Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 4.VCL155 The Content and Form
Uploaded by
Za-c Pelangi Senja60%(5)60% found this document useful (5 votes)
996 views27 pagesnth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
Original Title
Lecture 4.VCL155 the Content and Form
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
60%(5)60% found this document useful (5 votes)
996 views27 pagesLecture 4.VCL155 The Content and Form
Uploaded by
Za-c Pelangi Senjanth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
nth
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
The creative process
Muslim artist is aware of the importance of
content in their artwork.
It has to be addressed prior to the creation of
form.
It is the content that determine the form.
The message of Islam (tawhid) is being
transmitted through form.
In Islamic art,
the concept of tawhid formed the content of
the art work.
Based on the:
a. Al-Quran and Al-Hadith
b. Nature
There are two processes in creative
work:
a. The problem solving process
b. The creative process
(Process a is an activator assisting in the
process b)
Define
Analyze
Idea
Select
Implement
Evaluate
Form Generation
Stages in the creative process:
1. Imitation of nature
2. Stylization of nature (denaturalization of nature)
3. Abstraction of nature
Muslim artist imitate nature to produce art work.
He realized that man can never create Gods creation in
nature.
(Nothing in this world that can match the Wahyu i.e. Al-
Quran. Nature is also another form of the words of God)
In any instance, an artist cannot reproduce nature. He
can imitate nature but it is not the true thing an
illusion.
What he had created is in the form of stylization of
nature, which in other words - a denaturalized form. His
creation cannot be equated with the Gods creation.
The creative process had undergone stages of imitation and
stylization of nature (the denaturalization of nature), and
finally the stage of abstraction of nature.
The composition of the abstract form can be organic or
geometric, or both to create an Islimi design known from
the Ummayad to the present day.
Evidence of these stages can be seen in any Islamic art
work.
It can be either on the:
First stage: imitation of nature
Second stage: stylization of nature
Third stage: abstraction of nature
Or
An Islamic Art work may consists of any one of the
followings:
a. First and second stage
b. Second and third stage
c. First and third stage
d. All the three stages
Visual Elements of Form
Perception Theory
Communication Theory
Human Factors and Dimensions
Form Configuration, Structure, and Materials
Unity of Form
Visual and Physical Attributes of Form
Value/Tone,
Colour
Texture
Dimension
Shape
Proportion
Space, Depth, and Distance
(2- and 3-Dimensional Form Perception)
Light/Brightness
Illusions
Monocular Cues
(size, partial overlap, value, colour, aerial perspective, detail
perspective, linear perspective, texture gradient, shadow, blurring
detail, transparency)
Binocular Cues
(muscular cues, parallax cues)
Position
Orientation
Motion
Time
Organizational Principles in 2 and 3 Dimensions
Visual Perception
Concepts/Principles
1. Gestalt Theory
Figure Laws, Grouping Laws
2. Figure/Ground
Distinguishing Figure from Ground,
Ambiguous Figure, Stability / Instability,
Figure Closure, Figure / Ground Reversal,
Pattern & Figure / Ground Reversal, Figure
Overlap
Prescriptive Principles of Organization
1. Spatial Organization
Centralized, Linear, Radial, Clustered,
Grid / Lattice Systems
2. Symmetry Groups
Identity, States of Being, Operations
(translation, rotation, reflection, glide
reflection) Symmetry, Transformations
3. Compositional/Visual
Organization
Balance (symmetrical /
asymmetrical), Repetition,
Harmony, Rhythm, Variety,
Contrast, Dominance
4. Acquired Associations
Free Association, Familiarity,
Reading Order, Hierarchies of
Information general to specific,
specific to general, chronological
(affine, perspectivity, dilatative,
topological, golden section, root
rectangles)
3. Dynamic
Symmetry
Proportional Systems
(arithmatic, harmonic,
geometric), Proportional
Theories (Golden Section,
renaissance, the Modular,
anthropometrics)
Communication Theory
Verbal & Nonverbal Communication
Pattern Recognition
Human Recognition
(Relative to Social / Cultural Patterns
Visual Language
Semiotic
(Theory of Signs)
Theory by Charles Morris
Semiosis
Sign Vehicle, Designatum,
Interpretant
Syntactics
Semantics
Pragmatics
Communication Theory
Semiotic
(Theory of Signs)
Theory by Charles Morris
Syntactics
Formal Concept of Language, Syntactical
Rules (formation rules, transformational
rules)
Semantics
Relation of Signs to Their Designata,
Semantics Rule, Linguistic Structures,
Nonlinguistic Structures
Process by D. Berlo
Source
Message
Channel (Media)
Receiver
Semiotic
(Theory of Signs)
Pragmatics
Relation of Signs to the User, Pragmatical Rules
User Requirements
Social / Cultural Factors
Economic Factors
Anthropometrics / Human Dimensions
Structure and Material
Structure Systems
Static Structures
Solid,
Skeletal
Surface / Planar
Matrials and Their
Characteristics
Wood
Paper
Plastic
Metal
Fabric
Ceramics
Glass
Art Forms
Architecture
Design Forms
Visual Messages
Products
Structures
Interiors
Form
Media (art tools and materials)
The Elements of Art
Line, Shape Value, Texture, Color
The Principles of Organization
Harmony (involving rhythm-repetition) and Variety (involving
contrast-elaboration)
(Balance, Movement, Proportion, Dominance, Economy and space)
Unity means oneness,
an organization of parts
that fit into order of a whole
and become vital to it
Both two- and three-dimensional compositions
and forms are created by combining:
a. Subject matter
b. Meaning/intent with material/media
Artists/designers/architects manipulate components to
devise and produce meaningful Islamic art forms,
products, buildings, interior spaces, communications, and
so on.
