Professional Documents
Culture Documents
POST VEDIC PERIOD EDUCATION
Uploaded by
balwariaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
POST VEDIC PERIOD EDUCATION
Uploaded by
balwariaCopyright:
Available Formats
POST VEDIC PERIOD (1400 B.C to 600 B.
C)
Bhramanic age or Upanishadic period. Aim was remained intact to attain salvation. The place of Guru in society remained intact. No knowledge could come without the assistance from the Guru.
Post Vedic Period
According to the Upanishads truth, alone is the knowledge and the other worldly knowledge is untruth. The worldly knowledge was regarded as ignorance. Upanishads maintain that one cannot attain salvation through worldly knowledge because through this, one becomes involved in illusion (Maya).
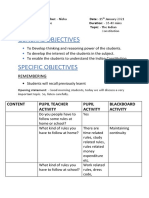
Features of Post Vedic Education
1) Upanayan Sanskar Upanayan ceremony was considered necessary for starting education. The Upanayan ceremony became so important during the post vedic period, that is was usually regarded as second birth of the individual. For the Brahmans this became very important. Brahmans began to be called as Dvij (the twice born or born again). It was after the Upanayan that a Brahaman boy could be called a Dvij.
2) The Important Place of the Teacher
During this period the teacher (Guru) enjoyed a predominant place not only in his Gurukul but in the entire society. During the vedic and post vedic period the teaches place was second to that of God only. It was belived that no knowledge could come without the assistance from the Guru. In other words, it was believed that attainment of saluation was not possible without the help of Guru.
3) Curriculum during post-Vedic Period
Ved Mantras (hymns and verses) were principally taught in the vedic period. During the post-vedic period various types of Literatures were produced pertaining to the different Vedas. It consisted of Vedas, History, Puranas, Grammar, Mathematics, Braham-Vidya, Nirukti (etymological interpretation of words), astronomy, dance, music etc. Question answer system prevailed during his period. Through this system difficult and abstract ideas were made simple.
4) Daily Routines of Students
During post vedic period the Ashramas (schools) were generally organized and run by Guru.
Agencies of education
Branch or Shakha. Originate from Veda later devote to various branches of all the Vedas. Different versions of Vedas were preserved in various Gurukuls and the expansions of these branches are not limited to Vedas. Charans. According to Panini only a group of disciples who studied in one branch or shakha was charan. On other was, individuals who study particular branch of Vedas and form a group. Such group of students is called charan. Parishad. Word means all the things expanded on all sides. Focus on philosophical problem. Gotra or Kula. Based on family traditions which
Society and Culture in Later Vedic Period
The society increased in size. Kingship evolved into the hereditary form in which the son of a ruling chief gets the throne after the chief. The caste division of the society. The Brahmanas were the priestly class who occupied the highest position in the society. The Kshatriyas were the warriors; the Vaishyas were the service class like businessmen and peasants. The Shudras were the lowest class of people who did jobs like removing garbage, cleaning up, etc.
Varna system and Education in Society
But during the post vedic period varna came to be determined by birth. four varnas Brahman, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, & Shudra. The position of varnas during the post vedic period had not degenerated so much as it is found today.
The system affected the education system in general. Bhramans were mainly authorized for Vedic study and of Spiritual knowledge but some Kshatriyas had also become great Rishi just as learned philosophers like Janak etc. Similarly many other Kshatriyas kings had also gained spiritual knowledge and tried for salvation (Mukti) eg. The prominence of spiritual knowledge of King Ajatashetru of Kashi was recognized and honored by Gargeya and Balaki Brahmins Acharyas. The aim of life of Vaishyas was laid down as agricultural trade and commerce. They did not take any instrest in the intellectual education. The conditions of shudras was even worse. They had to serve the three higher castes. Shudras were not free to get Vedic knowledge now as they could in Vedic period.
