Professional Documents
Culture Documents
f1 Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Suei Suhaniez SuriyatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
f1 Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Suei Suhaniez SuriyatCopyright:
Available Formats
BM Version
Forward
Exit
Chapter 1 : Introduction to Science
1.1 What is Science? What is science? Importance of science Career in science 1.2 A Science Laboratory Common laboratory apparatus Safety hazards 1.3 The Steps in a Scientific Investigation The steps in a scientific investigation 1.4 Physical Quantities and Their Units Physical quantities and their units
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Chapter 1 : Introduction to Science
1.5 Weight and Mass Weight Mass 1.6 Measuring Tools Measuring length Measuring area Measuring volume 1.7 The Importance of Standard Units The importance of standard units
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
1.1 What is Science?
Science is the systematic study of nature and how it affects us and our environment Science covers a broad field of knowledge that deals with observed facts and the relationship among those facts
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.1 What is Science?
Importance of science
Improve our standard of living Improve the quality of the environment Understand the world around us Increase food supply Prevention and treatment of diseases
Continue
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
1.1 What is Science?
Career in science
Doctor Architect Engineer Astronaut Veterinarian Pharmacist Chemist Computer programmer
Continue
Areas of science are biology, physics, chemistry, astronomy, geology, meteorology and biochemistry
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
1.2 A Science Laboratory
Common laboratory apparatus
Apparatus Crucible Test tube Stopwatch Caliper Uses Heating chemicals
Used to contain chemicals
To measure time
To measure diameters
Thermometer To measure temperature
Continue
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.2 A Science Laboratory
Common laboratory apparatus
Apparatus Uses Evaporating liquid from a solution
Evaporating dish
Cork and rubber Use as a stopper for test tubes or conical flasks stopper Hold specimen for observation Glass slide under a microscope Test tube holder Hold test tubes
Syringe Transfer small quantities of liquids
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.2 A Science Laboratory
Safety hazards
Corrosive
Radioactive
Toxic/poisonous
Harmful/irritant
Explosive
BM Version
Highly flammable
Menu Exit
Previous Forward
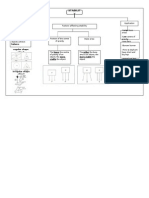
1.3 The Steps in a Scientific Investigation
Determine what to find out Analysing the data that has been collected Form a hypothesis Plan a systematic experiment for the hypothesis
Write down the data that has been observed
Making conclusion to decide whether the data is true or not
BM Version
Controlling of variables
Interpreting the data
Write a report on the scientific investigation
Menu Exit
Previous Forward
1.4 Physical Quantities and Their Units
A physical quantity is a quantity that can be measured Physical quantity SI unit Length () metre (m) Mass (m) kilogram (kg) Time (t) Temperature (T) second (s) kelvin (K) Instrument Metre rule Lever/beam balance Stopwatch Thermometer Ammeter
Menu Exit
Electric current (I) ampere (A)
BM Version
Previous Forward
1.4 Physical Quantities and Their Units
Prefix giga mega kilo centi milli micro nano pico Symbol G M k c m n p
BM Version
Value 1 000 000 000 1 000 000 1 000 0.01 0.001 0.000 001 0.000 000 001 0.000 000 000 001
Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.5 Weight and Mass
Weight
The pull of the Earth on an object The force that pulls the body towards the centre of the Earth is called gravitational force SI unit is Newton (N) The weight of an object is not always the same
