Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Welding Inspection: Weld Procedures
Uploaded by
anon_90890103Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Welding Inspection: Weld Procedures
Uploaded by
anon_90890103Copyright:
Available Formats
M.Rogers WI 3.
Welding Inspection
Weld Procedures
Course notes section reference 5
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
Example Code: BS EN 288
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
Producing a welding procedure involves:
Planning the tasks Collecting the data Writing a procedure for use of for trial
Making a test welds
Evaluating the results
Approving the procedure
Preparing the documentation
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
In most codes reference is made to how the procedure are to be devised and whether approval of these procedures is required. The approach used for procedure approval depends on the code: Example codes:
AWS D.1.1: Structural Steel Welding Code BS 2633: Class 1 welding of Steel Pipe Work API 1104: Welding of Pipelines BS 4515: Welding of Pipelines over 7 Bar
Other codes may not specifically deal with the requirement of a procedure but may contain information that may be used in writing a weld procedure EN 1011Process of Arc Welding Steels
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
Components of a welding procedure
Parent material Type (Grouping) Thickness Diameter (Pipes) Surface condition) Welding process Type of process (MMA, MAG, TIG, SAW etc) Equipment parameters Amps, Volts, Travel speed
Welding Consumables Type of consumable/diameter of consumable Brand/classification Heat treatments/ storage
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
Joint design Edge preparation Root gap, root face Jigging and tacking Type of baking Welding Position Location, shop or site Welding position e.g. 1G, 2G, 3G etc Any weather precaution Welding Variables Run sequences Back gouging Interpass temperatures Thermal heat treatments Preheat, temps Post weld heat treatments e.g. stress relieving
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
Approving the procedure:
When the data has been collected, the procedure must be validated by producing a test weld, weld procedure test (WPT). A number of standards provides information with regards to approving a procedure, but normally this will require the WPT to be tested by NDT and mechanical testing. The locations and tests required will be given in the applicable code or standard Most codes and standards provide a report format to record the results
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
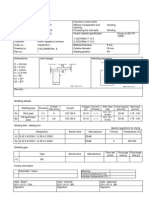
Examination and testing requirements of a WPT for procedure approval (BS EN 288)
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
After the testing is completed and all the relevant results collated, the results need to be assessed in accordance with the relevant code/standard. The results are then generally recorded. pWPS: Preliminary Welding Procedure Specification Before procedure approval. WPS: Welding Procedure Specification After procedure approval
WPAR (WPQR): Welding Procedure Approval Record
Welding procedure test record
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welding Procedures
Once the welding procedure has been approved, If any essential variable is changed during production the WPS may require re-approval. Most codes/procedures dealing with procedure qualifications provide a list of what is an essential or non-essential variable. Object of a welding procedure test
To give maximum confidence that the welds mechanical and metallurgical properties meet the requirements of the applicable code/specification. Each welding procedure will show a range to which the procedure is approved (extent of approval) If a customer queries the approval evidence can be supplied to prove its validity
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Example: Welding Procedure
Specification
(WPS)
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welder Approval
Example Code: BS EN 287
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welder Approval
Numerous codes and standards deal with welder qualification, e.g. BS EN 287. Once the content of the procedure is approved the next stage is to approve the welders to the approved procedure. A welders test know as a Welders Qualification Test (WQT).
Object of a welding qualification test . To give maximum confidence that the welder meets the requirements of the approved procedure (WPS). The test weld should be carried out on the same material and same conditions as for the site welds The welder who carries out the procedure qualification weld would automatically qualify when the procedure qualifies
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welder Approval
Information that should be included on a welders test certificate are: 1. Welders name and identification number 2. Date of test and expiry date of certificate 3. Standard/code e.g. BS EN 287 4. Test piece details 5. Welding process. 6. Welding parameters, amps, volts 7. Consumables, flux type and filler classification details 8. Sketch of run sequence, welding positions 9. Joint configuration details 10. Material type qualified, pipe diameter etc 11. Test results, remarks 12. Test location and witnessed by 13. Extent (range) of approval
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
BS EN 287
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Range of approval according to electrode flux type
Range of approval according material groups BS EN 287
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welder Approval
The inspection of a welders qualification test. It is normal for a qualified inspectors usually from an independent body to witness the welding. Under normal circumstances only one test weld per welder is permitted If the welder fails the test weld and the failure is not the fault of the welder e.g. faulty welding equipment then a re-test would be permitted. The testing of the test weld is done in accordance with the applicable code, but it is not normal to carry out test that test for the mechanical properties of welds e.g. tensile, charpy and hardness tests.
