Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Projectile Motion
Uploaded by
YukiC123Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Projectile Motion
Uploaded by
YukiC123Copyright:
Available Formats
2 dimensional motion
Horizontally projected
TSWBAT
Solve 2-d motion
problems
projected horizontally
projected at an angle
with initial displacement
2 Dimensional Motion
Lets review what we already
know...
2 dimensional motion is
simply the combination of
motion in the x direction
with motion in the y
direction
2 Dimensional Motion
The curved (parabolic)
shape of this motion is
the natural result of this
combination
The general motion
equation holds
2
2
1
t a t v s
i
A + A =
Equations
We get 2 versions of the
equations - x & y direction
These motion equations
simplify
2
2
1
t a t v s
x ix x
A + A = A
2
2
1
t a t v s
y iy y
A + A = A
Simplification
In the x direction the object
does not usually accelerate so
a
x
= 0
If it has a rocket motor, a
x
>0
If we include air resistance,
a
x
<0.
( )
2
2
1
t a t v s
ix x
A + A = A
0
0
Simplification
In the y direction the object
accelerates due to gravity so
a
y
= g = -9.8 m/s
2
2
2
1
) ( t g t v s
iy y
A + A = A
2
2
1
t a t v s
y iy y
A + A = A
For a horizontally projected object,
there is no initial vertical velocity, v
i
=0
2
2
1
) 8 . 9 ( t t v s
iy y
A + A = A
2
9 . 4 t t v s
iy y
A A = A
2
9 . 4 ) 0 ( t t s
y
A A = A
2
9 . 4 t s
y
A = A
2
2
1
t a t v s
y iy y
A + A = A
2-D
Equations
The object moves forward
at a constant speed only
while it is airborne!
Time is the same in both
equations
t v s
ix x
A = A
2
9 . 4 t s
y
A = A
Steps to Solution
You will be given information to
solve either the x-direction or
y-direction for time
Then use the time to solve for
the unknown direction
Usually you solve for the
y-direction first
Check for
Understanding
Try to answer the
following multiple choice
QUESTIONS before
advancing to the next
slide for the answer.
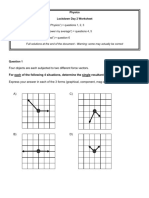
Question 1
A girl throws a ball straight up at
a speed of 10 m/s. Which
statement is true?
a - the ball accelerates all the time
it is in the air
b - the ball is always moving when
it is in the air
c - the height the ball rises to
depends on the balls weight
Question 1
A girl throws a ball straight up at
a speed of 10 m/s. Which
statement is true?
a - the ball accelerates all the time
it is in the air
b - the ball is always moving when
it is in the air
c - the height the ball rises to
depends on the balls weight
Question 2
A key to understanding projectile
motion is to know that:
a - gravity always causes the
velocity of an object to increase
b - horizontal motion is independent
of vertical motion
c - acceleration is zero at the
highest point in the trajectory
Question 2
A key to understanding projectile
motion is to know that:
a - gravity always causes the
velocity of an object to increase
b - horizontal motion is independent
of vertical motion
c - acceleration is zero at the
highest point in the trajectory
Question 3
Two bullets are fired horizontally
from the same height at the same
time. One has twice the velocity
of the other. Which hits the
ground first? ( no air resistance!)
a - the faster one
b - the slower one
c - they hit the ground at the
same time
Question 3
Two bullets are fired horizontally
from the same height at the same
time. One has twice the velocity
of the other. Which hits the
ground first? ( no air resistance!)
a - the faster one
b - the slower one
c - they hit the ground at the
same time
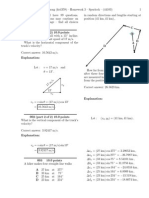
Sample - Thelma & Louise
A car is driven horizontally off a
100 m cliff at 25 m/s. How far
from the base of the cliff will
the wreckage be found?
x - direction y-direction
A s
x
= ? m A s
y
= -100 m
v
ix
= 25 m/s v
iy
= 0 m/s
a
x
= 0 m/s
2
a
y
= g = -9.8 m/s
2
A t = ?
