous selection of its product category at relatively low prices. d) Factory-outlet format: Owned and operated by the manufacturer e) Warehouse format: Large sale of discontinued merchandise, has large width and depth in many categories it retails. f) Single-price denomination format: Scrambled merchandise at just one price point, generally at a low one.
Retailing formats in India
Malls: The largest form of organized retailing today. Located mainly in metro cities, in proximity to urban outskirts. Ranges from 60,000 sq ft to 7,00,000 sq ft and above. They lend an ideal shopping experience with an amalgamation of product, service and entertainment, all under a common roof. Examples include Shoppers Stop, Piramyd, Pantaloon.
Department Stores: Departmental Stores are expected to take over the apparel business from exclusive brand showrooms. Among these, the biggest success is K Raheja's Shoppers Stop, which started in Mumbai and now has more than seven large stores (over 30,000 sq. ft) across India and even has its own in store brand for clothes called Stop!.
Specialty Stores: Chains such as the Bangalore based Kids Kemp, the Mumbai books retailer Crossword, RPG's Music World and the Times Group's music chain Planet M, are focusing on specific market segments and have established themselves strongly in their sectors. Discount Stores: As the name suggests, discount stores or factory outlets, offer discounts on the MRP through selling in bulk reaching economies of scale or excess stock left over at the season. The product category can range from a variety of perishable/ non perishable goods Department Stores: Large stores ranging from 20000-50000 sq. ft, catering to a variety of consumer needs. Further classified into localized departments such as clothing, toys, home, groceries, etc.
Hypermarts/Supermarkets: Large self service outlets, catering to varied shopper needs are termed as Supermarkets. These are located in or near residential high streets. These stores today contribute to 30% of all food & grocery organized retail sales. Super Markets can further be classified in to mini supermarkets typically 1,000 sq ft to 2,000 sq ft and large supermarkets ranging from of 3,500 sq ft to 5,000 sq ft. having a strong focus on food & grocery and personal sales. Convenience Stores: These are relatively small stores 400-2,000 sq. feet located near residential areas. They stock a limited range of highturnover convenience products and are usually open for extended periods during the day, seven days a week. Prices are slightly higher due to the convenience premium. MBOs : Multi Brand outlets, also known as Category Killers, offer several brands across a single product category. These usually do well in busy market places and Metros.
Global Retailing Facts
GLOBAL RETAIL (Source: CSO, MGI Study) Worlds largest private industry Above US $ 8 trillion sales worldwide annually Accounts for almost 10% of GDP in most countries Major employer in most economies 16% 15% 12% 7% in US in Brazil in Poland in China
Generates competition which results in reduction of prices
product and service innovation
enhanced customer experience Major driver for real estate and urban development
Biggest retail Sales countries of the world
U.S E.U JAPAN
market)
U.S $ 4 tn (13 times of Indian U.S $ 2 tn U.S $ 1 tn
CHINA
U.K
U.S $ 750 bn
U.S $ 444 bn
INDIA
RUSSIA
U.S $ 300 bn
U.S $ 200 bn
Evolution of Indian retail
Historic/Rural Reach Traditional/Pervasiv e Reach Government Supported Modern Formats/ International
Exclusive Brand Outlets Hyper/Super Markets Department Stores Shopping Malls
PDS Outlets Khadi Stores Cooperatives
Convenience Stores Mom and Pop/Kiranas Weekly Markets Village Fairs Melas
Source of Entertainment
Neighborhood Stores/Convenience
Availability/ Low Costs /
Shopping Experience/Efficiency
Current Scenario
Market size Current market size is roughly US$ 300 bn Only 3% is through organized retailing 96% of the 12 Million stores are less than 500 Sq. ft. Forecast Growth rate for the retailing industry is roughly 8.3% for 2003-2008 Sales from large format stores would rise by 24-49% Formal and modern format retailing would enjoy rapid growth
