Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 Cell Specialisation
Uploaded by
Veer RamloghunCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Cell Specialisation
Uploaded by
Veer RamloghunCopyright:
Available Formats
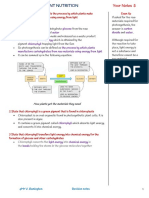
What are these cells? How are they specialised to perform their function?
CELL SPECIALISATION
Define terms differentiation & specialisation -erythrocytes, neutrophils, epithelial cells, sperm cells, palisade cells, root hair cells, xylem, Phloem & cambium
Which organism has the highest surface area to volume ratio?
The single celled Amoeba
Polar bear or other multi cellular organism
Which organism has the highest surface area to volume ratio?
The single celled Amoeba
12:8 = 3:2
Polar bear or other multi cellular organism
20:25
Single celled organisms
Multi-cellular organisms
Large s/a: volume All cells exposed to environment Effective exchange surface-for what? All cells perform all functions
Smaller s/a: volume Not all cells in contact with external environment Therefore: Specialised cells to perform different functions
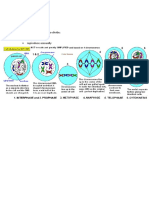
Young cell
Cell division
Cell growth
Cell specialisation
Mature cell
-Unlikely or unable to divide again
What is Differentiation When a cell becomes specialised to carry out a particular job/function What categories of differentiation are there? Change number of particular organelle e.g. muscle cell Change the shape of the cell e.g. root hair cell Change some of the contents of the cell e.g. RBC ALL 3!!
In your group, split the cells between you. Research your cell. Later you will need to explain your findings to the rest of the group
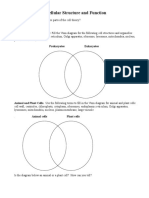
Specialised Cell Erythrocyte Neutrophil Sperm cell Palisade Cell Root hair cell Guard Cell Ciliated Epithelium
How the cell is specialised for its function
What are tissues, organs and organ systems?
Write a definition and an example of the following on the yellow post-its and stick under the appropriate heading: Tissue Organ Organ system
.
What are tissues, organs and organ systems?
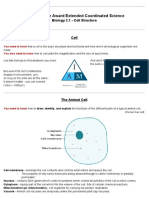
Cells make up TISSUES, groups of the same kind of cells performing a common function e.g. xylem and phloem in plants, muscle tissue in animals Groups of different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs e.g. the stomach consists of mucus membrane tissue, muscle tissue, etc Organs are grouped into systems e.g. respiratory system, reproductive system. organ systems consist of a number of organs working together to perform an overall life function
.
GROUP ESSAY
In this question, one mark is available for the quality of spelling, punctuation and grammar. Below is a picture of blood showing both red and white blood cells.
Describe how red blood cells, such as those shown in the picture are adapted for their function. (Allow one lined page). [6] Quality of Written Communication [1] [Total 7 marks] Think about the other side of the course too!!
1 haemoglobin/haem, carries oxygen/AW; 2 detail of no. of oxygen molecules carried; 3 small size/large SA:V ratio, so haemoglobin never far from cell surface/AW; 4 flexible/elastic/stretchy/changes shape/AW; 5 small size/stretchiness/AW, allows red cells to, fit/squeeze, into capillaries; 6 biconcave/AW [A dimpled], gives, increased/AW, surface area relative to volume (for diffusion); 7 no nucleus to maximise room for, haemoglobin/oxygen/AW; 8 contain carbonic anhydrase; 9 describe, the reaction catalysed by carbonic anhydrase/role in maintenance of diffusion gradient/AW; 10 transport of carbon dioxide as carbamino-haemoglobin/CO2 combines with Hb; 11 ref buffering effect; 12 AVP; e.g. further detail of oxygen carriage variable oxidation state of Fe idea that small size allows them to be close to tissue or cells lack of, other/named, named organelles, also increases room for Hb/O2 max 6 13 QWC legible text with accurate spelling, punctuation and grammar; 1[7]
You might also like
- Previous IB Exam Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesPrevious IB Exam Essay QuestionsCzesława KoniecznaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical KnowledgeFrom EverandStructure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- 02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document21 pages02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Pablo CostaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical Knowledge of the SubjectFrom EverandStructure and Functions of the Body: A Hand-Book of Anatomy and Physiology for Nurses and Others Desiring a Practical Knowledge of the SubjectNo ratings yet