Thank You.see you in the next
chapterInsyallah.
You might also like
- Fashion DrawingDocument64 pagesFashion DrawingLucian Cozma67% (6)
- Dart Manipulation Techniques For Flat PatternsDocument30 pagesDart Manipulation Techniques For Flat PatternsZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- VM Jugde Form Rev 2014Document1 pageVM Jugde Form Rev 2014Za-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Attitudes To Modernity in Ismail ZainDocument15 pagesAttitudes To Modernity in Ismail ZainNaz ImajinNo ratings yet
- Knit JumpsuitDocument2 pagesKnit JumpsuitJill Krahling100% (1)
- FRPDocument27 pagesFRPFarich FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- The City As Architecture - UnknownDocument144 pagesThe City As Architecture - UnknownRodrigo CerveiraNo ratings yet
- Slide 10 - Malay MosqueDocument52 pagesSlide 10 - Malay MosqueMuhammad Suhaimi100% (1)
- Malaysian Art (VCL 215) - NZ VerDocument310 pagesMalaysian Art (VCL 215) - NZ VerZa-c Pelangi Senja71% (7)
- Malaysian Art (VCL 215) - NZ VerDocument310 pagesMalaysian Art (VCL 215) - NZ VerZa-c Pelangi Senja71% (7)
- Sketches by Judith Rasband organizedDocument41 pagesSketches by Judith Rasband organizedReham Magdy100% (2)
- 2nd Periodical Test in Mapeh 6 2017Document5 pages2nd Periodical Test in Mapeh 6 2017Margie Macay Lastimosa86% (7)
- The Doom Seeker 1Document32 pagesThe Doom Seeker 1drachenfels6669117100% (1)
- A Tibetan FurnitureDocument5 pagesA Tibetan FurnitureEma StrnadNo ratings yet
- Modern Malaysian Art's Search for Cultural IdentityDocument22 pagesModern Malaysian Art's Search for Cultural IdentityAzzad Diah Ahmad Zabidi50% (2)
- Lagu Pandu PuteriDocument25 pagesLagu Pandu Puterinor anita ismailNo ratings yet
- Belle - September 2015 AUDocument228 pagesBelle - September 2015 AUMody BickNo ratings yet
- History of Art Development of Art in PenangDocument13 pagesHistory of Art Development of Art in PenangOliver WongNo ratings yet
- The Language of Towns & Cities A Visual DictionaryDocument4 pagesThe Language of Towns & Cities A Visual DictionaryBianca Nicolae100% (1)
- Vcs 265Document7 pagesVcs 265zeeraNo ratings yet
- Traditional Malaysian Hairpin Used to Secure HairstylesDocument6 pagesTraditional Malaysian Hairpin Used to Secure HairstylesarifinNo ratings yet
- VcsDocument27 pagesVcsPuteri AdlinNo ratings yet
- Fae Zah Bahar I ProposalDocument30 pagesFae Zah Bahar I Proposalfaezahuji100% (1)
- Pengurusan Kraftangan Anyaman Industri Desa (24pgs)Document24 pagesPengurusan Kraftangan Anyaman Industri Desa (24pgs)Ariff Aziz100% (1)
- Café Terrace at Night: Painting by Vincent Van GoghDocument12 pagesCafé Terrace at Night: Painting by Vincent Van GoghAbegail A. AraojoNo ratings yet
- Name: Nur Amalina Syahirah Binti Mohamad NO MATRIC: 2018222866 Class: Ad242 4A Subject: RMD 577Document6 pagesName: Nur Amalina Syahirah Binti Mohamad NO MATRIC: 2018222866 Class: Ad242 4A Subject: RMD 577Amalina Syahirah100% (2)
- RMD IntroDocument11 pagesRMD IntroFaiz Ismadi50% (2)
- Asingment SeniDocument22 pagesAsingment SeniAnonymous pT5AeGB100% (1)
- Form Follows CultureDocument9 pagesForm Follows CultureFarah PathiaNo ratings yet
- Gadis Menumbuk PadiDocument1 pageGadis Menumbuk PadiRedzuan nur akman100% (1)
- Modern Malaysia ArtDocument21 pagesModern Malaysia ArtLuqman Diah100% (1)
- Ismail LatiffDocument8 pagesIsmail LatiffFatin KhalilahNo ratings yet
- Quiz Vcs155Document3 pagesQuiz Vcs155HafizfayeNo ratings yet
- psv1Document113 pagespsv1olumisNo ratings yet
- Patrick NG Kah OnnDocument2 pagesPatrick NG Kah OnnZa-c Pelangi Senja0% (2)
- 10 Exercise Group 3Document17 pages10 Exercise Group 3agalyaNo ratings yet
