Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Look-Up Table: Solving Differential Equations
Uploaded by
gaurav_juneja_4Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Look-Up Table: Solving Differential Equations
Uploaded by
gaurav_juneja_4Copyright:
Available Formats
t-shifting s-shifting
T
i
m
e
d
o
m
a
i
n
L
a
p
l
a
c
e
d
o
m
a
i
n
Look-up table
) (t u
) (t o
1
s / 1
) ( * ) ( t g t f ) ( ) ( s G s F
L
a
p
l
a
c
e
t
r
a
n
s
f
o
r
m
A
p
p
l
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
s
Solving differential Equations
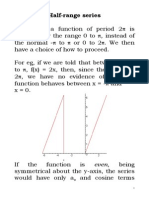
Review: Periodic Functions
0 p 2p 3p t
) (t f
) ( ) (
) ( ) (
) ( ) (
x h np x h
x g np x g
x f np x f
bg af h
= +
)
`
= +
= +
+ =
Review: Series
Sequence
Partial summation of a sequence
Convergence / divergence
? ) ) 1 sin( 2 sin (sin lim
? )
)! 1 (
1
! 3
1
! 2
1
! 1
1
1 ( lim
= + + +
=
+ + + + +
t t t n
n
n
n
n
1
, ,
3
1
,
2
1
, 1
=
=
N
n
N
n
S
1
1
Trigonometric Series
=
+ +
1
0
) sin cos (
n
n n
nx b nx a a
Form a basis linearly independent
Orthogonal
nx nx x x x x sin , cos , , 2 sin , 2 cos , sin , cos , 1
0 sin cos
) ( 0 sin sin
) ( 0 cos cos
=
}
= =
}
= =
}
t
t
t
t
t
t
nxdx mx
n m nxdx mx
n m nxdx mx
Fourier Series: p=2
=
+ + =
1
0
) sin cos ( ) (
n
n n
nx b nx a a x f
, 2 , 1 sin ) (
1
, 2 , 1 cos ) (
1
) (
2
1
0
=
}
=
=
}
=
}
=
n nxdx x f b
n nxdx x f a
dx x f a
n
n
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
Fourier Series may not converge to f(x)
+ +
=1
0
) sin cos ( ~ ) (
n
n n
nx b nx a a x f
Fourier Series: p=2L
+ + =
=1
0
) sin cos ( ) (
n
n n
x
L
n
b x
L
n
a a x f
t t
, 2 , 1 sin ) (
1
, 2 , 1 cos ) (
1
) (
2
1
0
=
}
=
=
}
=
}
=
n xdx
L
n
x f
L
b
n xdx
L
n
x f
L
a
dx x f
L
a
L
L
n
L
L
n
L
L
t
t
Even & Odd Functions
) ( ) ( x g x g =
) ( ) ( x h x h =
Even function:
Odd function:
Key facts
Even
Odd
Product of even and odd is odd
}
=
}
L L
L
dx x g dx x g
0
) ( 2 ) (
0 ) ( =
}
L
L
dx x h
Theorem 1
Fourier cosine series
f(x) is an even function
p=2L
+ =
=1
0
cos ) (
n
n
x
L
n
a a x f
t
Fourier sine series
f(x) is an odd function
p=2L
=
=1
sin ) (
n
n
x
L
n
b x f
t
, 2 , 1
cos ) (
2
) (
1
0
0
0
=
}
=
}
=
n
xdx
L
n
x f
L
a
dx x f
L
a
L
n
L
t
, 2 , 1
sin ) (
2
0
=
}
=
n
xdx
L
n
x f
L
b
L
n
t
Theorem 2
Fourier coefficients of f1+f2 are the sums of the
corresponding Fourier coefficients of f1 and f2
Fourier coefficients if cf are c times the
corresponding Fourier coefficients of f
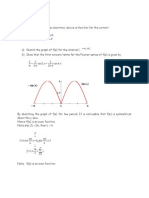
Half-range Expansions
, 0 ), ( For L x x f s s
) (t f
even
) (t f
odd
0 L
) (t f
You might also like
- FOURIER SERIESDocument31 pagesFOURIER SERIESSachi DhanandamNo ratings yet
- 2.odd Even Function1Document12 pages2.odd Even Function1Atikah JNo ratings yet
- X F X F: Even Function Half Range Series: A Series That IsDocument1 pageX F X F: Even Function Half Range Series: A Series That IsAtikah JNo ratings yet
- 5.periodic FunctionDocument7 pages5.periodic FunctionAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Uraian FourierDocument91 pagesUraian FourierAgus Dian PratamaNo ratings yet
- Maths for Petroleum Engineering EssentialsDocument73 pagesMaths for Petroleum Engineering EssentialsadobiNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument81 pagesFourier SeriesBunty PereraNo ratings yet
- 7.half Range SeriesDocument9 pages7.half Range SeriesAtikah JNo ratings yet
- Revision FourierDocument19 pagesRevision FourierHazim NaharNo ratings yet
- 1T4 Basic MathematicsDocument15 pages1T4 Basic MathematicsSimeonPetrovNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetHussain JiffryNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- Look-Up Table: Solving Differential EquationsDocument10 pagesLook-Up Table: Solving Differential EquationsDr. S. DasNo ratings yet
