Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classical Theory
Uploaded by
Deepali Singhai JainOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classical Theory
Uploaded by
Deepali Singhai JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Classical theory of employment
3/26/13
Bhawna Rajora 117510
3/26/13
Say's Law of Markets :
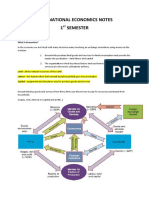
Say's Law of Markets Say's law of markets is the core of the classical theory of employment. An early 19th century french Economist, J.B.Say [1767-1882] enunciated the proposition that "Supply creates its own demand".
The classical economists believed in the existence of full employment in the economy. To them, full employment was a normal situation and any deviation from this regarded as something abnormal. the tendency of the economic systems is to automatically provide
3/26/13
3/26/13
ASSUMPTIONS
Says law of market Core of classical theory
3/26/13
Supply creates its own demand
(a) Full employment:
3/26/13
According to classical economists, the labour and the other resources are always fully employed. Moreover, the general over-production and general unemployment are assumed to be impossible. If there is any unemployment in the country, it is assumed to be temporary or abnormal. According to classical views of employment, the unemployment cannot be persisted for a long time, and there is always a tendency of full employment in the country. According to classical economists, the reasons for unemployment are: (i) Intervention by the government or private monopoly, (ii)Wrong calculation by entrepreneurs and inaccurate decisions, and (iii)Artificial resistance.
Wage Price Flexibility
3/26/13
Classical economist believed in full employment situation.
In case of unemployment, a general wage cut in money wages would take the economy to the full employment situation. Similarly, the unemployment could be cured by cutting down wages which would increase the demand for labour and would stimulate activity. Thus, if the prices and wages are allowed to move freely, unemployment would disappear and full employment level would be restored.
Labor Market 3/26/13 Equilibrium
Demand & supply of labour is function of wage rate. Demand for labour is decreasing function of wage rate . supply of labour is increasing function of wage rate. It was the theory on the basis of which classical economists thought that general over-production and general unemployment are not possible.
General Price Level in the economy depends on the supply of money. Total supply of money equals total value of output. Changes in supply of money causes proportionate change in price level. The classical economists are of the view that all the savings are spent automatically on investment goods. Savings and investments are interchangeable words and are equal to each other. If there is any gap between saving and investment, the rate of interest brings about equality between the two.
Money Market Equilibrium 3/26/13
3/26/13
Goods Market Equilibrium
Saving equals Investment Saving & Investment both Are the function of interest rate If Interest Rate is high there will be more saving and less investment
Criticism
3/26/13
Underemployment situation
Money not neutral
Refutation of wage cut
3/26/13
State intervention is essential Over production is possible
Refutation of says law
Long run analysis unrealistic
KEYNESIAN ECONOMICS : General Theory 3/26/13 of Emp: Interest & Money
1.
Full employment is not normal feature Unemployment equilibrium is normal. Short Run Theory : Amount of Capital, Population, labour Force, Technology, do not change. In the short run, higher level of income and employment can be attained by injection of macro economic measures which will lead to increase in aggregate demand for goods and services.
2.
3.
4. In a developed economy, employment depends on level of effective demand.
Aggregate Supply Price :
The minimum expected sale proceeds required to3/26/13 induce firms to produce and output and to provide employment on a given scale is called the aggregate supply price of that output. aggregate supply price increases with increase in the level of employment and vise versa.
At full employment , no increase in cost or sales proceeds can generate employment further.
Aggregate Demand Price :
Total money receipts expected by all the firms in the economy taken together from the sale of their products produced by a given number of workers. When the firms expect to earn through increased expenditure of the community on goods and services, they will employ more workers and vise versa.
Keynesian Theory of Employment 3/26/13 Concept of Effective Demand.
Aggregate Demand Function
(AD=total exp=C+I) aggregate supply function. As=F(N) AS is the aggregate supply price N=number of workers employed.
KEYNES ON CLASSICALS
3/26/13
Income saved does not necessarily Create Demand=AD<AS Investment demand < Desired savings causes unemployment Factors determining investment are different. Savings and
Savings depends on income, old age, social security network, education, marriage of children, housing need etc.
Investment depends upon
3/26/13
(a) Expected rate of profit. (b) Rate of interest. (c) Technological progress
(d) Population growth
Classical stood for Laissez faire policy; Keynes for active govt. intervention
and Important role for money supply in carrying out corrections in aggregate demand.
