Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
nikhil58555Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
nikhil58555Copyright:
Available Formats
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
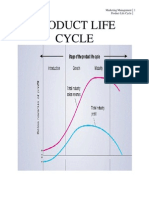
Product life cycle has five distinct stages Product development : Begins when the company finds and develops a new product idea. At this stage sales are zero, companys investment costs mount Introduction : A period of slow sales growth as product is introduced in the market. Profits are non existent at this stage because product introduction cost are high Growth : A period of rapid market acceptance and increasing profits Maturity : A period of slowdown in sales growth as product gets acceptance by almost all potential buyers. Profits level off or decline because of increased marketing outlay to defend the product against competition Decline : A period when sales fall off and profits drop
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
Exceptions in product life cycle stages
Some products are introduced and die quickly Some products continue to stay in the maturity stage for a long time Some enter the decline stage and are cycled back into the growth stage through strong promotion or repositioning
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
Product Life Cycle (PLC) concept can describe a product class (Laundry Soap), a product form (Powered Detergents) or a brand (Surf Excel) PLC concept applies differently in each case Product classes have the longest life cycles sales of many product classes stay in the mature stage for a long time Product forms in contrast tend to have the standard PLC shape. Product forms such as dial telephones, Videos, Computers pass through a regular history of introduction, rapid growth, maturity and decline. A specific brands life cycle can change quickly because of changing competitive attacks and responses
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
PLC concept can also be applied to What are known as styles,
fashion and fads
Style : basic distinct mode of expression. Styles appear in clothing (formal, casual, religious) ; art (realistic, surrealistic, abstract); homes (bungalows, flats, duplex).
1.
Style once invented lasts for generations, passing in and out of vogue. Style has a cycle showing several periods of renewed interest.
2.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
Fashion : Currently accepted or popular style in a given field. 1. The more formal business attire look of corporate dress of the 1980sad early 1990s has given way to the business casual look of today. Fashion tends to grow slowly , remain popular for a while and then decline slowly.
2.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
Fads : they are fashions that enter quickly, are adopted with great zeal, peak early and decline very quickly.
They last only for a short time and tend to attract only a limited following.
Example: Rubiks Cube, Ronaldo hair style,
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
PLC concept is applied by marketers as a useful framework for describing how products and markets work.
Using the PLC concept for forecasting product performance or developing marketing strategies present practical problems.
Managers have trouble identifying which stage which stage of the PLC the product is in, pinpointing when the product moves into the next stage, determining the factors responsible at each stage. Using PLC concept for developing marketing strategies can be difficult because strategy can be both a cause an the result of the products life cycle Yet, when used carefully, the PLC concept an help in developing good marketing strategies for different stages of the PLC.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE INTRODUCTION STAGE Starts when the product is first launched Takes time and the sales growth is slow Profits are negative or low as sales are low and distribution and promotion expenses are high As market is not ready to accept product refinement at this stage the firm produces a basic version of the product Selling is focused on those buyers who are ready to buy The market pioneer must choose a launch strategy consistent with the intended product positioning It should realize that it is the first step in the total marketing plan for the PLC If pioneer uses launch strategy to make a killing it sacrifices long revenue for short term gain As pioneer moves to later stages it will have to continually formulate new pricing , promotion and other marketing strategies.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE GROWTH STAGE If the new product satisfies the market, it will enter he growth stage. Sales will start climbing quickly. Early adopters will continue to buy, later buyers will start following their lead especially if they hear favourable word of mouth New competitors may now make an entry attracted by the profit opportunities by adding new features Market will now expand Increasing competition leads to an increase in number of distribution outlets Prices remain where they are or fall only slightly Promotion spending may be the same or slightly higher Goal is educating the customers and meeting competition Profits increase as promotion costs are over large volumes and unit manufacturing costs fall
