Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Top MGMT
Uploaded by
Ajay ShethiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Top MGMT
Uploaded by
Ajay ShethiaCopyright:
Available Formats
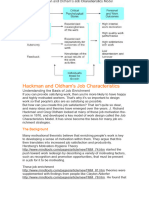
1 - FULFILLS KEY ROLES
(MINTZBERG, 73)
INTERPERSONAL ROLES
FIGUREHEAD LEADER LIASON
INFORMATIONAL ROLES
MONITOR DISSEMINATOR SPOKESPERSON
DECISIONAL ROLES
INNOVATOR / ENTREPRENEUR (PLANNER) DISTURBANCE HANDLER (CRISIS MANAGER) RESOURCE ALLOCATOR (SLICING-THE-PIE) NEGOTIATOR (BARGAINER)
2 PROVIDES CORPORATE LEADERSHIP
ARTICULATES A TRANSCENDENT GOAL FOR THE FIRM
PROVIDES A VISION OF THE FUTURE SEES THE FIRM NOT AS IT ISBUT AS IT CAN BECOME
COMMUNICATES HIGH PERFORMANCE STANDARDS
SHOWS CONFIDENCE IN SUBORDINATES PROVIDES GOALS, AUTONOMY, MENTORING
PRESENTS A ROLE FOR OTHERS TO IDENTIFY WITH
SETS AN EXAMPLE IN BEHAVIOR AND DRESS COMMUNICATES VALUES CLEARLY IN WORDS & DEEDS
3 PROVIDE OPERATIONAL AND FINANCIAL LEADERSHIP
OPERATIONAL LEADERSHIP
Operating policies include everything from hiring personnel to supervising the work of manufacturing workers to signing contracts with business partners.
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
They cover critical decisions regarding budgeting, cost accounting, financial accounting and corporate finance Budgeting and cost accounting help a company rein in waste and limit excessive spending
4 MANAGES STRATEGIC PLANNING
INITIATES/MANAGES THE STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS
A strategy is a plan of action designed to achieve a particular goal Devise operating policies, identify investment opportunities and devise tactics to outmatch the competition
SEEKS INFORMATION
LONG-RANGE PLANNING STAFF DIVISIONAL (SBU) MANAGERS FUNCTIONAL AND DEPARTMENTAL MANAGERS TOP MANAGEMENT TEAM
THE MASTER STRATEGIST CEO personally shapes the plan Depends on skills and vision of one person
DELEGATE IT TO OTHERS Uses a planning staff or task forces Lack of top-down direction and leadership COLLABORATIVE APPROACH Involve key people --- seek group consensus Can political games and compromises be avoided?
THE CHAMPION APPROACH Encourage subordinate managers to develop their own strategies Will a coherent, unified strategy emerge?
THE PLANNING STAFF SHOULD: Help gather and organize information Analyze industry and competitive conditions Administer annual reviews of strategy Distribute information on the firms strategic performance THE PLANNING STAFF SHOULD NOT: Prepare strategic plans for someone else to implement Seize the responsibilities of operating managers Make strategic decisions POTENTIAL PROBLEMS: A planning staff cannot be held accountable for results because they have no authority to implement. Non-acceptance by managers who do not feel ownership in the strategic plan
DETERMINE AND APPROVE THE ORGANIZATIONS MISSION AND STRATEGIC OPTIONS
EVALUATE AND INFLUENCE KEY MANAGEMENT DECISIONS AND ACTIONS
MONITOR AND EVALUATE THE ENVIRONMENT SURROUNDING THE ORGANIZATION MONITOR AND EVALUATE THE OVERALL PERFORMANCE OF THE ORGANIZATION
BOARDS DIRECT THE AFFAIRS OF THE FIRM, BUT DO NOT MANAGE THEM
PHANTOM BOARD May not even meet! Never knows what to do. No involvement. RUBBER-STAMP BOARD (Ceremonial 8 %) Permits officers to make all decisions Votes the officers recommendations No board agenda MINIMAL REVIEW BOARD (Passive 21 %) Reviews issues brought to its attention by the officers Members are notified what is on the agenda.but often come unprepared NOMINAL PARTICIPATION BOARD (Somewhat Active 45 %) Reviews performance of selected key decisions independently Occasionally questions officers actions and strategies Informal groups form within the board
ACTIVE PARTICIPATION BOARD (Very Active 21 %) Has active board sub-committees Conducts its own audits Gathers information about the organization independently Questions officers regularly on a wide variety of topics Makes final strategic decisions
CATALYST BOARD (Critical Contributor 5 %) Takes a leading role in establishing and modifying the mission, objectives, and strategies of the organization Has very active strategic planning sub-committees Officers do not propose or formulate strategiesbut are expected to implement them for the board
You might also like
- Coca Col Appt FinalDocument22 pagesCoca Col Appt FinalAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument8 pagesEthicsAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- Fa ReportDocument5 pagesFa ReportAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- Mahindra and Mahindra StrategyDocument21 pagesMahindra and Mahindra StrategySatender Kumar0% (1)
- What Is Your Evaluation of WelchDocument1 pageWhat Is Your Evaluation of WelchAjay Shethia100% (1)
- MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesMacroeconomicsAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- Fa ReportDocument5 pagesFa ReportAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- PM LeaderDocument14 pagesPM LeaderAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- Adder™ 882i: Intercom/Data Multiplexer Instruction ManualDocument27 pagesAdder™ 882i: Intercom/Data Multiplexer Instruction ManualAjay ShethiaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Motivationmodel HackmanDocument5 pagesMotivationmodel Hackmanricknl20029079No ratings yet
- Fall 2018 Internship HandbookDocument42 pagesFall 2018 Internship HandbookIrni LatifaNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Masiag, Inc.: Unit Learning PlanDocument3 pagesNotre Dame of Masiag, Inc.: Unit Learning PlanGjc ObuyesNo ratings yet
- Abm - InnovationDocument2 pagesAbm - Innovation12 MORIAH Darlene DulceNo ratings yet
- BPCC 112, 23-24 (E)Document4 pagesBPCC 112, 23-24 (E)prathamjiraineNo ratings yet
- Attitude and Competency (Skills) SurveyDocument2 pagesAttitude and Competency (Skills) SurveyJohn Reden Cortez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Evelyn L. Lazaro BEED 1: Linguistic DimensionsDocument8 pagesEvelyn L. Lazaro BEED 1: Linguistic DimensionsEvelyn LazaroNo ratings yet
- FDP On Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning ApplicationsDocument2 pagesFDP On Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning ApplicationsDr-Kiran Sree PokkuluriNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument8 pagesAction PlanMoon SunNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson 1Document42 pagesEapp Lesson 1angelicaNo ratings yet
- A Novel IdeaDocument19 pagesA Novel IdeaGing Du AnNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Khan KhanNo ratings yet
- Network Traf Fic Classification Using Multiclass Classi FierDocument10 pagesNetwork Traf Fic Classification Using Multiclass Classi FierPrabh KNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Activity Plan Modular Learning Delivery Modality Home Economics Grade 5Document27 pagesWeekly Home Learning Activity Plan Modular Learning Delivery Modality Home Economics Grade 5Sir RizalNo ratings yet
- Brief History of PsychologyDocument3 pagesBrief History of PsychologyMaria TariqNo ratings yet
- SBA SAMPLE 2 The Use of Simple Experiments and Mathematical Principles To Determine The Fairness of A Coin Tossed SBADocument11 pagesSBA SAMPLE 2 The Use of Simple Experiments and Mathematical Principles To Determine The Fairness of A Coin Tossed SBAChet Jerry AckNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Selecting Curriculum MaterialsDocument23 pagesIdentifying and Selecting Curriculum MaterialsCabral MarNo ratings yet
- Measuring Service Quality in BankingDocument16 pagesMeasuring Service Quality in BankingTar TwoGoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Aging Research: An International Journal Devoted To The Scientific Study of The Aging ProcessDocument18 pagesExperimental Aging Research: An International Journal Devoted To The Scientific Study of The Aging ProcessKentNo ratings yet
- Free Throw Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFree Throw Lesson Planapi-311869040No ratings yet
- The Case of Big Sarge: Overcoming Depression and Low Self-WorthDocument18 pagesThe Case of Big Sarge: Overcoming Depression and Low Self-WorthDennis HigginsNo ratings yet
- Theatre, Organization, and The Use of Metaphor PDFDocument23 pagesTheatre, Organization, and The Use of Metaphor PDF1pinkpanther99No ratings yet
- Bacnotan, La Union, Philippines: College of EducationDocument4 pagesBacnotan, La Union, Philippines: College of EducationCriselda Garcia SarioNo ratings yet
- Preparedness of Practice Teaching Internship of Beed Student of Central Philippines State UniverDocument15 pagesPreparedness of Practice Teaching Internship of Beed Student of Central Philippines State UniverRan TanNo ratings yet
- 2-Day Workshop on Communication SkillsDocument1 page2-Day Workshop on Communication SkillsAnantha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Scope and Limitation of The Study in Social Research: Research. Ibadan: Ibadan University Press. Pp. 105-114Document11 pagesScope and Limitation of The Study in Social Research: Research. Ibadan: Ibadan University Press. Pp. 105-114Cristine LaranjaNo ratings yet
- Stillness Speaks (Book No.1)Document6 pagesStillness Speaks (Book No.1)Hema ChitreNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Education 7: ValuesDocument3 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Education 7: ValuesRose Glaire Alaine Tabra100% (1)
- Universiti Teknologi Mara: Faculty of Business ManagementDocument12 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara: Faculty of Business ManagementPiji Zie SaiyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Learning To Communicate ProfessionallyDocument4 pagesChapter 8 - Learning To Communicate ProfessionallyKTNo ratings yet