Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid-Fluid/Solid Reactions (Non Catalytic)
Uploaded by
Mehul VarshneyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid-Fluid/Solid Reactions (Non Catalytic)
Uploaded by
Mehul VarshneyCopyright:
Available Formats
L 40: Fluid- Fluid/Solid Reactions (Non catalytic)
Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Delhi. kkpant@chemical.iitd.ac.in
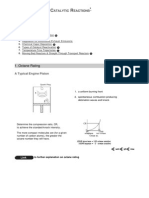
General rate expression
The absorption of A from gas is larger when reaction occurs within the liquid film than for straight mass transfer. Thus for the same concentrations at the two boundaries of the liquid film we have
E >1
Can be correlated with HATTA MODULUS/ NUMBER (MH)
Role of the Hatta Number, MH
To identify whether reaction is fast or slow, we focus on unit surface of gas-liquid interface, assume that gas-phase resistance is negligible, and we define a film conversion parameter
If MH >>1, all reaction occurs in the film, and surface area is the controlling rate factor. On the other hand, if MH <<1 no reaction occurs in the film, and bulk volume becomes the controlling rate factor. More precisely, it has been found that:
From Fig. 23.4, for
MH >1000
The enhancement factor for fluid-fluid reactions as a function of MH and Ei modified from the numerical solution of van Krevelens and Hoftijzer
To find the rate from the general expression, first evaluate Ei and MH. : 1. If MH > 2, reaction occurs in the film and we have Cases A, B, C,
D. Instantaneous rexn to fast reaction (CB) 2. If 0.02 < MH < 2, we then have the intermediate Cases E, F, G. 3. If MH < 0.02, we have the infinitely slow reaction of Case H.
(a) locate the resistance to reaction (what % is in the gas film, in the liquid film, in the main body of liquid) (b) locate the reaction zone (c) determine the behavior in the liquid film (whether pseudo first-order reaction, instantaneous, physical transport, etc.) (d) calculate the rate of reaction (mol/m3 hr)
For the special case of negligible gas-phase resistance, for example, if pure reactant is used, A in the gas phase, (kAg>high) then
= KAl CAi E , E = x0/x
Case C: Fast Reaction; Low CB The plane of reaction for case A now spreads into a zone of reaction in which A and B are both present. However, reaction is fast enough so that this reaction zone remains totally within the liquid film. Thus, no A enters the main body of liquid to react there. Since the last resistance term in the general rate equation, (I/k fl )is negligible (large k), the rate form for this case is
Case G: Slow Reaction with Respect to Mass Transfer. all
reaction occurs in the main body of the liquid; however, the film still provides a resistance to the transfer of A into the main body of liquid. Thus, three resistances enter into the rate expression, Thus
Case H: Infinitely Slow Reaction.
Factors to Consider in Selecting a Contactor (a) Contacting pattern.
Towers approximate plug G plug L. Bubble tanks approximate plug G / mixed L. Agitated tanks approximate mixed G / mixed L. Towers have the largest mass transfer driving force and in this respect have an advantage over tanks. Agitated tanks have the smallest driving force. (b) kg and kL. For liquid droplets in gas kg is high, kL, is low. For gas bubbles rising in liquid, kg is low, kL is high. (c) If the resistance is in the gas and or liquid films : Use a large interfacial
area "a," thus most agitated contactors and most columns. If the L film
dominates, stay away from spray contactors. If the G film dominates stay away from bubble contactors.
