Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physiology of The Heart: Electrocardiography (ECG)
Uploaded by
Siti Maryam NatadisastraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physiology of The Heart: Electrocardiography (ECG)
Uploaded by
Siti Maryam NatadisastraCopyright:
Available Formats
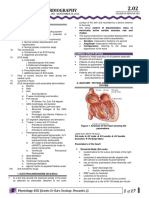
Physiology of The Heart Electrocardiography (ECG)
M. Djauhari Widjajakusumah Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia
Figure 111 Normal electrocardiogram.
Guyton & Hall: Textbook of Med Physiol 11th ed, 2006
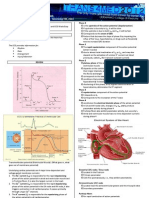
Effect of Heart Position on the Electrocardiogram
Figure 15-4 Transmembrane potential (Vm) of a cardiac muscle fiber varies inversely with the potassium concentration of the external medium. The straight line (EK) represents the change in transmembrane potential predicted by the Nernst equation for potassium. (Redrawn from Page E: Circulation 26:582, 1962.)
Figure 15-5 Concentration of sodium in the external medium is a critical determinant of the amplitude of the action potential in cardiac muscle (upper line) but it has very little influence on the resting membrane potential (lower line). (Redrawn from Weidmann S: Elektrophysiologie der Herzmuskelfaser, Bern, 1956, Verlag Hans Huber.)
Effects of [K+] on Cardiac Rate and Rhythm
Hyperkalemia Myocardium action potential: Lowers the resting membrane potential (resting Em ) Inactivates Na+ channels Na+ fast inward current action potential upstroke and amplitude slow conduction velocity widening of QRS complex the rate and extent of K+ channels re-opening accelerates repolarization shortens the plateau phase and duration of action potential peaked T waves slightly shortened Q-T interval
Pacemaker (SA node) action potential: Lowers the resting membrane potential (resting Em ) phase 4 slope no change in sinus rate (heart rate)
Effects of [K+] on Cardiac Rate and Rhythm
Hypokalemia Myocardium action potential: Nernst equation: resting membrane potential (resting Em ) [K+] < 3mM resting membrane potential slightly Normal action potential upstroke and amplitude Inhibits the re-opening of K+ channels delayed re-opening of K+ channels prolonged plateau, repolarization and duration of the action potential flat T waves prolonged Q-T interval Pacemaker (SA node) action potential: Lowers the resting membrane potential (resting Em ) phase 4 slope sinus rate (heart rate)
Effects of [Ca++] on Cardiac Rate and Rhythm
Hypercalcemia Myocardium action potential: [Ca++] o / [Ca++] I ratio Ca++ inward current the height of the plateau Normal action potential upstroke and amplitude Accelerates the re-opening of K+ channels shortened plateau, repolarization and duration of the action potential sagging S-T segments shortened Q-T interval Pacemaker (SA node) action potential: threshold potential sinus rate (heart rate)
Effects of [Ca++] on Cardiac Rate and Rhythm
Hypocalcemia Myocardium action potential: [Ca++] o / [Ca++] I ratio Ca++ inward current the height of the plateau Action potential upstroke and amplitude Slowing the re-opening of K+ channels prolonged plateau, repolarization and duration of the action potential prolonged Q-T interval Pacemaker (SA node) action potential: threshold potential sinus rate (heart rate)
Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia
Terima kasih
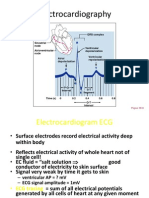
Electrocardiography (ECG)
M. Djauhari Widjajakusumah Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia
You might also like
- 2 02-Electrocardiography PDFDocument17 pages2 02-Electrocardiography PDFMiguel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECGDocument60 pagesElectrocardiography ECGSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument41 pagesECGmiguel mendezNo ratings yet
