Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Creation and Management of Competitive Advantage
Uploaded by
Ishaan TalwarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Creation and Management of Competitive Advantage
Uploaded by
Ishaan TalwarCopyright:
Available Formats
The Creation and Management of
Competitive Advantage
NEXT 3 Weeks
We will cover the internal and external analysis and
apply to Aldi
You should read about the relevant
models/frameworks and apply them to Aldi
Key Models
Value Chain Analysis
Porters five force model
12 Ps
4Cs
Mix map Model
Plc/Bcgm
Pest
Swot/Tows
McKinsey Matrix
Ansoff
Achieving competitive advantage
How can the business continue to survive or grow ?
How do the resources deliver profits?
Which resources enable the organisation to compete
i.e. Value added &
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Recognizing a firms core competences is
required if it is to make rational strategic
decisions
With an understanding of its external
environment it will drive the selection of
strategies
An inside- out approach.
Based on what we have got!
And. What we believe we can do.
Relative to competition
Pressures on marketing
Basic positioning options
Porters Generic Strategies
Cost/Price Leadership Differentiation
Differentiation Focus Cost/Price Focus
Sector of
Market
Whole Market
Distinct
Product
Lower Price
Strategic Advantage
Strategic
Target
Cost/Price Leadership
Lower prices than competition
Costs lower than competition
Often standardised commodity goods (hard to
differentiate)
Lower Costs enabled via economies of scale
Likely to require/result in large market share
Relies upon customers being price elastic
Normally used at latter stages of market/product
life cycle
Differentiation
Make products/services different to those of
competitors
Relies on customers perceiving and valuing their differences
Accepted by and recognised by whole market
Requires substantial investment in innovate
practices, R&D and marketing to inform the
customers of its differences.
Focus
Focus firms efforts on narrow sector of market-
niche/segment
Can be differentiated
Can be Cost/Price led (But can economies of scale
be developed?)
Example of strategic Group analysis
Firms
stuck in the middle
Winning
Cost Leader
Failing
Cost leader
Successful
Differentiators
Mixed Differentiation
Failing
Differentiators
Profitability
(Return on assets)
Cost Leadership
Generic Strategy
INTERNAL POSITIONING
Assumption - creating competitive advantage
- need for investment in physical and human
resources
- need to manage interface between internal
environment, technology and people
- opportunity through adaptability; lower costs;
product quality; enhanced service.
Components of Internal analysis leading to Competitive advantage,
Lynch 2000;Hitt 2001,
Resources
Tangible
Intangible
Capabilities
Strategic
Competitiveness
Competitive
Advantage
Discover Core
Competences
Competences
Value Chain
Analysis
7 Criteria of
Sustainable
Advantages
Tools
available
Capabilities
The firms ability to deploy resources effectively
Enable the firm to create and exploit external
opportunities and develop sustained advantages
when used with insight and adroitness.
Lengnick-Hall & Wolff 1999
Firms abilities are increasingly being
derived not from things:
But an ability to derive value from knowledge etc.
Increasingly about people
Resources
Critical -customers; competition; resources
Tangible - locations(city centre, airports) size and
facilities; technology (CRS); finance - supply &
quality; people
Intangible - Brand name; quality of people
Labour : capital ratio - productivity
Contribute to Adding value - inputs-process-
outputs
Core Competences
Manage current ones
Create new ones
current ones will be eroded
Not inherently valuable
Must manage and control to create value and
Competitive Advantage
Important to identify those that are core and those that
are not (just competences)
Establishing a Core Competence agenda
Premier plus 10
What new core
competencies will we need
to build to protect and
extend our franchise in
current markets?
Meg-opportunities
What new core
competencies will we need
to build to participate in
the most exciting markets
of the future?
Fill in the blanks
What is the opportunity to
improve our position in
existing markets by better
leveraging our existing
core competencies?
White Spaces
What new products or
services could we create
by creatively redeploying
or recombining our current
core competencies?