Continue
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
Type of tools for measuring weight
A spring balance
BM Version
A compression balance
Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.5 Weight and Mass
Mass
The quantity of matter in an object The mass of an object is constant and not affected by gravitational forces SI unit is kilogram (kg) The mass of an object does not change
Continue
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
Type of tools for measuring mass
A beam balance
A lever balance
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.6 Measuring Tools
Measuring length
Length is the distance between two points Its SI unit is the metre (m) Other units that can be used for length are kilometre (km), centimetre (cm) and millimetre (mm) The relationship between the units of length 1 cm = 10 mm 1 m = 100 cm = 1 000 mm 1 km = 1 000 m = 100 000 cm
Continue
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.6 Measuring Tools
Measuring the length of a straight line
Correct
Measuring the length of a curve
Continue
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
1.6 Measuring Tools
Measuring the external diameter
Measuring the internal diameter
BM Version
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
1.6 Measuring Tools
Measuring area
Area is a measure of the amount of a surface. Its SI unit is square metres (m2) The area of regular and irregular shapes can be estimated by tracing the shapes onto a piece of graph paper
BM Version
Estimating the area of a leaf
Previous Forward
Menu
Exit
1.6 Measuring Tools
Measuring volume
R
S
S is the correct eye position
Volume is a measure of the space occupied by a substances Its SI unit is cubic metres (m3) Tools for measuring volume of liquid are measuring cylinder, burette and pipette
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
1.7 The Importance of Standard Units
Makes it easier for people from different countries to communicate with each other A measurement in that unit has the same value anywhere in the world
BM Version Previous Forward Menu Exit
THE END
Versi BI
Keluar
Bab 1 : Pengenalan kepada Sains
1.1 Apakah itu Sains? Apakah itu sains? Kepentingan sains Kerjaya dalam sains 1.2 Makmal Sains Alat radas makmal Simbol berbahaya 1.3 Langkah-langkah dalam Penyiasatan Saintifik Langkah-langkah dalam penyiasatan saintifik 1.4 Kuantiti Fizik dan Unitnya Kuantiti fizik dan unitnya
Versi BI Keluar
Bab 1 : Pengenalan kepada Sains
1.5 Berat dan Jisim Berat Jisim 1.6 Alatan Pengukuran Mengukur panjang Mengukur luas Mengukur isipadu 1.7 Kepentingan Unit Piawai The importance of standard units
Versi BI
Keluar
1.1 Apakah itu Sains?
Sains adalah susunan pembelajaran ke atas alam sekeliling dan bagaimana kesannya kepada kita dan persekitaran Sains meliputi pelbagai bidang ilmu pengetahuan
Versi BI
Keluar
1.1 Apakah itu Sains?
Kepentingan sains
Meningkatkan taraf kehidupan Meningkatkan kualiti persekitaran Memahami dunia di sekeliling kita Menambahkan bekalan makanan Mencegah dan merawat penyakit
Versi BI
Keluar
Versi BI
Keluar
1.1 Apakah itu Sains?
Kerjaya dalam sains
Cabang dalam sains Doktor adalah seperti biologi, Arkitek fizik, kimia, astronomi, Jurutera geologi, meteorologi dan biokimia Ahli astronomi Doktor haiwan Ahli farmasi Ahli kimai Pakar komputer
Versi BI Keluar
Versi BI
Keluar
1.2 Makmal Sains
Alat radas makmal
Alat radas Kegunaan Memanaskan bahan kimia
Mangkuk pijar
Tabung uji Jam randik Kaliper Termometer
Mengisi bahan kimia
Mengambil bacaan
Mengukur diameter
Mengukur suhu
Versi BI Keluar
1.2 Makmal Sains
Alat radas makmal
Alat radas Makmal Menyejat cecair daripada suatu larutan Digunakan sebagai penutup tabung uji atau kelalang kon
Mangkuk penyejat Gabus dan penutup getap
Slaid kaca
Memegang spesimen untuk pemerhatian di bawah mikroskop
Memegang tabung uji Memindahkan sedikit cecair
Versi BI Keluar
