Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spinal and Brainstem Reflexes in Infant Development
Uploaded by
Ryan ZeinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spinal and Brainstem Reflexes in Infant Development
Uploaded by
Ryan ZeinCopyright:
Available Formats
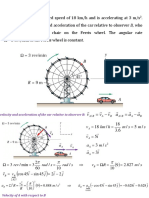
Primitive/Spinal Reflexes Flexor withdrawal
Stimulus Noxious stimulus (pinprick) to sole of foot. Tested In supine or Sitting position Noxious stimulus to ball of foot of extremity fixed in extension; tested in supine position.
Response Toes extend. foot doni6excs, entire leg flexes uncontrollalbly. Onset: 28 weeks gestation. lntegrared. 1-2 months Opposite lower extremity flexes. Then adducts and extends Onset: 28 weeks gestation Integrated. 1-2 months. Grasp and total flexion of the upper extremity. Onset: 28 weeks gestation Integrated : 2-5 months. Extension, abduction of upper extremities. hand opening. and crying followed byflexion, adduction of arms across chest. Onset: 28 weeks gestation Integrated: 5-6 months. Sudden extension or abduction of arms. crying. Onset: birth. integrated: persists Maintained flexion of fingers or toes. Onset: palmer, birth; plantar, 28 weeks gestation. Integrated: palmer, 4 -6 months; plantar, 9 months
Crossed extension
Traction
Grasp forearm and pull up from supine into sitting position.
Moro
Sudden change in position of head in relation to trunk; drop patient . backward from sitting position
Startle
Sudden loud or harsh noise
Grasp
Mainuined pressure to palm of hand (palmer grasp) or to ball of foot under toes (plantar grasp),
Tonic/Braintem reflexes Assymetrical tonic neck (ATNR)
Stimulus Rotation of the head to one side
Response Flexion of skull Iimbs. extension of the jaw limbs, "bow and arrow" or "fencing" posture. Onset: birth. Integrated. -1-6 months.
Symetrical tonic neck (STNR)
Flexion or extension of the head.
With head flexion: flexion of arms, extension of legs; With head extension: extension of arms, flexion of legs. Onset: 4-6 months. lntegrated. 8-12 months. With prone position: increased flexor tone/flexion of all limbs; Witth supine: increased tone/extension of all limbs. Onset: birth. Integrated: 6 months. Rigid extension (co-contraction) of the lower extremities. Onset: birth. Inregrared. 6 months.
Symetrical tonic labyrinthine (TLR or STLR)
Prone or supine position
Positive Supporting
Contact to the ball of the foot in upright standing position.
Associated reactions
Resisted voluntary movement in any part of the body.
Involuntary movement in a resting extremity. Onset. birth-3 months. Integrated. 8-9 years.
Midbraln/Cortical Reflexes Stimulus Response
Neck righting acrlon on the body (NOB)
Body righting acting on the body (BOB) Labvrinthine head righting (LR) Optical righting (OR) Body righting acting on head (BOH) Protecnve extension (PE)
Passively turn head to one side; tested in supine.
Body rotates as a whole (log rolls) to allign the body with the head. Onset: 4-6 months. Integrated. 5 years
Body segment not rotated follows to allign ihe body segments. Onset: -1-6 months ; Iruegrated. 5 years. Head orients to vertical positon with rnouth horizontal. Onset: btnh-2 months ; Integrated: persists Head orients to vertical position with mouth horizontal. Onset: birth-2 months ; Integrated. persists Head orients to verticalt position with rnouth horizontal. Onset: birth-2 months; Integrated. 5 years. Arms or legs extend arid abduct to support and to protect the body against falling. Onset: arms 4-6 months.,legs. 6-9 month ;Integrated. persists. Curvature of the trunk coward the Upward side along with extension and abduction of the extrimitiess on that side; protective extension on the opposite (downward) side. Onset: prone 6 months; supine : 7 -8 rnonths, Sitting 7-8 months; quadruped 9-12 months; sunding 12-21 months. Integrated: persists. Curvature of the trunk towardthe exrernal force with extension and abduction of the extrermities on the side to which rhe force was applied. Onset: prone 6 months; Supine 7-8 rnonthss ; sitting 7-8 months; quadruped 9-12 moorhs ; standing 12-21 months. Intcgrared. persists.
Passively rotate upper or lower trunk segment: tested in supine. Occlude vision; alter body position by tipping body in all directions. Alter body position by tipping body in all directions. Place in prone or supine position.
