Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mountains
Uploaded by
amber19995Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mountains
Uploaded by
amber19995Copyright:
Available Formats
MOUNTAINS
What is a Mountain?
A mountain is a large landform that stretches above the surrounding land in a limited area usually in the form of a peak. A mountain is generally steeper than a hill. The adjective montane is used to describe mountainous areas and things associated with them. The study of mountains is called Orography.
Type of Mountains:
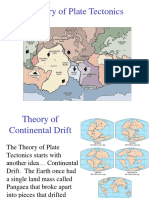
Mountains form in different ways. Sometimes the crust has folded and buckled, sometimes it breaks into huge blocks. In both cases, great areas of land are lifted upwards to form mountains. Other mountains are formed by the earth's crust rising into a dome, or by volcanic activity when the crust cracks open. There are five basic kinds of mountains: Fold Mountains (Folded Mountains) Fault-block Mountains (Block Mountains) Dome Mountains Volcanic Mountains Plateau Mountains
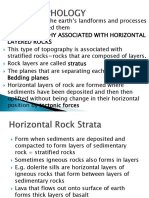
Fold Mountains: Fold mountains are the most common type of mountain. The worlds largest mountain ranges are fold mountains. These ranges were formed over millions of years.Fold mountains are formed when two plates collide head on, and their edges crumbled, much the same way as a piece of paper folds when pushed together. Eg: Himalayan Mountains in Asia Alps in Europe Andes in South America Rockies in North America Urals in Russia
Anticlines
Synclines
The Himalayan Mountains were formed when India crashed into Asia and pushed up the tallest mountain range on the continents.In South America, the Andes Mountains were formed by the collision of the South American continental plate and the oceanic Pacific plate
Fault-block Mountains These mountains form when faults or cracks in the earth's crust force some materials or blocks of rock up and others down. Instead of the earth folding over, the earth's crust fractures (pulls apart). It breaks up into blocks or chunks. Sometimes these blocks of rock move up and down, as they move apart and blocks of rock end up being stacked on one another. Often fault-block mountains have a steep front side and a sloping back side. Eg: Sierra Nevada mountains in North America Harz Mountains in Germany
Dome Mountains Dome mountains are the result of a great amount of melted rock (magma) pushing its way up under the earth crust. Without actually erupting onto the surface, the magma pushes up overlaying rock layers. At some point, the magma cools and forms hardened rock. The uplifted area created by rising magma is called a dome because of looking like the top half of a sphere (ball). The rock layers over the hardened magma are warped upward to form the dome. But the rock layers of the surrounding area remain flat. Eg: Black Hills of South Dakota , USA
Volcanic Mountains As the name suggests, volcanic mountains are formed by volcanoes. Volcanic Mountains are formed when molten rock (magma) deep within the earth, erupts, and piles upon the surface. Magna is called lava when it breaks through the earth's crust. When the ash and lava cools, it builds a cone of rock. Rock and lava pile up, layer on top of layer. Egs: Mount St. Helens in North America Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines Mount Kea and Mount Loa in Hawaii
Plateau Mountains (Erosion Mountains) Plateau mountains are not formed by internal activity. Instead, these mountains are formed by erosion. Plateaus are large flat areas that have been pushed above sea level by forces within the Earth, or have been formed by layers of lava. The dictionary describes these as large areas of high levels of flat land, over 600 meters above sea level. Plateau mountains are often found near folded mountains. As years pass, streams and rivers erode valleys through the plateau, leaving mountains standing between the valleys. The mountains in New Zealand are examples of plateau mountains
You might also like
- The Book Thief CompleteDocument287 pagesThe Book Thief Completeamber1999563% (8)
- Midterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111Document7 pagesMidterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111mhadd071No ratings yet
- How Mountains FormDocument3 pagesHow Mountains Formapi-321767399No ratings yet