Pemegang tabung uji Picagari
1.2 Makmal Sains
Simbol berbahaya
Mengakis
Beradioaktif
Beracun
Merangsang Mudah meletup Mudah terbakar
Versi BI Keluar
1.3 Langkah-langkah dalam Penyiasatan Saintifik
Menentukan tujuan eksperimen Membentuk
hipotesis
Merancang eksperimen secara sistematik
Menganalisis data yang telah dikumpul
Merekod data yang diperhatikan Membuat kesimpulan
Mengawal pembolehubah
Menginterpretasi data
Menulis laporan
Versi BI Keluar
sama
1.4 Kuantiti Fizik dan Unitnya
Kuantiti fizik adalah kuantiti yang boleh diukur Kuantiti fizik Panjang () Pembaris Jisim (m) Masa (t) Suhu (T) Arus elektrik (I) Unit SI Peralatan meter (m) kilogram (kg) Neraca tuas saat (s) kelvin (K) ampere (A) Jam randik Termometer Ammeter
Versi BI Keluar
1.4 Kuantiti Fizik dan Unitnya
Imbuhan awal giga mega kilo senti mili mikro nano piko Simbol G M k c m n p Nilai 1 000 000 000 1 000 000 1 000 0.01 0.001 0.000 001 0.000 000 001 0.000 000 000 001
Versi BI Exit
1.5 Berat dan Jisim
Berat
Tarikan Bumi ke atas objek Daya yang menarid jasad ke arah pusat Bumi dikenali sebagai daya graviti Unit SI adalah Newton (N) Berat sesuatu objek tidak selalunya sama
Versi BI
Keluar
Jenis alat untuk mengukur berat
Neraca spring
Neraca pemampat
Versi BI
Keluar
1.5 Berat dan Jisim
Jisim
Kuantiti jirim dalam sesuatu objek Jisim objek adalah tetap dan tidak dipengaruhi oleh daya graviti Unit SI adalah kilogram (kg) Jisim sesuatu objek adalah tidak berubah
Versi BI
Keluar
Jenis alat untuk mengukur jisim
Neraca palang
Neraca tuas
Versi BI Keluar
1.6 Alatan Pengukuran
Mengukur panjang
Panjang adalah jarak di antara dua titik Unit Sinya adalah meter (m) Unit lain yang boleh digunakan untuk panjang adalah kilometer (km), sentimeter (cm) and milimeter (mm) Hubungan antara unit-unit sukatan panjang 1 cm = 10 mm 1 m = 100 cm = 1 000 mm 1 km = 1 000 m = 100 000 cm
Versi BI Keluar
1.6 Alatan Pengukuran
Mengukur panjang garisan lurus
Mengukur panjang garisan melengkung
Versi BI
Keluar
Mengukur diameter luar
Mengukur diameter dalam
Versi BI
Keluar
1.6 Alatan Pengukuran
Mengukur luas
Luas adalah ukuran jumlah permukaan. Unit Sinya adalah meter persegi (m2) Luas objek sekata dan objek tidak sekata boleh ditentukan dengan melakar bentuk objek di atas sekeping kertas graf
Menganggar luas daun
Versi BI
Keluar
1.6 Alatan Pengukuran
Mengukur isipadu
R
S
Isipadu adalah ukuran yang memenuhi ruang oleh bahan terlarut Unit SInya adalah meter padu (m3) Alatan untuk mengukur isipadu cecair adalah silinder penyukat, buret and pipet
T S adalah kedudukan mata yang betul
Versi BI
Keluar
1.7 Kepentingan Unit Piawai
Memudahkan orang ramai dari negara yang berlainan berkomunikasi Unit pengukurannya adalah sama di mana-mana tempat di dunia
Versi BI
Keluar
tAMAT
You might also like
- Bab 1 Pengenalan Kepada SainsDocument50 pagesBab 1 Pengenalan Kepada SainsmikhaeluzairNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Pengenalan Kepada SainsDocument50 pagesBab 1 Pengenalan Kepada SainsEila AriffinNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 1Document50 pagesf1 Chapter 1dweomer2005No ratings yet
- Introduction to Science EssentialsDocument50 pagesIntroduction to Science Essentialsfadzlin84100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Introduction To ScienceDocument53 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To ScienceSumi VjNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document20 pagesChap 1Nor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeDocument51 pages1.1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeTee Qi ENNo ratings yet