Comparison Between Classicals and Keynesians 3/26/13 Classical Keynesians
Economy is always in full employment. Full employment equilibrium is an exception. Wage and interest flexibilities restoresGeneral reduction in wages throughout the full employment equilibrium, if disturbed. economy can lead to fall in demand.
Monetary expansion may create inflation. Inflation will arise only after full employment has been achieved.
Interest rate brings about equality betweenSavings & investment is influenced by level of Savings and investment income and expected return on investment. Investment is interest elastic. Interest sensitivity of investment may not be adequate.
Classical depend on monetary policy forKeynesians depend on Fiscal Policy raising the level of income employment(public expenditure, deficit financing) for etc. reaching full employment equilibrium. 3/26/13 Classical place great emphasis onKeynes treats supply (Y) as given and supply side for establishing equilibrium. attaches great significance to demand.
S & I decisions are made by same groupS & I decisions are taken by different of people and interest rate brings aboutgroups of people changes in the equality between the investment andeconomy are the result of changes in savings. income and expenditure and not the rate of interest. Works in long run. Works in short run All are dead in the long run
3/26/13
You might also like
- Public-Private Partnership in Indian Infrastructure Development: Issues and OptionsDocument41 pagesPublic-Private Partnership in Indian Infrastructure Development: Issues and OptionsPoonam JaiswalNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument71 pagesNational IncomeMayurRawoolNo ratings yet
- National Income and Economic WelfareDocument12 pagesNational Income and Economic Welfarerajesh_scribd1984100% (1)
- Notes - EconomicsDocument69 pagesNotes - EconomicsHaktan OdabasiNo ratings yet
- Allmacroeconomicsppts 130321114704 Phpapp02Document291 pagesAllmacroeconomicsppts 130321114704 Phpapp02infoeduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - OutputDocument39 pagesChapter 01 - Outputrabbani haque100% (1)
- National IncomeDocument13 pagesNational IncomeEashwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument24 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyAri HaranNo ratings yet
- The Law of EquiMarginal UtilityDocument14 pagesThe Law of EquiMarginal Utilitynaveenshukla46100% (1)
- The IS-LM Model: Equilibrium: Goods and Money Markets Understanding Public PolicyDocument37 pagesThe IS-LM Model: Equilibrium: Goods and Money Markets Understanding Public PolicyShashank Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Costs of UnemploymentDocument15 pagesCosts of UnemploymentNandy Raghoo GopaulNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument19 pagesFiscal PolicyShreya SharmaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument32 pagesEconomicsSahil BansalNo ratings yet
- Classical Economics Vs Keynesian Economics Part 1Document5 pagesClassical Economics Vs Keynesian Economics Part 1Aahil AliNo ratings yet
- International Labour MovementDocument11 pagesInternational Labour MovementShaikh AlamNo ratings yet
- PE Slide 4Document13 pagesPE Slide 4Ajay PasiNo ratings yet
- Harrod Model of GrowthDocument6 pagesHarrod Model of Growthvikram inamdarNo ratings yet
- Social and Environmental Acc.Document15 pagesSocial and Environmental Acc.Ňïł Chowdhury JoyNo ratings yet
- Indian Tax SystemDocument17 pagesIndian Tax SystemSachin RanaNo ratings yet
- ECO-Self Examination Questions PDFDocument66 pagesECO-Self Examination Questions PDFadnan sheikNo ratings yet
- Modern Theory of WageDocument6 pagesModern Theory of Wagegazal1987No ratings yet
- hw3s HO SFM f11Document12 pageshw3s HO SFM f11Saurabh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Eco Dev - OrendayDocument17 pagesEco Dev - OrendayZhaira OrendayNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Keynesian Theory To The Current EconomicDocument15 pagesRelevance of Keynesian Theory To The Current EconomicSiva Krishna Reddy NallamilliNo ratings yet
- Say's Law of MarketDocument14 pagesSay's Law of MarketHaren ShylakNo ratings yet
- IB Theories of TradeDocument42 pagesIB Theories of TradevijiNo ratings yet
- Public Economics Tax IncidenceDocument38 pagesPublic Economics Tax IncidencejayaniNo ratings yet
- Central Problems of An Economy - GeeksforGeeksDocument10 pagesCentral Problems of An Economy - GeeksforGeeksAKSHAT TANWAR100% (1)
