Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gravitation of Newton
Uploaded by
Rahma Diana YulistiahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gravitation of Newton
Uploaded by
Rahma Diana YulistiahCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard of Competency
Analyzing natural phenomenon and its regularity in
terms of point object mechanical
Menganalisis gejala alam dan keteraturannya dalam
cakupan mekanika benda titik
Basic Competency
Analyzing the regularity of planet motion in the solar
system based on Newton laws
Menganalisis keteraturan gerak planet dalam
tatasurya berdasarkan hukum-hukum Newton
INDICATOR
analyzing relationship between gravitation
force with the objects mass and its distance
calculating the resultant of gravitation force
on point object in a system
comparing gravitation acceleration and the
strength of gravitation field on different
position
analyzing planet motion in the solar system
based on kepplers law
NEWTONS LAW GRAVITATION
CHAPTER 2
Around 1600 -> german mathematician and astronomer ->
Johannes Kepler -> PLANET MOTION.
Three keplers law about planetary motion :
1. The path of each planet revolving the sun is elliptical
with the sun as the center lies on one of the focus
point
2. An imaginary line connecting the center of the sun to
that of the planets will sweep out the equal areas in
equal time interval
3. The ratio of the square of two planets periods is equal
to the ratio of their average distances from the sun
cubes
A. Phenomenon of Gravitation
Around 1686 -> Isaac newton -> British
physicist and mathematician .
Opinion of Isaac Newton :
1. How the planets revolve the sun while
staying on their elliptical orbits.
2. How the moon could stay on its circular orbit
while revolving the earth.
Gravitational acceleration is 9.8 m/s^2
Moon acceleration can be calculated from
moon centripetal acceleration
2
2
2
2
0027 . 0
4
2
s
m
a
T
R
R
T
R
R
v
a
s
s
=
=
|
.
|
\
|
= =
t
t
) 10 36 . 2 (
) 10 8 . 3 (
6
8
s x period moon T
m x orbit moon of radius R
=
=
B. GRAVITATIONAL FORCE
2
1
) / 10 67 . 6 ( tan
:
2
1
2 2 11
2
2 1
object of mass is m
object of mass is m
Kg Nm x t cons n gravitatio Universal is G
f orce nal gravitatio is F
where
r
m m
G F
g
g
=
Example on page 71
2
13
2
12
0
13 12
2
13
2
12
, 90
2
F F F
become F so is angle the if
Cos F F F F F
FORCE NAL GRAVITATIO OF RESULTANT
+ =
+ + = o
C. GRAVITATIONAL FIELD or
GRAVITATIONAL ACCELERATION
2
2
,
r
M
G
m
r
Mm
G
g
m
F
g so
g a
m
F
a
= =
=
=
=
Example page 78
COMPARE GRAVITATIONAL
ACCELERATION
2
2 2
2
2
2
A
B
B
A
B
B
A
A
B
B
A
A
B
A
r
r
x
m
m
m
r
x
r
m
r
m
G
r
m
G
g
g
= = =
Looking for gravitational acceleration between
two planets
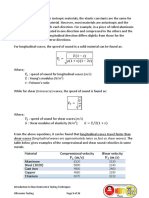
D. POTENTIAL ENERGY
r
m M
G PE
r x
r
m M
G PE
s x F PE
W PE
s x F W
W PE
g
g
=
=
=
=
=
=
2
We know that energy (E) is same as work (W)
Tanda NEGATIF menyatakan bahwa untuk memindahkan benda
bermassa m dari titik yang berjarak r terhadap pusat massa ke titik
yang jauh terhadap pusat massa DIPERLUKAN USAHA
Usaha yang diperlukan untuk memindahkan
sebuah benda dari jarak r1 ke jarak r2 adalah
Suatu benda bermassa 1.6 Kg akan dipindahkan dari permukaan
bumi ke tempat yang memiliki ketinggian satu kali jari-jari Bumi.
Jika massa Bumi 6 x 10 ^24 Kg, jari-jari Bumi 6400 Km, dan
G = 6.7 x 10^-11 dalam SI, berapakah usaha yang harus dilakukan.
1 2 2 1
EP EP W =
>
J x W
R
GMm
R
GMm
W
EP EP W
7
2 1
2 1
1 2 2 1
10 5
......
2
=
=
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
=
>
>
>
E. Relationship between newtons law
of gravitation and keplers law
k
GM
r
T
GM
r r
T
GM
r
M
G
T
r
r
M
G
T
r
=
=
=
=
=
|
.