Solution
Solve y-direction first to find
time
-100m=(0m/s)At+0.5(-9.8m/s
2
)At
2
-100m=-4.9m/s
2
At
2
(-100 m)/(-4.9m/s
2
) = At
2
20.4 s
2
= At
2
At
2
= \20.4 s
2
At = 4.5 s
2
2
1
t g t v s
iy y
A + A = A
Solution
Then solve x direction
using time found
s
x
= 25 m/s (4.5s)
s
x
= 112.5 m
t v s
ix x
A = A
Parametric equations
These results could also be found
by graphing
recall: A s = s
f
- s
i
So s
fx
=s
ix
+ v
ix
At + a
x
At
2
And s
fy
=s
iy
+ v
iy
At + gAt
2
Using the parametric mode:
X
T1
= 0 + 25T + 0.5(0)T
2
Y
T1
= 100 + 0T + 0.5(-9.8)T
2
0
0
0
25 T
100 - 4.9 T
2
Practice Problem
A ball is thrown
horizontally off a 20 m high
tower at 15 m/s.
How long is it in the air?
Where does it hit the ground?
What is the magnitude of its
velocity when it hits the
ground?
Answer:
t = 2.02 s, s
x
= 30.3 m
First, pick out known & unknown
values from the problem.
x - direction y-direction
A s
x
= ? m A s
y
= -20 m
v
ix
= 15 m/s v
iy
= 0 m/s
a
x
= 0 m/s
2
a
y
= g = -9.8 m/s
2
A t = ?
Solution
Solve y-direction first to find
time
-20m=(0m/s)At+0.5(-9.8m/s
2
)At
2
(-20 m)/(-4.9m/s
2
) = At
2
4.04 s
2
= At
2
At
2
= \4.04 s
2
At = 2.02 s
2
2
1
t g t v s
iy y
A + A = A
Solution
Then solve x direction
using time found
s
x
= 15 m/s (2.02s)
s
x
= 30.3 m
t v s
ix x
A = A
Solution
The same thing can be
done with the velocity
equation, x and y are still
independent:
v
f
= v
i
+ aAt
So in the x direction:
v
fX
= v
iX
+ a
X
At
a
x
=0 so v
fx
= v
ix
= 15 m/s
http://www.
physicsclassroom.
com/mmedia/
vectors/hlp.html
Solution
And in the y direction:
v
fY
= v
iY
+ a
Y
At
v
fy
= 0m/s + (-9.8 m/s
2
)(2.02s)
v
fy
= -19.8 m/s
Then combine the vectors!
Solution
v
fx
= 15 m/s v
fY
= -19.8 m/s
Use Pythagorean theorem to
get the magnitude and &
inverse tangent to get
direction.
v
f
= 24.8 m/s, 307degrees
) (
2 2
fy fx f
v v v + =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
fx
fy
v
v
1
tan u
On Your Own
Class work
Worksheets on horizontally
projected motion
2 dimensional motion
Part 2 - At an angle
TSWBAT
Solve 2-d motion
problems
projected horizontally
projected at an angle
with initial displacement
2-D Motion Equations
These same equations we used in the
first case (horizontally projected)
hold true when the object is initially
thrown at an angle.
BUT Initial velocity in the y direction
is NOT zero, so it does NOT cancel
out!
t v s
ix x
A = A
2
2
1
t g t v s
iy y
A + A = A
2 - d projected at an angle
The initial velocity must be
broken down into an x and y
component using right triangle
trigonometry
Then the problem is solved like
before.
v
ix
= v
i
cos
v
iy
= v
i
sin
v
i
v
ix
v
iy
u
http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/ph
ys/mmedia/vectors/nhlp.html
Without gravity
With gravity
Note:
The path of our (Case 2) projectile
is a symmetric parabola.
Speed at takeoff = speed at
landing.
Angles are equal in magnitude,
opposite in direction.
Check your understanding
http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci
/phys/Class/vectors/u3l2b.html
And now, the math
Sample Problem
The six million dollar man kicks
a ball at a 30 degree angle
giving it a velocity of 100 m/s.
How long is it in the air?
How far away does it land?
How fast is it going when it
hits the ground?
How high does it rise?
http://www.phys.virginia.edu/classes/109N/more_
stuff/Applets/ProjectileMotion/jarapplet.html
Gather x & y variables
Step 1- resolve the velocity
into x & y components
v
ix
= v
i
cos
= 100 cos 30 = 86.6 m/s
v
iy
= v
i
sin
= 100 sin 30 = 50 m/s
x-
direction
y-
direction
Displacement s(m) ? ?
Velocity v(m/s) 8.66 5
Acceleration
a(m/s
2
)
0 -9.8
Time t(s) ? ?