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE GROWTH STAGE The firm uses several strategies to sustain rapid growth as long as possible It improves product quality and adds new product features and models It enters new market segments and develops new distribution channels Shifts some advertising from building product awareness to product conviction and purchase It lowers product prices to at the right time to attract more buyers At his stage the firm faces a trade off between high market share and high current profit By spending a lot of money on product improvement, promotion, and distribution the firm can capture a dominant position In doing so it gives up maximum current profit which it hopes to make up in the next stage
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE MATURITY STAGE At some point of time the products sales growth slows down and the product enters the maturity stage This stage lasts longer than the previous stages The slowdown in sales growth results in many producers with many products to sell The overcapacity in the market leads to greater competition Competitors begin marking down prices, increasing their advertising and sales promotion The R&D budgets are increased to find better versions of the product These steps lead to a drop in profit Weaker competitors start dropping out (decline) The market eventually contains only well established competitors Most successful products are in a stage of continuous evolution to meet changing customer needs and preferences
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE MATURITY STAGE At this stage firms may also chose to modify he market , the product or he marketing mix In modifying the market the firm tries to increase the consumption of the current market It looks for new users and market segments. Looks for ways to increase usage among present customers The firm may also try modifying the product by changing the characteristics such as quality, features, or style to attract the new users and inspire more usage It may improve the products quality and performance, its durability, reliability, speed and taste The firm can also try modifying the marketing mix to improve sales by changing one or more marketing mix elements. Can cut prices to attract new users and competitors customers. Better ad campaigns, aggressive sales promotion, trade deals. New and improved services.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE DECLINE STAGE At this stage sales of most product forms and brands eventually dip. Decline may be slow or rapid Sales may plunge to zero or they may drop to a low level where they continue for many years Sales decline may be due to technological advances, shifts in consumer tastes, and increased competition As sales and profits decline some firms withdraw from the market Those remaining prune their product offering, drop smaller market segments and marginal trade channels Some firms cut the promotion budget and reduce the prices further Carrying a weak product is costly for a firm Products failing reputation can cause customer concerns about firm and its other products Keeping a weak product delays the search for replacements, creates a lopsided product mix, hurts current profits, weakens companys foothold on the future.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE STRATEGIES
THE DECLINE STAGE At this stage a firm needs to pay more attention to the ageing products . The firms task is to identify those products in the decline stage by regularly reviewing sales, market share, costs and profit trends The firms has to decide whether to maintain, harvest or drop each of these declining products Firm may decide to maintain the brand in the hope that competitors will leave the industry May also decide to reposition or reformulate the brand in the hope of moving it back to the growth stage Firm may decide to harvest the product, which means reducing various costs (plant and equipment, maintenance, R&D, advertising, sales force) and hoping that sales hold up. Harvesting, if successful, increases firms profit in the short run Firm may also decide to drop the product from its line May sell it to another firm or liquidate it at salvage value
You might also like
- Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesProduct Life CycleGajanurNo ratings yet
- You Should Answer Question 2 From The Below Text. You Must Give Example From Your Own. There Are Several Topics Sepereted by Lines.Document8 pagesYou Should Answer Question 2 From The Below Text. You Must Give Example From Your Own. There Are Several Topics Sepereted by Lines.Mohammad Golam MostafaNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument13 pagesThe Product Life CycleWahid Ibn Nazrul100% (2)
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument11 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementmsmgectNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument10 pagesThe Product Life CycleZer GuNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument11 pagesThe Product Life CycleamritabhosleNo ratings yet
- Presented To: Ms. Rupali MadanDocument19 pagesPresented To: Ms. Rupali MadanNeha BhograNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument6 pagesProduct Life CycleYugandhara Sudhakar PatilNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle of Tata ComDocument11 pagesProduct Life Cycle of Tata ComRahul Kamble0% (1)
- Product life cycle stagesDocument19 pagesProduct life cycle stagesabhishek00lohiaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument21 pagesProduct Life Cyclenuplin.zain100% (7)
