Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOFISIKA Bio Termofisika
Uploaded by
LalitakuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOFISIKA Bio Termofisika
Uploaded by
LalitakuCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOFISIKA
BIO-TERMOFISIKA
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH
Cooling the body
D E M A M
Sensor Perubahan Suhu pada Mahluk Hidup
PENCITRAAN SUHU
METABOLISME TUBUH
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ PANAS/DINGIN
hot and cold are only a
sensation that we can feel
(mostly by touching it)
how hot or cold an object
is described by term called
temperature
temperature is quantification of how hot or
cold an object is
Temperature is being measured using thermometer.
Familiar thermometers are celcius, fahrenheit and
Kelvin
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ PEMUAIAN
Area Expansion
Volume Expansion
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/thexp2.html#c2
Linear Expansion
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ PEMUAIAN
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ KALOR & PERPINDAHANNYA
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ KALOR & PERPINDAHANNYA
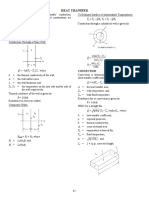
Conduction
.
L
T kA
t
Q
SI Unit of Thermal
Conductivity:
J/(s m C)
Fouriers Law of Conduction
Convection
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ KALOR & PERPINDAHANNYA
breezes come from the ocean in the day
and from the land at night
Styrofoam
Black Body Radiation
REVIEW: SIFAT TERMAL BENDA ~ KALOR & PERPINDAHANNYA
The StefanBOLTZMANN
Law Of Radiation
.
4
eAT P
t
Q
= 5.67 .10
-8
W/m
2
.K
4
.
Absorbing Solar Radiation
Qabs = S A vfs a
Rate of absorption of solar energy depends on:
The intensity of the radiation (S)
Surface area of the animal (A)
Proportion of the animals surface
that is exposed to the radiation (vfs)
Absorptivity, proportion of the energy
that is absorbed rather than reflected (a)
Herps have substantial control
over the amount of solar radiation
they absorb
Absorbing Solar Radiation
Move between sun and shade
Change the amount of surface area
exposed to the sun
Change orientation to the sun
Change color (albedo) to change
absorptivity
Concentrate pigments in
melanophores to expose reflective
pigments and cast off light.
Disperse melanin to absorb light
Thermos Bottle
Stopper- minimize conduction.
Double-walled glass vessel with the space
between the walls is evacuated to minimize
energy losses due to conduction and
convection.
The silvered surfaces reflect most of the
radiant energy that would otherwise enter or
leave the liquid in the thermos.
A thermos bottle minimizes energy transfer
due to convection, conduction, and
radiation
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH
Mekanisme perpindahan kalor berpengaruh pada pengaturan suhu tubuh
http://www.colorado.edu/intphys/Class/IPHY3430-200/021metabolism-energy.htm
Homeostasis Control Principles
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a
relatively constant state in a system
where the state can change.
Set point - the desired level of a state
that is to be maintained.
Negative Feedback Control - the
most common control system used to
achieve homeostasis.
For an endothermic homeotherm to control body temperature at a
constant level:
Heat production rate (H) must balance heat loss rate (Q).
= C (T
B
- T
A
) H = Q
C = Conductance (the ease with which heat leaves the body)
and
is the reciprocal of insulation (I).
T
B
= Core body temperature
T
A
= Ambient (environmental) temperature
I
C
1
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH:
Linear Heat Transfer Equation
36
37
38
39
40
0 10 20 30 40
B
o
d
y
T
e
m
p
e
r
a
t
u
r
e
,
o
C
0
1
2
3
4
0 10 20 30 40
Ambient Temperature,
o
C
M
e
t
a
b
o
l
i
c
R
a
t
e
Thermal
Neutral Zone
T
LC
T
UC
Heat
Production
T
LC
= Lower critical temperature; T
UC
= Upper critical temperature
Within the Thermal Neutral Zone, heat loss is
controlled by changing conductance (C).
H = Q = C (T
B
- T
A
)
0
1
2
3
4
0 10 20 30 40
Ambient Temperature,
o
C
M
e
t
a
b
o
l
i
c
R
a
t
e
Thermal
Neutral
Zone
Erection of hairs or feathers to increase thickness of the body surface
covering.