Variables
86.6
50
Hang time:
How long is it in the air?
Before it is kicked and when it hits the
ground, its height above the ground is
zero so its change in height s
y
= 0.
s
y
= v
iy
At + 0.5 g A t
2
0 = 50 At - 4.9 A t
2
0 = At (50 - 4.9 A t)
0 = At 0 = 50 - 4.9 A t
50 = 4.9 A t
A t = 10.2 s
Range:
How far away does it land?
s
x
= v
ix
t
s
x
= 86.6 m/s (10.2s)
s
x
= 884 m
Velocity:How fast is it going?
Find v
fx
& v
fy
@ t=1.02 s using: v
f
= v
i
+ at
v
fx
= v
ix
+ a
x
t v
fy
= v
iy
+ a
y
t
v
fx
= 86.6m/s + 0t = 86.6 m/s
v
fy
= 50 m/s +(-9.8m/s
2)
(10.2s)
= -49.96 m/s
Use Pythagorean theorem & trig
V
f
= ((86.6)
2
+ (-49.96)
2
)
= 99.98 m/s =
~ 100 m/s
u = tan
-1
(-4.996/8.66) = -30
in quadrant IV v
f
= 100 m/s, 330
Max height
Just like the case of a ball
thrown vertically upward,
Max height occurs when v
fy
= 0.
V
fy
2
= v
iy
2
+ 2a
y
s
y
0
2
= 50
2
+ 2(-9.8)s
y
-2500 = -19.6s
y
s
y
= 128 m
Check our solution
http://www.phys.virginia.edu/classe
s/109N/more_stuff/Applets/Proje
ctileMotion/jarapplet.html
Practice Problem 2 -
Try this on your own before
checking your answer
A ball is kicked at a 60 degree
angle at 20 m/s.
How long is it in the air?
Where does it hit the ground?
How high is it at its highest point?
What is the magnitude of its
velocity when it hits the ground?
x-direction y-direction
Displacement s(m) ? ?
Velocity v(m/s) 10 17.3
Acceleration a(m/s
2
) 0 -9.8
Time t(s) ? ?
Variables
Resolve the velocity into components
v
ix
= v
i
cos u= 20 cos 60 = 10 m/s
v
iy
= v
i
sin u= 20 sin 60 = 17.3 m/s
Solve y direction
Before it is kicked and when it hits
the ground, its height above the
ground is zero so its change in height
s
y
= 0.
s
y
= v
iy
At + 0.5 g A t
2
0 = 17.3 At - 4.9 A t
2
0 = At (17.3 - 4.9 A t)
0 = At 0 = 17.3 - 4.9 A t
17.3 = 4.9 A t
A t = 3.53 s
Solve x direction
s
x
= v
ix
t
s
x
= 10 m/s (3.53s)
s
x
= 35.3 m
Max height
Max height occurs when v
fy
= 0.
v
fy
2
= v
iy
2
+ 2 g s
y
0
= (17.3)
2
- 19.6 s
y
19.6 s
y
= 299.3
s
y
= 15.3 m
Solve velocity
Find v
fx
& v
fy
@ t = 3.53 s using
v
f
= v
i
+ at and then use
Use Pythagorean theorem &
trigonometry to find v
f
OR
APPLY symmetry
V
f
= v
iy
= 20 m/s
u
f
= - u
i
= -60 in quadrant IV
so v
f
= 20 m/s, 300
Follow-up
Worksheet #2 Projected at an
angle
2 dimensional motion
Horizontal & at an angle
TSWBAT
Solve 2-d motion
problems
projected horizontally
projected at an angle
with initial displacement
Initial displacement
If the object is initially some
height above the ground when it
is projected at an angle, it is
usually necessary to use the
quadratic formula. It will not
easily factor!
If its initial height is 0, then
you can factor out a t!
Sample Problem
A ball is kicked off a 50 m tower
at a 30 degree angle giving it a
velocity of 10 m/s.
How long is it in the air?
How far away does it land?
At what velocity does it hit the
ground?
How high does it rise?
Solve
Step 1- resolve the velocity into x & y
components
v
ix
= v
i
cos u= 10 cos 30 = 8.66 m/s
v
iy
= v
i
sin u= 10 sin 30 = 5 m/s
x direction y direction
s ? -50 m
v
i
8.66 m/s 5 m/s
a 0 m/s
2
-9.8 m/s
2
t ? = ?