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Welder Approval
Tests methods required for welder qualification (BS EN 287)
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Example: Welder Approval
Qualification
Certification
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Stages in Welding and Welder Approval
Application standard Contract Project specifications DEVELOPMENT OF PROCEDURE
pWPS
BE 288 ASTM IX AWS D1.1 APPROVAL OF PROCEDURE
WPAR/WPQR
WELDER APPROVAL CERTIFICATE
6 MONTHS + PROLONGATION
FINALISATION OF PROCEDURE
Welding Procedure Specification
RELEASE WPS FOR PRODUCTION
WORK INSTRUCTIONS
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Any Questions
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
M.Rogers WI 3.1
Questions
Welding Procedures
QU 1. State six essential variables in a welding procedure. QU 2. What do you understand by the term extent of approval and give four examples. QU 3. Describe what you understand by a welding procedure specification, A welding procedure approval record and a welder certificate QU 4. What is the reason for approving a welding procedure and a welder QU 5. Give three reasons why a welder may require requalification.
Copyright 2005 TWI Ltd
World Centre for Materials Joining Technology
You might also like
- Senior Welding Inspection: Weld Procedures Course Reference WIS 10Document21 pagesSenior Welding Inspection: Weld Procedures Course Reference WIS 10Harkynollar HarkyntehyeNo ratings yet
- WPQR6Document3 pagesWPQR6Dimitris NikouNo ratings yet
- Contact Us: Guides in PDF: (Member Access) Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Document4 pagesContact Us: Guides in PDF: (Member Access) Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Maulik PatelNo ratings yet
- TWI CSWIP 3.1 Wis 5 Welding Inspection Practical Visual Inspection of Pipe WeldsDocument11 pagesTWI CSWIP 3.1 Wis 5 Welding Inspection Practical Visual Inspection of Pipe WeldsJohn DareNo ratings yet
- Welding & Pipe Inspection Training ManualDocument48 pagesWelding & Pipe Inspection Training ManualpunitdubeyNo ratings yet
- WI 01 - Introduction To WI ModuleDocument14 pagesWI 01 - Introduction To WI ModuledayalramNo ratings yet
- Application Form For CSWIP 10 Year Assessment (Overseas) No LogbookDocument10 pagesApplication Form For CSWIP 10 Year Assessment (Overseas) No LogbookKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Morning Day 4 QuestionsDocument62 pagesMorning Day 4 Questionshaoues23No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Methods API 941 Annex E Draft 3 CleanDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Methods API 941 Annex E Draft 3 CleanRupam BaruahNo ratings yet
- FILL COURSE ENROLMENT FORMDocument3 pagesFILL COURSE ENROLMENT FORMRaja Guru100% (1)
- A Brief Synopsis ofDocument54 pagesA Brief Synopsis ofNO ONENo ratings yet
- Welding Technology Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesWelding Technology Exam QuestionsVijaya BaraniNo ratings yet
- Afternoon Quiz Set 4Document66 pagesAfternoon Quiz Set 4pchakkrapani100% (1)
- Cswip Question and Answers: ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesCswip Question and Answers: Responsibilitiesfery0% (1)
- Twi - Welding Inspection - SteelsDocument209 pagesTwi - Welding Inspection - Steelsenels77No ratings yet
- CSWIP Practical Plate Exe 2007Document6 pagesCSWIP Practical Plate Exe 2007Walid SaadaniNo ratings yet
- Fluoroscopy and Radiography InterpretationDocument56 pagesFluoroscopy and Radiography InterpretationFongJeremyNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between API-1104 21st Ed & 22nd EdDocument13 pagesComparison Between API-1104 21st Ed & 22nd EdsadashiwNo ratings yet
- Asme 9 TipsDocument13 pagesAsme 9 TipsnasrpkNo ratings yet
- CSWIP 3.1 - Question With Answer and Explanation - Part 16 - General Technical KnowledgeDocument7 pagesCSWIP 3.1 - Question With Answer and Explanation - Part 16 - General Technical KnowledgeDENSIN0% (1)
- Qw-482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)Document8 pagesQw-482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)Muhammad HannanNo ratings yet