Control of blood flow to the body surface.
Blood vessels can constrict to slow blood flow to a specific region.
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH MANUSIA:
Adjusment of Insulation
Heat Conduction to the Skin
The skin and the subcutaneous tissues especially the fat form a
heat insulator system for the body.
This system maintains the normal core temp., although the temp. of
the skin may approach the temp.of the surrounding.Blood vessels
penetrate the fatty subcutaneous tissues and are distribution
beneath the skin.
The amount of heat reaching the skin from the deep tissues
depends upon the blood flow into the cutaneous blood vessels
which is determined by the degree of vasoconstriction of the
vessels.
This vasoconstriction in turn is controlled almost entirely by the
sympathetic nervous system.
The rate of heat conduction to the skin is known as tissue
conductance.
Heat loss from the skin surface
Radiation Human body radiates heat rays in all directions but is
also exposed to heat rays radiated from the surrounding.
Therefore, heat is lost by this method when the temp. of the
surrounding is less than the body temp. At normal temp. about
60% of the total heat loss from a nude person occurs by radiation.
Conduction Only minute amount of heat are normally
lost from the body by direct conduction to other objects
such as a chair or bed (3%). On the other hand large
amounts of heat are lost by conduction to air.
Convection It is the removal of heat from the body by convection air
currents.Heat must first be conducted to the air and then carried away by
the convection current.About 12% of heat loss from the body occurs by
conduction to the air and then by convection.When the body is exposed to
wind heat loss by convection is greatly increased.
Heat loss from the skin surface
Evaporation
Evaporation of 1g water removes about 0.6 Kcal. Of heat. Even when a person
is not sweating a certain amount of water still evaporates from the skin and
lungs at a rate of about 600 ml/day. This is known as the insensible water
loss.
Sweating provides a very important way of heat loss from the body which can be
regulated. As long as skin temp. is greater than the temp. of surrounding,
heat can be lost by radiation & conduction, but when the temp. of the body
gains heat by radiation& conduction.
.
Urine & Feces Small amount of heat are removed
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH MANUSIA:
Adjusment of Insulation
Shivering
Thermogenesis:
High frequency, uncoordinated
contractions of opposing skeletal
muscles.
Nonshivering
Thermogenesis:
Elevated metabolic rate in many tissues releases
heat, especially in brown adipose tissue (brown
fat).
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH:
Mechanisms of Heat Production
H+ channels
inserted.
PENGATURAN SUHU TUBUH:
Brown Adipose tissue Heat Generation
Cooling of the Human Body
H
m
= H
c
+ H
r
+ H
s
+ H
l
H
m
= kalor dr metabolime (70 1400 kkal/h)
H
C
= kalor hilang konveksi
= 6,1 A (T
s
T
a
) kkal/h
H
r
= kalor hilang radiasi
= 5,6 A (T
s
T
a
) kkal/h
H
s
= kalor hilang evaporasi keringat
= 580r kkal/h
H
l
= kalor hilang evaporasi dr paru-paru
= 9 kkal/h
A = luas bidang tubuh
T
s
= suhu kulit ; T
a
= suhu udara
r = laju keringat (kg/h)
The cooling effect of perspiration evaporation makes use of the very large heat of
vaporization of water. This heat of vaporization is 540 calories/gm at the boiling
point, but is even larger, 580 cal/gm, at the normal skin temperature.
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/coobod.html#c1
Simplified model of the process by which the human body gives off heat. Even
when inactive, an adult male must lose heat at a rate of about 90 watts as a result
of his basal metabolism.
Cooling of the Human Body
Newtons Law of Cooling
. . . . . . .