- Notes Rmd577 (Research Proposal)Document42 pagesNotes Rmd577 (Research Proposal)Husna Rahman100% (1)
- Lpe 2501 SCL Worksheet 5 (Answer Key)Document2 pagesLpe 2501 SCL Worksheet 5 (Answer Key)Sharip MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Zakaria Ali - Me N My Parents As ZapatistasDocument2 pagesZakaria Ali - Me N My Parents As ZapatistasLeong Tuck YeeNo ratings yet
- Art & Design Appreciation: An OverviewDocument10 pagesArt & Design Appreciation: An Overviewines0% (4)
- Wau Bulan: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesWau Bulan: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaWan Farabel100% (1)
- Instructions For Students: UHL2412/SEM22018/2019DEL/CMLHS/UMPDocument5 pagesInstructions For Students: UHL2412/SEM22018/2019DEL/CMLHS/UMPwan nur mursyidahNo ratings yet
- Wednesday Art GroupDocument20 pagesWednesday Art GroupZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Tajuk 1 Peranan Seni Dalam Teknologi Maklumat Dan Komunikasi (Ict) Serta Menggunakan MultimediaDocument19 pagesTajuk 1 Peranan Seni Dalam Teknologi Maklumat Dan Komunikasi (Ict) Serta Menggunakan MultimediaMelissa ChoongNo ratings yet
- Related Sharifah Fatimah Syed Zubir With Al-Ghazali's Theory of PhilosophyDocument18 pagesRelated Sharifah Fatimah Syed Zubir With Al-Ghazali's Theory of PhilosophyNazrin SharifNo ratings yet
- Islamic TextilesDocument3 pagesIslamic TextilesAlisha MasonNo ratings yet
- LoosDocument52 pagesLoosARIF98ARIF98No ratings yet
- Film Analysis: Munafik 2 and Why It Was a SuccessDocument12 pagesFilm Analysis: Munafik 2 and Why It Was a SuccessSiti RuzanaNo ratings yet
- Cheong LaitongDocument28 pagesCheong LaitongNur IntanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 Definition, Concept and Creative ProcessDocument67 pagesLECTURE 1 Definition, Concept and Creative ProcessFaizFitri2415% (13)
- EDU 701 Term Paper Nabila Hanis 2018617236Document8 pagesEDU 701 Term Paper Nabila Hanis 2018617236Nabila HanisNo ratings yet
- Patrick NG Kah OnnDocument2 pagesPatrick NG Kah OnnNie Shirly0% (3)
- Chapter 18 PDFDocument53 pagesChapter 18 PDFMencam AsongNo ratings yet
- Name: Nur Amalina Syahirah Binti Mohamad NO MATRIC: 2018222866 Class: Ad242 4A Subject: RMD 577Document4 pagesName: Nur Amalina Syahirah Binti Mohamad NO MATRIC: 2018222866 Class: Ad242 4A Subject: RMD 577Amalina SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Raja Shahriman: Killing Tools, Dancing Warriors: Tools (1994) Signals His Nascent Foray Into The Malaysian Art Scene. byDocument6 pagesRaja Shahriman: Killing Tools, Dancing Warriors: Tools (1994) Signals His Nascent Foray Into The Malaysian Art Scene. byVener JS100% (1)
- The Implementation of The 21st Century Education in Malaysia: A Preliminary Review Perlaksanaan Pendidikan Abad Ke-21 Di Malaysia: Satu Tinjauan AwalDocument6 pagesThe Implementation of The 21st Century Education in Malaysia: A Preliminary Review Perlaksanaan Pendidikan Abad Ke-21 Di Malaysia: Satu Tinjauan AwalNur Azlin IdayuNo ratings yet
- Archiscience Assignment 1Document22 pagesArchiscience Assignment 1Muhammad SyahmizzatNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Artists Ceramic WorksDocument20 pagesMalaysian Artists Ceramic Workssida idaNo ratings yet
- Seating Furniture in Open Spaces and Their Contribution To The Social LifeDocument20 pagesSeating Furniture in Open Spaces and Their Contribution To The Social LifeNur Arief RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Hisham Al BakriDocument21 pagesHisham Al BakriRamsrajNo ratings yet
- Kenyah Bakung Oral Literature PDFDocument57 pagesKenyah Bakung Oral Literature PDFpian100% (1)