Find time in air
Its height above the ground is 50m so its
change in height s
y
= -50m.
A s
y
= v
iy
At + 0.5 g A t
2
-50 = 5 At - 4.9 A t
2
4.9t
2
- 5t - 50 = 0
a = 4.9 b = -5 c = -50
Use quadratic formula - discard negative answer
t = (-b \ b
2
- 4ac) / (2a)
t = (-(-5) \ (-5)
2
- 4(4.9)(-50) ) / (2(4.9))
t = - 2.7, 3.7s so t = 3.7s when it hits the
ground
How far away does it land?
s
x
= v
ix
At
s
x
= 8.66 m/s (3.7s)
s
x
= 32.04 m
Velocity:How fast is it going?
Find v
fx
& v
fy
@ t=3.7 s using: v
f
= v
i
+ at
v
fx
= v
ix
+ a
x
t v
fy
= v
iy
+ a
y
t
v
fx
= 8.66m/s + 0t = 8.66 m/s
v
fy
= 5 m/s +(-9.8m/s
2)
(3.7s)
= -31.26 m/s
Use Pythagorean theorem & trig
V
f
= ((8.66)
2
+ (-31.26)
2
)
= 32.4 m/s
u = tan
-1
(-31.26/8.66) = -74.5
in quadrant IV v
f
= 32.4 m/s, 285.5
Max height
Just like the case of a ball thrown
vertically upward,
Max height occurs when v
fy
= 0.
V
fy
2
= v
iy
2
+ 2a
y
s
y
0
2
= 5
2
+ 2(-9.8)s
y
-25 = -19.6s
y
s
y
= 1.28 m above starting point OR
50 m + 1.28 m = 51.28 m above the
ground
Practice Problem
A ball is projected off a
120 m high tower at a 50
degree angle at 25 m/s.
How long is it in the air?
Where does it hit the ground?
What is the magnitude of its
velocity when it hits the
ground?
Solutions
t = -3.4, 7.3 s so t = 7.3 s
when it hits the ground
s
x
= 117.3 m
v
f
= 54.8 m/s, 290
s
y
= 18.7 m above starting point
OR 120 m + 18.7 m = 138.7 m
above the ground
Solve
Step 1- resolve the velocity into x & y
components
v
ix
= v
i
cos u= 25 cos 50
o
= 16.07 m/s
v
iy
= v
i
sin u= 25 sin 50
o
= 19.15 m/s
x direction y direction
s ? -120 m
v
i
16.07 m/s 19.15 m/s
a 0 m/s
2
-9.8 m/s
2
t ? = ?
Find time in air
Its height above the ground is 50m so its
change in height s
y
= -50m.
A s
y
= v
iy
At + 0.5 g A t
2
-120 = 19.15 At - 4.9 A t
2
4.9t
2
- 19.15t - 120 = 0
a = 4.9 b = -19.15 c = -120
Use quadratic formula - discard negative answer
t = (-b \ b
2
- 4ac) / (2a)
t=(-(-19.15) \(-19.15)
2
-4(4.9)(-120))/(2(4.9))
t = -3.4, 7.3 s so t = 7.3 s when it hits the
ground
How far away does it land?
s
x
= v
ix
At
s
x
= 16.07 m/s (7.3s)
s
x
= 117.3 m
Velocity:How fast is it going?
Find v
fx
& v
fy
@ t=3.7 s using: v
f
= v
i
+ at
v
fx
= v
ix
+ a
x
t v
fy
= v
iy
+ a
y
t
v
fx
= 16.07m/s + 0t = 16.07 m/s
v
fy
= 19.15 m/s +(-9.8m/s
2)
(7.3s)
= -52.39 m/s
Use Pythagorean theorem & trig
V
f
= ((19.15)
2
+ (-52.39)
2
)
= 54.8 m/s
u = tan
-1
(-52.39/19.15) = -70
in quadrant IV v
f
= 54.8 m/s, 290
Max height
Just like the case of a ball thrown
vertically upward,
Max height occurs when v
fy
= 0.
V
fy
2
= v
iy
2
+ 2a
y
s
y
0
2
= 19.15
2
+ 2(-9.8)s
y
-366.7 = -19.6s
y
s
y
= 18.7 m above starting point OR
120 m + 18.7 m = 138.7 m
above the ground
Projectile Motion
Review of Concepts and Cases
X & Y directions
2 dimensional motion is simply
the combination of motion in
the x direction with motion in
the y direction
The x and y direction motions
are independent of each other
and are solved separately.