- Peter Attia Measuring Cardiovascular Disease Risk and The Importance of ApoBDocument14 pagesPeter Attia Measuring Cardiovascular Disease Risk and The Importance of ApoBabhimanyu50% (2)
- Sally Aburumman Bushra SaleemDocument75 pagesSally Aburumman Bushra SaleemAbdulrahman AlsayyedNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALDocument16 pagesBasic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALCharlotte James100% (5)
- Applied Combinatorics, Second Edition by Fred S Roberts, Barry TesmanDocument889 pagesApplied Combinatorics, Second Edition by Fred S Roberts, Barry TesmanAnil kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography IDocument19 pagesElectrocardiography IsalochinNo ratings yet
- ECG1Document67 pagesECG1Farhan RosliNo ratings yet
- ECG Normal and AbnormalDocument74 pagesECG Normal and Abnormalawaniedream8391100% (1)
- ElectrocardiogramDocument29 pagesElectrocardiogramMahnoor ZafarNo ratings yet
- ECG-Dr.Allam منقول PDFDocument11 pagesECG-Dr.Allam منقول PDFRaouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (1)
- Physiology Slides UsmleDocument46 pagesPhysiology Slides Usmlejustseas100% (1)
- Cardiac Physiology NotesDocument11 pagesCardiac Physiology Notespunter11100% (1)
- Ordinary Dierential Equations Principles and ApplicationsDocument349 pagesOrdinary Dierential Equations Principles and ApplicationsSokratis Spyrou100% (1)
- Revised AntiarrhythmicsDocument29 pagesRevised AntiarrhythmicsDang CuevasNo ratings yet
- Seguridad Electrica 4Document28 pagesSeguridad Electrica 4salo081018No ratings yet
- CO2 Production PlantsDocument4 pagesCO2 Production PlantsBoojie Recto100% (1)
- Physiology of The Heart Revealed in ECGDocument50 pagesPhysiology of The Heart Revealed in ECGChintya Ayu ChampakaNo ratings yet
- Final Q Bank CVS Upto Cardiac Output (13-01-2017)Document2 pagesFinal Q Bank CVS Upto Cardiac Output (13-01-2017)faris babuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Physiology SDocument54 pagesCardiac Physiology Smutthineni.sushma28No ratings yet
- Perioperative ArrthymiasDocument9 pagesPerioperative ArrthymiasDrshoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CyclecosedasapereNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleEdi HidayatNo ratings yet
- 2012 ECG HandoutDocument40 pages2012 ECG Handoutlizzy596No ratings yet
- Arrhythmogenic Ion-Channel Remodeling in The Heart: Heart Failure, Myocardial Infarction, and Atrial FibrillationDocument34 pagesArrhythmogenic Ion-Channel Remodeling in The Heart: Heart Failure, Myocardial Infarction, and Atrial FibrillationPio ArayaNo ratings yet
- PIIS0007091217355952Document9 pagesPIIS0007091217355952Said Qadaru ANo ratings yet
- Electrical Activity of Excitable Cells: The Resting StateDocument19 pagesElectrical Activity of Excitable Cells: The Resting State정은규No ratings yet
- Arrythmia by AbnetDocument509 pagesArrythmia by AbnetAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- ECG For BeginnersDocument61 pagesECG For Beginnersblndffl100% (2)
- 7InitialDraft 4Document8 pages7InitialDraft 4pigzeniNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument27 pagesAtrial FibrillationOnon EssayedNo ratings yet
- 4 1Document2 pages4 1Raj BulaNo ratings yet
- 05 - Fisiologi - Jantung PDFDocument63 pages05 - Fisiologi - Jantung PDFfadhila dzatu rifqiNo ratings yet
- ECG Analysis and Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument6 pagesECG Analysis and Cardiac Dysrhythmiasrui_kaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rhythm Disorders With RMP and Inactivcating Sodium ChannelsDocument37 pagesCardiac Rhythm Disorders With RMP and Inactivcating Sodium ChannelsAniket MittalNo ratings yet
- CV AnatomyDocument49 pagesCV AnatomymichaelNo ratings yet
- Obat AntiarritmiaDocument22 pagesObat AntiarritmiaOcie SatyoNo ratings yet
- Hotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PDocument145 pagesHotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PkangheriNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Cardiac Arrhythmias: A. Thompson and J. R. BalserDocument9 pagesPerioperative Cardiac Arrhythmias: A. Thompson and J. R. BalsererzaraptorNo ratings yet
- ECG Self-Study GuideDocument24 pagesECG Self-Study GuideShamsuzzaman SharifNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CyclebhatsindhoorNo ratings yet
- Jamaneurology West 2018 LD 170009Document4 pagesJamaneurology West 2018 LD 170009Dah Saadah AkasiaNo ratings yet
- ECG Complete LectureDocument33 pagesECG Complete LectureDr. SUVA NATHNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography ECG: Dana KaremDocument13 pagesElectrocardiography ECG: Dana KaremDana KaremNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle Physiology and Cardiovascular System FunctionDocument183 pagesCardiac Muscle Physiology and Cardiovascular System FunctionArdhian Yudha CandraNo ratings yet
- ST Segment and T Waves:: Ischemia, Infarction, Drug & Electrolyte EffectsDocument34 pagesST Segment and T Waves:: Ischemia, Infarction, Drug & Electrolyte EffectsHibba NasserNo ratings yet
- Cardio Physiology FullDocument11 pagesCardio Physiology FullSara Lee Wei LiNo ratings yet
- Cardiologia - EletrocardiografiaDocument40 pagesCardiologia - EletrocardiografiaDANIEL ALEJANDRONo ratings yet
- Hexeberg 1993Document4 pagesHexeberg 1993CARLOS FRANCISCO MANTILLA MONTALVONo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2021 1292271Document34 pagesMUCLecture 2021 1292271Kouka MahfoudiNo ratings yet
- I. The Standard 12 Lead ECGDocument2 pagesI. The Standard 12 Lead ECGapi-376925250% (2)
- HHS Public Access: The Electrophysiology of Hypo-And HyperkalemiaDocument21 pagesHHS Public Access: The Electrophysiology of Hypo-And HyperkalemiaDickyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoDocument53 pagesCardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoAnisha NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument82 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyAminah Al-NafisahNo ratings yet
- Download ebook Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology And Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Hupperts Notes Pathophysiology And Clinical Pearls For Internal Medicine Pdf full chapter pdfmartha.delancey633100% (22)
- Heart Failure PharmDocument7 pagesHeart Failure PharmAmitShettyNo ratings yet
- ECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateDocument17 pagesECG Tutorial - Basic Principles of ECG Analysis - UpToDateImja94No ratings yet
- Cardiac L3Document18 pagesCardiac L3Qutaybah JahmanyNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Vascular PhysiologyDocument155 pagesSection 3 Vascular Physiologyraanja2No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: (Review)Document42 pagesCardiovascular System: (Review)Leichel AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Be 3600 Biomedical Instrumentation (Lab) - : Experiment 4Document5 pagesBe 3600 Biomedical Instrumentation (Lab) - : Experiment 4Abhay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pigmentary Disorders 2015 Topical Lightening Cream VS Topical LC Oral PE and PF PDFDocument6 pagesJournal of Pigmentary Disorders 2015 Topical Lightening Cream VS Topical LC Oral PE and PF PDFSiti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi KasusDocument20 pagesInterpretasi KasusSiti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Cover Makalah Case 3Document1 pageCover Makalah Case 3Siti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Hasil Hadi Cruris OsteomyelitisDocument1 pageHasil Hadi Cruris OsteomyelitisSiti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension ImagingDocument12 pagesPulmonary Hypertension ImagingSiti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Atrium FlutterDocument11 pagesAtrium FlutterSiti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Cover Makalah Case 7Document1 pageCover Makalah Case 7Siti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Dis SemVDocument21 pagesKawasaki Dis SemVSiti Maryam NatadisastraNo ratings yet