- EOC Review Packet 2013Document25 pagesEOC Review Packet 2013Danielle WiltseNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument12 pagesCellsneelamNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Cells Revision LessonDocument44 pagesYear 9 Cells Revision LessonValeria L. GiliNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsDocument5 pagesCells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- EngageDocument2 pagesEngageLesNo ratings yet
- All Document Reader 1713202404640Document34 pagesAll Document Reader 1713202404640kanyangakapusu72No ratings yet
- Cell, Tissues, Glands, and Membranes BryDocument15 pagesCell, Tissues, Glands, and Membranes BryBrychyll SojorNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Summary Notes As BiologyDocument22 pagesUnit 1 Summary Notes As Biologyeyheth50% (2)
- Caveats To The Cell TheoryDocument9 pagesCaveats To The Cell Theorynevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Biology 2.1 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesIGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science: Biology 2.1 - Cell StructureIndah ParamithaNo ratings yet
- BIO Cell Structure Function UnChilled.8532Document9 pagesBIO Cell Structure Function UnChilled.8532Anna WrightNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its StructureDocument70 pagesCell and Its StructureEDLYN BRAZILNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDocument11 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Ocr Biology Unit f221 Revision Notes 1231102726226412 1Document14 pagesOcr Biology Unit f221 Revision Notes 1231102726226412 1Liam GalvinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cells (1.1) :: The Cell TheoryDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Cells (1.1) :: The Cell Theoryelvira sta.mariaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell ModificationsDocument62 pages1 Cell ModificationsJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Vacuoles and Vesicles Peroxisomes Centrosomes Cytoskeleton Nucleoid Nucleus Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Interphase 1Document14 pagesVacuoles and Vesicles Peroxisomes Centrosomes Cytoskeleton Nucleoid Nucleus Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Interphase 1cfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- (Cellular Structure and Its Functions) SHREYASI PDFDocument9 pages(Cellular Structure and Its Functions) SHREYASI PDFShreyasi Dongre100% (1)
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of Living OrganismsMai Hoa GranatiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Origin of CellsDocument9 pagesCell Division: Origin of CellselizabethNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument35 pagesCell Biology NotesShreyank TomarNo ratings yet
- Ib Biology Unit 1Document17 pagesIb Biology Unit 1Grace FanNo ratings yet
- 3 Reasons Why Cells Need To Divide: To Grow They Die Reproduce AsexuallyDocument4 pages3 Reasons Why Cells Need To Divide: To Grow They Die Reproduce AsexuallyElle Na nagaraNo ratings yet
- SPM Form 4Document23 pagesSPM Form 4tqahazliNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Test Study GuideDocument2 pagesCell Biology Test Study Guideapi-257190713100% (1)
- BIOLOGY 0610iDocument17 pagesBIOLOGY 0610imimoakal24No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 5 NotesSunali BhojwaniNo ratings yet
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocument4 pagesOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- CSEC Biology (4th Form) - Transport in Man (Circulatory System)Document106 pagesCSEC Biology (4th Form) - Transport in Man (Circulatory System)Russell HewittNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointDocument24 pagesCells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointJhyvril GulacNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Syllabus Points With Mark SchemeDocument29 pagesIB Biology Syllabus Points With Mark Schemeemy4147100% (3)
- 7A - Cells Summary Notes: Movement Respiration SensitivityDocument5 pages7A - Cells Summary Notes: Movement Respiration SensitivityThanusha DhanarajNo ratings yet
- Cell Types TissuesDocument26 pagesCell Types Tissueskurtandreinace04No ratings yet
- Notes On CellsDocument11 pagesNotes On Cellsritu_mishh9983No ratings yet
- Specialized TissueDocument83 pagesSpecialized TissueMaria Jeadelle PabloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument12 pagesLesson 2 - Cell Structures and Functionsc6h6o2tvtNo ratings yet
- Cell FunctionDocument43 pagesCell FunctionLi KimNo ratings yet
- Unit 7A Cells: The Body's Building Bricks: Name: .Document15 pagesUnit 7A Cells: The Body's Building Bricks: Name: .irene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- CELL Words (Compilation Got From Diff. Pages)Document14 pagesCELL Words (Compilation Got From Diff. Pages)ivoryshin daluroNo ratings yet
- Biology 10-12 FinalDocument106 pagesBiology 10-12 FinalAngel JereNo ratings yet