You might also like
- Copeland Refrigeration Manual - Part 1 - Fundamentals of RefrigerationDocument40 pagesCopeland Refrigeration Manual - Part 1 - Fundamentals of RefrigerationMohammad Amer100% (1)
- Fe Heat TransferDocument6 pagesFe Heat Transfervzimak2355No ratings yet
- Principles of Food Preservation, Processing and PackagingDocument46 pagesPrinciples of Food Preservation, Processing and PackagingAshok Yadav100% (1)
- Thermoregulation: Physiological Responses and Adaptations To Exercise in Hot and Cold EnvironmentsDocument34 pagesThermoregulation: Physiological Responses and Adaptations To Exercise in Hot and Cold Environmentsvishal pundirNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics Chapter A and BDocument59 pagesErgonomics Chapter A and BSifat E Noor SahibaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Heat Loss From The Human BodyDocument13 pagesMechanism of Heat Loss From The Human BodyEbrahim Abd El HadyNo ratings yet
- Climate and Thermal ComfortDocument30 pagesClimate and Thermal ComfortVAGEESHANo ratings yet
- Heat Loses From The BodyDocument7 pagesHeat Loses From The BodyaliNo ratings yet
- Heat and ColdDocument147 pagesHeat and ColdCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- BUILDING UTILITIES 2 Thermal ComfortDocument63 pagesBUILDING UTILITIES 2 Thermal Comfortjona serranoNo ratings yet
- Body Temp.Document35 pagesBody Temp.Sreenivasulu TalariNo ratings yet
- Body Temp.Document35 pagesBody Temp.Seemeer SahuNo ratings yet
- Temperature RegulationDocument27 pagesTemperature RegulationRabia RaufNo ratings yet
- Thermal ComfortDocument18 pagesThermal ComfortIlham AndiNo ratings yet
- Temperature Regulation & Mobility Lecture MorganitesDocument57 pagesTemperature Regulation & Mobility Lecture MorganiteslouradelNo ratings yet
- Temperature Regulation During Exercises: Dr. Ghousia ShahidDocument26 pagesTemperature Regulation During Exercises: Dr. Ghousia ShahidAflaha KhanNo ratings yet
- Clothing & Thermoregulation Interaction by George HavenithDocument14 pagesClothing & Thermoregulation Interaction by George HavenithMayayo: Carrerasdemontana.comNo ratings yet
- Body TempratureDocument16 pagesBody TempratureMustafa MustafaNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Body TemperatureDocument108 pagesAlterations in Body TemperatureJosephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Part BDocument12 pagesModule 1 Part BSam KOkeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Environmental Factors Influencing Human PerformanceDocument22 pagesChapter 11 - Environmental Factors Influencing Human PerformanceHyperHodgeyNo ratings yet
- Comfort ZoneDocument19 pagesComfort ZoneKapil AroraNo ratings yet
- NOTES Module 2Document13 pagesNOTES Module 2Paarth AgrawalNo ratings yet
- A-Vasodilation of Skin Blood Vessels - in Almost All Areas of The Body, The Skin Blood VesselsDocument7 pagesA-Vasodilation of Skin Blood Vessels - in Almost All Areas of The Body, The Skin Blood VesselsHebsiba PonnayyanNo ratings yet
- 08 - 4 FDB PPT - ComfortDocument41 pages08 - 4 FDB PPT - ComfortJayachandran KNo ratings yet
- Laws of Thermodynamics and The Human BodyDocument2 pagesLaws of Thermodynamics and The Human BodyCHANDRA SHEKAR BESTA100% (3)
- 2nd Lecture Human ComfortDocument52 pages2nd Lecture Human ComfortJ ANo ratings yet
- Day 1 - What Is HVACDocument16 pagesDay 1 - What Is HVACnareshbv749No ratings yet
- Report On Human ComfortDocument8 pagesReport On Human ComfortBrijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Skenario 2 Blok 3 - 2Document5 pagesSkenario 2 Blok 3 - 2Arifin NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIaDocument4 pagesChapter IIaJESPER BAYAUANo ratings yet
- HVAC - Practical Basic Calculation PDFDocument37 pagesHVAC - Practical Basic Calculation PDFmohdrashid100% (2)
- Altered ThermoregulationDocument29 pagesAltered Thermoregulationsreekala100% (1)