Existing
Existing
New
New
Market
Core
Competence
Source: Hill C. W., Jones G. R. (2002, pp354)
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Is achieved when firms implement a value-
creating strategy that is grounded in their own
unique resources, capabilities and core
competencies. Vignali et al., (2008)
The key issue in strategy research-Rouse 1999
The basic notion behind strategy is that a
successful, high performing business requires a
distinctive (or core) competence or competitive
advantage. Hooley et al., (2011)
Continuous development of Competitive
advantage is required
CRITERIA OF SUSTAINABLE ADVANTAGES
Core competences are a firms source of
competitive advantage
Competitive Advantage is also a function of its
relative resource uniqueness (sustainability)
Acquired resources; innovative capability;
competitiveness; substitutability;
appropriability; durability; imitability
About creating value (perceived or real)
Value- The creation and management of..
Performance characteristics and attributes for which
customers are willing to pay
Created by exploiting core competences
Firms use strategy to create value for customers
Continuously
Throughout the firm
Value will be duplicated over time
Must continually seek new value
A relative concept
Adding Value?
The key goal of strategy
The outputs are considered to be worth more than
the cost of the inputs to operationalise the delivery.
Value management is about maximising value
addition, which results in profit maximisation.
Identifying Value/Potential Value
The value chain - an attempt to identify key
activities within the organisation, their
relationships and how the creation of core
competence's (skills/knowledge) deliver
synergistic benefits.
The flow of products and services within the
organisation - the chain or links between primary
and secondary activities.
Add it as cheaply as possible and capture the value
The Value Chain
Before the service establishment - the supply
chain- control, sourcing, frills or not.
Inside the service establishment - stocks, labour,
culture, work in progress,
Delivery process- scheduling, labour costs,
overheads, techniques/procedures, repair &
maintenance
Service delivery and after - finished experience,
complaint handling, relationship marketing.
Use to determine where the firm has the potential
to create and capture value
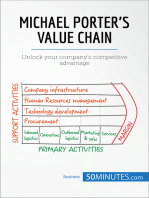
Firm infrastructure
Human resource management
Technology development
Procurement
Inbound
logistics
Operation Outbound
logistics
Marketing &
sales
Service
margin
Primary Activities
Support
Activities
The Value Chain
Adopted from
Porter M. 1985
R&D
Production
Outputs
Summary
Operations take time to plan/build and change can be
difficult.
Analysis is often around how to add value, internally (value
chain) and externally (supply chain)
influenced by identification of CSFs, resource utilisation, core
competences, technologies, global behaviour, cost
management.
Adapt products/services to customer needs
deliver better services than competitors
enhance performance or quality
cut costs
But - will service quality rely on humans - training/dev!
Workshop Activity 1 :Choose an organization of your
choice and answer the following (35mins)
1. Core Competences identify the organization's
core competences ?
2. Why are they core ?
3. How can their advantage be preserved?
4. What are the Critical Success Factors?
5. What evidence is there of unique resource
utilisation (7 elements Lynch pp280-282)
6. What impact do these have on the Value chain
and value system ?
Workshop Activity 2 :Read the assessment case and
apply the following to Lidl (40mins)
1. Core Competences identify the organization's
core competences ?
2. Why are they core ?
3. How can their advantage be preserved?
4. What are the Critical Success Factors?
5. What evidence is there of unique resource
utilisation (7 elements Lynch pp280-282)
6. What impact do these have on the Value chain
and value system ?