- (A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Document15 pages(A) If F (X) and G (X) Have Period P, Show That H (X) Af (X) + BG (X) (A, B, Constant)Heather JohnsonNo ratings yet
- LaplaceDocument19 pagesLaplaceBlackArmy88No ratings yet
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- Finite Fourier TransformDocument8 pagesFinite Fourier TransformGoh Kek BoonNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesFourier SeriesPurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaDocument4 pagesMaths Formulamickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus Formulas GuideDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Formulas Guidevignes011No ratings yet
- Polynomial Interpolation Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation: J J J J JDocument2 pagesPolynomial Interpolation Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation: J J J J JPH2303327No ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Table of Fourier Transform PairsDocument8 pagesTable of Fourier Transform PairsmayankfirstNo ratings yet
- Table of Common Fourier Transform PairsDocument8 pagesTable of Common Fourier Transform Pairsmain2510No ratings yet
- Fourier Series M302Document21 pagesFourier Series M302ranscrib300No ratings yet
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 pagesX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039No ratings yet
- Examples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Document8 pagesExamples 1: Fourier Series: F1.3YF2 Mathematical Techniques 1Shaibal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems FormulasDocument3 pagesSignals and Systems FormulasKPRBTNo ratings yet
- The Fourier Series EditedDocument46 pagesThe Fourier Series EditedSarah HillmanNo ratings yet
- Final Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinal Formula SheetwhatnononoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MatlabDocument59 pagesChapter 3 - MatlabZe SaNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- 1T4: Some Basic Mathematics: Xavier SerraDocument15 pages1T4: Some Basic Mathematics: Xavier Serrajabeur rahmaNo ratings yet
- List of exercises on series and sequencesDocument8 pagesList of exercises on series and sequencesp1tru1mariusNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Set ADocument17 pagesFinal Exam Set AAtikah J100% (1)
- Multivariable calculus exam with 7 problemsDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus exam with 7 problemslieth-4No ratings yet
- W3 L1 SlidesDocument13 pagesW3 L1 SlidesVicente ReisNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods for Physicists - Hermite FunctionsDocument9 pagesMathematical Methods for Physicists - Hermite FunctionsAhmed AssafNo ratings yet
- F (X) Is C (A, B) Let X, X (A, B) Then F (X) P (X) + R (X) WhereDocument9 pagesF (X) Is C (A, B) Let X, X (A, B) Then F (X) P (X) + R (X) WhereAlbert WillyNo ratings yet
- Odes: Power Series Solutions and Special Functions IDocument2 pagesOdes: Power Series Solutions and Special Functions IRaulNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio CNDocument7 pagesFormula Rio CNJoana Alves QuitérioNo ratings yet
- Revision of Fourier SeriesDocument37 pagesRevision of Fourier SeriesGeorges YoussefNo ratings yet
- SeriesDocument1 pageSeriesAnsikhan KingkhanNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- 4 FS - FT and WT - Sept - 2022 PDFDocument120 pages4 FS - FT and WT - Sept - 2022 PDFSahethiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document8 pagesProblem Set 2سام النعمانNo ratings yet
- List of Derivative RulesDocument1 pageList of Derivative RulesEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- 1T4 Basic MathematicsDocument15 pages1T4 Basic MathematicsZenPhiNo ratings yet