|
\
|
2
3
2 2
2
2 2
2
2 2
2
4
4
4
4
2
t
t
t
t
t
r
M
G
v
r
M
G
r
v
r
Mm
G
r
v
x m
r
Mm
G a x m
F F
s
g s
=
=
=
=
=
2
2
2
2
2
2
You might also like
- Spec RafinateDocument1 pageSpec RafinateRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Bpsfile Ammonium Nitrate ImporDocument1 pageBpsfile Ammonium Nitrate ImporRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties - PerryDocument1 pageThermodynamic Properties - PerryRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Analisa Aliran Fluida Pada Mixing Crude Oil Storage Tank Dengan CFDDocument10 pagesAnalisa Aliran Fluida Pada Mixing Crude Oil Storage Tank Dengan CFDRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Materi Pendahuluan: Abdullah Saleh, Farida Ali & SelfianaDocument33 pagesMateri Pendahuluan: Abdullah Saleh, Farida Ali & SelfianafpsdilaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument16 pagesChemistryRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument3 pagesApplication LetterRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Patent Process and Plant of Production Sulphuric Acid. Patent No. US 7837970B2Document24 pagesPatent Process and Plant of Production Sulphuric Acid. Patent No. US 7837970B2Rahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument6 pagesParticulate Nature of MatterRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Element in Periodic TableDocument7 pagesProperties of Element in Periodic TableRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- The Used of RadioactiveDocument4 pagesThe Used of RadioactiveRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Material: Compiled By: Kadek Windy HDocument9 pagesThe Structure of Material: Compiled By: Kadek Windy HRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Grammar Corner: Simple Past, Past Continuous & Perfect TensesDocument4 pagesGrammar Corner: Simple Past, Past Continuous & Perfect TensesRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- Theories of Acids and BasesDocument33 pagesTheories of Acids and BasesRahma Diana YulistiahNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- General Data Model for Hotel Canopy StructureDocument23 pagesGeneral Data Model for Hotel Canopy StructureTAHANo ratings yet
- JM302 Material Technology Buoyancy Case StudyDocument5 pagesJM302 Material Technology Buoyancy Case StudyJeffery YipNo ratings yet
- Two-Way Slabs: Triangularly Distributed Load (Elastic Analysis) Two-Way Slabs: Triangularly Distributed Load (Collapse Method)Document1 pageTwo-Way Slabs: Triangularly Distributed Load (Elastic Analysis) Two-Way Slabs: Triangularly Distributed Load (Collapse Method)Ehsan ShNo ratings yet
- FM & F Machines 2013 PDFDocument355 pagesFM & F Machines 2013 PDFChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- ICE-2312 Lab Experiment 3 Diffraction Gratings: Students Name Address DateDocument15 pagesICE-2312 Lab Experiment 3 Diffraction Gratings: Students Name Address DateZack NduatiNo ratings yet
- AISC SCM2013 - Designexample Chapter E Design of Members For CompressionDocument81 pagesAISC SCM2013 - Designexample Chapter E Design of Members For CompressionOktavia PutriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Apparatus Design: Chapter-1Document53 pagesChemical Engineering Apparatus Design: Chapter-1Eshetu ShemetNo ratings yet
- Journal Bearing Lubrication Theory and DesignDocument17 pagesJournal Bearing Lubrication Theory and DesignAndres Alberto Osorio YupanquiNo ratings yet
- (1.0 Credit) : Structural Analysis and Design Sessional-IDocument34 pages(1.0 Credit) : Structural Analysis and Design Sessional-IAnonymous aE0YYlCOKNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument2 pagesMy TestLim Chin YangNo ratings yet
- 2007 Echeverri, Measurements and CFD Simulation of The Flow in Vacuum PansDocument13 pages2007 Echeverri, Measurements and CFD Simulation of The Flow in Vacuum PansnghiNo ratings yet
- Settlement of shallow foundations estimated using elastic theoryDocument9 pagesSettlement of shallow foundations estimated using elastic theoryAllan GóesNo ratings yet
- 1 Projectile Motion Case I and IIDocument40 pages1 Projectile Motion Case I and IIMa. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Field Material DerivativeDocument1 pageAcceleration Field Material DerivativeLit Pao WongNo ratings yet
- Tension 20180815 PDFDocument83 pagesTension 20180815 PDFIrish TambisNo ratings yet
- 최신대학물리학 5판 Ch12Document33 pages최신대학물리학 5판 Ch12아기상어No ratings yet
- Quality Control Materials ConstructionDocument74 pagesQuality Control Materials ConstructionMark James MateoNo ratings yet
- MSMBM Oct 2022 - 2Document2 pagesMSMBM Oct 2022 - 2battuarunNo ratings yet
- Ensuring ductility in RC designDocument5 pagesEnsuring ductility in RC designTabrez AhmedNo ratings yet
- 03 Assignment-3 Circular Motion SCDocument9 pages03 Assignment-3 Circular Motion SCPiyush PandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula SheetFrozen FlameNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Steel - Concrete Composite Beams by RfemDocument6 pagesModeling of Steel - Concrete Composite Beams by RfemTomasz WróblewskiNo ratings yet
- Phy PreDocument7 pagesPhy PreNaveen JhaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsabvincenzo78sNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5 Shear Strength in Soil UploadDocument34 pagesChapt 5 Shear Strength in Soil UploadabdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Momentum WsDocument4 pagesMomentum WsHalil Çelik AykentNo ratings yet
- Wind Load CalculationsDocument32 pagesWind Load Calculationsvirat_dave100% (2)
- Ultrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 9-12Document4 pagesUltrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 9-12Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Contact and Noncontact Forces StationDocument12 pagesContact and Noncontact Forces StationDemanda GookinNo ratings yet
- Home Package Physics Form Five 24/03/2020 Answer All QuestionsDocument26 pagesHome Package Physics Form Five 24/03/2020 Answer All QuestionsBaraka bryceson100% (1)