- Revealed Preference TheoremDocument10 pagesRevealed Preference TheoremelinexaxaNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument18 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyJayesh GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Money & BankingDocument46 pagesMoney & BankingAbdihakimNo ratings yet
- Consumer AwarenessDocument15 pagesConsumer AwarenessRavi ChandranNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Effects of Customs Union - Part2Document24 pagesStatic and Dynamic Effects of Customs Union - Part2djvapidNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument4 pagesNational Incomesubbu2raj3372No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational Incomeshahidul0No ratings yet
- Law of Comparative AdvantageDocument11 pagesLaw of Comparative Advantage12jaya21No ratings yet
- Measuring The EconomyDocument34 pagesMeasuring The EconomyJoanaMarie CaisipNo ratings yet
- Consumer SurplusDocument16 pagesConsumer Surplusparamjeet kourNo ratings yet
- Consumer Surplus and Producer Surplus - Handout PDFDocument4 pagesConsumer Surplus and Producer Surplus - Handout PDFShashank KrrishnaNo ratings yet
- Economic Inequality in Egypt: Mayar Abdelaziz, Seif Altamimi and Rania AbukeshekDocument12 pagesEconomic Inequality in Egypt: Mayar Abdelaziz, Seif Altamimi and Rania AbukeshekSeif TamimiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Concentration: Meaning and Its Measurement Economics BY Prof.B.Sudhakar ReddyDocument40 pagesIndustrial Concentration: Meaning and Its Measurement Economics BY Prof.B.Sudhakar ReddyProf B Sudhakar Reddy100% (1)
- Assignment On Intermediate Macro Economic (ECN 303) - USEDDocument6 pagesAssignment On Intermediate Macro Economic (ECN 303) - USEDBernardokpeNo ratings yet
- Econ Base Vs Input-Output ModelsDocument19 pagesEcon Base Vs Input-Output ModelsNiraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Hec Ohlin TheoryDocument13 pagesHec Ohlin TheoryPavithra PRabhuNo ratings yet
- Samuelson and Nordhaus ch22 PDFDocument30 pagesSamuelson and Nordhaus ch22 PDFVictor ManatadNo ratings yet
- Fiscal and Monetary Policies of IndiaDocument13 pagesFiscal and Monetary Policies of IndiaRidhika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Marshallian & Walrasian Equilibrium AnalysisDocument29 pagesMarshallian & Walrasian Equilibrium AnalysisPalak100% (1)
- Second Law of GossenDocument2 pagesSecond Law of GossenPrerna GillNo ratings yet
- A Note On Welfare Propositions in EconomicsDocument13 pagesA Note On Welfare Propositions in EconomicsmkatsotisNo ratings yet
- Household Behavior Consumer ChoiceDocument40 pagesHousehold Behavior Consumer ChoiceRAYMUND JOHN ROSARIONo ratings yet
- Eco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbDocument10 pagesEco MCQ 1 Multiple Choice Questions MCQ For Economics 1 BallbbballbsanchiNo ratings yet
- Week 01-The Fundamentals of EconomicsDocument33 pagesWeek 01-The Fundamentals of EconomicsPutri WulandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Claasical& Non Classical TheoryDocument35 pagesUnit 2 - Claasical& Non Classical TheoryGlendsss RjndlrNo ratings yet
- Trade in The Global Economy. Theories, Performance and Institutional StructuresDocument64 pagesTrade in The Global Economy. Theories, Performance and Institutional StructuresJemaicaNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Basic Concept of Macroeconomics PDFDocument16 pagesCH-2 Basic Concept of Macroeconomics PDF1630 Gursimran Saluja ANo ratings yet
- Theory of EmploymentDocument7 pagesTheory of EmploymentRotaba MahikNo ratings yet
- Module C: Simple Theory of Income DeterminationDocument11 pagesModule C: Simple Theory of Income DeterminationGolamSarwarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Income and EmploymentDocument9 pagesTheory of Income and EmploymentsureshNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Brief Introduction To The Thought Of Keynes" By Dudley Dillard: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Brief Introduction To The Thought Of Keynes" By Dudley Dillard: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Classical Model 1Document6 pagesClassical Model 1blipbruceNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce in Mobile Computing: Presented byDocument42 pagesE-Commerce in Mobile Computing: Presented byDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Types of Service EntitiesDocument8 pagesTypes of Service EntitiesDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Defining Supply Chain ManagementDocument7 pagesDefining Supply Chain ManagementVampyPhanNo ratings yet