- 6 Science Midterm Resource MaterialllDocument11 pages6 Science Midterm Resource MaterialllKhalid TabasumNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCellular Structure and FunctiondonnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 A & P Check PointsDocument11 pagesChapter 1 A & P Check PointsRobin Wilfong89% (9)
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument15 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesCrystal Wong100% (14)
- Revision Flash Cards: © Pearson Education LTD 2008 This Document May Have Been Altered From The OriginalDocument4 pagesRevision Flash Cards: © Pearson Education LTD 2008 This Document May Have Been Altered From The OriginalAroop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8general ScienceUnits of MatterDocument8 pagesGrade 8general ScienceUnits of MatterPauline WaltersNo ratings yet
- b2 Revision Mind Maps - Sets 1-5Document33 pagesb2 Revision Mind Maps - Sets 1-5api-320022467No ratings yet
- Specialized CellsDocument29 pagesSpecialized CellsTrisha OxalesNo ratings yet
- Notes of Cell ChapterDocument15 pagesNotes of Cell ChapterSudha SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To BiologyManan SachdevaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Cell 2023Document36 pagesCH 2 Cell 2023mohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument31 pagesCELLSlynguyentbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Cell Sturucture)Document86 pagesChapter 1 (Cell Sturucture)faatin najihaNo ratings yet
- Class9-The Fundamental Unit of Life Long Answer QuestionsDocument8 pagesClass9-The Fundamental Unit of Life Long Answer QuestionsAnisha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Who Is Responsible and WhyDocument4 pagesWho Is Responsible and Whyradhika anand100% (2)
- Eukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 2 QP PDFDocument14 pagesEukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 2 QP PDFVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Document2 pagesCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Eukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 5 QPDocument13 pagesEukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 5 QPVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 3 QPDocument14 pagesEukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 3 QPVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- BG Assignment 1.1 and 1.2Document3 pagesBG Assignment 1.1 and 1.2Veer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument18 pagesHuman NutritionVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Human Gas ExchangeDocument9 pagesHuman Gas ExchangeVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Tuesday 21 May 2013 - Afternoon: As Gce BiologyDocument16 pagesTuesday 21 May 2013 - Afternoon: As Gce BiologyVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument19 pagesPlant NutritionVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument4 pagesRespirationVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument9 pagesExcretionVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- L As GCE Biology 2803 01 June 2008 InsertDocument2 pagesL As GCE Biology 2803 01 June 2008 InsertVeer Ramloghun100% (1)
- A GCE Biology 2805 04 January 2006 Question PaperDocument16 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 04 January 2006 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- As GCE Biology 2802 01 January 2008 InsertDocument2 pagesAs GCE Biology 2802 01 January 2008 InsertVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 04 June 2006 Question PaperDocument20 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 04 June 2006 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- AS Level GCE Biology Specimen Assessment Materials Unit F211 PDFDocument24 pagesAS Level GCE Biology Specimen Assessment Materials Unit F211 PDFVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2006 Question PaperDocument24 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2006 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Jan 06 P 1Document16 pagesJan 06 P 1ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- As GCE Biology 2803 01 January 2008 Question PaperDocument12 pagesAs GCE Biology 2803 01 January 2008 Question Paperramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- L A Level Biology 2805 04 Jun 2005 Question PaperDocument20 pagesL A Level Biology 2805 04 Jun 2005 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- L As GCE Biology 2801 June 2008 Question PaperDocument12 pagesL As GCE Biology 2801 June 2008 Question Paperramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- L As GCE Biology 2803 01 June 2008 InsertDocument2 pagesL As GCE Biology 2803 01 June 2008 InsertVeer Ramloghun100% (1)
