Professional Documents
Culture Documents
II.1 Theoretical Seismology 2: Wave Propagation
Uploaded by
Хеманг ГолвелкарOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
II.1 Theoretical Seismology 2: Wave Propagation
Uploaded by
Хеманг ГолвелкарCopyright:
Available Formats
Rays
Snells Law
Structure of the Earth
Seismic Waves
Near-Field Terms (Static Displacements)
Far-Field Terms (P, S, Surface waves)
Normal modes
Free oscillations of the Earth
II.1 Theoretical Seismology 2: Wave Propagation
Magnitude for Local Tsunami
(Example)
JMA Magnitude (Tsuboi, 1954)
M=log 10A + 1.73 log10 0.83
A : Half of maximum total amplitude [m]
: Epicentral distance [km]
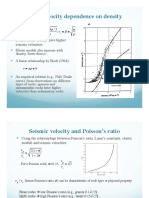
Seismic waves
Faulting
Travel Time and Distance
Hypocentral distance
(distance between hypocenter and station)
L
a
p
s
e
t
i
m
e
f
r
o
m
t
h
e
o
r
i
g
i
n
(
t
r
a
v
e
l
t
i
m
e
)
Station A
Station B
Station C
S wave
P wave
S-P time
Homogeneous Earth
o
1
o
o
1
< o
2
u
1
u
2
Ray Paths in a Layered Medium
o
1
o
o
1
> o
2
u
1
u
2
lower
Faster
Faster
Slower
Andrija Mohorovicic (1857-1936)
Found seismic discontinuity at
30 km depth in the Kupa Valley
(Croatia).
Mohorovicic discontinuity or Moho
Boundary between crust and mantle
Moho
o
1
o
2
o
3
Ray Paths in a Layered Medium
1/o
1
1/o
2
1/o
3
Distance
Time
Structure in the Earth
Crust-Mantle
Core-Mantle
440 km
660 km
Forward Branch
Backward Branch
Forward Branch
Backward Branch
Forward Branch
Shadow Zone
Forward
Branch
Backward Branch
Forward Branch
Shadow
Zone
PcP
1912 Gutenberg observed shadow zone 105
o
to 143
o
1939 Jeffreys fixed depth of core at 2898 km
(using PcP)
Forward
Branch
Backward
Branch
Forward
Branch
P
PcP
PKP
Shadow
Zone
PcP
Core Reflections
Why are observed seismograms so
complicated ?
Structure: Free Surface
Earth is a not homogenous whole-space
Free surface causes many complications
- surface waves
- reflections (pP, sP, sS)
depth phase
Surface Wave and Maximum Amplitude
Observed in
Japan.
=57(deg)
Max Amp.,
40 min after
occurrence.
(Ms, 20 deg 160 deg)
Seismogram of a distant earthquake
( LR: Rayleigh wave, LQ: Love wave )
Fig.16
January 26, 2001 Gujarat, India Earthquake (Mw7.7)
Recorded in Japan at a distance of 57
o
(6300 km)
Love Waves
vertical
radial
transverse
Rayleigh Waves
Aspects of Waves not Explained by Ray Theory
Different types of waves (P, S)
Surface Waves
Static Displacements
Frequency content
Seismic Waves
Body waves
PS
0.01 to 50 sec 50 m to 500 km
Surface waves
10 to 350 sec 30 to 1000 km
Free Oscillations
350 to 3600 sec
(6 min to 1 hour)
1000 to 10000 km
Static
Displacements
-
Period
Wavelength
Static Displacements
Bei-Fung Bridge near Fung-Yan city, 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan earthquake
Static displacements
Co-seismic deformation
of 2003 Tokachi-oki
Earthquake (M8.0)
Houseman http://earth.leeds.ac.uk/~greg/?Sphar/index.html
Free Oscillations l=1 m=1
Summary
Rays
Earth structure causes complicated ray paths
through the Earth (P, PKP, PcP)
Wave theory explains
P and S waves
Static displacements
Surface waves
Normal Modes
The Earth rings like a bell at long periods
Thank you for your attention
Snells Law
Fermats Principle
u
1
u
2
sin u
1
/ sin u
2
= n
21
Air
Water
Rays
Wave Equation
2
1
2
2
1
1
2
1
t
u
c x
u
c
c
=
c
c
1-D wave equation
c = propagation speed
Slinky: constant velocity
wave propagation, no mass transfer, different from circulation eq.