- Product Life Cycle AnswerDocument5 pagesProduct Life Cycle AnswerRituNo ratings yet
- BBA Student's Marketing Subject SubmissionDocument6 pagesBBA Student's Marketing Subject SubmissionHasnain SaleemNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument1 pageProduct Life CycleTrans Lanka EnterprisesNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle: BY Arun Tripathi Abhishek Ojha Amrinder Singh BakshiDocument36 pagesProduct Life Cycle: BY Arun Tripathi Abhishek Ojha Amrinder Singh Bakshiabhi9998No ratings yet
- Session 5 - PLCDocument11 pagesSession 5 - PLCShameel JavedNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management IDocument10 pagesMarketing Management IDamodar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategiesDocument41 pagesMarketing StrategiesSairaj MohantyNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument9 pagesProduct Life CycleDeepti ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 11 Life Cycle StrategiesDocument7 pages11 Life Cycle StrategiesSarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- PLC Stages Guide Product DevelopmentDocument6 pagesPLC Stages Guide Product DevelopmentJosé Alfredo Moreno Jr.No ratings yet
- Pioneer Institute of Professional StudiesDocument14 pagesPioneer Institute of Professional StudiesKhushiyal M. KatreNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument49 pagesProduct Life Cycle19vermanaresh100% (1)
- Product Life CycleDocument20 pagesProduct Life Cycledivjn3No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle TheoryDocument14 pagesProduct Life Cycle TheoryBilal TariqNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Power Point - Chapt 7 Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument29 pagesMicrosoft Power Point - Chapt 7 Product Life Cycle Managementj0r3lmNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument11 pagesProduct Life CycleASHWINI SINHANo ratings yet
- Stages of Product Life CycleDocument16 pagesStages of Product Life Cycleanon_952No ratings yet
- Assignment On Marketing ManagementDocument29 pagesAssignment On Marketing Managementdiplococcous90% (10)
- Session 14 - MABDDocument12 pagesSession 14 - MABDHarshit Raj KarnaniNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle FinalDocument27 pagesProduct Life Cycle FinalPrathamesh Gawade100% (1)
- Product Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesDocument17 pagesProduct Life Cycle & Marketing Strategiesakansha02No ratings yet
- Itc ProjectDocument15 pagesItc ProjectprachyarathoreNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Marketing Mix Decisions: Product Planning and DevelopmentDocument22 pagesUnit Iii Marketing Mix Decisions: Product Planning and DevelopmentLords PorseenaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Ôntroduction: Ôntroduction Growth Maturity DeclineDocument4 pages3.1 Ôntroduction: Ôntroduction Growth Maturity Declinelyn_30278No ratings yet
- SM Manual 09 Market Life Cycle Model Etc.Document7 pagesSM Manual 09 Market Life Cycle Model Etc.Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies for Product Life Cycle StagesDocument2 pagesMarketing Strategies for Product Life Cycle StagesJerissa Joy TaongNo ratings yet
- POM Lecture Managing New Product DevelopmentDocument27 pagesPOM Lecture Managing New Product DevelopmentAlina KhanNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument3 pagesThe Product Life Cyclechowa fellonNo ratings yet
- GRIET DMS SM PBAR Product Life Cycle Model AnalysisDocument7 pagesGRIET DMS SM PBAR Product Life Cycle Model AnalysisSuryaNo ratings yet
- Ass 1Document2 pagesAss 1Biruk Chuchu NigusuNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesDocument17 pagesProduct Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesAkshi BhagiaNo ratings yet
- The product life cycle stagesDocument12 pagesThe product life cycle stagesRajithaNo ratings yet
- PLC BasicDocument28 pagesPLC BasicTwinkal chakradhariNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument1 pageProduct Life CycleNesyraAngelaMedalladaVenesaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument3 pagesProduct Life Cyclekumar9030No ratings yet
- The Product Life Cycle (2nd AssingmentDocument15 pagesThe Product Life Cycle (2nd AssingmentShaheen SktNo ratings yet
- Describe The Stages of The Product Life Cycle and How Marketing Strategies Change During The Product Life Cycle?Document6 pagesDescribe The Stages of The Product Life Cycle and How Marketing Strategies Change During The Product Life Cycle?Fassy ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- PLC StagesDocument5 pagesPLC StagesMehedul Islam Sabuj0% (1)
- Strategic Marketing Project: Submitted By, Athira M Nair Rollno:9 MBA, T6Document10 pagesStrategic Marketing Project: Submitted By, Athira M Nair Rollno:9 MBA, T6AMNNo ratings yet
- How companies adapt marketing strategies over a product's life cycleDocument16 pagesHow companies adapt marketing strategies over a product's life cyclesanjaysundayNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument8 pagesProduct Life CycleBiswajit mallickNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy and the Product Life Cycle DashboardDocument23 pagesMarketing Strategy and the Product Life Cycle DashboardIsmatullah ZazaiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management for Beginners: How to Create and Establish Your Brand With the Right Marketing Management, Build Sustainable Customer Relationships and Increase Sales Despite a Buyer’s MarketFrom EverandMarketing Management for Beginners: How to Create and Establish Your Brand With the Right Marketing Management, Build Sustainable Customer Relationships and Increase Sales Despite a Buyer’s MarketNo ratings yet
- Dealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)From EverandDealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)No ratings yet
- Model Answer: Launch of a laundry liquid detergent in Sri LankaFrom EverandModel Answer: Launch of a laundry liquid detergent in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- The Secret to Business Immortality: The Impact Business Life CycleFrom EverandThe Secret to Business Immortality: The Impact Business Life CycleNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument14 pagesFinancial Marketsnikhil58555No ratings yet
- Branding StrategyDocument17 pagesBranding Strategynikhil58555No ratings yet
- CH IV Non Verbal CommunicationDocument9 pagesCH IV Non Verbal Communicationnikhil58555No ratings yet
- CH II Business Communication IIDocument10 pagesCH II Business Communication IInikhil58555No ratings yet
- Oganizational Communication Channels-VDocument14 pagesOganizational Communication Channels-Vnikhil58555No ratings yet
- 2 Business Letter-1Document1 page2 Business Letter-1nikhil58555No ratings yet
- CH III Nonverbal Communication IIIDocument10 pagesCH III Nonverbal Communication IIInikhil58555No ratings yet
- CH I Business Communication IDocument13 pagesCH I Business Communication Inikhil58555No ratings yet
- Inflation, 9Document5 pagesInflation, 9nikhil58555No ratings yet
- Functional Level Strategies-Ch7Document24 pagesFunctional Level Strategies-Ch7nikhil58555No ratings yet
- Sampling 2011Document14 pagesSampling 2011nikhil58555No ratings yet
- How Horlicks became India's most trusted health drink brandDocument21 pagesHow Horlicks became India's most trusted health drink brandbadboy123456789067% (6)
- Atlas Incorporated - Marketing Management ReportDocument38 pagesAtlas Incorporated - Marketing Management Reportagreen89No ratings yet
- Poma PPT Slides-Chapter 9-171869 MarketingDocument83 pagesPoma PPT Slides-Chapter 9-171869 MarketingIzzaty RohimiNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument23 pagesProduct Life CycleDrArjun GawasNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Stages and StrategiesDocument18 pagesProduct Life Cycle Stages and StrategiesRohit SemlaniNo ratings yet
- Kotler New Product DevelopmentDocument36 pagesKotler New Product DevelopmentMs. Joy96% (24)
- Presentation POM L3Document33 pagesPresentation POM L3Naoman ChNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Competitive DynamicsDocument41 pagesChapter 5 Competitive DynamicsMehmoud HusenNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Management (MarDocument3 pagesProduct Life Cycle Management (MarAnirban GhoshNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesProduct Life CycleSujeewa LakmalNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Product Life Cycle Stages Growth Tata Sky DTHDocument20 pagesMarketing Management Product Life Cycle Stages Growth Tata Sky DTHmarch20poojaNo ratings yet
- IntrotomarketingsaDocument5 pagesIntrotomarketingsaSteve SmithNo ratings yet
- Unilever's Sustainable Product ManagementDocument11 pagesUnilever's Sustainable Product ManagementYogesh Kumar0% (1)
- GBM Assignment 1Document2 pagesGBM Assignment 1Shehroz ChouhanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentrapworld66No ratings yet
- Case 1 Kelloggs - Using New Product Development To Grow A BrandDocument4 pagesCase 1 Kelloggs - Using New Product Development To Grow A BrandJackyHoNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument14 pagesProduct Life CycleAby MitNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Management Research - IMR VIIDocument990 pagesInterdisciplinary Management Research - IMR VIIEFOS ManagementNo ratings yet
- PLC StagesDocument5 pagesPLC StagesMehedul Islam Sabuj0% (1)
- Product Design and DevelopmentDocument25 pagesProduct Design and DevelopmentAvni Dodia RathodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Developing New Products - Managing The Product Life CycleDocument32 pagesChapter 8 - Developing New Products - Managing The Product Life Cyclexueting100% (1)
- Crafting The Brand PositioningDocument29 pagesCrafting The Brand PositioningAbhishek Raj PatelNo ratings yet
- PDT Life CycleDocument15 pagesPDT Life CycleBhumika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument2 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementneilNo ratings yet
- Product Lifecycles & Adoption CurveDocument20 pagesProduct Lifecycles & Adoption CurveAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- L12.1a Adressing Competition and Driving GrowthDocument53 pagesL12.1a Adressing Competition and Driving GrowthAshish kumar Thapa100% (2)
- 2.2.1 ProductDocument42 pages2.2.1 ProductdisgracedtrashNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle-Marketing StrategiesDocument14 pagesProduct Life Cycle-Marketing StrategiesNida MAlik0% (2)
- Itc ProjectDocument15 pagesItc ProjectprachyarathoreNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle: Ken HomaDocument45 pagesProduct Life Cycle: Ken HomaDaedalus MoonNo ratings yet