10
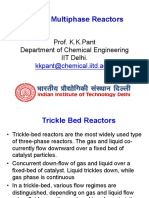
Fluid Solid non catalytic Reactions
You might also like
- Cre Ii - 39Document28 pagesCre Ii - 39Mehul Varshney100% (1)
- Multiphase Reactors: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument49 pagesMultiphase Reactors: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiBikashGuptaNo ratings yet
- CREII-Module-5 - Lecture 20 & 21 PDFDocument23 pagesCREII-Module-5 - Lecture 20 & 21 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- CRE - Fluid-Fluid ReactionDocument43 pagesCRE - Fluid-Fluid Reactionandono kusuma jatiNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Fluid Reactions (Non Catalytic)Document22 pagesFluid-Fluid Reactions (Non Catalytic)BikashGuptaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Cre Ii L24-26Document32 pages2019 Cre Ii L24-26Aman PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor Design: 7 Sem, B.Tech. Chemical EnggDocument14 pagesChemical Reactor Design: 7 Sem, B.Tech. Chemical EnggMohammad Ajaz DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Bypassing Inefficient Mixing Presence of Dead Zones: Reactor Design & OperationDocument31 pagesBypassing Inefficient Mixing Presence of Dead Zones: Reactor Design & OperationChem-Youth FestNo ratings yet
- Fluid Fluid Reaction Kinetics Lecture Notes IncompleteDocument49 pagesFluid Fluid Reaction Kinetics Lecture Notes IncompleteAliRashid0% (1)
- Chemical Reactor Design: 7 Sem, B.Tech. Chemical EnggDocument20 pagesChemical Reactor Design: 7 Sem, B.Tech. Chemical EnggMohammad Ajaz DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document8 pagesTutorial 2Ng JoshuaNo ratings yet
- CRE-II - Chapter-04 Fluid-Particle Systems - HKB 2.10.18Document42 pagesCRE-II - Chapter-04 Fluid-Particle Systems - HKB 2.10.18Ananya DaveNo ratings yet
- Fluid Fluid Reaction KineticsDocument27 pagesFluid Fluid Reaction KineticsIlyas AzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18: Reactions at Solid SurfacesDocument12 pagesLecture 18: Reactions at Solid SurfacesGanesh Chandra BaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Review SolutionsDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Review SolutionshelloblargNo ratings yet
- N THE Name OF Llah THE Most Gracious Ever MercifulDocument43 pagesN THE Name OF Llah THE Most Gracious Ever MercifulSabeeh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Concentration Distributions in Different Phases at LaminarDocument23 pagesConcentration Distributions in Different Phases at LaminarHayder HusseinNo ratings yet
- Concentration Distributions in Different Phases at LaminarDocument23 pagesConcentration Distributions in Different Phases at LaminarHayder HusseinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1NoranierahNohoNo ratings yet
- Isothermal Kinetics in Solids - 1ADocument30 pagesIsothermal Kinetics in Solids - 1AGil RolunaNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer (Topic 2)Document23 pagesMass Transfer (Topic 2)Siswand BIn Mohd Ali0% (1)
- St. Joseph's College of Engineering Chemical Engineering: Ai A Bi BDocument2 pagesSt. Joseph's College of Engineering Chemical Engineering: Ai A Bi BThirunavuk KarasuNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Reactors: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Delhi. Kkpant@chemical - Iitd.ac - inDocument17 pagesMultiphase Reactors: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Delhi. Kkpant@chemical - Iitd.ac - inMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Chbe550 LHHW ModelDocument5 pagesChbe550 LHHW ModelGuhan ChendurnathanNo ratings yet
- (BEN-AVRAHAM Et Al., 1990) Saturation Transition in A Monomer-Monomer Model of Heterogeneous CatalysisDocument17 pages(BEN-AVRAHAM Et Al., 1990) Saturation Transition in A Monomer-Monomer Model of Heterogeneous CatalysisfernandadezideiroNo ratings yet
- TRK 16.2Document23 pagesTRK 16.2adoxaNo ratings yet
- 10 Text & ExamplsDocument46 pages10 Text & ExamplstarhuniNo ratings yet
- S17 2170501 CreDocument3 pagesS17 2170501 CremorganNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph'S College of EngineeringDocument5 pagesSt. Joseph'S College of EngineeringThirunavuk KarasuNo ratings yet
- 9.1 - Gas-Liquid and Gas-Liquid-Solid ReactionsDocument100 pages9.1 - Gas-Liquid and Gas-Liquid-Solid ReactionsHendriyana StNo ratings yet
- Design of Absorber With ReactionDocument23 pagesDesign of Absorber With ReactionMALIK ZARYABBABARNo ratings yet
- Lectures 6 PDFDocument6 pagesLectures 6 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Mass Transfer Coefficients: Assignment ProblemsDocument3 pagesModule 3: Mass Transfer Coefficients: Assignment ProblemsShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04Document2 pagesAssignment 04Rashmi SahooNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 09Document2 pagesProblem Sheet 09Rashmi SahooNo ratings yet
- CREII-Module-I - Lecture 4 PDFDocument34 pagesCREII-Module-I - Lecture 4 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Absorption Chemical ReactionDocument5 pagesAbsorption Chemical ReactionSundar SkNo ratings yet
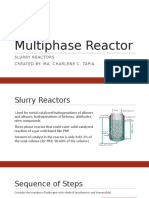
- Multiphase ReactorDocument37 pagesMultiphase ReactorMaria Charlene Caraos TapiaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Mass Transfer2Document24 pages11 - Mass Transfer2sanelisofuturemoyoNo ratings yet
- Two Film TheoryDocument25 pagesTwo Film TheoryamirulNo ratings yet