Acceleration
By definition a projectile does
not accelerate and in high school
physics we generally ignore air
resistance so a
x
=0.
The objects only acceleration is
due to the attractive force
between it and the planet so a
y
=
g = -9.8m/s
2
Velocity
When an object is projected
horizontally (0
o
) all of the velocity is
horizontal, none vertical so...
v
ix
= v
i
& v
iy
= 0.
When an object is projected
at an angle it has both an x and y
components.
v
ix
= v
i
cos u
v
iy
= v
i
sin u
note: when u = 0
o
,
v
ix
= v
i
& v
iy
= 0.
Displacement
Remember that delta means the
change between final and initial so
As = s
f
-s
i
This means we can rewrite to create
the general projectile motion
equations
As
x
= (v
i
cos u) At
s
fy
= s
iy
+ (v
i
sin u) At + g At
2
Velocity equations
v
fx
= v
i
cos u
v
fy
= v
i
sin u + gAt
These equations always work, but
you may find it easier to use the
special case equations depending on
your algebra skills.
Note:
The path of our projectile is a parabola.
At the same height the speed going up
is the same as the speed falling down.
At its highest point, v
y
= 0, but v
x
does
not change throughout the arc.
You might also like
- Projectile MotionDocument74 pagesProjectile MotionAlvin Tung Kwong ChoongNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and Dynamics Concepts ExplainedDocument51 pagesKinematics and Dynamics Concepts ExplainedArilSharilNo ratings yet
- Solving Accelerated Motion ProblemsDocument23 pagesSolving Accelerated Motion ProblemsrhazoorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Rectilinear Translation MotionDocument39 pagesLesson 1: Rectilinear Translation MotionAaron EserNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Honors PhysicsDocument29 pagesProjectile Motion Honors PhysicsDeepanshu GautamNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: A Two - Dimensional MotionDocument34 pagesProjectile Motion: A Two - Dimensional MotionNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight LineDocument22 pagesMotion Along A Straight LineChan EnglandNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument7 pagesKinematicsNicole WheelerNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 2 Vectors 2d MotionDocument11 pagesPractice Test 2 Vectors 2d MotionLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNo ratings yet
- Motion of A Projectile: Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesDocument14 pagesMotion of A Projectile: Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiessohamdeyNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2012 1 Projectile 2013Document101 pagesProjectile Motion 2012 1 Projectile 2013Socorro Mari Vivas KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies 2 1Document17 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies 2 1vladz grabadorNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument58 pagesProjectile Motionrain diapoletNo ratings yet
- Work On It Together, Finish It at HomeDocument10 pagesWork On It Together, Finish It at HomeChanseNo ratings yet
- Projectile Practice Problems Solutions 2021Document33 pagesProjectile Practice Problems Solutions 2021HAN SEUL SHIMNo ratings yet
- (P2) Resume Kinematics in One Dimensions ExampleDocument10 pages(P2) Resume Kinematics in One Dimensions Examplekaneki kenNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear MotionDocument24 pagesRectilinear Motionkennethfox12311No ratings yet
- Free FallDocument24 pagesFree FallMarArizalaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument74 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesArah Louise ApostolNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionsDocument43 pagesMotion in Two DimensionsJessiee YeoNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsDocument22 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- 2d Motiontest - 5R Review - KEYDocument6 pages2d Motiontest - 5R Review - KEYKristel Jade MontaNo ratings yet
- Mod3 Practice SolutionsDocument4 pagesMod3 Practice SolutionsShanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - CH 3 Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesAP Physics 1 - CH 3 Projectile MotionEarl Clyde BañezNo ratings yet
- Homework 3 SolutionsDocument34 pagesHomework 3 Solutionsewwiekimmie100% (2)
- Lecture 4-Kinematics in Two DimensionsDocument56 pagesLecture 4-Kinematics in Two DimensionsMariaLuzNo ratings yet
- 2 - Proj MotionDocument23 pages2 - Proj MotionkookNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument64 pagesProjectileRegine BataNo ratings yet