- A GCE Biology 2806 01 January 2007 Question PaperDocument16 pagesA GCE Biology 2806 01 January 2007 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 01 January 2008 Question PaperDocument20 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 01 January 2008 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Jan 06 P 4Document20 pagesJan 06 P 4Veer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- As GCE Biology 2802 January 2007 Question PaperDocument12 pagesAs GCE Biology 2802 January 2007 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperDocument16 pagesA GCE Biology 2805 03 January 2008 Question PaperVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- A GCE Biology 2806 01 June 2006 InsertDocument2 pagesA GCE Biology 2806 01 June 2006 InsertVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- CnidariaDocument50 pagesCnidariacalvinleow1205No ratings yet
- HumanbodyDocument190 pagesHumanbodyapi-431347330No ratings yet
- Section A Look at The Picture. Rearrange The Words To Form Correct Sentences. (10 Marks)Document5 pagesSection A Look at The Picture. Rearrange The Words To Form Correct Sentences. (10 Marks)Hassan BachaNo ratings yet
- İNGİLİZCE 7 (501) - 1.dönem Soru Ve Cevapları - 2021: Yöneticilere Ve Emeği Geçenlere Teşekkür EderizDocument3 pagesİNGİLİZCE 7 (501) - 1.dönem Soru Ve Cevapları - 2021: Yöneticilere Ve Emeği Geçenlere Teşekkür EderizDybbukimNo ratings yet
- 4BI1 1BR Que 20190515Document32 pages4BI1 1BR Que 20190515crocusozan92% (12)
- Bermuda Harness Pony Racing 2022 New Years Day Holiday January ResultsDocument1 pageBermuda Harness Pony Racing 2022 New Years Day Holiday January ResultsBernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- Dhasal's Mumbai My Dear WhoreDocument18 pagesDhasal's Mumbai My Dear WhoreSantosh RathodNo ratings yet
- Katia Crochet MagazineDocument159 pagesKatia Crochet MagazineMaria Louisa Wessels100% (5)
- An Introduction To Animal Behavior: by Essam M. Abdelfattah BSC., MSC., PHDDocument62 pagesAn Introduction To Animal Behavior: by Essam M. Abdelfattah BSC., MSC., PHDDarartu muleta100% (1)
- 2019 Jellycat Catalogo1Document59 pages2019 Jellycat Catalogo1Cláudia100% (1)
- My Small and Large Intestines: © Teacher Created Resources, Inc. #211 My BodyDocument3 pagesMy Small and Large Intestines: © Teacher Created Resources, Inc. #211 My Bodyalana reneNo ratings yet
- Thy Neighbor's Wife Chap5Document7 pagesThy Neighbor's Wife Chap5Sammymac656No ratings yet
- International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma ResearchDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Researchtanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection Lab Report StudentDocument6 pagesFrog Dissection Lab Report StudentLester100% (2)
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaSheila Mae Escalante67% (3)
- Prioritization Problem Category JustificationDocument2 pagesPrioritization Problem Category JustificationRuth Lea Cabrera100% (1)
- Zoology PDFDocument734 pagesZoology PDFJames SoeNo ratings yet
- 20084222614756Document24 pages20084222614756masoodaeNo ratings yet
- Pink Notes in Legal Medicine (Complete)Document8 pagesPink Notes in Legal Medicine (Complete)Fruitie SyNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDocument29 pagesTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- Modern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsDocument77 pagesModern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsLavander BlushNo ratings yet
- Oap Ncii-Raise Organic Small RuminantsDocument72 pagesOap Ncii-Raise Organic Small RuminantsArlene LlacerNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Daily Language ActivitiesDocument31 pagesGrade 3 Daily Language ActivitiessaranNo ratings yet
- Training TestsDocument17 pagesTraining TestsВіка ГиманNo ratings yet
- D - Amico - Functional Occlusion of The Natural Teeth of ManDocument17 pagesD - Amico - Functional Occlusion of The Natural Teeth of ManMeidad ChassidNo ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocument15 pagesForest and Wildlife ResourcesNazia NaushinNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Living Things Study PresentationDocument26 pagesOrganisation of Living Things Study PresentationRUIZ CANO EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Inguinal HerniaDocument19 pagesInguinal HerniaArdham ChesukoruNo ratings yet
- Afropop DiscographyDocument4 pagesAfropop DiscographyThe Neverending Story100% (2)
- University of Chicago Press Fall 2009 CatalogueFrom EverandUniversity of Chicago Press Fall 2009 CatalogueRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- University of Chicago Press Fall 2009 Distributed TitlesFrom EverandUniversity of Chicago Press Fall 2009 Distributed TitlesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)