You might also like
- EDUCATION SYSTEM IN ANCIENT INDIA LatestDocument37 pagesEDUCATION SYSTEM IN ANCIENT INDIA LatestDharma Teja100% (2)
- Indian Education During Ancient PeriodDocument9 pagesIndian Education During Ancient Periodsrishti bhateja100% (2)
- BEdCourseCode201 Unit1Unit2Document11 pagesBEdCourseCode201 Unit1Unit2Seema GulNo ratings yet
- NCF 2005Document16 pagesNCF 2005Palwinder33% (3)
- Hartog Committee ReportDocument14 pagesHartog Committee Reportsurajitpal4u92% (13)
- Sargent Report 1944Document15 pagesSargent Report 1944Kamran Abdullah100% (1)
- Notes Educational Technology B. Ed. 1-5Document9 pagesNotes Educational Technology B. Ed. 1-5Mehmood HassanNo ratings yet
- PRESENTATION ON WOOD'S DESPATCH (1854) AashuutoshDocument9 pagesPRESENTATION ON WOOD'S DESPATCH (1854) Aashuutoshradhay mahajanNo ratings yet
- Ignou Ma Edu NotesDocument13 pagesIgnou Ma Edu Noteshi67% (3)
- Role of Calcutta University Commission in shaping India's education policyDocument5 pagesRole of Calcutta University Commission in shaping India's education policyAvisek SilNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Education FeaturesDocument15 pagesBuddhist Education FeaturesDr. Aarif Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Indian Education Commission - 1882Document7 pagesIndian Education Commission - 1882surajitpal4uNo ratings yet
- Sargent Report 1994Document20 pagesSargent Report 1994Akasha Komaleeswaran100% (1)
- Gyan Darshan and InflibnetDocument12 pagesGyan Darshan and InflibnetChinnu Anie TomNo ratings yet
- Sadler CommissionDocument26 pagesSadler Commissionshreya guha50% (4)
- Institutional Planning in India - Meaning, Definition, Objectives, Scope and ApproachesDocument33 pagesInstitutional Planning in India - Meaning, Definition, Objectives, Scope and ApproachesA KNo ratings yet
- Dramatisation Method of TeachingDocument14 pagesDramatisation Method of TeachingRingle Job100% (3)
- Assignment On Agencies of EducationDocument9 pagesAssignment On Agencies of Educationmaya verma100% (7)
- Meaning and Facets of KnowledgeDocument20 pagesMeaning and Facets of KnowledgePratik Sah100% (4)
- Glaser's Basic Teaching ModelDocument3 pagesGlaser's Basic Teaching ModelNisha Pandey100% (2)
- Wardha Scheme of Basic EducationDocument3 pagesWardha Scheme of Basic EducationAlok Rai100% (1)
- Emerging Trends in Evaluation and CCEDocument8 pagesEmerging Trends in Evaluation and CCECharis Israel AnchaNo ratings yet
- Gyan DarshanDocument13 pagesGyan DarshanRINU JAMES100% (2)
- Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA)Document65 pagesRashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA)dasadiyajaydip25No ratings yet
- NCF 2005Document30 pagesNCF 2005geetkumar1850% (2)
- Analyzing English TextbookDocument12 pagesAnalyzing English TextbookCool Boy100% (2)
- Issues and Concerns in Secondary EducationDocument78 pagesIssues and Concerns in Secondary EducationGunjan Arora100% (1)
- National Knowledge Commision and Its Implication in Higher EducationDocument73 pagesNational Knowledge Commision and Its Implication in Higher Educationabhi301280100% (1)
- Main Features of RTE Act 2009Document7 pagesMain Features of RTE Act 2009sachin106567% (3)
- REPORT ON INTERNSHIP EXPERIENCES Vidya Mandir - 074208Document22 pagesREPORT ON INTERNSHIP EXPERIENCES Vidya Mandir - 074208Munmun GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum LoadDocument10 pagesCurriculum Loadnavy100% (1)
- National Curriculum Framework 2005Document4 pagesNational Curriculum Framework 2005JIJIDEVI100% (1)
- Movie Review Knowledge Is FreeDocument9 pagesMovie Review Knowledge Is Freesinshan50% (2)
- Textbook AnalysisDocument6 pagesTextbook AnalysisAry Rahmat Hariadi50% (2)
- Hunter Commission 1882 Primary Education ReformsDocument5 pagesHunter Commission 1882 Primary Education ReformsPankaj Chetry100% (1)
- Constitutional Provisions in Relation To EducationDocument2 pagesConstitutional Provisions in Relation To EducationZhoveyi Venuh100% (2)