- Serii Fourier TeorieDocument7 pagesSerii Fourier TeorieSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- 工數傅立葉級數Document35 pages工數傅立葉級數Chaihong LoNo ratings yet
- Sas SeriesDocument8 pagesSas SerieskganesharunNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument11 pagesFourier SeriesJohnson Ken100% (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- How Bits and Bytes WorkDocument7 pagesHow Bits and Bytes Workapi-19737301No ratings yet
- 2.1 ICAO EUROCONTROL RTCA BiggsDocument12 pages2.1 ICAO EUROCONTROL RTCA BiggsvinaysuleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Jet Propulsion: Strong and Reliable Muscles For The AircraftDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Jet Propulsion: Strong and Reliable Muscles For The Aircraftgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Assignment Problem: Ans:e (3cos 3t - 5sin3t)Document3 pagesAssignment Problem: Ans:e (3cos 3t - 5sin3t)gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Fourier Transform PropertieZsDocument13 pagesFourier Transform PropertieZsgaurav_juneja_4100% (1)
- Digital Communication Signals & Systems OverviewDocument221 pagesDigital Communication Signals & Systems Overviewgaurav_juneja_4100% (1)
- Signal Representation & Analysis IntroductionDocument21 pagesSignal Representation & Analysis Introductiongaurav_juneja_40% (1)
- Quick Start Guide 2015Document1 pageQuick Start Guide 2015aishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy Project: PMJDY, Loans, Savings & Banking ServicesDocument7 pagesFinancial Literacy Project: PMJDY, Loans, Savings & Banking Servicesgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- 16100lectre39 CJDocument3 pages16100lectre39 CJefe_011No ratings yet
- Filter 2Document18 pagesFilter 2gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Fourier Theory Made Easy (?)Document30 pagesFourier Theory Made Easy (?)gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Freq Mod - 8Document127 pagesFreq Mod - 8gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Definition and Key FunctionsDocument8 pagesFourier Transform Definition and Key Functionsgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- History of Optical Storage MediaDocument56 pagesHistory of Optical Storage Mediagaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Part 1Document12 pagesChapter 10 Part 1gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Power Divider, Combiner and CouplerDocument60 pagesPower Divider, Combiner and Couplergaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechDocument63 pagesDigital Modulation Techgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Analogy BW Vector ND SignalsDocument7 pagesAnalogy BW Vector ND Signalsgaurav_juneja_450% (2)
- B P Lathi - Modern Digital and Analog Communication SystemsDocument400 pagesB P Lathi - Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systemsnnn100% (1)
- Principles of Communication Systems by Taub & SchillingDocument119 pagesPrinciples of Communication Systems by Taub & SchillingInsane Clown Prince40% (5)
- MicrowavesDocument26 pagesMicrowavesgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document13 pagesPresentation 2gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Sampling TheoremDocument34 pagesSampling Theoremgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Switch & HubDocument10 pagesSwitch & Hubgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Day07 3Document8 pagesDay07 3gaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Catalyst Switch OperationsDocument61 pagesCatalyst Switch Operationsgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Catalyst Switch OperationsDocument61 pagesCatalyst Switch Operationsgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- SwitchDocument21 pagesSwitchgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- 5957-Pan Flute Tone RangesDocument1 page5957-Pan Flute Tone Rangesdaniel_gheoldus5867No ratings yet