- Assignment 1 Ffm124 (Individual)Document4 pagesAssignment 1 Ffm124 (Individual)Muhammad Amjad HanifNo ratings yet
- National Philosophy of Education (FPN) & Philosophy of Teacher Education (FPG)Document18 pagesNational Philosophy of Education (FPN) & Philosophy of Teacher Education (FPG)Yush KipliNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary & Synopsis Sing-To-The-dawnDocument6 pagesChapter Summary & Synopsis Sing-To-The-dawnperagas100% (1)
- Contextualizing The Metaphor of Malay BaDocument18 pagesContextualizing The Metaphor of Malay BaTasneem DeebNo ratings yet
- Taha A - 2009 - Museum in Malaysia Challenges and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesTaha A - 2009 - Museum in Malaysia Challenges and Developmentراحا سليمانNo ratings yet
- Lpe 2501 SCL Worksheet 3 (Week 5-6)Document6 pagesLpe 2501 SCL Worksheet 3 (Week 5-6)AmirahNo ratings yet
- Effective Interview AnswersDocument4 pagesEffective Interview AnswersYAN WENHUI / UPMNo ratings yet
- W14 - Bumiputera Students IssuesDocument31 pagesW14 - Bumiputera Students IssuesRazman RamleNo ratings yet
- WUS101-BUSINESS PLAN FORMAT - English MAC2020Document19 pagesWUS101-BUSINESS PLAN FORMAT - English MAC2020Ahmad Mujahid Che RahimiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.VCS155 The Content and Form - DONEDocument34 pagesLecture 4.VCS155 The Content and Form - DONEMUHAMMAD SYAHIN SAIFULNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4.VCS155 The Content and FormDocument31 pagesLecture 4.VCS155 The Content and FormkkreateNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PDFDocument29 pagesWeek 3 PDFAleyna BorNo ratings yet
- Fashion Evolution 1900-2000Document2 pagesFashion Evolution 1900-2000Za-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- History of Fashion 1900-2000 Timeline - Timetoast Timelines 2Document18 pagesHistory of Fashion 1900-2000 Timeline - Timetoast Timelines 2Za-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Design in Fashion - Purushu ArieDocument18 pagesElements of Design in Fashion - Purushu ArieZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 22 Dec 2019 at 9:20 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 22 Dec 2019 at 9:20 PMZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
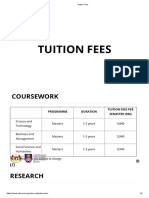
- Tuition FeesDocument2 pagesTuition FeesZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument5 pagesWelcomeCatNo ratings yet
- Fees 29mac2019Document5 pagesFees 29mac2019Anonymous XdMm448cGKNo ratings yet
- Safari - 25 Aug 2019 at 8:22 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 25 Aug 2019 at 8:22 PMZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 25 Aug 2019 at 8:22 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 25 Aug 2019 at 8:22 PMZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Fashion FigureDocument1 pageFashion FigureZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 26 Mar 2019 at 6:24 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 26 Mar 2019 at 6:24 PMZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
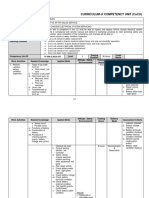
- Curriculum of Competency Unit (Cocu)Document12 pagesCurriculum of Competency Unit (Cocu)Hanif HalinNo ratings yet
- Visual MerchandiserDocument14 pagesVisual MerchandiserZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument5 pagesWelcomeCatNo ratings yet