- Temperature and Heat 3Document18 pagesTemperature and Heat 3Samud MorrisNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics: Wollo University (WU)Document6 pagesDepartment of Physics: Wollo University (WU)Garbe ChukuluNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Measurement of Non-Electrical ParametersDocument17 pagesUnit IV Measurement of Non-Electrical ParametersAleesha100% (7)
- Ch-5 Work &energyDocument34 pagesCh-5 Work &energyLindsey AdalsonNo ratings yet
- REGULATION of Body Temperature: by Dr. Ranadhi Das MD (PGT) Department of PhysiologyDocument33 pagesREGULATION of Body Temperature: by Dr. Ranadhi Das MD (PGT) Department of Physiologyamrendra100% (1)
- Term o RegulationDocument10 pagesTerm o Regulationfinna kartikaNo ratings yet
- HeatTransfer2010Document54 pagesHeatTransfer2010Nurul Izzati Raihan RamziNo ratings yet
- A-Level Biology: Temperature RegulationDocument17 pagesA-Level Biology: Temperature RegulationNaduku EridadNo ratings yet
- Climate Engineering: Anthropogenic HeatDocument3 pagesClimate Engineering: Anthropogenic HeatMaan MirallesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Biomaterial NewDocument10 pagesThermal Properties of Biomaterial NewOjo MojolaoluwaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chap12 074Document8 pagesHeat Chap12 074Kerem GönceNo ratings yet
- Altered Body TemparatureDocument31 pagesAltered Body TemparatureReshma Rinu100% (1)
- 05B-Thermal InsulationDocument25 pages05B-Thermal InsulationRitikaNo ratings yet
- Tamura 2017Document27 pagesTamura 2017Bobby IgnatichNo ratings yet
- BnsDocument19 pagesBnsHadia NoorNo ratings yet
- Heat and Cold in MedicineDocument33 pagesHeat and Cold in Medicineاحمد احمدNo ratings yet
- Jsunil: Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur PH: 9835859669Document6 pagesJsunil: Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur PH: 9835859669ravilullaNo ratings yet
- Ifra Assignment 09.06.2020 (1) HNDDocument10 pagesIfra Assignment 09.06.2020 (1) HNDHAFIZ MUHAMMAD IMTIAZNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The RelationshipsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The Relationshipslarison09No ratings yet
- Predicting The Effect of Relative HumidityDocument11 pagesPredicting The Effect of Relative HumidityhaschereNo ratings yet
- 1-HVAC Concepts and Fundamentals R1Document88 pages1-HVAC Concepts and Fundamentals R1Tony HuangNo ratings yet
- Fisiología en Ambientes CalurososDocument80 pagesFisiología en Ambientes CalurososEmilio CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics 1 of 3 2Document24 pagesThermal Physics 1 of 3 2Barbie DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- HVAC Training at DCS, HyderabadDocument19 pagesHVAC Training at DCS, HyderabadDCS Pvt. Ltd.100% (1)
- Bioclimatic Design - 06 - HumanBodyMechanismsDocument18 pagesBioclimatic Design - 06 - HumanBodyMechanismsABHISHEK J 19ABARC001No ratings yet
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseFrom EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Studi Komparasi Perilaku Masyarakat Dalam Upaya Pencegahan Demam Berdarah Dengue Terhadap Keberadaan Nyamuk Sebagai VektorDocument6 pagesStudi Komparasi Perilaku Masyarakat Dalam Upaya Pencegahan Demam Berdarah Dengue Terhadap Keberadaan Nyamuk Sebagai VektorLalitakuNo ratings yet
- Studi Komparasi Perilaku Masyarakat Dalam Upaya Pencegahan Demam Berdarah Dengue Terhadap Keberadaan Nyamuk Sebagai VektorDocument6 pagesStudi Komparasi Perilaku Masyarakat Dalam Upaya Pencegahan Demam Berdarah Dengue Terhadap Keberadaan Nyamuk Sebagai VektorLalitakuNo ratings yet
- Tabel Distribusi Probabilitas Normal Baku 1Document5 pagesTabel Distribusi Probabilitas Normal Baku 1Aul CooperNo ratings yet
- Tabel Distribusi Probabilitas Normal Baku 1Document5 pagesTabel Distribusi Probabilitas Normal Baku 1Aul CooperNo ratings yet