- Cathodic Disbondment Test of Pipeline Coatings (Attached Cell Method)Document4 pagesCathodic Disbondment Test of Pipeline Coatings (Attached Cell Method)Alex OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Field Artillery Journal - Jul 1918Document187 pagesField Artillery Journal - Jul 1918CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Learn TagalogDocument11 pagesLearn TagalogShim CharenNo ratings yet
- Building Technology 4 Week 4Document42 pagesBuilding Technology 4 Week 4Xette FajardoNo ratings yet
- The preparation, dyeing and finishing of cotton knit goodsDocument67 pagesThe preparation, dyeing and finishing of cotton knit goods郭哲宏100% (1)
- Password CrackingDocument13 pagesPassword CrackingBlue MagicNo ratings yet
- The 20 Amino Acids and Their Role in Protein Structures: Torsion AnglesDocument3 pagesThe 20 Amino Acids and Their Role in Protein Structures: Torsion AnglesDaleNo ratings yet
- Exploring Novel Isocractic HPLC Method For Quantitative Determination of Cinnarizine and Piracetam in Their Capsule Preparations 1920 4159 1000225Document5 pagesExploring Novel Isocractic HPLC Method For Quantitative Determination of Cinnarizine and Piracetam in Their Capsule Preparations 1920 4159 1000225Adolfo OlmosNo ratings yet
- Shearwall Design of RCCCC Structure 111111222222298909Document77 pagesShearwall Design of RCCCC Structure 111111222222298909Shams KhattakNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering - A. Mittle and V. N. Mittle PDFDocument212 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering - A. Mittle and V. N. Mittle PDFSajal Singh Patel0% (5)
- Protect transformers from over excitation with relay coordinationDocument7 pagesProtect transformers from over excitation with relay coordinationAnonymous zxtBoTT100% (1)
- Primo Theory Volume 5 Secured - Unlocked PDFDocument60 pagesPrimo Theory Volume 5 Secured - Unlocked PDFmsmali100% (1)
- Bus 172Document5 pagesBus 172api-538674995No ratings yet
- EBS e PDFDocument92 pagesEBS e PDFRowan Cornelius100% (2)
- Past Papers CXC MathsDocument77 pagesPast Papers CXC MathsShanice Henry96% (27)
- Design, Construction and Test of Prop System of Solar UAVDocument126 pagesDesign, Construction and Test of Prop System of Solar UAVNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Naming by Aravind AroraDocument30 pagesIUPAC Naming by Aravind Aroratanish gehlotNo ratings yet
- Transformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument32 pagesTransformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaParvezKhanNo ratings yet
- Description of The Courses - Transportation Eng - 2013 v2 PDFDocument5 pagesDescription of The Courses - Transportation Eng - 2013 v2 PDFVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Session GuideDocument6 pagesSession GuideLuisa GarcillanNo ratings yet
- Ferraris Wright & HaloscaleDocument4 pagesFerraris Wright & HaloscaleJORGE NAVARRONo ratings yet
- Kubota Front Loader La 211Document29 pagesKubota Front Loader La 211Mark Dubravec40% (5)
- Pile CAP CALCULATIONSDocument9 pagesPile CAP CALCULATIONSJUAN MANUEL VIZCAINONo ratings yet
- Actuarial Valuation LifeDocument22 pagesActuarial Valuation Lifenitin_007100% (1)
- Serway PSE Quick Ch21Document17 pagesSerway PSE Quick Ch21music manNo ratings yet
- SpO2 and Temp Monitoring FinalDocument39 pagesSpO2 and Temp Monitoring FinalWaltas KariukiNo ratings yet
- Introduction and operating system structure syllabusDocument29 pagesIntroduction and operating system structure syllabusRadhika BadbadeNo ratings yet
- mc34164 PDFDocument12 pagesmc34164 PDFAnonymous ZNsW2aNUT5No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1eddy50% (2)























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)