- JURNAL PRAKTIKUM FISIKA DASAR 1: DASAR-DASAR PENGUKURANDocument48 pagesJURNAL PRAKTIKUM FISIKA DASAR 1: DASAR-DASAR PENGUKURANNur MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeDocument57 pages1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeGunalan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- FinallDocument21 pagesFinallNovitiaa LatifaahNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Fisika Geografi Alat Ukur DasarDocument16 pagesLaporan Praktikum Fisika Geografi Alat Ukur DasarAnonymous grrnqvrXNNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS PRACTICUM MEASUREMENT - Iwan M Simbolon - 4223111066 - MESP 2022Document18 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS PRACTICUM MEASUREMENT - Iwan M Simbolon - 4223111066 - MESP 2022Iwan Martua SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Measurement and UnitsDocument10 pagesMeasurement and UnitsHanan MdSomNo ratings yet
- Physics G7 Week 1 B1 Ch.13 MeasurementsDocument32 pagesPhysics G7 Week 1 B1 Ch.13 MeasurementsAyesha DuaNo ratings yet
- Fisbing - Tugas - 3Document18 pagesFisbing - Tugas - 3ummysalmahNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Units LectureDocument57 pagesIntroduction to Units LectureUpal PramanickNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesLab Report 1 PhysicsAzam Aziz100% (3)
- Pengenalan Kepada SainsDocument112 pagesPengenalan Kepada SainsJalilah TaibNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeDocument54 pages1.1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeTee Qi EN0% (1)
- Form 1 C1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeDocument1 pageForm 1 C1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeYuhannNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Module Quarter IIDocument69 pagesGrade 7 Module Quarter IIJoeyGansan100% (1)
- Revisi - Nur Mutmainnah - Kimia - ADocument49 pagesRevisi - Nur Mutmainnah - Kimia - ANur MutmainnahNo ratings yet
- Use The DiagramDocument11 pagesUse The DiagramyokekeannNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeNur AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Basic Masurment and UncertainlyDocument29 pagesBasic Masurment and UncertainlyHelny LydarisboNo ratings yet
- Physics For Nurses CON PIMSDocument89 pagesPhysics For Nurses CON PIMSBheru Lal100% (1)
- Measurement of Length Mass Volume DensitDocument21 pagesMeasurement of Length Mass Volume DensitIvan Jeremy AbilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MeasurementsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 MeasurementsChristian Guimmayen ArizoNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Science f1Document50 pagesPowerpoint Science f1amirahNo ratings yet
- Measuring Physical QuantitiesDocument4 pagesMeasuring Physical Quantitiesdishore312No ratings yet
- PengukuranDocument22 pagesPengukuranAnnisa NoerfadillahNo ratings yet
- Measurements: Units of MeasurementDocument29 pagesMeasurements: Units of MeasurementannisaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY IntroDocument76 pagesCHEMISTRY IntroLeanneNo ratings yet
- Lab Report I, Practical Work I A01654147 Samantha Monserrat Hernandez HerreraDocument8 pagesLab Report I, Practical Work I A01654147 Samantha Monserrat Hernandez HerreraSamantha Monserrat Hernández HerreraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Science Chapter 1Document56 pagesIntroduction to Science Chapter 1Halizah Ramthan88% (16)
- DressmaingDocument74 pagesDressmaingJexylon Tenedero0% (1)
- Lab Techniques Experiment 1Document2 pagesLab Techniques Experiment 1Jayson RiveraNo ratings yet
- Measurement TechniqueDocument27 pagesMeasurement TechniquejidopawNo ratings yet
- Physics_Book-1Document31 pagesPhysics_Book-1Abel Wisimaji MsiskaNo ratings yet
- Measurement & Significant FiguresDocument65 pagesMeasurement & Significant FiguresJim Marco100% (1)
- Science Form1 Chapter 1Document41 pagesScience Form1 Chapter 1Che Norasiykin89% (9)
- Quetions and Answers First TermDocument4 pagesQuetions and Answers First TermXaik Ziya Ash NeeNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Bab 1Document23 pagesScience Form 1 Bab 1Nurul Aqilah80% (10)