No FDI is allowed in multiple brand retailing 100% FDI allowed in cash & carry format(e.g Walmart-Bharti) 51% FDI allowed in single brand retailing(Nike,Gucci,Versace,Mcdonal d)
You might also like
- Presentation 2Document15 pagesPresentation 2hhaiderNo ratings yet
- Types of Intermediaries - L3Document55 pagesTypes of Intermediaries - L3vijaikumarankamNo ratings yet
- Module V Retail Formats Most Suitable For Fashion Products Quad 2Document58 pagesModule V Retail Formats Most Suitable For Fashion Products Quad 2Richa TiwariNo ratings yet
- Retailing: Retail Industry Service and Product RetailingDocument20 pagesRetailing: Retail Industry Service and Product Retailing222sameerNo ratings yet
- MM Chap 18, RetailingDocument76 pagesMM Chap 18, RetailingTejus ChincholkarNo ratings yet
- RetailingDocument6 pagesRetailingSonakshi WadhwaNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of RetailersDocument26 pages3 Types of Retailersavijit_singh_6No ratings yet
- Retail Managment Basic ConceptDocument7 pagesRetail Managment Basic Conceptaminshahzad7100% (1)
- Chap 10. Channel Institutions - RetailingDocument18 pagesChap 10. Channel Institutions - RetailingAnkur MehtaNo ratings yet
- RTM NotesDocument41 pagesRTM NotesmonstermageshmonsterNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAnand BhartiNo ratings yet
- Retail Management: A Theoritical and Practical PerspectiveDocument14 pagesRetail Management: A Theoritical and Practical PerspectiveJaved KhanNo ratings yet
- RetailDocument20 pagesRetailAdarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Retail Industry (Meaning) : Retail Consists of TheDocument19 pagesRetail Industry (Meaning) : Retail Consists of TheDevi ShreeNo ratings yet
- Global Retailing Scenario: & Its FutureDocument38 pagesGlobal Retailing Scenario: & Its FutureAnkit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Types of RetailerDocument9 pagesTypes of Retailerivanaperez38No ratings yet
- RETAIL MANAGEMENT - by Anant Dhuri (MMS - Marketing Notes) PDFDocument58 pagesRETAIL MANAGEMENT - by Anant Dhuri (MMS - Marketing Notes) PDFAnant Dhuri78% (32)
- Etymology: Retail Consists of TheDocument6 pagesEtymology: Retail Consists of Themaurya526_glaNo ratings yet
- Global Retailing Scenario: & Its FutureDocument38 pagesGlobal Retailing Scenario: & Its FuturejainsanilNo ratings yet
- Retail Project ReportDocument69 pagesRetail Project ReportRaman100% (1)
- Retail Managment by Abhishek JoshiDocument7 pagesRetail Managment by Abhishek Joshiabhijerk2222No ratings yet
- RetailingDocument9 pagesRetailingVarun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Types of RetailersDocument23 pagesTypes of RetailersNisarg ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Retail Consists of The: RetaillerDocument4 pagesRetail Consists of The: RetaillerNaveen ManjeshNo ratings yet
- Types of Retail FormatsDocument19 pagesTypes of Retail FormatsTabish ChishtiNo ratings yet
- Retail ManagementDocument35 pagesRetail Managementpriyarp5075No ratings yet
- Retail: Drawing of A Self-Service StoreDocument6 pagesRetail: Drawing of A Self-Service StoreAmit Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Types of Retail FormatsDocument24 pagesTypes of Retail FormatsMohit LalchandaniNo ratings yet
- Retailing: Retail Consists of TheDocument11 pagesRetailing: Retail Consists of TheVidya SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Retail Format & Their Value PropositionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Retail Format & Their Value PropositionRelly Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Principles of Retailing 1Document64 pagesPrinciples of Retailing 1Keerthi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mansi Manisha PPT - PPTMDocument25 pagesMansi Manisha PPT - PPTMvinit PatidarNo ratings yet
- Retailing: "Retail" and "Retail Stores" Redirect Here. For The Comic Strip by Norm Feuti, SeeDocument12 pagesRetailing: "Retail" and "Retail Stores" Redirect Here. For The Comic Strip by Norm Feuti, SeehariarikatlaNo ratings yet
- What Is RetailDocument8 pagesWhat Is RetailAnjana BaruahNo ratings yet
- 1.basics of Retailing - 1Document27 pages1.basics of Retailing - 1anshushah_144850168No ratings yet
- Retail FormatsDocument33 pagesRetail Formatsyogendra857No ratings yet
