Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pronoun Antecedentpowerpoint 100716213357 Phpapp02
Uploaded by
Pratik MehtaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pronoun Antecedentpowerpoint 100716213357 Phpapp02
Uploaded by
Pratik MehtaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pronouns and Antecedents
Review
Pronoun
A word that substitutes for a noun
Types:
Personal Pronouns (specific persons/things): I, me, you, she, her,
he, him, it, we, us, you, them, they
Possessive Pronouns (show ownership): my, mine, your, yours,
her, hers, his, its, our, ours, your, yours, their, theirs
Intensive/Reflexive (emphasize a particular noun): myself, yourself,
himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Relative/Interrogative (used in subordinate clauses): who,
whom,whose, which, that
Demonstrative (identify and point to nouns): this, that, these, those
Indefinite (do not refer to specific person/thing): anything,
everyone, everything, nobody, anyone, all, any, anybody, anything,
both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many,
neither, none, no one, nothing, one, several, some, somebody,
someone, something
Review
Antecedent
Noun that the pronoun is replacing
Examples
Wanda (noun)= She (pronoun)
The students (noun)=They (pronoun)
Driver (noun)=He/She (pronoun)
Elephant (noun)=It (pronoun)
General Rule for Pronoun-
Antecedent Agreement
Antecedent and pronoun must match in
number, person (1st, 2nd, 3rd) and gender.
Singular antecedent (noun)=singular
pronoun
Plural antecedent (noun)=plural pronoun
Examples
Alex (singular 3rd person)= he (singular 3rd person)
Marbles (plural 3rd person)=those (plural 3rd person)
Gender
Male or female
Note about Gender
If you arent sure of the gender of the
antecedent, use she or he,
his/her, him/her as the pronoun
Example: The police officer always carries
his/her badge when on duty.
Things and animals dont have
genderuse it, its to refer to
non-human objects/groups.
Example: The team won its game.
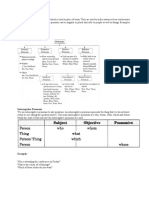
Person
What is it? Singular Plural
1st
Person
Refers to self I, me We
2nd
Person
Person/thing
speaking to
You You
3rd
Person
Someone/
Thing
separate
from you
He, She, It
(or nouns
referring to
he, she, it)
They (or
nouns
referring to
they)
Steps for Determining if Pronouns
and Antecedents Agree
Find the pronouns in the sentence.
Example: Sally went to her boyfriends house, but he
wasnt home.
Decide what nouns the pronouns are referring
to (ie. find the antecedents)
Example: Sally went to her boyfriends house, but he
wasnt home.
Ask yourself What person/number/gender is the
antecedent? Does the pronoun match the
antecedent in number and person?
Example:
Sally (3rd person, singular)=her (3rd person, singular)
Boyfriend (3rd person, singular)=he (3rd person, singular)
Special Cases
Tricky Pronoun-Antecedent
Situations
1) Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronoun=pronoun that does not
refer to specific people or things
For the most part indefinite pronouns are
SINGULAR
EXCEPT
Both, few, some, several (PLURAL)
Ways to Deal with Indefinite
Pronouns
To make an indefinite pronoun and a pronoun
agree (in the same sentence):
Use she/he or his/her with the SINGULAR indefinite
pronoun
Example: In class everyone performs at his or her own fitness
level.
Use they or their with the PLURAL indefinite pronoun
Example: Both of the boys perform at their own fitness level.
Ways to Deal with Indefinite
Pronouns
OR
Make the antecedent a plural noun.
When someone has been drinking, they
are likely to speed. WRONG
When drivers have been drinking, they
are likely to speed. RIGHT
2) Collective Nouns
Collective noun=noun names a class
or group (made up of several
individuals)
They should be considered singular
unless individuals are emphasized
(then plural).
Examples of Collective Nouns:
committee, class, crowd, family
Pronoun-Antecedent
Agreement w/ Collective Nouns
As a unit: (singular)
The committee granted its permission to
build.
Individuals emphasized: (plural)
The committee put their signatures on
the document.
3) EVERY, EACH, ONE
When every, each, or one is
the antecedent, the pronoun should
be singular.
Every student should complete his/her
teachers survey by the end of the week.
Each piece of silverware is in its place in
the drawer.