- Animation - WikipediaDocument14 pagesAnimation - WikipediaZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Music Instrumental Judging FormDocument1 pageMusic Instrumental Judging FormZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- BM 201808Document2 pagesBM 201808Za-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument1 pageHTTPZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Mini ShowDocument3 pagesMini ShowZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Japan Script Roleplay ADT3JADocument2 pagesJapan Script Roleplay ADT3JAZa-c Pelangi Senja100% (4)
- Ujian MarchDocument6 pagesUjian MarchZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Mood BoardDocument7 pagesMood BoardZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
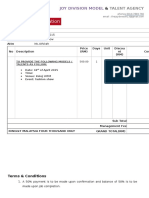
- Joy Division Model Agency Fashion Show QuotationDocument2 pagesJoy Division Model Agency Fashion Show QuotationZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- Presentation by Athirah HamzahDocument17 pagesPresentation by Athirah HamzahZa-c Pelangi SenjaNo ratings yet
- GE11Document2 pagesGE11Ivan BermundoNo ratings yet
- Newburyport Pottery Exhibit Antiques & Auction News November 22, 2019Document1 pageNewburyport Pottery Exhibit Antiques & Auction News November 22, 2019Justin W. ThomasNo ratings yet
- A Critical Evaluation of Public SpaceDocument19 pagesA Critical Evaluation of Public SpaceindianteenvNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 4 - Q2 - W3Document6 pagesDLL - Mapeh 4 - Q2 - W3Divine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Work of Szyk, Whose Romantic Art Glorified 20th-Century Jewry, Comes To BerkeleyDocument4 pagesWork of Szyk, Whose Romantic Art Glorified 20th-Century Jewry, Comes To BerkeleymagnesmuseumNo ratings yet
- Ronnie Renteria: Skills & AbilitiesDocument1 pageRonnie Renteria: Skills & Abilitiesapi-458020266No ratings yet
- BBGC QS RR-302 07 2023 Water ProofDocument7 pagesBBGC QS RR-302 07 2023 Water ProofChikku NiyasNo ratings yet
- Sikagard 905 W IDDocument2 pagesSikagard 905 W IDilhamNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Modern MastersDocument3 pagesTrabajo Modern Mastersmaria torres martinNo ratings yet
- Still Life Drawing TechniquesDocument8 pagesStill Life Drawing Techniquesabuka.felixNo ratings yet
- EAA 384 – Construction Technology of Civil Engineering BuildingDocument65 pagesEAA 384 – Construction Technology of Civil Engineering BuildingArvinthran Raja KumaranNo ratings yet
- James BondDocument2 pagesJames Bondptite_patateNo ratings yet
- Édouard Vuillard: Family GuideDocument20 pagesÉdouard Vuillard: Family GuideLucianoCRPNo ratings yet
- Understanding the ArtsDocument24 pagesUnderstanding the ArtsИванNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Daily ScheduleDocument2 pagesKindergarten Daily ScheduleEstiErnawatiNo ratings yet
- Dissociation + RadioheadDocument15 pagesDissociation + RadioheadFennelstratocasterNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Roachs Introductory Clinical Pharmacology 10th Edition by Susan M Ford MN RN Cne Sally S RoachDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Roachs Introductory Clinical Pharmacology 10th Edition by Susan M Ford MN RN Cne Sally S Roachgainerhanukkah.zv28wx100% (42)
- 300nb Fire Water Line - BEEL - 071953Document2 pages300nb Fire Water Line - BEEL - 071953irshadiiitNo ratings yet
- Walkhtrough Chrono CrossDocument306 pagesWalkhtrough Chrono Crossfiqar_xixNo ratings yet
- LubezkiDocument9 pagesLubezkiPeter Hearn100% (1)
- Family and Friends 2nd Edition 6 Tests Answer KeyDocument7 pagesFamily and Friends 2nd Edition 6 Tests Answer Keydime dimeNo ratings yet
- Weekly Lesson Plan Cross Curricular Four Years Old Sample Unit 5Document7 pagesWeekly Lesson Plan Cross Curricular Four Years Old Sample Unit 5Cristina MihuNo ratings yet