- Izod Impact Test - ManualDocument3 pagesIzod Impact Test - Manualamber19995100% (1)
- Comunicacions 14Document216 pagesComunicacions 14jmvictoria6870No ratings yet
- Geography Pamphlet Grade 10-12Document82 pagesGeography Pamphlet Grade 10-12Kingdavid Waitolo91% (11)
- How Mountains Form: 5 Types of MountainsDocument6 pagesHow Mountains Form: 5 Types of MountainsJemuel Bucud Lagarto100% (2)
- Moutains TypesDocument2 pagesMoutains Typesapi-339674004No ratings yet
- Types of MountainsDocument15 pagesTypes of MountainsIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- SaviDocument14 pagesSaviHargun KaurNo ratings yet
- Mountain Formation PDF 97Document4 pagesMountain Formation PDF 97Sanjana DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Fold Mountains (Folded Mountains)Document3 pagesFold Mountains (Folded Mountains)mineNo ratings yet
- Mountains: Made by - Naman Gupta Class-VICDocument9 pagesMountains: Made by - Naman Gupta Class-VICnamanNo ratings yet
- Nikki Faults and MountainDocument8 pagesNikki Faults and MountainHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- Nikki Faults and MountainDocument3 pagesNikki Faults and MountainHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- Types of Mountains and Mountain RangesDocument28 pagesTypes of Mountains and Mountain RangestsukkisdinosaurplushNo ratings yet
- Everest's Mighty North FaceDocument23 pagesEverest's Mighty North FaceEureka Kris TañedoNo ratings yet
- Deformation of The CrustDocument28 pagesDeformation of The CrustJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Types of Mountains Upsc Notes 45Document3 pagesTypes of Mountains Upsc Notes 45my072025iasNo ratings yet
- Mountain Formation and WeatheringDocument16 pagesMountain Formation and Weatheringlura castroNo ratings yet
- Topographic Maps and Relief Maps I. Topographic MapDocument11 pagesTopographic Maps and Relief Maps I. Topographic Maphussain korirNo ratings yet
- Classification of Mountains, Types of FoldsDocument67 pagesClassification of Mountains, Types of FoldsRodalyn BarroNo ratings yet
- LandformsDocument3 pagesLandformsJacki Pauline VinoyaNo ratings yet
- 3000m Is Said To Be A Hill How Can It Shows Hills and Mountains and Also The Rise and Falls of The LandDocument12 pages3000m Is Said To Be A Hill How Can It Shows Hills and Mountains and Also The Rise and Falls of The Landhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Mountains FormedDocument3 pagesMountains FormedMar JayaNo ratings yet
- Types of Mountains ExplainedDocument9 pagesTypes of Mountains ExplainedEureka Kris TañedoNo ratings yet
- CE 203-Class Note 2 (Part 1) - SKSDocument21 pagesCE 203-Class Note 2 (Part 1) - SKSKNOWLEDGE HUBNo ratings yet
- TalampasDocument2 pagesTalampasJade SamonteNo ratings yet
- GeoDocument6 pagesGeomohammadshadankhan5No ratings yet
- Earth Surface and ClimateDocument7 pagesEarth Surface and ClimateSofia MeloNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF MOUNTAIN REPORTDocument8 pagesTYPES OF MOUNTAIN REPORTRafiqul Islam NoyonNo ratings yet
- 1stquaweek ppt5Document28 pages1stquaweek ppt5Gyan Ishirose CulalaNo ratings yet
- G10 SL 5 - Mountain Ranges Ay 2021-2022Document4 pagesG10 SL 5 - Mountain Ranges Ay 2021-2022Mark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Science (3rd)Document18 pagesReviewer For Science (3rd)MJ ArazasNo ratings yet
- SST ProjectDocument14 pagesSST ProjectHafsa SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Types and Characteristics of Major Landforms:: MountainsDocument14 pagesTypes and Characteristics of Major Landforms:: MountainsPappu DiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 GeologyDocument6 pagesLecture 14 GeologynattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Landforms of The EarthDocument4 pagesLandforms of The EarthSrinjon SahaNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument27 pagesTypes of VolcanoesMfoeu WidhiNo ratings yet
- How Do We Describe Features of Earth's SurfaceDocument24 pagesHow Do We Describe Features of Earth's SurfaceJoan ClerigoNo ratings yet
- WWVN E7 Ov Lof Ko 6 Aa OPe 7Document3 pagesWWVN E7 Ov Lof Ko 6 Aa OPe 7Raminder KaurNo ratings yet
- The Mountain LandformDocument4 pagesThe Mountain LandformmarkNo ratings yet
- Mountains PowerpointDocument17 pagesMountains Powerpointapi-297580036No ratings yet