1-D Wave Equation
2
1
2
2
1
1
2
1
t
u
c x
u
c
c
=
c
c
LW 3.2.1
e
t 2
= T
T = wave period
e = angular frequency
)] / ( sin[ ) , ( c x t A t x u = e
Solution
Wave Period and Wavelength
wavelength 300 km
Velocity 6 km/s
Velocity = Wavelength / Period
x
t
wavelength
period
Space
Time
period 50 s
frequency = 1/period= 0.02 hz
) ( ) ( ) 2 (
2
2
u u f
t
u
V V V V + + =
c
c
3-D Wave Equation with Source
source
spatial 2nd derivative
Solution
t t t
t
|
o
d t M
r
A t x u
r
r
N
) (
1
4
1
) , (
/
/
0
4
=
}
) (
1
4
1
) (
1
4
1
0
2 2
0
2 2
| t| o to
r
t M
r
A
r
t M
r
A
IS IP
+ +
) (
1
4
1
) (
1
4
1
0
3
0
3
| t| o to
r
t M
r
A
r
t M
r
A
FS FP
+ +
Near-field Terms (Static Displacements)
Far-field Terms (P, S Waves)
Near-field terms
Static displacements
Only significant close to the fault
Source of tsunamis
r/o r/|
t
r/o r/|
Far-field Terms
Propagating Waves
No net displacement
P waves
S waves
) (
1
4
1
) (
1
4
1
0
3
0
3
| t| o to
r
t M
r
A
r
t M
r
A
FS FP
+ +
Surface Waves
S
Shearer, Fig. 8.1
Period (sec)
Love
Rayleigh
G
r
o
u
p
V
e
l
o
c
i
t
y
(
k
m
/
s
e
c
)
Generation of Tsunami from Near-field Term
Normal Modes
(Daishinji, Fukui Prefecture)
Free Oscillations of the Earth
1960 Chile Earthquake
Useful for studies of
Interior of the Earth
Largest earthquakes
(Stein and Gellar 1978)
Houseman http://earth.leeds.ac.uk/~greg/?Sphar/index.html
Free Oscillations l=1 m=2
Houseman http://earth.leeds.ac.uk/~greg/?Sphar/index.html
Free Oscillations l=1 m=3
Toroidal and Spheroidal Modes
Toroidal
Spheroidal
Dahlen and Tromp Fig. 8.5, 8.17
Natural Vibrations of the Earth
Shearer Ch.8.6
Lay and Wallace, Ch. 4.6
You might also like
- Seismology - Lecture 2 Normal Modes and Surface Waves: Barbara Romanowicz Univ. of California, BerkeleyDocument60 pagesSeismology - Lecture 2 Normal Modes and Surface Waves: Barbara Romanowicz Univ. of California, BerkeleyC.yrillNo ratings yet
- Seismic Waves, Location of Epicenter and Moment MagnitudeDocument11 pagesSeismic Waves, Location of Epicenter and Moment MagnitudeMa. Antonette CaragNo ratings yet
- Elementary SeismologyDocument77 pagesElementary SeismologyvinitsloveNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Session 01 Slides 1Document32 pagesLecture 02 Session 01 Slides 1Elena ChristodoulouNo ratings yet
- Principles of Seismology and Seismic EngineeringDocument77 pagesPrinciples of Seismology and Seismic EngineeringFASIH KAZAINULLAHNo ratings yet
- Seismology Sep27 29Document28 pagesSeismology Sep27 29Lisette SilvaNo ratings yet
- SeismicDocument93 pagesSeismicSuhe Prikitiew50% (2)
- GY305 Lecture4 SeismologyDocument26 pagesGY305 Lecture4 Seismologytarek mahmoudNo ratings yet
- GRL2000 Turkey YagiDocument11 pagesGRL2000 Turkey Yagionta ontaNo ratings yet
- Seismic ReflectionDocument84 pagesSeismic Reflectionginozky100% (5)
- 1 EQEpicentersDocument17 pages1 EQEpicentersGrim Fandango0% (2)
- Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresDocument29 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of StructuresBimalBhandariNo ratings yet
- EXAM 3 Study GuideDocument24 pagesEXAM 3 Study GuideIsmael MorenoNo ratings yet
- Determining The Epicentre Location Hampir FiiixDocument21 pagesDetermining The Epicentre Location Hampir Fiiixasri mNo ratings yet
- Source Inversion of The 1988 Upland, CaliforniaDocument12 pagesSource Inversion of The 1988 Upland, CaliforniabuitrungthongNo ratings yet
- Takeru Suzuki - A Solution To The Coronal Heating and Solar Wind Acceleration in The Coronal Holes: Non-Linear Alfven WavesDocument49 pagesTakeru Suzuki - A Solution To The Coronal Heating and Solar Wind Acceleration in The Coronal Holes: Non-Linear Alfven WavesOlmnopNo ratings yet
- Fisika Matahari Dan Cuaca AntariksaDocument46 pagesFisika Matahari Dan Cuaca AntariksaIkrar PramudyaNo ratings yet
- PartChapter 2Document27 pagesPartChapter 2Destiar Putri RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- 50 Years of Schumann ResonanceDocument15 pages50 Years of Schumann ResonanceMA-DocNo ratings yet
- Seismogram InterpletationDocument9 pagesSeismogram InterpletationGustavo Adolfo Morán RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Design Wind SpeedDocument29 pagesDesign Wind SpeedEman AgiusNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Lect Soil Dynamics Wo MachineDocument275 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Lect Soil Dynamics Wo MachineFekadu WubNo ratings yet