Displace center of gravity outside the base of support.
Equlllibrium reactions tillting (ER)
Displace the Center of gravity by tilting or moving the support surface (e.g .with a movable object such as an equilibrium board or ball).
Equilibrium reactions postural fixation
Apply a displacing force to the body, altering the center of gravity in its relation to the base ofsupport; can also be observed during voluntary acrivirv.
You might also like
- Dominate Sports BettingDocument38 pagesDominate Sports Bettingmaximaurelian50% (2)
- Cerebral Palsy Road Map:: What To Expect As Your Child GrowsDocument40 pagesCerebral Palsy Road Map:: What To Expect As Your Child GrowsSergio Curtean100% (1)
- 5 Strategies For Choosing ExercisesDocument5 pages5 Strategies For Choosing ExercisesFabianinhoLacerdaNo ratings yet
- Components of Training - IDocument17 pagesComponents of Training - IYouTube MirchiNo ratings yet
- NDT by Dr. Rati.Document13 pagesNDT by Dr. Rati.Anup PednekarNo ratings yet
- Prob 2 MR PDFDocument19 pagesProb 2 MR PDFFelipe Isaí Enriquez MendizábalNo ratings yet
- Eddy Anderson, The Founder of Rebound Therapy, Answers The Question: What Is Rebound Therapy?Document4 pagesEddy Anderson, The Founder of Rebound Therapy, Answers The Question: What Is Rebound Therapy?aaronjdriver2248No ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesThe Muscular SystemAirene Mae Lamputi SupilarNo ratings yet
- Sensory-Motor Development in The First Year: By:Yohannes PurwantoDocument39 pagesSensory-Motor Development in The First Year: By:Yohannes PurwantoAndrew AlandNo ratings yet
- Gross Motor Function MeasureDocument4 pagesGross Motor Function MeasureRio HafidzNanoNo ratings yet
- Functional Movement Screen and Y-Balance Test: Validity in Hamstring Injury Risk Prediction?Document74 pagesFunctional Movement Screen and Y-Balance Test: Validity in Hamstring Injury Risk Prediction?NICOLÁS ANDRÉS AYELEF PARRAGUEZNo ratings yet
- Hippo TherapyDocument23 pagesHippo TherapyNameeta Shroff JainNo ratings yet
- Improve Posture with Foam Roll ExercisesDocument3 pagesImprove Posture with Foam Roll ExercisesTomBrambo100% (1)
- Muscular DystrophyDocument48 pagesMuscular DystrophySai BruhathiNo ratings yet
- HEP2GO Carpal Tunnel Program PDFDocument2 pagesHEP2GO Carpal Tunnel Program PDFBetty OberackerNo ratings yet
- 10RS45010080 en PDFDocument283 pages10RS45010080 en PDFmliugong100% (2)
- Hold the foot firmly in dorsiflexion to relax the gastrocnemiusmuscle and expose the Achilles tendon fullyDocument13 pagesHold the foot firmly in dorsiflexion to relax the gastrocnemiusmuscle and expose the Achilles tendon fullyNurul Huda M ShahrinNo ratings yet
- The Bobath Concept - A Model To Illustrate Clinical PracticeDocument14 pagesThe Bobath Concept - A Model To Illustrate Clinical PracticeCynthia Arriagada Olavarria100% (1)
- Groin Strain Rehabilitation PDFDocument3 pagesGroin Strain Rehabilitation PDFOscar NgNo ratings yet
- Motor Control Motor LearningDocument56 pagesMotor Control Motor LearningJune EpeNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Fitness & Gross Motor Development: A Gross Motor Skills and Athletic Development GuideFrom EverandAdaptive Fitness & Gross Motor Development: A Gross Motor Skills and Athletic Development GuideNo ratings yet
- FMS Kitforparents Stability SkillsDocument26 pagesFMS Kitforparents Stability SkillsStevieKligsNo ratings yet
- Hip Displacement in Cerebral PalsyDocument9 pagesHip Displacement in Cerebral PalsyJohannesSchoppmannNo ratings yet
- Pediatrictone Management: Sathya Vadivelu,, Anne Stratton,, Wendy PierceDocument10 pagesPediatrictone Management: Sathya Vadivelu,, Anne Stratton,, Wendy PierceDeborah SalinasNo ratings yet
- RMAX Instruction ManualDocument40 pagesRMAX Instruction ManualGuille Gimeno100% (1)
- Bobath ConceptDocument5 pagesBobath ConceptdrprasantNo ratings yet