One of the girls snuck out of her house on
Friday night.
4) Antecedents Joined by
AND
Treat as plural--Make pronoun plural
Jill and John moved to Luray, where they
built a cabin.
Mickey and Minnie live in Disneyland in
their special mouse castle.
5) Antecedents Joined by NOR
or OR or beginning with
NEITHER, EITHER
Make the pronoun agree with the
antecedent nearest to the pronoun
Either Bruce or Tom should receive first
prize for his poem.
Neither the mouse nor the rats could find
their way through the maze.
5) Antecedents Ending in -s
Some antecedents ending in s are
not plural because they focus on just
one itemMake the pronoun
singular
Mathematics, economics
The College of Arts and Sciences
6) Titles of Books, Movies and
Companies
Each of these are singular regardless
of whether the item ends in s or is
joined by AND
The Grapes of Wrath
Romeo and Juliet
Einstein Brothers Bagels
You might also like
- GMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsFrom EverandGMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Pronouns 2Document9 pagesPronouns 2StevenCullenNo ratings yet
- Pronouns - Basic NotesDocument4 pagesPronouns - Basic NotesFrancis Guerrero TimbalNo ratings yet
- PronoundsDocument10 pagesPronoundsAbigail GoloNo ratings yet
- Packet UpdatedDocument70 pagesPacket UpdatedTien Thanh Le,No ratings yet
- 2 Forum InglesDocument4 pages2 Forum InglesRaimundo AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Pronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519Document102 pagesPronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519vivek singhNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument41 pagesPronounsThinagaran GunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument35 pagesTypes of PronounsmakgeolliNo ratings yet
- Pronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01Document41 pagesPronouns 100425004955 Phpapp01Parameswari PerumalNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNSDocument22 pagesPRONOUNSDAYANA ABRIL VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 1N (Remedial English) The Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesENGLISH 1N (Remedial English) The Parts of Speechnaldima06No ratings yet
- Pronoun English Grammar LessonDocument5 pagesPronoun English Grammar LessonProbo SantosoNo ratings yet
- Pronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UyDocument26 pagesPronouns: Refuerzo, Reyes, Santos, UydeniseNo ratings yet
- Pronoun - Types of Pronouns With Useful Examples - Pronouns ListDocument16 pagesPronoun - Types of Pronouns With Useful Examples - Pronouns ListAdelina Elena Ghiuţă100% (1)
- Definition: A Pronoun Is A Word Which Is Used in Place of Noun. They Are Used To Make Sentences Less CumbersomeDocument4 pagesDefinition: A Pronoun Is A Word Which Is Used in Place of Noun. They Are Used To Make Sentences Less CumbersomeBIPUL the otakuNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech GomezDocument25 pagesParts of Speech GomezsingcosweindinglasaNo ratings yet
- Lets Learn PronounsDocument3 pagesLets Learn PronounsAllen AdrienNo ratings yet
- Week No 2 PronounsDocument32 pagesWeek No 2 PronounsMuhammad Nouman YasinNo ratings yet
- English Proficiency ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Proficiency ReviewerlenNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument18 pagesParts of SpeechAlee ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Pronoun English Grammar LessonDocument6 pagesPronoun English Grammar LessonLee mardenNo ratings yet
- Complementary Help in English (Advance & Intermediates)Document32 pagesComplementary Help in English (Advance & Intermediates)halconfenixNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument6 pagesPronounsMark VargasNo ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument11 pagesTypes of PronounsReynaldo Aluyen Guinoden Jr.No ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument6 pagesTypes of NounsVan Angel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eight Parts of SpeechDocument70 pagesEight Parts of SpeechHector ZarateNo ratings yet
- Nish-Handouts 2 (Long 2 Copies)Document4 pagesNish-Handouts 2 (Long 2 Copies)Souma MagarangNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns: Demonstrative PronounsDocument12 pagesTypes of Nouns: Demonstrative Pronounsanon_132777102No ratings yet
- PronounDocument4 pagesPronounmohammadadan424No ratings yet