- Applications With Surface Waves Extracted From Ambient Seismic NoiseDocument21 pagesApplications With Surface Waves Extracted From Ambient Seismic NoiseJennifer WatsonNo ratings yet
- A Field Experiment On The Mechanics of Irregular Gravity WavesDocument14 pagesA Field Experiment On The Mechanics of Irregular Gravity WavesNikiforos KypraiosNo ratings yet
- Seismology Master2014Document126 pagesSeismology Master2014AnjaneyNo ratings yet
- 04-05 Pertemuan IV - Seismologi PDFDocument60 pages04-05 Pertemuan IV - Seismologi PDFI2OI5OOI8Cintya Agnessa SitorusNo ratings yet
- 6 Seismic MomentDocument20 pages6 Seismic MomentSandeepVermaNo ratings yet
- Magnetotellurics-Field Techniques - Week 7Document7 pagesMagnetotellurics-Field Techniques - Week 7shabila gadisNo ratings yet
- Earthquake ReviewDocument8 pagesEarthquake ReviewminaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Waves, Travel Times, Locating EarthquakesDocument43 pagesSeismic Waves, Travel Times, Locating EarthquakesKhalid KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Wave?: Wave Is S A Disturbance That Travels Through A Medium From ToDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Wave?: Wave Is S A Disturbance That Travels Through A Medium From ToYaser YasinNo ratings yet
- EqDocument30 pagesEqChar CharNo ratings yet
- The Spatial Properties of Breaking Wave Generated and Bedload Transport Generated Noise in The Sediment Layer of A Shallow Water Wave Guide.Document7 pagesThe Spatial Properties of Breaking Wave Generated and Bedload Transport Generated Noise in The Sediment Layer of A Shallow Water Wave Guide.julianpalacinoNo ratings yet
- Seismics BasicsDocument86 pagesSeismics Basicssandeepmev100% (1)
- Geology 3Document4 pagesGeology 3Pia DebbieNo ratings yet
- 13-Legrand GRL 2005 PDFDocument5 pages13-Legrand GRL 2005 PDFAlan Fernando Rendon GutierrezNo ratings yet
- EA41 Nishida RevDocument43 pagesEA41 Nishida RevJesus GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- Waves ELP @UnacademyNEETelpDocument27 pagesWaves ELP @UnacademyNEETelpAbhijeet PandeyNo ratings yet
- Seismo 1 ShearerDocument39 pagesSeismo 1 ShearerSerruchin 84No ratings yet
- Earthquakes (2) : Waveform Modeling, Moment Tensors, & Source ParametersDocument42 pagesEarthquakes (2) : Waveform Modeling, Moment Tensors, & Source ParametershanumabendadiNo ratings yet
- Introduccion To SeismologyDocument7 pagesIntroduccion To SeismologyLuis AlbertoNo ratings yet
- CE 7014 Chap2 Part 2Document51 pagesCE 7014 Chap2 Part 2Anonymous ep7LE5ZdP5No ratings yet
- Theoretical Seismology 1: Understanding Earthquake SourcesDocument37 pagesTheoretical Seismology 1: Understanding Earthquake SourcesJohannes LatrasNo ratings yet
- EQ: Understanding EarthquakesDocument45 pagesEQ: Understanding EarthquakesRaja RaiNo ratings yet
- Basic Relations Between Tsunamis Calculation and Their Physics-IiDocument20 pagesBasic Relations Between Tsunamis Calculation and Their Physics-Iizlatan_p100% (2)
- 8.00 Seismic WavesDocument36 pages8.00 Seismic WavesMohammad AlhajNo ratings yet
- Seismic Methods: Mapping Subsurface Geology Using Reflected Seismic WavesDocument62 pagesSeismic Methods: Mapping Subsurface Geology Using Reflected Seismic WavesGita SakaNo ratings yet
- Sea-Surface Observations of The Magnetic Signals of Ocean SwellsDocument8 pagesSea-Surface Observations of The Magnetic Signals of Ocean SwellsMilan StepanovNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics Part IDocument62 pagesWave Optics Part IAt TanwiNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Soil DynamicsDocument21 pagesEarthquakes: Soil DynamicsJulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33Document26 pagesLecture 33anurag pawarNo ratings yet
- Wave HydrodynamicsDocument60 pagesWave HydrodynamicsCaesar Adza Mahendra100% (1)