- Study of HR Processes and Practices in Reliance Retail 2Document62 pagesStudy of HR Processes and Practices in Reliance Retail 2ghoshsubhankar18440% (1)
- Startegies of RetailingDocument129 pagesStartegies of RetailingDheeraja Raj100% (3)
- Retail FormatsDocument36 pagesRetail FormatsShaurya ThakurNo ratings yet
- Shree Ganeshaya Namah.: End-User Products Manufacturers Consumer Door-To-Door DeliveryDocument8 pagesShree Ganeshaya Namah.: End-User Products Manufacturers Consumer Door-To-Door Deliverynishanth_sudhakaranNo ratings yet
- Case Study TrentDocument11 pagesCase Study TrentKirti SainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Types of Retailers: HDCS 3303 - Section 12711 Introduction To Merchandising Evangeline CaridasDocument45 pagesChapter 2: Types of Retailers: HDCS 3303 - Section 12711 Introduction To Merchandising Evangeline Caridasvenkat_guezzNo ratings yet
- Types of Retailers: Prof. (DR.) CK Dash IMIS, BhubaneswarDocument30 pagesTypes of Retailers: Prof. (DR.) CK Dash IMIS, BhubaneswarChandni SheikhNo ratings yet
- Types of Retail Outlets: Marketplace Market Square City SquareDocument3 pagesTypes of Retail Outlets: Marketplace Market Square City Squarejenkins1989No ratings yet
- Abseentee Assignment - Big BazaarDocument11 pagesAbseentee Assignment - Big Bazaarviplav_nigam95No ratings yet
- The Retail IndustryDocument10 pagesThe Retail Industrydisha_kackerNo ratings yet
- Traditional Retailing of IndiaDocument42 pagesTraditional Retailing of IndiaPradeep SinghalNo ratings yet
- Retail Sector - Group 7Document81 pagesRetail Sector - Group 7Shantveer DodamaniNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Shahbaz Abdullah Mba 3 Sem. 12MBAK-02Document19 pagesPresented By: Shahbaz Abdullah Mba 3 Sem. 12MBAK-02Anonymous 1ClGHbiT0JNo ratings yet
- RETAILINGDocument15 pagesRETAILINGUmer ShirgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Retail Is The Sale of Goods and Services From Individuals or Businesses To TheDocument8 pagesRetail Is The Sale of Goods and Services From Individuals or Businesses To TheashuNo ratings yet
- Retail - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesRetail - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJaya Simha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Updated Rural Retail Store Formats 2019Document16 pagesUpdated Rural Retail Store Formats 2019abhijit sahaNo ratings yet
- The Indian Retail SectorDocument23 pagesThe Indian Retail Sectorkartheek_aldiNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Retail - PoojaDocument32 pages1 Introduction To Retail - PoojaAbhay ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On PantaloonDocument27 pagesProject Report On PantaloonAnilGoyalNo ratings yet
- Retail: Inline CitationsDocument8 pagesRetail: Inline Citationsswap2390No ratings yet
- Branding a Store: How To Build Successful Retail Brands In A Changing MarketplaceFrom EverandBranding a Store: How To Build Successful Retail Brands In A Changing MarketplaceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Long Tail (Review and Analysis of Anderson's Book)From EverandThe Long Tail (Review and Analysis of Anderson's Book)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Trading Up (Review and Analysis of Silverstein and Fiske's Book)From EverandTrading Up (Review and Analysis of Silverstein and Fiske's Book)No ratings yet
- An A-Z Index of The Windows XP Command LineDocument5 pagesAn A-Z Index of The Windows XP Command LineJohn Angelo MartinNo ratings yet
- Basic Email SkillsDocument15 pagesBasic Email SkillsDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Banking - CRM Makes The DifferenceDocument19 pagesBanking - CRM Makes The DifferenceDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Nestle - ZakaDocument11 pagesNestle - ZakazakavisionNo ratings yet