- Types of PronounsDocument5 pagesTypes of PronounsImran SiddNo ratings yet
- A Pronoun Is Defined As A Word or Phrase That Is Used As A Substitution For ADocument3 pagesA Pronoun Is Defined As A Word or Phrase That Is Used As A Substitution For Astar sawalNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - S1 - PronounsDocument12 pagesWeek 2 - S1 - PronounsTechnical InformationNo ratings yet
- Eng Mod1Document26 pagesEng Mod1Tivar VictorNo ratings yet
- A Noun Is A Word Used As The Name of A PersonDocument18 pagesA Noun Is A Word Used As The Name of A PersonSharib SheraziNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument5 pagesPronounzk4039271No ratings yet
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Document47 pagesUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderNo ratings yet
- Pronoun S: - Words That Take Place of or Stand For The Noun PhraseDocument38 pagesPronoun S: - Words That Take Place of or Stand For The Noun PhraseChie ChieNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument15 pagesParts of SpeechBEO.Teacher ChuNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeachDocument6 pagesParts of Speachnavadeep149No ratings yet
- The Tell-Tale Heart 0Document12 pagesThe Tell-Tale Heart 0Lore JimenezNo ratings yet
- 10 Kinds of Pronouns in EnglishDocument5 pages10 Kinds of Pronouns in EnglishRizal TambunanNo ratings yet
- Eng Worksheet Grammar 2Document12 pagesEng Worksheet Grammar 2Neha KalraNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument64 pagesEnglishjohnedward.gerondioNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument15 pagesSpeechMahboob RiazNo ratings yet
- TKT GrammarDocument36 pagesTKT GrammarJairen RiosNo ratings yet
- Pronoun: What Is A Pronoun?Document4 pagesPronoun: What Is A Pronoun?Retno Dhini LarasatiNo ratings yet
- CS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFDocument25 pagesCS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFMark Anthony CasupangNo ratings yet
- Eight Parts of SpeechDocument69 pagesEight Parts of Speechhector zarateNo ratings yet
- Subject PronounsDocument25 pagesSubject PronounsSirikan SriwisanNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument45 pagesParts of SpeechVitaManiezt100% (3)
- Grammar Review II (Eng 101)Document25 pagesGrammar Review II (Eng 101)Gloria RamosNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument3 pagesPronounsredouanestudiesNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar RulesDocument12 pagesBasic Grammar RulesJose HernandezNo ratings yet
- 10 Kinds of PronounsDocument3 pages10 Kinds of PronounsCOMPRA CLOVIN MARI P.No ratings yet
- 2nd LectureDocument71 pages2nd LectureRAjeSh YadaV100% (1)
- The Eight Parts of Speech FiDocument31 pagesThe Eight Parts of Speech Fiagnes n. marquez100% (1)
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraDocument34 pagesGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyDocument18 pagesParts of Speech Rejoice & Happy After Seeing This Type of Late ST TechnologyKrishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nouns, Verb, Adjective FullDocument5 pagesNouns, Verb, Adjective FullIbnu ShinaNo ratings yet
- SecuritisationDocument28 pagesSecuritisationPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Abbott Piramal Merger: Abbott Laboratories Bought Piramal Healthcare Ltd.'s Branded GenericDocument4 pagesThe Abbott Piramal Merger: Abbott Laboratories Bought Piramal Healthcare Ltd.'s Branded GenericPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Attitudes Perception For 25th OctDocument25 pagesAttitudes Perception For 25th OctPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Group - 2: - Shruti Vyas - 6 - Priyanka SardaDocument41 pagesGroup - 2: - Shruti Vyas - 6 - Priyanka SardaPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Banking IndustryDocument29 pagesThe Banking IndustryPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Rules On Subject-Verb Agreement: A Powerpoint Presentation by Mrs. Suzette P. BalgosDocument18 pagesRules On Subject-Verb Agreement: A Powerpoint Presentation by Mrs. Suzette P. BalgosPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- India's Pattern On DevelopmentDocument70 pagesIndia's Pattern On DevelopmentPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Booker Prize Winners ListDocument3 pagesBooker Prize Winners ListPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- 100 Quant Facts Every CAT Aspirant Must KnowDocument8 pages100 Quant Facts Every CAT Aspirant Must Knowkumar5singhNo ratings yet