Workshop Activity 3 (30mins)
1. Read the chapter on Value Chain Analysis which
has been applied to Zara. Now apply the value
chain to Lidl
For Next Week
Complete workshop tasks 2 & 3 using information
from published sources. Each group should prepare
2 PowerPoint slides to present this information
ready for discussion next week
You might also like
- S & EPM Unit 2Document30 pagesS & EPM Unit 2SaikatPatraNo ratings yet
- Strategic Capabilities and Competitive Advantage: Question of ValueDocument6 pagesStrategic Capabilities and Competitive Advantage: Question of ValueGummadi Banu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Prelim Topics BM 2Document32 pagesPrelim Topics BM 2ME ValleserNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Chapter1Document30 pagesStrategic Management Chapter1Arshad BashirNo ratings yet
- MKTG Env AnalysisDocument39 pagesMKTG Env AnalysisRajvi SoniNo ratings yet
- M Strategy2Document18 pagesM Strategy2Mohammad AlfatehNo ratings yet
- SMBP - Compre - Main PointsDocument25 pagesSMBP - Compre - Main PointsRahul RNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Strategic Position-Strategic CapabilityDocument28 pagesTopic 4 Strategic Position-Strategic CapabilityDumisani NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies and Capabilities-2Document33 pagesCore Competencies and Capabilities-2Ranjith PNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Competitive AdvantageDocument49 pagesSustainable Competitive AdvantageakashniranjaneNo ratings yet
- Resources and CapabilitiesDocument12 pagesResources and CapabilitiesKeith NavalNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage Version2Document20 pagesCompetitive Advantage Version2Kathita GoelNo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL PROCESSES FOR STRATEGIC EXCELLENCEDocument48 pagesMANAGERIAL PROCESSES FOR STRATEGIC EXCELLENCEVasundhara KediaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management 3-4Document16 pagesStrategic Management 3-4Semih EminiNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument60 pagesCompetitive AdvantageFibin Haneefa100% (1)
- Strategy Samenvatting: Powerpoint 3Document10 pagesStrategy Samenvatting: Powerpoint 3Boyan SasNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Strategic Marketing ManagementDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Strategic Marketing Managementayesha zafirNo ratings yet
- PARTS AnalysisDocument6 pagesPARTS AnalysisAshish BhakuniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Business StrategyDocument43 pagesLecture 3 - Business StrategyTsegaye TamratNo ratings yet
- The Core Competence of The OrganizationDocument27 pagesThe Core Competence of The OrganizationKriti UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Organizational Strategy Organizational Design, Competences and TechnologyDocument42 pagesOrganizational Strategy Organizational Design, Competences and TechnologyPrashant NarulaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: The Strategy ConceptDocument16 pagesStrategic Marketing: The Strategy ConceptRoshan DhopariNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument27 pagesCompetitive Advantagekiranaisha100% (1)
- RESOURCES ! Entrepreneurial Processes ! STRATEGIC POSITIONING ! Innovative Strategies Development ! INDUSTRY STRUCTUREDocument7 pagesRESOURCES ! Entrepreneurial Processes ! STRATEGIC POSITIONING ! Innovative Strategies Development ! INDUSTRY STRUCTUREkvakxeNo ratings yet
- Program Doktor Ilmu Akuntansi Universitas Airlangga: Corporate Strategy: A Resource Based Approach (Summary Chapter 1-5)Document20 pagesProgram Doktor Ilmu Akuntansi Universitas Airlangga: Corporate Strategy: A Resource Based Approach (Summary Chapter 1-5)David FelkaiNo ratings yet
- 042 F 613 A 576 e 6 FC 143 B 7Document18 pages042 F 613 A 576 e 6 FC 143 B 7Renan VillaceranNo ratings yet
- SWOC Porter Strategies Tech AdvancementDocument4 pagesSWOC Porter Strategies Tech AdvancementSarithaNo ratings yet
- Staffing strategies support business goalsDocument21 pagesStaffing strategies support business goalsKv PraveenNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Competetive StrategyDocument15 pagesSustainable Competetive StrategysaurabhNo ratings yet
- Strategic Options Approaches To Sustainable Competitive AdvantageDocument9 pagesStrategic Options Approaches To Sustainable Competitive AdvantageMukhtar Hussain100% (1)