- Slurry Reactors: A Powerpoint Presentation OnDocument25 pagesSlurry Reactors: A Powerpoint Presentation OnKanchan NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Ester Hydrolysis Reactions in A Chromatographic Reactor Using Equilibrium Theory and A Rate ModelDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Ester Hydrolysis Reactions in A Chromatographic Reactor Using Equilibrium Theory and A Rate ModelCarlos Andrés Martínez CristanchoNo ratings yet
- 5 Gas TransferDocument78 pages5 Gas TransferselamitspNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document111 pagesUnit 4Hariharan MothilalNo ratings yet
- CREII-Module-I - Lecture 3 PDFDocument27 pagesCREII-Module-I - Lecture 3 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- CRE - Fluid-Particle ReactionDocument42 pagesCRE - Fluid-Particle Reactionandono kusuma jatiNo ratings yet
- Document 1 2Document14 pagesDocument 1 2karem ahmedNo ratings yet
- Convective and Interphase Mass Transfer (Exam)Document2 pagesConvective and Interphase Mass Transfer (Exam)Dozdi100% (1)
- Introduction & Overview To Chemical Reaction Engineering IIDocument12 pagesIntroduction & Overview To Chemical Reaction Engineering IIshubhamNo ratings yet
- Turbulent Mixing and Chemical Reaction in Stirred Tanks: André Bakker Julian B. FasanoDocument9 pagesTurbulent Mixing and Chemical Reaction in Stirred Tanks: André Bakker Julian B. FasanozadghaffariNo ratings yet
- Mass BalanceDocument17 pagesMass BalanceKimal WasalathilakeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Yi Hong LowNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Part - 2Document29 pagesChemical Kinetics Part - 2smi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Reactor (Trickle Bed Reactor)Document20 pagesMultiphase Reactor (Trickle Bed Reactor)BikashGuptaNo ratings yet
- Ion Association in Proton Transfer Reactions: Use of ESR for the Quantitative Determination of Gas Phase Atom and Radical ConcentrationsFrom EverandIon Association in Proton Transfer Reactions: Use of ESR for the Quantitative Determination of Gas Phase Atom and Radical ConcentrationsNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentFrom EverandPhysico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Applied Colloid and Surface ChemistryFrom EverandIntroduction to Applied Colloid and Surface ChemistryNo ratings yet
- L16 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument25 pagesL16 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Hul 234HUL234Document5 pagesHul 234HUL234Mehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE L18 Catalyst DeactivationDocument25 pagesCRE L18 Catalyst DeactivationMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE L19 Catalyst DeactivationDocument18 pagesCRE L19 Catalyst DeactivationMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- L - 17 Catalyst Deactivation: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument23 pagesL - 17 Catalyst Deactivation: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- The Partial Oxidation of Methane To Syngas in A Palladium Membrane Reactor: Simulation and Experimental StudiesDocument11 pagesThe Partial Oxidation of Methane To Syngas in A Palladium Membrane Reactor: Simulation and Experimental StudiesMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L6: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument19 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L6: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- L - 21 External Mass Transfer Effects: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument57 pagesL - 21 External Mass Transfer Effects: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- L15 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument15 pagesL15 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L8: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument32 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L8: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Cre Ii L9Document21 pagesCre Ii L9Mehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Reactors: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Delhi. Kkpant@chemical - Iitd.ac - inDocument17 pagesMultiphase Reactors: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Delhi. Kkpant@chemical - Iitd.ac - inMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- L14 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument50 pagesL14 CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L7: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument18 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L7: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Fluid/Solid Reactions (Non Catalytic)Document21 pagesFluid/Solid Reactions (Non Catalytic)Mehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L4: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument26 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L4: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument56 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L10: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument13 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L10: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L11: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument17 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L11: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument42 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul Varshney100% (1)
