Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases
Uploaded by
Ahmed HamzaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases
Uploaded by
Ahmed HamzaCopyright:
Available Formats
An acid is any substance that releases hydrogen ions, H+, into water.
Blue litmus paper turns red in the presence of hydrogen ions. Blue litmus is used to test for acids.
Acids have a sour taste; lemons, limes, and vinegar are acidic.
Strong Bases - ionize 100% NaOH KOH
Strong Acids - ionize 100% HCl HI HNO3 HBr H2SO4 HClO4 Weak Acids - partially ionize HF CH3COOH
A base is a substance that releases hydroxide ions, OH , into water. Red litmus paper turns blue in the presence of hydroxide ions. Red litmus is used to test for bases. Bases have a slippery, soapy feel. Bases also have a bitter taste; milk of magnesia is a base.
Chapter 15
Recall that an acid and a base react with each other in a neutralization reaction. When an acid and a base react, water and a salt are produced.
For example, nitric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium nitrate and water:
HNO3(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
Chapter 15
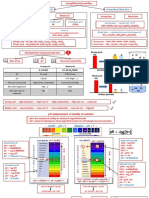
A pH value expresses the acidity or basicity of a solution. Most solutions have a pH between 0 and 14. Acidic solutions have a pH less than 7.
As a solution becomes more acidic, the pH decreases.
Basic solutions have a pH greater than 7.
As a solution becomes more basic, the pH increases.
Chapter 15
A solution can be classified according to its pH:
Strongly acidic solutions have a pH less than 2.
Weakly acidic solutions have a pH between 2 and 7.
Weakly basic solutions have a pH between 7 and 12. Strongly basic solutions have a pH greater than 12.
Neutral solutions have a pH of 7.
7
Recall, an acid neutralizes a base to produce a salt and water.
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
The reaction produces the aqueous salt NaCl. If we have an acid with two hydrogens (sulfuric acid, H2SO4), we need two hydroxide ions to neutralize it.
H2SO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) Na2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
Chapter 15
A solution that changes color as the pH changes is an acidbase indicator.
Three common indicators are methyl red, bromothymol blue, and phenolphthalein. Each has a different color above and below a certain pH.
Chapter 15
Shown below are the three indicators at different pH values
Methyl Red
Bromothymol Blue Phenolphthalein
Chapter 15
10
A titration is used to analyze an acid solution using a solution of a base. A measured volume of base is added to the acid solution. When all of the acid has been neutralized, the pH is 7. One extra drop of base solution after the endpoint increases the pH dramatically. When the pH increases above 7, phenolphthalein changes from colorless to pink indicating the endpoint of the titration.
Chapter 15
11
Recall that pH is a measure of the acidity of a solution. A neutral solution has a pH of 7, an acidic solution has a pH less than 7, and a basic solution has a pH greater than 7. The pH scale uses powers of ten to express the hydrogen ion concentration. Mathematically: pH = log[H+]
[H+] is the molar hydrogen ion concentration
12
pH is a measurement scale for acid concentration measurement pH = -log [H+] and pOH = -log [OH-] Calculate pH of a solution that is 0.00100 M Acid
A small amount of water ionizes by itself Water molecules are continually ionizing and then reforming H2O (l) <==> H+ (aq) + OH-(aq) Amount of H+ for neutral solution is 1 X 10-7 M
For an acidic [H+] = 1 X 10-5 M solution What is the pH?
What is pOH?