- Cswip3.2 Content ONLYDocument3 pagesCswip3.2 Content ONLYSathishkumar. KNo ratings yet
- Cswip3.2 Introduction ONLYDocument3 pagesCswip3.2 Introduction ONLYSathishkumar. KNo ratings yet
- Cswip 31 Practical PDFDocument4 pagesCswip 31 Practical PDFJigar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco: Company General UseDocument8 pagesSaudi Aramco: Company General UseMasudhBashaNo ratings yet
- Wps Sp14 Reva PDFDocument9 pagesWps Sp14 Reva PDFravi00098No ratings yet
- CWI TEST Flashcards PDFDocument30 pagesCWI TEST Flashcards PDFGary Oporto cabasNo ratings yet
- Guide For Make WPSDocument84 pagesGuide For Make WPSvohuu1102100% (1)
- Cswip 3 1 Macro PDFDocument36 pagesCswip 3 1 Macro PDFtheNo ratings yet
- Cswip IitsDocument5 pagesCswip IitsSafiq UddinNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection and CertificationDocument30 pagesWelding Inspection and CertificationtuvuNo ratings yet
- Module 9.qualification 1.welding PerformanceDocument6 pagesModule 9.qualification 1.welding PerformanceMohd NizamNo ratings yet
- 24B-Pactical Pipe Inspection 2006Document17 pages24B-Pactical Pipe Inspection 2006Morg ActusNo ratings yet
- Weld Joint Geometry - Welding and NDE SymbolsDocument124 pagesWeld Joint Geometry - Welding and NDE Symbolstuvu100% (1)
- CSWIP WIS 5 General Quiz: TWI Training & Examination ServicesDocument63 pagesCSWIP WIS 5 General Quiz: TWI Training & Examination Serviceshaoues23No ratings yet
- SB410 (JIS) - Worldwide Equivalent Grades 11Document1 pageSB410 (JIS) - Worldwide Equivalent Grades 11valli raju100% (1)
- CSWIP 3.1 Welding Inspector exam detailsDocument2 pagesCSWIP 3.1 Welding Inspector exam detailsSalahuddin Farooqui100% (1)
- En ASME ComparisonDocument18 pagesEn ASME ComparisonPeterWay100% (1)
- Tech E 2 or B PDFDocument4 pagesTech E 2 or B PDFkathirNo ratings yet
- ASME U & R STAMPS GUIDEDocument12 pagesASME U & R STAMPS GUIDEShaheen Andre ChikkuNo ratings yet
- 'TWI CSWIP Macro Practical Inspection (Compatibility Mode)Document36 pages'TWI CSWIP Macro Practical Inspection (Compatibility Mode)Veeralekshmanan KumarNo ratings yet
- Safe Practices For Welding InspectorsDocument39 pagesSafe Practices For Welding Inspectorstuvu100% (2)
- Senior Welding Inspector DutiesDocument59 pagesSenior Welding Inspector Dutiesnagu100% (1)
- Write WPS ISO 15614Document10 pagesWrite WPS ISO 15614Hoang LamNo ratings yet
- TWI CSWIP 3.1 Wis 5 Welding Inspection: World Centre For Materials Joining TechnologyDocument26 pagesTWI CSWIP 3.1 Wis 5 Welding Inspection: World Centre For Materials Joining TechnologyDanem HalasNo ratings yet
- RT Acceptance Criteria GuideDocument1 pageRT Acceptance Criteria GuidevikasNo ratings yet
- WPS - EngineerDocument20 pagesWPS - Engineerhunghoanglong100% (1)
- Hydrogen Cracking Causes and PreventionDocument6 pagesHydrogen Cracking Causes and Preventionshahid khanNo ratings yet
- Cswip 3.1 GeneralDocument3 pagesCswip 3.1 GeneralPrabhu MakeshNo ratings yet
- Exam Narative Cswip 3.2Document5 pagesExam Narative Cswip 3.2yuwantoniNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Weld Geometry and Welding Symbols-1Document87 pagesModule 4 Weld Geometry and Welding Symbols-1Miki JaksicNo ratings yet
- ASME PQR - MMA/SMAW Fillet Welds on OGAP Supplies PartsDocument1 pageASME PQR - MMA/SMAW Fillet Welds on OGAP Supplies Partssathi_mechNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Examination of WeldsDocument4 pagesMagnetic Particle Examination of WeldsshruthiNo ratings yet
- TWI CSWIP 3.1 Wis 5 Welding Inspection Four Factors: World Centre For Materials Joining TechnologyDocument7 pagesTWI CSWIP 3.1 Wis 5 Welding Inspection Four Factors: World Centre For Materials Joining TechnologyOnur AltuntaşNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure SpecificationDocument21 pagesWelding Procedure Specificationboypardede100% (7)
- Wis5 WPS 05Document22 pagesWis5 WPS 05Gibson FisherNo ratings yet
- WPS N WQTDocument21 pagesWPS N WQTHUNG LENo ratings yet
- WPS, PQR, WQT, WPQ: BBW30103 Teknologi Kimpalan BerautomasiDocument12 pagesWPS, PQR, WQT, WPQ: BBW30103 Teknologi Kimpalan BerautomasiNazrin GLNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure SpecificationsDocument14 pagesWelding Procedure SpecificationsBasavaraj KaraningNo ratings yet