- Fluid - Fluid Non Catalytic ReactionsDocument12 pagesFluid - Fluid Non Catalytic ReactionsMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Cre Ii - 42Document14 pagesCre Ii - 42Mehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- CRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L3: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument14 pagesCRE II Heterogeneous Catalysis L3: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Reactors: Design Approach: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument22 pagesMultiphase Reactors: Design Approach: Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Cre Ii - 33 - 34Document37 pagesCre Ii - 33 - 34Mehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Cre Ii - 33 - 34Document37 pagesCre Ii - 33 - 34Mehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument11 pagesProf. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Prof. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiDocument11 pagesProf. K.K.Pant Department of Chemical Engineering IIT DelhiMehul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module For Remidial ClassDocument52 pagesChemistry Module For Remidial ClassMuktaar HassenNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 7 (7.1) and CalorimeterDocument5 pagesTOPIC 7 (7.1) and CalorimetersumathiNo ratings yet
- Thermo Electron North America LLC Lot 1 Equipment & InstrumentsDocument66 pagesThermo Electron North America LLC Lot 1 Equipment & Instrumentsproyectos serimetcNo ratings yet
- SMK Simanggang: Physics SPM Analysis Table (By Topic)Document4 pagesSMK Simanggang: Physics SPM Analysis Table (By Topic)safrahjNo ratings yet
- StandardizationDocument18 pagesStandardizationCHEA MICH L. ABELLANONo ratings yet
- PH Impact On The Sol Gel Preparation of Calcium Hydroxyapatite Ca10 Po4 6 Oh 2 Using A Novel Complexing Agent Dcta PDFDocument8 pagesPH Impact On The Sol Gel Preparation of Calcium Hydroxyapatite Ca10 Po4 6 Oh 2 Using A Novel Complexing Agent Dcta PDFfishvalNo ratings yet
- BlowersDocument58 pagesBlowersmahmad61100% (1)
- Design, Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Powered by Solar Using NanofluidDocument5 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Powered by Solar Using NanofluidchilakaprakashNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Wave Behavior: Marquez Heron Dondre SaveryDocument10 pagesPresentation On Wave Behavior: Marquez Heron Dondre SaveryMARQUEZ HERONNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 PPT IrDocument21 pagesUnit 13 PPT Irapi-237496924No ratings yet
- Vol 31 PhotochemistryDocument69 pagesVol 31 PhotochemistryRicardo Gamboa CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - SolutionsDocument13 pagesLesson 8 - SolutionsscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Health, Safety and Environment (Hse) CGE653 Assignment: Fire and Explosion PO5, CO2, C4Document4 pagesHealth, Safety and Environment (Hse) CGE653 Assignment: Fire and Explosion PO5, CO2, C4LouisNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations 1: List of Books Information of CrystallizationDocument13 pagesMass Transfer Operations 1: List of Books Information of CrystallizationZaid MansuriNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension With The Ring Method (Du Nouy Method) : (Item No.: P2140500)Document6 pagesSurface Tension With The Ring Method (Du Nouy Method) : (Item No.: P2140500)Eduard VanegasNo ratings yet
- From Mark-Houwink Equation,: ViscometryDocument24 pagesFrom Mark-Houwink Equation,: ViscometryAnushka SunamNo ratings yet
- PP ManualDocument50 pagesPP ManualMohammad RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab 1Document4 pagesChemistry Lab 1Call Mi BlacksNo ratings yet
- Nature Comm - 41467 - 2018 - 4699 - MOESM1 - ESMDocument14 pagesNature Comm - 41467 - 2018 - 4699 - MOESM1 - ESMdupuytrenNo ratings yet
- Investigations On Heterogenously Catalysed Condensations of Glycerol To Cyclic Acetals PDFDocument8 pagesInvestigations On Heterogenously Catalysed Condensations of Glycerol To Cyclic Acetals PDFFahmi rezaNo ratings yet
- Metastable IonsDocument10 pagesMetastable IonsKavya ENo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Coordination ChemistryDocument818 pagesComprehensive Coordination Chemistryrace egrNo ratings yet
- M.tech. Textile TechnologyDocument26 pagesM.tech. Textile TechnologyNilesh Shingote100% (1)
- A Comprehensive Review of Latent Heat Energy Storage For Various Applications: An Alternate To Store Solar Thermal EnergyDocument38 pagesA Comprehensive Review of Latent Heat Energy Storage For Various Applications: An Alternate To Store Solar Thermal EnergyPranav OmkarNo ratings yet
- Castrol Alphasyn EP 220Document2 pagesCastrol Alphasyn EP 220Vusal HasanovNo ratings yet
- PDF PDFDocument107 pagesPDF PDFCar MelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction & Fick's LawDocument19 pagesChapter 1 Introduction & Fick's LawRenu SekaranNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet Air Conditioning (Perfect Gas)Document8 pagesLab Sheet Air Conditioning (Perfect Gas)JIJENDERKUMAR A/L VIJAYAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Corrosion and Corrosion ControlDocument49 pagesUnit - Ii Corrosion and Corrosion ControlBavikati Vira Siva KumariNo ratings yet
- All Isotonic CalculationDocument21 pagesAll Isotonic CalculationRajuNo ratings yet