- Introduction To The Sargent Report On EducationDocument26 pagesIntroduction To The Sargent Report On EducationvamsibuNo ratings yet
- Shantiniketan: (Also Known As)Document12 pagesShantiniketan: (Also Known As)shilpi_kesarwani67% (3)
- Tagore's Life, Philosophy and Educational ThoughtsDocument4 pagesTagore's Life, Philosophy and Educational Thoughtsapfg50% (2)
- Deficit Theory & Discontinuity TheoryDocument3 pagesDeficit Theory & Discontinuity TheoryAthira I P100% (2)
- Importance of Language in EducationDocument8 pagesImportance of Language in EducationBipasha SenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Social Science Teacher As A Reflective Practitioner: Use of Action ResearchDocument24 pagesUnit 5 Social Science Teacher As A Reflective Practitioner: Use of Action ResearchSagar Gawas100% (2)
- National Policy on Education 1986 ObjectivesDocument10 pagesNational Policy on Education 1986 ObjectivesSwami Gurunand100% (3)
- Problems and Issues in Secondary EducationDocument7 pagesProblems and Issues in Secondary Educationmaanu86No ratings yet
- Education As A Liberal DisciplineDocument3 pagesEducation As A Liberal DisciplineAshee Gupta50% (4)
- Master of arts in education (syllabus 2015) - Content analysis of secondary textbook from HUMAN RIGHTS perspectiveDocument13 pagesMaster of arts in education (syllabus 2015) - Content analysis of secondary textbook from HUMAN RIGHTS perspectiveWaseem Khan50% (2)
- Approaches To Organize Social Science CurriculumDocument52 pagesApproaches To Organize Social Science CurriculumBiny Rajwanssh90% (10)
- Education As DisciplineDocument47 pagesEducation As DisciplineReshmi Kannan100% (1)
- Kothari Commission (1964-1966) : (1) Free and Compulsory EducationDocument6 pagesKothari Commission (1964-1966) : (1) Free and Compulsory EducationThirumalNo ratings yet
- Woods Despatch of 1854Document12 pagesWoods Despatch of 1854Richa Raj67% (12)
- VKCTE Merit List 2021 - 2022Document7 pagesVKCTE Merit List 2021 - 2022Vivekananda Kendra Vidyalaya Arunachal Pradesh TrustNo ratings yet
- UEE and SSA: Concept, Objectives and StrategiesDocument7 pagesUEE and SSA: Concept, Objectives and StrategiesFrancis RiveroNo ratings yet
- Approaches of Educational TechnologyDocument7 pagesApproaches of Educational TechnologySalma Jan100% (1)
- The Rcem ApproachDocument3 pagesThe Rcem ApproachMANICA92% (12)
- Indian Constitution Explained for StudentsDocument8 pagesIndian Constitution Explained for StudentsNISHA BijarniaNo ratings yet
- Later-Vedic Edn SystemDocument14 pagesLater-Vedic Edn SystemsatyaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Education in India from Vedic to Buddhist EraDocument4 pagesEvolution of Education in India from Vedic to Buddhist ErabalwariaNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT INDIAN EDUCATION SYSTEMDocument15 pagesANCIENT INDIAN EDUCATION SYSTEMlovleshrubyNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Buddhism and JainismDocument60 pagesFoundations of Buddhism and JainismlabizaNo ratings yet
- Theme 4 Thinkers Beliefs and Buildings HssliveDocument9 pagesTheme 4 Thinkers Beliefs and Buildings HssliveRAM RAWATNo ratings yet
- GrepDocument25 pagesGrepbalwariaNo ratings yet
- Right To EducationDocument4 pagesRight To EducationbalwariaNo ratings yet
- Channels of EducationDocument3 pagesChannels of EducationbalwariaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Education in India from Vedic to Buddhist EraDocument4 pagesEvolution of Education in India from Vedic to Buddhist ErabalwariaNo ratings yet
- Agencies of EducationDocument4 pagesAgencies of Educationbalwaria100% (1)
- Vedic PeriodDocument12 pagesVedic PeriodbalwariaNo ratings yet
- National SeminarDocument2 pagesNational SeminarbalwariaNo ratings yet
- Habit 5Document14 pagesHabit 5balwariaNo ratings yet
- Vedic PeriodDocument12 pagesVedic PeriodbalwariaNo ratings yet