- WIS5 Symbols 05Document52 pagesWIS5 Symbols 05anon_90890103No ratings yet
- DefectDocument2 pagesDefectanon_90890103100% (1)
- TWI Course EnrolmentDocument1 pageTWI Course Enrolmentanon_90890103No ratings yet
- TWI Exam EnrolmentDocument2 pagesTWI Exam EnrolmentAndriNo ratings yet
- Daily ReportDocument12 pagesDaily Reportanon_90890103No ratings yet
- Floor SocketDocument1 pageFloor Socketanon_90890103No ratings yet
- Inventor 4 ExercisesDocument2 pagesInventor 4 Exercisesanon_90890103No ratings yet
- Primera Ley Sistemas CerradosDocument68 pagesPrimera Ley Sistemas CerradospimpollompNo ratings yet
- Conduction Through LiquidDocument1 pageConduction Through LiquidMuskan RangrejNo ratings yet
- Distillation Ch4 ReboilerDocument27 pagesDistillation Ch4 Reboilerkphk1979No ratings yet
- Unit-1: Mode Theory of Circular WaveguideDocument16 pagesUnit-1: Mode Theory of Circular WaveguideRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Ucalgary 2017 Hudecek Martin PDFDocument495 pagesUcalgary 2017 Hudecek Martin PDFPaul Ciprian TeglaNo ratings yet
- Wood Bending Analysis Reveals Strength PropertiesDocument6 pagesWood Bending Analysis Reveals Strength PropertiesPatrice Suerte FelipeNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument5 pagesLaws of Motionkatie4834No ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure and Winds ExplainedDocument26 pagesAtmospheric Pressure and Winds ExplainedR AmravatiwalaNo ratings yet
- Mike WeaverDocument35 pagesMike WeavervilukNo ratings yet
- Nooter Eriksen HRSG AdvantagesDocument3 pagesNooter Eriksen HRSG Advantagesaliscribd46No ratings yet
- Corrosion and Its Control NFDocument93 pagesCorrosion and Its Control NFAayu JainNo ratings yet
- 1998 Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument43 pages1998 Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete DesignAlb MetalNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Improvement of Flat Plate Solar Collector Using ReflectorDocument6 pagesEfficiency Improvement of Flat Plate Solar Collector Using ReflectorAnonymous iHJPiQI7No ratings yet
- Flying Windmills: Conventional WindmillDocument7 pagesFlying Windmills: Conventional WindmillGógul100% (1)
- Development of Database of Cyclic Soil Properties From 94 Tests On 47 SoilsDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Database of Cyclic Soil Properties From 94 Tests On 47 SoilsJulio BetancurNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry (BCHY101L) : Energy DevicesDocument84 pagesEngineering Chemistry (BCHY101L) : Energy DevicesDeepali Mishra 21BCE3440No ratings yet
- Wassce / Waec Chemistry Syllabus: 1. Structure of The AtomDocument30 pagesWassce / Waec Chemistry Syllabus: 1. Structure of The AtomJesse Lartey100% (1)
- Protocol-XRD XRF SEM OE PDFDocument16 pagesProtocol-XRD XRF SEM OE PDFShyamNo ratings yet
- Activity Session 5 Earth Science ConseminoDocument32 pagesActivity Session 5 Earth Science ConseminoFatimah D. Rubin-Cansancio100% (2)
- Analytical Chemistry TransesDocument16 pagesAnalytical Chemistry TransesLouisse Alessandra Paderna-DecalNo ratings yet
- Light Interference Tutorial and AssignmentsDocument4 pagesLight Interference Tutorial and AssignmentsRitesh MeelNo ratings yet
- Apchap7and8 PEandConservationofE1718Document17 pagesApchap7and8 PEandConservationofE1718Alaa HassanNo ratings yet
- Macam-Macam Dan Sifat Bahan Resin Kedokteran Gigi - Bimo RintokoDocument18 pagesMacam-Macam Dan Sifat Bahan Resin Kedokteran Gigi - Bimo Rintokodayanara_245104654No ratings yet
- Prelim Examination Set A Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesPrelim Examination Set A Solutions PDFOxy GenNo ratings yet
- 472Document35 pages472Nahida BanoNo ratings yet
- Raytools BM109 spare parts listDocument1 pageRaytools BM109 spare parts listremus popescuNo ratings yet
- Duct Velocity D - 928 PDFDocument7 pagesDuct Velocity D - 928 PDFTeo Pei SanNo ratings yet
- Doctoral Thesis by S ChaterjeeDocument159 pagesDoctoral Thesis by S ChaterjeeSaikat ChaterjeeNo ratings yet
- Turbidimetry NotesDocument2 pagesTurbidimetry NotesJessa MayNo ratings yet