- Physics Lockdown Day 2 WorksheetDocument7 pagesPhysics Lockdown Day 2 WorksheetwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line: Initial PositionDocument7 pagesMotion in A Straight Line: Initial PositionEngelbert Bicoy AntodNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Guide For AP Physics 1Document27 pagesProjectile Motion Guide For AP Physics 1renenutet100% (2)
- Projectile MotionDocument36 pagesProjectile MotionChezka GuerzonNo ratings yet
- Project LeDocument26 pagesProject LeBelle FriasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 PhysicsDocument43 pagesLesson 4 PhysicsGen Z LearnersNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement ExplainedDocument37 pagesDistance and Displacement ExplainedHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Motion Under GravityDocument5 pagesMotion Under GravityRizul thakurNo ratings yet
- Motion in 2 DDocument12 pagesMotion in 2 DVenesia Ayu Dewanti0% (1)
- CH 2Document4 pagesCH 2Civil NutNo ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated and Free Fall MotionDocument26 pagesUniformly Accelerated and Free Fall MotionMarianne EdullanNo ratings yet
- 7.2 ProjectMotDocument3 pages7.2 ProjectMotSubramanyam Vangara100% (1)
- PHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Document8 pagesPHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Dnhdj JdhsjdNo ratings yet
- PHY 2325-ch4Document4 pagesPHY 2325-ch4biatris pNo ratings yet
- Free Fall - Austria, Joyce NicoleDocument3 pagesFree Fall - Austria, Joyce NicoleJoyce AustriaNo ratings yet
- Projectiles SolutionsDocument9 pagesProjectiles SolutionsNickolas RogersNo ratings yet
- Physics 40A Midterm Solutions Winter 2013Document7 pagesPhysics 40A Midterm Solutions Winter 2013Mt RushNo ratings yet
- Uniform and Non Uniform MotionDocument31 pagesUniform and Non Uniform MotionちゃんミカNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Equations and ExamplesDocument22 pagesProjectile Motion Equations and ExamplesKhairul HafizNo ratings yet
- Solve Dynamic Problem 3Document4 pagesSolve Dynamic Problem 3usama naeemNo ratings yet
- PhyI Assign&Answers 2011Document16 pagesPhyI Assign&Answers 2011Austin Phua Yun Hock100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - MotionDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - MotionSalina MohmadNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Description of MotionDocument30 pagesKinematics: Description of MotionMind ControlNo ratings yet
- Motion Fundamentals ExplainedDocument30 pagesMotion Fundamentals ExplainedMind ControlNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Description of MotionDocument30 pagesKinematics: Description of MotionMind ControlNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Description of MotionDocument30 pagesKinematics: Description of MotionMind ControlNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Physics Previous Year Questions With Solutions On Kinematics 1DDocument9 pagesJEE Main Physics Previous Year Questions With Solutions On Kinematics 1DRajNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 2: November 2012Document31 pagesMechanics 2: November 2012Adnan FaisalNo ratings yet
- HW02 SolutionsDocument5 pagesHW02 Solutionshansony_2100% (3)
- Motion of A Projectile (Section 12.6) Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesDocument15 pagesMotion of A Projectile (Section 12.6) Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesbigbangmelvanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- CE Rotation List M3Document5 pagesCE Rotation List M3YukiC123No ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF ANTIBIOTIC SELECTION FOR COMMON INFECTIONSDocument2 pagesPRINCIPLES OF ANTIBIOTIC SELECTION FOR COMMON INFECTIONSYukiC123No ratings yet
- ERAS Statistics Preliminary Data - Residency 11.15.2022 2Document39 pagesERAS Statistics Preliminary Data - Residency 11.15.2022 2YukiC123No ratings yet
- MCAT ReviewDocument162 pagesMCAT ReviewYukiC123No ratings yet
- Change ManagementDocument36 pagesChange ManagementYukiC123No ratings yet
- LP ProblemsDocument9 pagesLP ProblemsYukiC123No ratings yet
- Giddens Chapter 1Document15 pagesGiddens Chapter 1YukiC123No ratings yet
- 3.2 Logarithmic FunctionsDocument19 pages3.2 Logarithmic FunctionsYukiC123No ratings yet
- 3.0 Exponents Review SheetDocument1 page3.0 Exponents Review SheetYukiC123No ratings yet
- 3.2 Log Graphing SheetDocument2 pages3.2 Log Graphing SheetYukiC123No ratings yet
- Apush Cis 6Document1 pageApush Cis 6YukiC123No ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam ReviewDocument2 pagesChemistry Exam ReviewYukiC123No ratings yet