- Human Resource Management (Competitive Advantage)Document30 pagesHuman Resource Management (Competitive Advantage)Jacob MclaughlinNo ratings yet
- The Internal AssessmentDocument9 pagesThe Internal AssessmentFatimah Binte AtiqNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing: The Strategy ConceptDocument16 pagesStrategic Marketing: The Strategy ConceptVenkatesh VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ORGANIZATIONAL ANALYSIS AND COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGEDocument23 pagesChapter 5 ORGANIZATIONAL ANALYSIS AND COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGEjecille magalongNo ratings yet
- Strategic CompetitivenessDocument28 pagesStrategic CompetitivenessAhmad Abdel WahabNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Assessing The INTERNAL Environment of An OrganizationDocument44 pagesUnit IV Assessing The INTERNAL Environment of An Organizationmacs emsNo ratings yet
- Organisational ResourcesDocument119 pagesOrganisational ResourcesAli AghapourNo ratings yet
- The Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageDocument5 pagesThe Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageHenny ZahranyNo ratings yet
- OF Strategic Planning ConceptsDocument61 pagesOF Strategic Planning ConceptsHarshal NaikNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessDocument31 pagesStrategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessAmmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Internal Environment: Chapter-5Document34 pagesAnalysis of Internal Environment: Chapter-5Farhan Israq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Models Version 2.1 (Last Updated - July 2010)Document24 pagesValue Chain Models Version 2.1 (Last Updated - July 2010)kashalisahNo ratings yet
- Strat MannnnnDocument3 pagesStrat MannnnnKerb6 AngalaNo ratings yet
- Crafting StrategyDocument20 pagesCrafting StrategySameer PatelNo ratings yet
- Competitive Advantage of Information Systems (Porter'S Wheel)Document6 pagesCompetitive Advantage of Information Systems (Porter'S Wheel)JimshegsNo ratings yet
- International Strategic Management Mid 2Document17 pagesInternational Strategic Management Mid 2Md HimelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic Marketing Management: Faisal K. QureishiDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Strategic Marketing Management: Faisal K. QureishiAhmed IhsanNo ratings yet
- Essay - Management of Process & Competitive AdvantageDocument8 pagesEssay - Management of Process & Competitive AdvantageMohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 - Internal Environment AnalysisDocument9 pagesChapter4 - Internal Environment AnalysisNigar Ul SeharNo ratings yet
- Internal Scanning and Organizational AnalysisDocument40 pagesInternal Scanning and Organizational AnalysisJedNur KusayinNo ratings yet
- International Business Strategy & Global ExpansionDocument12 pagesInternational Business Strategy & Global ExpansionduaNo ratings yet
- The Resource Based View of The FirmDocument19 pagesThe Resource Based View of The FirmHassan Bin Shahid50% (2)
- Stratman ReviewDocument9 pagesStratman Reviewleiqiao saturneNo ratings yet
- Module II A Strategy Formulation at The Business LevelDocument35 pagesModule II A Strategy Formulation at The Business Levelmacs emsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Organizational Analysis and Competitive Advantage PDFDocument47 pagesLesson 5 Organizational Analysis and Competitive Advantage PDFLadybellereyann A TeguihanonNo ratings yet
- STM Concepts AnsersDocument8 pagesSTM Concepts AnsersKarthick Nathan ShanmuganathanNo ratings yet
- Core CompetencesDocument9 pagesCore CompetencesTrishna JoshiNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- Michael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageFrom EverandMichael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- EVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESFrom EverandEVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESNo ratings yet