- Lembar Kerja Siswa Praktikum Fisika TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/2018Document4 pagesLembar Kerja Siswa Praktikum Fisika TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/2018PayudiNo ratings yet
- Mtp7 0501 q2 FPFDocument29 pagesMtp7 0501 q2 FPFMarvin GatilaNo ratings yet
- Daily Science Lesson Plan Form 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesDaily Science Lesson Plan Form 1 IntroductionSahrulRashidNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 1 KSSMDocument226 pagesF1 Chapter 1 KSSMnorhmsNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument40 pagesChap 1 Introduction To ScienceSyazwana ElleasNo ratings yet
- MODULES-IN-PHYSICAL-SCIENCE WithnyouuuDocument10 pagesMODULES-IN-PHYSICAL-SCIENCE WithnyouuuHesoyam HesoyamNo ratings yet
- Physical MeasurementDocument27 pagesPhysical Measurementmohamady.sciNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Statistical Tasks 1Document8 pagesMeasurement and Statistical Tasks 1Agum GhifariNo ratings yet
- SFL3011 Physic Laboratory Report Experiment 1Document13 pagesSFL3011 Physic Laboratory Report Experiment 1Liyana Hamdan85% (13)
- Phys 1011 Module AAUDocument388 pagesPhys 1011 Module AAUDaniel100% (1)
- GP1 Q1 W1 SLK1 Units and MeasurementsDocument32 pagesGP1 Q1 W1 SLK1 Units and MeasurementsJC VillartaNo ratings yet
- Form 1: Mass /jisimDocument1 pageForm 1: Mass /jisimSiti NabilahNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument5 pagesMeasurementssana.incubationNo ratings yet
- LEARNING MODULE 1 Introduction To PhysicsDocument12 pagesLEARNING MODULE 1 Introduction To PhysicsanthonneacNo ratings yet
- Step in A Scientific InvestigationDocument11 pagesStep in A Scientific InvestigationNick LeeNo ratings yet
- Forecast Verification: A Practitioner's Guide in Atmospheric ScienceFrom EverandForecast Verification: A Practitioner's Guide in Atmospheric ScienceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Composition Properties Respiration Combustion Pollution Importance AirDocument62 pagesComposition Properties Respiration Combustion Pollution Importance AirSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Subheading Goes HereDocument2 pagesPresentation Title: Subheading Goes HereSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 HeatDocument12 pagesChapter 7 Heatnaza977583% (6)
- BM Version: Exit ForwardDocument64 pagesBM Version: Exit ForwardSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Science Exercises Form 1 140104032809 Phpapp02Document7 pagesScience Exercises Form 1 140104032809 Phpapp02jecjocNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 1)Document4 pagesSains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 1)JeyShidaNo ratings yet
- T1 Bab 5Document6 pagesT1 Bab 5Nurulqaseh WafiNo ratings yet
- Ujian Sains Tingkatan 1Document14 pagesUjian Sains Tingkatan 1SITI ZAIDAH AHMAD64% (11)
- f1 Chapter 1Document50 pagesf1 Chapter 1Suei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Classifying Matter and Separating MixturesDocument3 pagesClassifying Matter and Separating MixturesSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Stability and BalanceDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Stability and BalanceSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 3Document48 pagesf1 Chapter 3Suei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 1)Document4 pagesSains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 1)JeyShidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Ting2Document9 pagesRancangan Tahunan Sains Ting2Suei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 3 3.1 What Is Matter?: Electricity Gas Weight Sound Water Mass Light Space SugarDocument7 pagesRevision Chapter 3 3.1 What Is Matter?: Electricity Gas Weight Sound Water Mass Light Space SugarSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 PendulumDocument2 pagesChap 1 PendulumSuei Suhaniez SuriyatNo ratings yet