Kw = [H+] [OH-] -log Kw = -log ([H+] [OH-]) -log Kw = -log [H+] - log [OH-] -log Kw = pH + pOH pKw = pH + pOH 14 = pH + pOH
Acid - is a proton donor Base - is a proton acceptor Acid HCl donates a H+ to the solution Base NaOH donates OH- to solution with reacts with the H+
Weak acids and Weak bases do not ionize 100% in an aqueous solution Conjugate acid - base pair are two substances related to each other by the transfer of a proton NH3(aq) + H2O(l) => NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) NH3 and NH4+ are conjugate base and acid pair
H2CO3 is a weak acid and HCO3- is a weak base HF is a weak acid
Metals as acids
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lecture 02 Levelling (CH 4-5)Document24 pagesLecture 02 Levelling (CH 4-5)Ahmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- FACT SHEET For Shopping MallDocument1 pageFACT SHEET For Shopping MallAhmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 (Answers)Document14 pagesTutorial 2 (Answers)sudhanshu shekharNo ratings yet
- Approved Drawing-9123 PDFDocument1 pageApproved Drawing-9123 PDFAhmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- CIV401-Ch22 Numerical MethodsDocument9 pagesCIV401-Ch22 Numerical MethodsAhmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- CIV206 - Mechanics of MaterialsDocument5 pagesCIV206 - Mechanics of MaterialsAhmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- CIV 343 Hydraulics Lec 1Document4 pagesCIV 343 Hydraulics Lec 1Ahmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- StairsDocument21 pagesStairstomnubiNo ratings yet
- Acid Alkaline 1008Document6 pagesAcid Alkaline 1008api-171980623No ratings yet
- Na5600 Instalação PDFDocument484 pagesNa5600 Instalação PDFDinis MartinsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6'SDocument12 pagesExperiment 6'SShennyKoh67% (3)
- Surface and Interfacial PhenomenaDocument33 pagesSurface and Interfacial PhenomenaRana Mehul GNo ratings yet
- Acid/Base Equilibria - Chapter 16Document19 pagesAcid/Base Equilibria - Chapter 16aniedorfNo ratings yet
- PH Theory Guide - EN - 230113 PDFDocument98 pagesPH Theory Guide - EN - 230113 PDFraiedNo ratings yet
- 4.3 - Propagation of UncertaintyDocument8 pages4.3 - Propagation of UncertaintyjahmanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal and Vertical Soilless Growing Systems Under Cyprus ConditionsDocument5 pagesHorizontal and Vertical Soilless Growing Systems Under Cyprus ConditionsShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Learning Materials in Practices of Crop Production and Management 2Document32 pagesLearning Materials in Practices of Crop Production and Management 2paulo sabidoNo ratings yet
- 3 D Ethylene Glycol - Uninhibited PDFDocument4 pages3 D Ethylene Glycol - Uninhibited PDFvladimir ciovarnacheNo ratings yet
- AMT NU 1st Year Detail Syllabus Pub Date 30012019Document20 pagesAMT NU 1st Year Detail Syllabus Pub Date 30012019hasan mdNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management SSR PDFDocument131 pagesSoil Fertility and Nutrient Management SSR PDFSrikanth Reddy KuthuruNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentZia KhanNo ratings yet
- A Versatile Non-Cyanide Gold Plating System: by Ronald J. MorrisseyDocument5 pagesA Versatile Non-Cyanide Gold Plating System: by Ronald J. Morrisseyامين الدينNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Indicators For Use in TitrationDocument7 pagesAcid-Base Indicators For Use in TitrationMaxNo ratings yet
- Report (Mud Weight, Viscosity, PH)Document15 pagesReport (Mud Weight, Viscosity, PH)Ahmad BedihiNo ratings yet
- Hanna Instruments HI 98107 Phep PH Tester With +/-0.1 AccuracyDocument2 pagesHanna Instruments HI 98107 Phep PH Tester With +/-0.1 AccuracyIBJSC.comNo ratings yet
- Stability - Study - of - The - Pigment - Extract - From - A - Wild - SangineusDocument8 pagesStability - Study - of - The - Pigment - Extract - From - A - Wild - SangineusEmilyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ques PDFDocument20 pagesChemistry Ques PDFSameen ShahgirNo ratings yet
- All ExperimentsDocument14 pagesAll ExperimentsLujainNo ratings yet
- Multivitamin StabilityDocument5 pagesMultivitamin Stabilityanand1540100% (1)
- 1.physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WaterDocument203 pages1.physical, Chemical and Biological Characteristics of WaternikhilNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument3 pages1 PBHaola andaniNo ratings yet
- Strong Acid/Weak Acid Strong Base/ Weak BaseDocument22 pagesStrong Acid/Weak Acid Strong Base/ Weak BasetriNo ratings yet
- Environmental Case Study of Water Quality and Climate Change Resulting A Mass Mortality of Fish at Taj Boudi of BijapurDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Case Study of Water Quality and Climate Change Resulting A Mass Mortality of Fish at Taj Boudi of BijapurIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument38 pagesChemistry PDFAddict- ionNo ratings yet
- ASTM E70-07 Standard Test Method For PH of Aqueous Solutions With The Glass ElectrodeDocument10 pagesASTM E70-07 Standard Test Method For PH of Aqueous Solutions With The Glass Electrodederek vaughnNo ratings yet
- Enzyme AssayDocument23 pagesEnzyme AssayTanvir JawadNo ratings yet
- Gerald OoooooooDocument65 pagesGerald OoooooooOluwatobiloba IbrahimNo ratings yet