- 3.1 Exponential FunctionsDocument19 pages3.1 Exponential FunctionsYukiC123No ratings yet
- 3.1 Exponential Graphing SheetDocument2 pages3.1 Exponential Graphing SheetYukiC123No ratings yet
- Polynomial Solution MethodsDocument35 pagesPolynomial Solution MethodsYukiC123No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument27 pagesVectorsYukiC123No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 CISDocument2 pagesChapter 11 CISYukiC123No ratings yet
- 1.6 Inverse FunctionsDocument14 pages1.6 Inverse FunctionsYukiC1230% (1)
- AP Euro ReviewDocument26 pagesAP Euro ReviewYukiC123No ratings yet
- Renaissance Discovery and PhilosophersDocument2 pagesRenaissance Discovery and PhilosophersYukiC123No ratings yet
- 1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsDocument16 pages1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsYukiC123No ratings yet
- Surge Control PDFDocument14 pagesSurge Control PDFMohamed Guezguez100% (1)
- LRV InglesDocument88 pagesLRV Inglesjose ruben jimenezNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation LectureDocument16 pagesBernoulli Equation LectureabasNo ratings yet
- Edwards J. - Piping Workbook. Solving Piping and Header Networks Using Chemcad Version 6.2Document73 pagesEdwards J. - Piping Workbook. Solving Piping and Header Networks Using Chemcad Version 6.2نزار الدهاميNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop Calculation - Primary Pump & Secondary PumpDocument6 pagesPressure Drop Calculation - Primary Pump & Secondary PumpAzher ANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field MappingDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Field MappingLim Hui Wen100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump and Mechanical Seal FormulasDocument3 pagesCentrifugal Pump and Mechanical Seal FormulasRam Babu Ramzz100% (1)
- Unit 2: Lesson 2 Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument11 pagesUnit 2: Lesson 2 Kinetic and Potential EnergysharonNo ratings yet
- Friction FactorDocument13 pagesFriction FactorRaju KsnNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document72 pagesCH 8Charles ChungNo ratings yet
- Angle Bar Dimension & WeightDocument1 pageAngle Bar Dimension & Weightanjangandak2932No ratings yet
- Environment Micro-ProjectDocument15 pagesEnvironment Micro-ProjectGanesh GoreNo ratings yet
- Types of Fluid Flow: Steady, Compressible, Viscous & MoreDocument9 pagesTypes of Fluid Flow: Steady, Compressible, Viscous & MoreHammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Coanda EffectsDocument33 pagesCoanda EffectsNeyMarNo ratings yet
- Pump Head CalculationsDocument65 pagesPump Head CalculationsAnonymous TjdHCuNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Unit MDDF TVDDF Tvdss Gradient Pressure: InternalDocument27 pagesReservoir Unit MDDF TVDDF Tvdss Gradient Pressure: InternalYber LexNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT MECHANICSDocument19 pagesTRANSPORT MECHANICSMariAntonetteChangNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Viscosity Measurement Via Falling Ball Method PDFDocument11 pagesLab 5 - Viscosity Measurement Via Falling Ball Method PDFrenel augustinNo ratings yet
- Forebay DesignDocument14 pagesForebay DesignOmar Shahid100% (1)
- History and Trends of Fluid MechanicsDocument8 pagesHistory and Trends of Fluid MechanicsMd. Rahimul IslamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - Flow Lab Worksheet - With DataDocument2 pagesExperiment 6 - Flow Lab Worksheet - With DataMohsin MumtazNo ratings yet
- Sempell Valve PDFDocument2 pagesSempell Valve PDFAnand K. MouryaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDocument12 pagesWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- Guha Smiley IMechE PartA 2010 Tesla TurbineDocument18 pagesGuha Smiley IMechE PartA 2010 Tesla Turbineemir__dNo ratings yet
- Machines Hydraulics TOC CH 4-7Document4 pagesMachines Hydraulics TOC CH 4-7xan mianNo ratings yet
- Forced convection over cylinders and spheresDocument17 pagesForced convection over cylinders and spheresananth2012No ratings yet
- Projectile and Circular MotionDocument43 pagesProjectile and Circular MotionFelix BermeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Summary & Solution To PS1)Document28 pagesChapter 1 (Summary & Solution To PS1)RITCHIE LOU CAGULADANo ratings yet
- Cap ListDocument329 pagesCap ListNay AungNo ratings yet
- Types of ValvesDocument13 pagesTypes of ValvesRajkumar ANo ratings yet