- Steel Castings, Welding, Qualifications of Procedures and PersonnelDocument15 pagesSteel Castings, Welding, Qualifications of Procedures and PersonnelRafael CossolinoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition, Properties, and Standards of Steel Grade 42CrMo4 (1.7225Document1 pageChemical Composition, Properties, and Standards of Steel Grade 42CrMo4 (1.7225ADITYA_PATHAK100% (1)
- Clients Class Workbook v5.1 CBTDocument192 pagesClients Class Workbook v5.1 CBTmich0pNo ratings yet
- 11 - Biennial - Form/3 Component Uphole Survey For Estimation of SHDocument5 pages11 - Biennial - Form/3 Component Uphole Survey For Estimation of SHVishal PandeyNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 - Signpost 2011Document4 pagesPractical 4 - Signpost 2011Percy Percival50% (2)
- Pages 296-298 Module 6 ReviewDocument4 pagesPages 296-298 Module 6 Reviewapi-332361871No ratings yet
- UNIT 7 - Atomic TransactionsDocument30 pagesUNIT 7 - Atomic TransactionslavanyatumuNo ratings yet
- Hkts 210 Sub/Hkts 200 Sub: SubwooferDocument6 pagesHkts 210 Sub/Hkts 200 Sub: SubwooferDan PopNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Rise Desnita, M.Si., AptDocument41 pagesSolutions: Rise Desnita, M.Si., Aptdeput_rprNo ratings yet
- Project PBLDocument19 pagesProject PBLAdam LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Power Max India PVT LTD Extra Work Done at VMW Shed WorksDocument4 pagesPower Max India PVT LTD Extra Work Done at VMW Shed WorksparthaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: in Order To Decrease Cross Sectional Area of Structural Members, Ultra High StrengthDocument16 pagesSynopsis: in Order To Decrease Cross Sectional Area of Structural Members, Ultra High StrengthHector Alberto Garcia LopezNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulations of The Effects of Non-Uniform Temperature Distributions On Lateral Torsional Buckling Resistance of Steel I-BeamsDocument8 pagesNumerical Simulations of The Effects of Non-Uniform Temperature Distributions On Lateral Torsional Buckling Resistance of Steel I-BeamsReaditReaditNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Ee8205 PDFDocument4 pagesProblem Set Ee8205 PDFksajjNo ratings yet
- Supervision Circuito de DisparoDocument10 pagesSupervision Circuito de DisparoedwinoriaNo ratings yet
- Columns and preconditions reportDocument2 pagesColumns and preconditions reportIndradeep ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Manual Fx2n 485 BDDocument8 pagesManual Fx2n 485 BDaxo_vfrNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Logic: An Alternative Approach To Low Power Application CircuitsDocument6 pagesAdiabatic Logic: An Alternative Approach To Low Power Application CircuitsBibartan DasNo ratings yet
- Format RAB SUHU DAN TEMPERATUR RUANGANDocument18 pagesFormat RAB SUHU DAN TEMPERATUR RUANGANmeliana314No ratings yet
- Appendix B DAX ReferenceDocument174 pagesAppendix B DAX ReferenceTomislav Mališ100% (1)
- Xy6112 EtcDocument4 pagesXy6112 EtcJalal AsadianNo ratings yet
- One Plus 7Document114 pagesOne Plus 7Priyanka ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- M4 4 Synthetic Surface Modeling Bezier and Bspline PatchesDocument40 pagesM4 4 Synthetic Surface Modeling Bezier and Bspline PatchesNANDULA GOUTHAM SAINo ratings yet
- AtmegaDocument22 pagesAtmegaMUKILANNo ratings yet
- SMD Meter User's ManualDocument2 pagesSMD Meter User's ManuallucianoNo ratings yet