- Ray Theory BasicsDocument34 pagesRay Theory BasicsonlyshreyNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Geophysics Teacher: DR K. I. Konstantinou Lesson 3: Propagation of Body Waves in The EarthDocument25 pagesTheoretical Geophysics Teacher: DR K. I. Konstantinou Lesson 3: Propagation of Body Waves in The EarthhiskiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AcousticsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To AcousticsMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- E S 07 Eng PDFDocument2 pagesE S 07 Eng PDFMekanNo ratings yet
- System Earthing Methods and TechniquesDocument70 pagesSystem Earthing Methods and TechniquesBasudev PatraNo ratings yet
- Low Z Differential Relay Protection SettingsDocument9 pagesLow Z Differential Relay Protection SettingsandrejcerneNo ratings yet
- Fluids and forcesDocument22 pagesFluids and forcesLeo WongNo ratings yet
- Non-Contact Power Meter MIT ThesisDocument121 pagesNon-Contact Power Meter MIT ThesisTrần LinhNo ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic FoundationDocument15 pagesBeams On Elastic FoundationIngeniero EstructuralNo ratings yet
- A9-22-00 220-230V 50Hz Contactor Product DetailsDocument4 pagesA9-22-00 220-230V 50Hz Contactor Product DetailsWhendi BmNo ratings yet
- Laser Light Controlling SystemDocument121 pagesLaser Light Controlling SystemJanvi Mayank JainNo ratings yet
- Wilson2011 PDFDocument4 pagesWilson2011 PDFPabloHongoNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Equilibrium: Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesVectors and Equilibrium: Key ConceptshassanNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits FundamentalsDocument13 pagesDC Circuits FundamentalsRoland MartinezNo ratings yet
- Generation of Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesGeneration of Rotating Magnetic FieldSUNIL MAURYANo ratings yet
- Electric Flux and CurrentDocument5 pagesElectric Flux and CurrentthuniNo ratings yet
- Structured Question (Forces in Equilibrium II)Document3 pagesStructured Question (Forces in Equilibrium II)leelee1127No ratings yet
- Technical Specifications For Door Trim Panel Assembly: PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDocument15 pagesTechnical Specifications For Door Trim Panel Assembly: PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDiego CamargoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics NotesDocument115 pagesClass 12 Physics NotesAiden Pearce100% (1)
- ELEC4612-12 Exp 2 Power FlowDocument5 pagesELEC4612-12 Exp 2 Power FlowDavid VangNo ratings yet
- CH2 Describing Motion, Kinematics in One DimensionDocument38 pagesCH2 Describing Motion, Kinematics in One DimensionEpic WinNo ratings yet
- The Standard AtmosphereDocument19 pagesThe Standard AtmosphereAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- AMT 221 P1 Definition & System ArchitectureDocument63 pagesAMT 221 P1 Definition & System ArchitectureJennifer GazoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Effects of Force On ObjectsDocument26 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Effects of Force On ObjectsJobelle Canlas100% (1)
- P2 Forces and Terminal Velocity HigherDocument12 pagesP2 Forces and Terminal Velocity HigherdownendscienceNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter NotesDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter NotesAmrit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanic Industrial Electronics.150171925Document28 pagesMechanic Industrial Electronics.150171925swami061009No ratings yet
- Mikroniek - Professional Journal On Precision EngineeringDocument68 pagesMikroniek - Professional Journal On Precision EngineeringViñu LittleMonkey0% (1)
- Vehicle System Dynamics: International Journal of Vehicle Mechanics and MobilityDocument30 pagesVehicle System Dynamics: International Journal of Vehicle Mechanics and MobilityLakshmipathy PNo ratings yet
- (Lecture# 8) SubstationDocument42 pages(Lecture# 8) SubstationTatta Maruthi100% (3)
- DC Machines and Batteries: EEE 3 Lecture 05Document53 pagesDC Machines and Batteries: EEE 3 Lecture 05No OneNo ratings yet
- Module 4 EASADocument15 pagesModule 4 EASAMK SINGHNo ratings yet
- IBN PE Mesh BN: Parallel Earthing Conductor (PEC)Document1 pageIBN PE Mesh BN: Parallel Earthing Conductor (PEC)mahmoud12122012No ratings yet
- JS Atomic Lecture5-6Document19 pagesJS Atomic Lecture5-6Sandile SynthaxError MabikaNo ratings yet