- Phenomenon of LightDocument5 pagesPhenomenon of LightPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Black BookDocument148 pagesBlack BookPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Phenomenon of LightDocument5 pagesPhenomenon of LightPratik MehtaNo ratings yet
- Voca-Book (Good Will Hunting)Document25 pagesVoca-Book (Good Will Hunting)Анастасия ВознесенскаяNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Scientific WritingDocument1 pageCharacteristics of Scientific WritingMuhammad HaikalNo ratings yet
- Eng 8 (3RD Quarter Exam)Document3 pagesEng 8 (3RD Quarter Exam)Chiclette GanganNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 14, Clase I, Ingles IIIDocument5 pagesCapitulo 14, Clase I, Ingles IIIXzpita12No ratings yet
- Resume The English Material Conjunction: 1. Coordinating ConjunctionsDocument7 pagesResume The English Material Conjunction: 1. Coordinating ConjunctionsNina AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Syntax Tree Diagram in Japanese Tree Diagram in Japanese From Deep StructureDocument94 pagesDokumen - Tips - Syntax Tree Diagram in Japanese Tree Diagram in Japanese From Deep StructureAdisaka M HendiyantoNo ratings yet
- Sentence PDFDocument2 pagesSentence PDFLicense Sure ReviewersNo ratings yet
- 50 Regular VerbsDocument5 pages50 Regular VerbsIkhwan ZamanNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 8 - Q1 - Mod2 - Coping With The New Normal PDFDocument14 pagesENGLISH 8 - Q1 - Mod2 - Coping With The New Normal PDFMarilou Cabadonga67% (3)
- Present Perfect Continuous - With JessicaDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous - With JessicaMely Del RealNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice Theory and Practice Upper Intermediate AndadvancedDocument15 pagesThe Passive Voice Theory and Practice Upper Intermediate AndadvancedJabiportu100% (3)
- Cls.a 10-A A - Mission L1Document2 pagesCls.a 10-A A - Mission L1Alina AnghelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Kinds of VerbsDocument13 pagesLesson 3 - Kinds of VerbsĐỗ Công TrìnhNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Exercises - Past and FutureDocument2 pagesPassive Voice Exercises - Past and FutureRickson HernandezNo ratings yet
- English 9 - Unit 14 - Lesson 2 - Types of VerbalsDocument24 pagesEnglish 9 - Unit 14 - Lesson 2 - Types of VerbalsMaria Liza CuetoNo ratings yet
- Explaining The Difference Between "AS" and "LIKE"Document7 pagesExplaining The Difference Between "AS" and "LIKE"Abu bakar AwanNo ratings yet
- Tired of Not Getting Band 4 On TKT?Document117 pagesTired of Not Getting Band 4 On TKT?Anonymous HAIBhtNo ratings yet
- English Literature Module: Prepositional PhrasesDocument8 pagesEnglish Literature Module: Prepositional PhrasesNadya Ilmi HanifaNo ratings yet
- Infinitive, Gerund, and ParticipleDocument15 pagesInfinitive, Gerund, and ParticipleCOSTELNo ratings yet
- Stage 35 Grammar PowerpointDocument11 pagesStage 35 Grammar PowerpointJoseph GibbsNo ratings yet
- SAT Intensive Course - Grammar Lesson 1Document17 pagesSAT Intensive Course - Grammar Lesson 1Belinda Filippelli Whittaker100% (1)
- Virginia Tufte Syntax As StyleDocument26 pagesVirginia Tufte Syntax As Styleshami12100% (3)
- A Guide To English GrammarDocument157 pagesA Guide To English GrammarOanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MY German Notes: Starke Verben - Strong Verbs - A-FDocument8 pagesMY German Notes: Starke Verben - Strong Verbs - A-FSohaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- Theme 6. Adjective: Degrees of ComparisonDocument5 pagesTheme 6. Adjective: Degrees of ComparisonAlla KulynychNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Concordance HANDOUTDocument3 pagesSubject Verb Concordance HANDOUTlvincent7No ratings yet
- Book 01 Chapter IndexDocument26 pagesBook 01 Chapter IndexfzaabaNo ratings yet
- Types and Position of AdverbsFinalDocument15 pagesTypes and Position of AdverbsFinalalzubair alojaliNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesParts of Speech Lesson PlanPlanco Abibiason Bengie Anthony91% (33)
- Clause in Grammar, A Clause Is A Pair of WordsDocument3 pagesClause in Grammar, A Clause Is A Pair of Wordsstephanie456No ratings yet