- Lancashire Business School: MK3002 Strategic Marketing Academic Year 2013-14Document11 pagesLancashire Business School: MK3002 Strategic Marketing Academic Year 2013-14Ishaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Organisational CultureDocument18 pagesLec 5 Organisational CultureIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Organisational CultureDocument18 pagesLec 5 Organisational CultureIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Space Allocation in The Retail IndustryDocument16 pagesSpace Allocation in The Retail IndustryIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Store LayoutDocument20 pagesStore LayoutIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- KittyDocument23 pagesKittyIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Strategic ThinkingDocument23 pagesStrategic ThinkingIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Steve JobsDocument23 pagesSteve JobsIshaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Vatavaran 2Document5 pagesVatavaran 2Ishaan TalwarNo ratings yet
- Agile Manufacturing: The Drivers, Concepts and Attributes: Y.Y. Yusuf, M. Sarhadi, A. GunasekaranDocument11 pagesAgile Manufacturing: The Drivers, Concepts and Attributes: Y.Y. Yusuf, M. Sarhadi, A. GunasekaranC BNo ratings yet
- Application Methodology Value Improvement PracticesDocument18 pagesApplication Methodology Value Improvement Practicessopon567No ratings yet
- Professor Dr. Moyassar I.A. Aljoboury QMS ConsultantDocument65 pagesProfessor Dr. Moyassar I.A. Aljoboury QMS ConsultantSolhaNo ratings yet
- IT Leader's Guide to Transforming IVK CorporationDocument7 pagesIT Leader's Guide to Transforming IVK CorporationNada EttanjiNo ratings yet
- About The Baldrige Excellence FrameworkDocument3 pagesAbout The Baldrige Excellence FrameworkRonaldoEtMariannaGuedesNo ratings yet
- SWOTDocument4 pagesSWOTRaine RealNo ratings yet
- Interactive Study Plan AAADocument96 pagesInteractive Study Plan AAAFahad Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Bahria TownDocument18 pagesBahria Townas221167% (3)
- F.20 Polaris & Victory QuestionsDocument3 pagesF.20 Polaris & Victory QuestionsGopiGuniganti0% (1)
- Strategic PlanningDocument27 pagesStrategic PlanningDr. Pooja DubeyNo ratings yet
- Mbis 7Document143 pagesMbis 7Dipesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- TDS - CMS Imperative For OEDocument13 pagesTDS - CMS Imperative For OEBruno TelesNo ratings yet
- Job Design JOB ANALYSISDocument2 pagesJob Design JOB ANALYSISAshish Kumar GwalNo ratings yet
- Zara Case StudyDocument14 pagesZara Case StudyBedlb BeNo ratings yet
- Audit TheoryDocument80 pagesAudit TheoryMarriz Bustaliño TanNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Exam StrategiesDocument2 pagesOperations Management Exam StrategiesAlok Kumar Chaurasia0% (1)
- AP-09 - "Formato Brief - Campaña Publicitaria en Inglés"Document6 pagesAP-09 - "Formato Brief - Campaña Publicitaria en Inglés"Edisleny Ortiz0% (2)
- Hotel HellDocument4 pagesHotel HellHriday AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Summary Selling Today Partnering To Create Value Chapter 1 PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Selling Today Partnering To Create Value Chapter 1 PDFAayush SinhaNo ratings yet
- SGCE - SWOT and Scenario PlanningDocument14 pagesSGCE - SWOT and Scenario PlanningM IsmailNo ratings yet
- Name: Job Title: Division / Unit: Start Date: Separation Date: Total Length of ServiceDocument3 pagesName: Job Title: Division / Unit: Start Date: Separation Date: Total Length of ServiceCassie E. ZernaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions on Strategic ManagementDocument33 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on Strategic ManagementAzeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business ManagementDocument72 pagesIntroduction To Business ManagementHope Ekwensi100% (2)
- Pastaville: An Executive Summary of a Proposed Pasta RestaurantDocument26 pagesPastaville: An Executive Summary of a Proposed Pasta RestaurantBernardd BasaNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 - HutchinsonDocument2 pagesISO 9001 - HutchinsonUğurNo ratings yet
- PPT2 AnsDocument5 pagesPPT2 Anskristelle0marisseNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development Cia IiiDocument12 pagesEntrepreneurship Development Cia IiiEKANSH DANGAYACH 20212619No ratings yet
- Employee Satisfaction at Himalaya Engineering CompanyDocument49 pagesEmployee Satisfaction at Himalaya Engineering CompanymitNo ratings yet
- Pranshu and DiwasDocument1 pagePranshu and DiwasVarunMalik2No ratings yet
- CSR Strategy FormulationDocument20 pagesCSR Strategy FormulationEr Vipul VermaNo ratings yet