- Gs Study Notes SSC 16-01-19 EnglishDocument12 pagesGs Study Notes SSC 16-01-19 EnglishKESHAB BHOINo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Environmental Science Earths LithosphereDocument104 pagesLesson 3 Environmental Science Earths LithosphereNino Amarillo AnticamaraNo ratings yet
- Mountain Building C20Document12 pagesMountain Building C20Rowel Borlagdan CampolloNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology GR 11Document85 pagesGeomorphology GR 11YONDELA MbandezeloNo ratings yet
- Earth InteriorDocument20 pagesEarth InteriorDesi RahmawatyNo ratings yet
- Note 2023-06-01 21-42-57Document2 pagesNote 2023-06-01 21-42-57Roberto LengweNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Theory ExplainedDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics Theory ExplainedApple Grace Marie SebastianNo ratings yet
- LandformsDocument28 pagesLandformsapi-429825109No ratings yet
- Mountains Volvanoes and Earthquake Epicenter With Plate TectonicsDocument28 pagesMountains Volvanoes and Earthquake Epicenter With Plate TectonicsJona Geron ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Build The Earth UpDocument18 pagesBuild The Earth UpDawud MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Gs 2 GJHXSQ CR 1 Quco 50 e JDocument4 pagesGs 2 GJHXSQ CR 1 Quco 50 e JRaminder KaurNo ratings yet
- Major Landforms of The EarthDocument29 pagesMajor Landforms of The EarthRajiv Mahajan100% (1)
- Formation of Fold Mountains at Destructive Plate BoundariesDocument1 pageFormation of Fold Mountains at Destructive Plate BoundariesMary Davies100% (2)
- Mountain Building PowerpointDocument26 pagesMountain Building Powerpointjoie gucci100% (3)
- Plate Tectonics ARTICLEDocument3 pagesPlate Tectonics ARTICLEC A E L I D A L U S U N GNo ratings yet
- Mountain Backgrounds Green Variant by SlidesgoDocument5 pagesMountain Backgrounds Green Variant by SlidesgoImaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Notes: Section 1 How Rock DeformsDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Notes: Section 1 How Rock DeformsPrincess KimberlyNo ratings yet
- 2 PlateauDocument18 pages2 PlateauAnuj SinghNo ratings yet
- Volcanism and Igneous Activity PDFDocument71 pagesVolcanism and Igneous Activity PDFYlla JovillanoNo ratings yet
- Major Landforms of The Earth NotesDocument3 pagesMajor Landforms of The Earth NotesSIMMA SAI PRASANNANo ratings yet
- Hills vs. Mountains : Knowing the Difference - Geology Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandHills vs. Mountains : Knowing the Difference - Geology Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemDocument57 pagesWater Distribution Systemamber1999588% (8)
- Plant Location and Layout !!Document32 pagesPlant Location and Layout !!amber19995No ratings yet
- Structural Analysis I Assignment for Civil Engineering StudentsDocument1 pageStructural Analysis I Assignment for Civil Engineering Studentsamber19995No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Word Documentamber19995No ratings yet
- Rush ExerptDocument3 pagesRush Exerptamber19995No ratings yet
- Runge Kuta MethodDocument4 pagesRunge Kuta Methodamber199950% (1)
- D DocumentDocument22 pagesD Documentamber19995No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - IM (Work Study)Document81 pagesLecture Notes - IM (Work Study)amber19995No ratings yet
- D DocumentDocument22 pagesD Documentamber19995No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Ii 10/01/2014 Tutorial - IDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics - Ii 10/01/2014 Tutorial - Iamber19995No ratings yet
- Geronimo StiltonDocument11 pagesGeronimo Stiltonamber1999544% (9)
- Drag Force Word DocumentDocument31 pagesDrag Force Word Documentamber19995No ratings yet
- Charlotte Brontë, author of Jane EyreDocument18 pagesCharlotte Brontë, author of Jane Eyreamber19995No ratings yet
- William Penn: Founder of PennsylvaniaDocument1 pageWilliam Penn: Founder of Pennsylvaniaamber19995No ratings yet
- TaskDocument1 pageTaskamber19995No ratings yet
- What is a Mountain? Types of Mountains Formed in Different WaysDocument7 pagesWhat is a Mountain? Types of Mountains Formed in Different Waysamber19995No ratings yet
- Images PDF Files Csp2013Document93 pagesImages PDF Files Csp2013Amit GuptaNo ratings yet
- MineralogyDocument27 pagesMineralogyamber19995100% (1)
- Emily DickinsonDocument5 pagesEmily Dickinsonamber19995No ratings yet