- Tabel Distribusi Probabilitas Normal Baku 1Document5 pagesTabel Distribusi Probabilitas Normal Baku 1Aul CooperNo ratings yet
- @kul 2 SHM - Circular - EnergiDocument31 pages@kul 2 SHM - Circular - EnergiLalitakuNo ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Quick RevisionDocument16 pagesMaths IGCSE Quick Revisionlindy musekaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Food MaterialsDocument30 pagesPhysical Properties of Food MaterialsimranaitNo ratings yet
- Convection BLDocument77 pagesConvection BLAHMED EL HAMRINo ratings yet
- Jewell 2018 JSR 1.A34147Document15 pagesJewell 2018 JSR 1.A34147Anand RajendranNo ratings yet
- Phys Answers 2nd QuarterDocument15 pagesPhys Answers 2nd QuarterRomel Salamoding33% (3)
- Me6603 Fea Rejinpaul Iq Am19Document5 pagesMe6603 Fea Rejinpaul Iq Am19shivesh rockesNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Heat Conduction EquationDocument10 pagesOne Dimensional Heat Conduction EquationMonowarul IslamNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024 9th Grade YEARLY PLANDocument110 pages2023-2024 9th Grade YEARLY PLANOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiationnavketsharma6280100% (1)
- Ansys Fluent: Industry SolutionsDocument4 pagesAnsys Fluent: Industry Solutionsameen hassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Temperature Heat PDFDocument8 pagesChapter-6 Temperature Heat PDFMohammad Fuad HasanNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document10 pagesExp 1Essam AbuasabNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG Grade7 HEATDocument1 pageDAILY LESSON LOG Grade7 HEATseoraksan50% (2)
- Estimating Heat Sink Thermal ResistanceDocument6 pagesEstimating Heat Sink Thermal ResistanceRAHUL VEERNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Summary: HEC3521 Process Heat Transfer Experiment 1: Thermal Conductivity of Liquids and GasesDocument11 pages1.0 Summary: HEC3521 Process Heat Transfer Experiment 1: Thermal Conductivity of Liquids and GasesGracylla RoseNo ratings yet
- Overview of Geophysical MethodsDocument41 pagesOverview of Geophysical MethodsVaqas Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Heat and Mass Transfer Rme 502 2018 19 PDFDocument2 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Heat and Mass Transfer Rme 502 2018 19 PDFSuryaNo ratings yet
- Charny - Mathematical Models of Bioheat TransferDocument137 pagesCharny - Mathematical Models of Bioheat TransferMadalena PanNo ratings yet
- An Infrared Thermography Study On The Thermal Load PDFDocument14 pagesAn Infrared Thermography Study On The Thermal Load PDFalialbadryNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction in Rectangular Solids With InternaDocument13 pagesHeat Conduction in Rectangular Solids With InternaDinda Dwiananda putriNo ratings yet
- Applications in Convective Heat Transfer With Emphasis On Blade Cooling Flows Part I, Background & MethodologiesDocument26 pagesApplications in Convective Heat Transfer With Emphasis On Blade Cooling Flows Part I, Background & MethodologiesDhesa HidayatNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Physics Form 4Document29 pages4.2 Physics Form 4871226No ratings yet
- 4 21665444-Calculation-of-Conductor-Temperatures-and-AmpacitiesDocument10 pages4 21665444-Calculation-of-Conductor-Temperatures-and-AmpacitiesANTHONY J. CHAVEZ CAMPOSNo ratings yet
- 3 MDM Curriculum AsOn 04nov2011Document25 pages3 MDM Curriculum AsOn 04nov2011Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesThe First Law of ThermodynamicsArpit PatelNo ratings yet
- 51 Transfer of Heat by RadiationDocument5 pages51 Transfer of Heat by RadiationS'chneider AgudeloNo ratings yet
- 27 Assignment4 PDFDocument8 pages27 Assignment4 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Mse 255 Lecture 6Document43 pagesMse 255 Lecture 6percydziksNo ratings yet