- A Foot Core Approach To Treating Plantar Fasciitis SmallDocument4 pagesA Foot Core Approach To Treating Plantar Fasciitis SmallLeticia MeleganNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental Therapy for Children with CP and DysarthriaDocument10 pagesNeurodevelopmental Therapy for Children with CP and DysarthriaPiyush Malviya0% (1)
- 2014 SAAO Forum For 10-18-11 Cranial IntroDocument5 pages2014 SAAO Forum For 10-18-11 Cranial IntroRoger NakataNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Info SheetDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy Info Sheetapi-263996400100% (1)
- Nurture 8Document56 pagesNurture 8danyalmehdi2296No ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing of Infants, Toddlers, & Preschool ChildrenDocument7 pagesManual Muscle Testing of Infants, Toddlers, & Preschool Childrendeasy100% (1)
- Restricted Ankle Dorsiflexion: Methods To Assess and Improve Joint FunctionDocument9 pagesRestricted Ankle Dorsiflexion: Methods To Assess and Improve Joint FunctionJorge Lucas JimenezNo ratings yet
- Komatsu D41A-6 Parts ManualDocument243 pagesKomatsu D41A-6 Parts ManualrobertoNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Manual Therapy Chadcook3rdPTMASUDDocument30 pagesOrthopedic Manual Therapy Chadcook3rdPTMASUDHisham Al ShamiNo ratings yet
- CS4L SummaryDocument2 pagesCS4L SummarySpeed Skating Canada - Patinage de vitesse CanadaNo ratings yet
- Application of Facilitatory Approaches in Developmental DysarthriaDocument22 pagesApplication of Facilitatory Approaches in Developmental Dysarthriakeihoina keihoinaNo ratings yet
- Adult Acute and Subacute Low Back Pain PDFDocument92 pagesAdult Acute and Subacute Low Back Pain PDFJuan Carlos Sánchez SuárezNo ratings yet
- ApproachDocument37 pagesApproachAshu AshNo ratings yet
- Principles For Proper Body Mechanics: Self-Study GuideDocument8 pagesPrinciples For Proper Body Mechanics: Self-Study GuideSLCNtc100% (1)
- Developing Fundamental Movement Skills: Connecting LearningDocument16 pagesDeveloping Fundamental Movement Skills: Connecting LearningArif MazlandNo ratings yet
- AOPA Handout NewParadigms Sciences IMPDocument34 pagesAOPA Handout NewParadigms Sciences IMPAnup PednekarNo ratings yet
- Bird-Dog Exercise More Than Rotary StabilityDocument4 pagesBird-Dog Exercise More Than Rotary Stabilityryan9871No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Based On The Bobath ConceptpdfDocument6 pagesPhysiotherapy Based On The Bobath ConceptpdfmatsNo ratings yet
- Otago Exercise ManualDocument72 pagesOtago Exercise ManualIiys NurulNo ratings yet
- 4 Pillar Playoffs The ChallengeDocument2 pages4 Pillar Playoffs The ChallengeSashaNo ratings yet
- Early Identification and Treatment Techniques in Babies WithDocument47 pagesEarly Identification and Treatment Techniques in Babies WithDr.GK. JeyakumarNo ratings yet
- OS2016 High Performance Nutrition ProgramDocument25 pagesOS2016 High Performance Nutrition ProgramFlorentina Ganea BejenarNo ratings yet
- Home Base Intervention OtDocument9 pagesHome Base Intervention OtPaulinaNo ratings yet
- Stretching With Children With Cerebral Palsy What.8 PDFDocument6 pagesStretching With Children With Cerebral Palsy What.8 PDFNurul FadhillahNo ratings yet
- Babkin Palmomental ReflexTextDocument3 pagesBabkin Palmomental ReflexTextdankopsNo ratings yet
- Gross Motor: USD #232 Special ServicesDocument9 pagesGross Motor: USD #232 Special ServicesSusiChelsea FanNo ratings yet
- Mike ReinoldDocument20 pagesMike ReinoldVikas Kashnia0% (1)
- Throwing and Catching Activities for Under 5'sDocument8 pagesThrowing and Catching Activities for Under 5'sIon100% (1)
- Gmi PDFDocument71 pagesGmi PDFAlma GlinacNo ratings yet
- Hydrotherapy Knee OA Exercise SheetDocument6 pagesHydrotherapy Knee OA Exercise SheetMuhammad Faishal Imam AfifNo ratings yet