- Working GP Enggg Roads-2559550717Document19 pagesWorking GP Enggg Roads-2559550717amber19995No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane AustenDocument217 pagesPride and Prejudice by Jane Austenamber19995No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics GraphicsDocument13 pagesEngineering Mechanics Graphicsamber19995No ratings yet
- On "Lady Lazarus": Eillen M. AirdDocument20 pagesOn "Lady Lazarus": Eillen M. Airdamber19995No ratings yet
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane AustenDocument217 pagesPride and Prejudice by Jane Austenamber19995No ratings yet
- Amish TripathiDocument6 pagesAmish Tripathiamber19995No ratings yet
- Ode To The West WindDocument2 pagesOde To The West Windamber19995No ratings yet
- Having A Coke With YouDocument1 pageHaving A Coke With YouKris MortisNo ratings yet
- Geol 104 Practice Exam I Spr1857 PDFDocument9 pagesGeol 104 Practice Exam I Spr1857 PDFDrake WellsNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 11-Abm A (Group 5)Document14 pagesPerformance Task 11-Abm A (Group 5)kenrick09No ratings yet
- What Happens When Volcanoes EruptDocument27 pagesWhat Happens When Volcanoes EruptMaika JulianNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint: Anisah AbdulssalamDocument20 pagesCambridge Lower Secondary Checkpoint: Anisah AbdulssalamAnisahNo ratings yet
- Philippines Science 9 Summative TestDocument6 pagesPhilippines Science 9 Summative TestHAIDEENo ratings yet
- Activity 1 and 2 Intervention - 1st QuarterDocument2 pagesActivity 1 and 2 Intervention - 1st QuarterJessa TirambuloNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional - Gunung Api Indonesia - CompressedDocument18 pagesJurnal Internasional - Gunung Api Indonesia - CompressedSyuk riyahNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards, Mitigation, and AdaptationDocument15 pagesNatural Hazards, Mitigation, and AdaptationSheryll BayyaNo ratings yet
- Bom 807 4759 Finalstudymaterial2ndterm8science1Document52 pagesBom 807 4759 Finalstudymaterial2ndterm8science1Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualAntonioCohensirt100% (32)
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceHani CasipleNo ratings yet
- DK Did You Know Earth PDFDocument144 pagesDK Did You Know Earth PDFThuy Pham82% (11)
- Geography guide to earth's interior, processes, and climateDocument15 pagesGeography guide to earth's interior, processes, and climatemotu179No ratings yet
- Y3 Human-and-Natural-Disasters-Knowledge-OrganiserDocument1 pageY3 Human-and-Natural-Disasters-Knowledge-OrganiserD BromleyNo ratings yet
- M1 VolcanoDocument69 pagesM1 VolcanoClaudie MabiniNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Earth's Internal HeatDocument24 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Earth's Internal HeatJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Science!!Document21 pagesPortfolio in Science!!Michaela Damian BertulanoNo ratings yet
- Training on Disaster Risk Reduction: The Role of DOST Regional Offices in Addressing Volcanic HazardsDocument64 pagesTraining on Disaster Risk Reduction: The Role of DOST Regional Offices in Addressing Volcanic HazardsJason LeonaNo ratings yet
- Abm Grade 11 Els 7 What I KnowDocument4 pagesAbm Grade 11 Els 7 What I Knowangel ann0% (1)
- Viscosity Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesViscosity Lesson Planapi-406512450No ratings yet
- Medical Imaging Signals and Systems 2nd Edition Prince Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesMedical Imaging Signals and Systems 2nd Edition Prince Solutions ManualCodyDavisncfp100% (49)
- Bahasa Inggris SMP/MTS: EarthquakeDocument8 pagesBahasa Inggris SMP/MTS: EarthquakeAndri YuliprasetioNo ratings yet
- 6 Landforms - SCIENCEDocument9 pages6 Landforms - SCIENCEArwen MargalloNo ratings yet
- SLK SCI9 Q3 W2-With-Beta EDITEDDocument12 pagesSLK SCI9 Q3 W2-With-Beta EDITEDrolan benNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Test Practice - CompressedDocument117 pagesIELTS Reading Test Practice - CompressedPhuongAnhNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Title: Three Main Categories of RocksDocument39 pagesEarth & Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Title: Three Main Categories of RocksTeacher MelNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Exam in ScienceDocument3 pages4TH Quarter Exam in ScienceReyna GianNo ratings yet