- Sectors of The Indian EconomyDocument5 pagesSectors of The Indian EconomyDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- FruitcakeDocument7 pagesFruitcakeDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Transit Damage ReportDocument1 pageTransit Damage ReportDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- SmarteduDocument1 pageSmarteduDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- MM-03 Inventory Management & Physical InventoryDocument38 pagesMM-03 Inventory Management & Physical InventoryDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Questioner For Exit InterviewDocument5 pagesQuestioner For Exit InterviewDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Designer Operating InstructionsDocument10 pagesDesigner Operating InstructionsDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan Asian Bazar Group 12Document27 pagesMarketing Plan Asian Bazar Group 12Toukir Hossain BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - InferenceDocument16 pagesQuiz 1 - Inferencevasuca2007No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ABM Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementDocument13 pagesLesson Plan ABM Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Managementmarystel b. Borbon100% (1)
- Retail Sales Management AssignmentDocument50 pagesRetail Sales Management AssignmentVarun KatochNo ratings yet
- Pom Exam - 22184Document11 pagesPom Exam - 22184Tooba IqbalNo ratings yet
- Organized Retailing and Its Impact On Traditional Retailing in India: A Case Study of Guwahati CityDocument20 pagesOrganized Retailing and Its Impact On Traditional Retailing in India: A Case Study of Guwahati CityShubhangi KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Public Places DirectionsDocument45 pagesPublic Places DirectionsTheo Simon SulcaNo ratings yet
- ATK - 10 Steps To Win in Fresh CategoriesDocument8 pagesATK - 10 Steps To Win in Fresh Categoriesapritul3539No ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument49 pagesProject ReportNasir RaineNo ratings yet
- PantaloonsDocument90 pagesPantaloonsNavank Vashishtha100% (1)
- Decision-Making Processes Shaping The Home Food Environments ofDocument10 pagesDecision-Making Processes Shaping The Home Food Environments ofOscarNo ratings yet
- Grocery Stores - Industry Report - SIC Code 5411Document12 pagesGrocery Stores - Industry Report - SIC Code 5411ravimuddanaNo ratings yet
- Grocery Sustainability: The Path Forward ForDocument6 pagesGrocery Sustainability: The Path Forward ForPatricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- F&V RetailDocument13 pagesF&V RetailasheeshnigamNo ratings yet
- Tesco Fail Japan-1Document20 pagesTesco Fail Japan-1Tasfiq Wahed0% (1)
- MarketingDocument18 pagesMarketingMia PeruchoNo ratings yet
- Literature - Mixed UseDocument43 pagesLiterature - Mixed UseHULE ADDIS ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet
- Specialization 1 2016Document9 pagesSpecialization 1 2016jjNo ratings yet
- Reliance Major-Products-And-BrandsDocument11 pagesReliance Major-Products-And-BrandsClubdeals RealtyNo ratings yet
- Winn-Dixie Stores, Inc. v. Dolgencorp, LLC, 11th Cir. (2014)Document72 pagesWinn-Dixie Stores, Inc. v. Dolgencorp, LLC, 11th Cir. (2014)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Case3 Tesco Supply Management PDFDocument19 pagesCase3 Tesco Supply Management PDFRacing Sangers82% (11)
- Retail Business in BangladeshDocument2 pagesRetail Business in BangladeshJohn CarterNo ratings yet
- Learning Supermarket and Grocery Store Vocabulary Using Pictures English LessonDocument10 pagesLearning Supermarket and Grocery Store Vocabulary Using Pictures English LessonMehmet Hanif100% (1)
- Opportunity Evaluation BigBasketDocument11 pagesOpportunity Evaluation BigBasketamitcmsNo ratings yet
- Factors Influence The Location of Retail Store ANSHUL JAINDocument98 pagesFactors Influence The Location of Retail Store ANSHUL JAINRASHID AHMED SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- Laurent Products Is A Manufacturer of Plastic Packaging ProductsDocument1 pageLaurent Products Is A Manufacturer of Plastic Packaging ProductsAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Rise and Fall of SubhikshaDocument19 pagesRise and Fall of SubhikshadagnivNo ratings yet
- Michael Phelps: Strategy Formulation & ImplementationDocument16 pagesMichael Phelps: Strategy Formulation & ImplementationTushar Dey100% (1)
- 2014feb Mock Ans EngDocument24 pages2014feb Mock Ans EngKaito MagicNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis Between Tesco and Sainsbury'sDocument53 pagesComparative Analysis Between Tesco and Sainsbury'sJahid Hasan100% (4)