- JoshhagerlessonplanupupupperbodystrengthDocument3 pagesJoshhagerlessonplanupupupperbodystrengthapi-256469641No ratings yet
- The PNF (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation) Stretching Technique - A Brief ReviewDocument6 pagesThe PNF (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation) Stretching Technique - A Brief ReviewDiane Troncoso Alegria0% (1)
- Reinold Little League ProgramDocument2 pagesReinold Little League ProgrammikereinoldNo ratings yet
- HydrotherapyDocument21 pagesHydrotherapy7e9oo90% (1)
- Mcimt NDT Kids at 1Document12 pagesMcimt NDT Kids at 1api-485106673No ratings yet
- Fundamental Movement Curriculum PDFDocument168 pagesFundamental Movement Curriculum PDFJakob D BersinNo ratings yet
- 12 The-Performance-Digest-Issue-12-September-17Document27 pages12 The-Performance-Digest-Issue-12-September-17Soylo Amado Rubio100% (1)
- Immobilization Protocol for Extensor Tendon RepairDocument2 pagesImmobilization Protocol for Extensor Tendon RepairFatin NawarahNo ratings yet
- Pendraken Catalogue Jan 2021Document61 pagesPendraken Catalogue Jan 2021GrumpyOldManNo ratings yet
- Gold Medal Heights - SL TYPE 2Document23 pagesGold Medal Heights - SL TYPE 2Guillermo EsquedaNo ratings yet
- Unifirst CatalogDocument8 pagesUnifirst CatalogMark Izsm AmersonNo ratings yet
- 2017 ATB Ascent Riding Program 100km FINAL PDFDocument14 pages2017 ATB Ascent Riding Program 100km FINAL PDFAvinash DesamangalamNo ratings yet
- L&T Panel Accessories Price List 01JUL2017Document44 pagesL&T Panel Accessories Price List 01JUL2017TarunPatraNo ratings yet
- 2011 Cannondale Flash F1Document67 pages2011 Cannondale Flash F1MarcoBastosNo ratings yet
- Pan Am Sports Women's 100m RankingsDocument68 pagesPan Am Sports Women's 100m RankingsAna MattioNo ratings yet
- Video Games SalesDocument846 pagesVideo Games SalesAli MunawarNo ratings yet
- Main Fuel Pump Overhauling Procedure Step-by-StepDocument5 pagesMain Fuel Pump Overhauling Procedure Step-by-StepAnoop Vijayakumar100% (1)
- Scouts Camp Activity 2023Document4 pagesScouts Camp Activity 2023Mhel PerezNo ratings yet
- Er Est Tter Ttest R ST Ier Iest: (Than)Document3 pagesEr Est Tter Ttest R ST Ier Iest: (Than)Barbara NevesNo ratings yet
- PT Rock Medical Company ProfileDocument10 pagesPT Rock Medical Company ProfileRahmat AnwarNo ratings yet
- One Horse Town ChordsDocument2 pagesOne Horse Town ChordselbersenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Final DraftDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Final Draftapi-284490400No ratings yet
- Parts List of Engine Assy of FMX 440 (PC-24) - TP-836Document1 pageParts List of Engine Assy of FMX 440 (PC-24) - TP-836Cws0% (1)
- VeveveveveDocument3 pagesVeveveveveYassine HalouaNo ratings yet
- Resident Evil 4 - Wii Edition (USA) (En, De)Document5 pagesResident Evil 4 - Wii Edition (USA) (En, De)Valentino RaynaldiNo ratings yet
- AustinJohnHOMELivingDexSV 1.1Document523 pagesAustinJohnHOMELivingDexSV 1.1blazingdragon0510No ratings yet
- Tenses Class 11Document4 pagesTenses Class 11harshitaNo ratings yet
- 1616 ToDocument4 pages1616 TohamzajmorshedNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs MCQ Ebbok Part-1Document16 pagesCurrent Affairs MCQ Ebbok Part-1azmalkandiNo ratings yet
- Future Heroes (2023)Document4 pagesFuture Heroes (2023)The Livingston County NewsNo ratings yet
- Safety PPE Tools and Equipments by Spectrum Industries in QatarDocument18 pagesSafety PPE Tools and Equipments by Spectrum Industries in Qatarfarhan1712No ratings yet
- Quantum Cat: An Aberration That Defies Space and TimeDocument2 pagesQuantum Cat: An Aberration That Defies Space and TimempotatoNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes: STO U AndriivDocument6 pagesFault Codes: STO U AndriivAtochkavNo ratings yet