- Habit 5Document14 pagesHabit 5balwariaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Aids A V AidsDocument34 pagesTeaching Aids A V AidsbalwariaNo ratings yet
- Computer History1Document37 pagesComputer History1cuteguy_madzNo ratings yet
- FlyerDocument1 pageFlyerbalwariaNo ratings yet
- M. Ed Optional Paper II: Educational TechnologyDocument11 pagesM. Ed Optional Paper II: Educational TechnologybalwariaNo ratings yet
- The Present ScenarioDocument26 pagesThe Present ScenariobalwariaNo ratings yet
- Goan Social StudyDocument37 pagesGoan Social StudyKushal RaoNo ratings yet
- Society in Tribal India (PDFDrive)Document270 pagesSociety in Tribal India (PDFDrive)SivaKumarNo ratings yet
- Surinder S Jodhka - Caste in Contemporary India Routledge 2019 22092023 103901amDocument275 pagesSurinder S Jodhka - Caste in Contemporary India Routledge 2019 22092023 103901amHussain Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- UPSC PRAHAAR: Key Features of Indian Society and DiversityDocument163 pagesUPSC PRAHAAR: Key Features of Indian Society and DiversityBibek BoxiNo ratings yet
- Hinduism's Varna System and Jāti Castes ExplainedDocument12 pagesHinduism's Varna System and Jāti Castes Explainedraju87vadhwanaNo ratings yet
- 5 6069129908435550654 PDFDocument192 pages5 6069129908435550654 PDFalluri bhaskarNo ratings yet
- Ancient India: The Origins of Culture and CivilizationDocument38 pagesAncient India: The Origins of Culture and CivilizationRajesh Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Caste in South AsiaDocument23 pagesCaste in South AsiaRamanNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument80 pagesHistoryJitendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Social Diversity in IndiaDocument40 pagesSocial Diversity in IndiaManasa P SNo ratings yet
- Dharma in AncientDocument32 pagesDharma in AncientAnish Kartik100% (1)
- 1.social Diversity Levels of Social DiversityDocument24 pages1.social Diversity Levels of Social DiversityHELAN M AUGUSTINNo ratings yet
- Fess105 PDFDocument11 pagesFess105 PDFdell 7No ratings yet
- India - Report ManuscriptDocument21 pagesIndia - Report ManuscriptAJ BlazaNo ratings yet
- Annihilation of Caste of AmbedkarDocument12 pagesAnnihilation of Caste of Ambedkariamrakeshj75% (4)
- Hindu Caste System Explained: Brahmins and KshatriyasDocument7 pagesHindu Caste System Explained: Brahmins and KshatriyasRamachandra DharNo ratings yet
- Dalit WritingsDocument11 pagesDalit WritingsSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Malhotra SurnameDocument8 pagesMalhotra SurnameDr. Ashok MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 2733 Subedi CasteDocument18 pages2733 Subedi Castepattabi8No ratings yet
- Indian Historiography and Ambedkar Readi-1 PDFDocument22 pagesIndian Historiography and Ambedkar Readi-1 PDFJyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- Dalit MovementDocument76 pagesDalit Movementnidhi A. kumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Political Thought Block 1 PDFDocument96 pagesIndian Political Thought Block 1 PDFआई सी एस इंस्टीट्यूट100% (1)
- National Law Institute University Bhopal: Sociologyl-2Document19 pagesNational Law Institute University Bhopal: Sociologyl-2Guddu SinghNo ratings yet
- Castas IndiaDocument103 pagesCastas IndiajosebardamuNo ratings yet
- To StudentsDocument177 pagesTo StudentsgudasanNo ratings yet
- Gayatri Sadhana FDocument44 pagesGayatri Sadhana FcarolNo ratings yet
- Reflections On GitaDocument486 pagesReflections On GitaAna Vaughn100% (1)
- Purity, Impurity and UntouchabilityDocument15 pagesPurity, Impurity and Untouchabilitytuku67No ratings yet
- Introduction To Vedanta: Topics 3 and 4 Talk 2 On 5 August 2018Document31 pagesIntroduction To Vedanta: Topics 3 and 4 Talk 2 On 5 August 2018Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Medieval India Agrarain ExpansionDocument6 pagesMedieval India Agrarain ExpansionHimanshu Thakuria100% (27)