- Brands QuizDocument47 pagesBrands QuizDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Central Bank: Chapter # 5Document15 pagesCentral Bank: Chapter # 5Deepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- WagesDocument34 pagesWagesDeepali Singhai Jain100% (2)
- Demand Supply Theory of MoneyDocument8 pagesDemand Supply Theory of MoneyDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Central Bank: Chapter # 5Document15 pagesCentral Bank: Chapter # 5Deepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument6 pagesNotesDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- NCVT NotesDocument10 pagesNCVT NotesDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Work DesignDocument47 pagesWork DesignDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Hydro Corr TestDocument19 pagesHydro Corr TestPramoth NarashimmanNo ratings yet
- How Do I Upgrade From Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 To Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Document12 pagesHow Do I Upgrade From Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 To Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Shailendra MathurNo ratings yet
- 74HC4049Document11 pages74HC4049jnax101No ratings yet
- Вправи на Past SimpleDocument4 pagesВправи на Past SimpleLiliaNo ratings yet
- Everyday Conversation 3CDocument10 pagesEveryday Conversation 3Cjiyoon KimNo ratings yet
- HTJ22 StarsDocument6 pagesHTJ22 StarsCruzKevin20No ratings yet
- Instruction Manual PC Interface RSM 100: TOSHIBA Corporation 1999 All Rights ReservedDocument173 pagesInstruction Manual PC Interface RSM 100: TOSHIBA Corporation 1999 All Rights ReservedHuy Truong GiaNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Health Lesson Plan - Portfolio - BloomsDocument3 pages6th Grade Health Lesson Plan - Portfolio - Bloomsapi-475320683No ratings yet
- Strategic Planning For Implementing E-Government in Iran: Formulating The StrategiesDocument8 pagesStrategic Planning For Implementing E-Government in Iran: Formulating The StrategiesTantri Mulia KarinaNo ratings yet
- VMGODocument3 pagesVMGOklirt carayoNo ratings yet
- BOSS GLOBAL CONCEPTS LTD - AML Policy-UpdatedDocument46 pagesBOSS GLOBAL CONCEPTS LTD - AML Policy-UpdatedtwaseemdttNo ratings yet
- The Urban Footprint: Trece Martires City, CaviteDocument1 pageThe Urban Footprint: Trece Martires City, CaviteJubileo Paul Lara LiganNo ratings yet
- 6 Tutorial The Rail Dispute DebriefDocument16 pages6 Tutorial The Rail Dispute DebriefjesseNo ratings yet
- Op QuesDocument7 pagesOp QuessreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- Soal PAT Bhs Inggris Kelas XII Semester GenapDocument12 pagesSoal PAT Bhs Inggris Kelas XII Semester GenapSt HarlisNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Tarun Kumar A.B, Ullas AnandDocument13 pagesMaxillary Sinus Augmentation: Tarun Kumar A.B, Ullas Anandyuan.nisaratNo ratings yet
- Atma Rama Anandha Ramana - Scenes PDFDocument2 pagesAtma Rama Anandha Ramana - Scenes PDFKoushik KattaNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis: Kumar SaurabhDocument11 pagesSecurity Analysis: Kumar Saurabhakhil vermaNo ratings yet
- Transient Torque Rise of A Modern Light Duty Diesel Engine With Variable Valve ActuationDocument12 pagesTransient Torque Rise of A Modern Light Duty Diesel Engine With Variable Valve ActuationdheepanasNo ratings yet
- CNC 8060/70 LASER: Fagor AutomationDocument12 pagesCNC 8060/70 LASER: Fagor AutomationRoberto SilvaNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementCheryl AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Learning Principle PRINTDocument5 pagesThe Learning Principle PRINTnurulNo ratings yet
- NCP On Mental RetardationDocument20 pagesNCP On Mental RetardationSARITA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Rooftop Package Air Conditioner: Installation ManualDocument32 pagesRooftop Package Air Conditioner: Installation Manualyusuf mohd sallehNo ratings yet
- Air ConditionerDocument131 pagesAir ConditionerRahul AnsariNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Work ImmersionDocument24 pagesBusiness Plan Work ImmersionAvrylle Maneja67% (3)
- Coverpage BLDG Projects F.Y. 2021Document4 pagesCoverpage BLDG Projects F.Y. 2021Adrian PachecoNo ratings yet
- Youth Protection WaiverDocument1 pageYouth Protection WaiverKatie McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Part 1b - Selection and Literature Review of A CultureDocument3 pagesPart 1b - Selection and Literature Review of A Cultureapi-535208903No ratings yet
- 100kva DG Set - 100kva Koel GensetDocument3 pages100kva DG Set - 100kva Koel GensetMothilalNo ratings yet