Professional Documents
Culture Documents
634706883771902500
Uploaded by
Hafiz Abdul WahabOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
634706883771902500
Uploaded by
Hafiz Abdul WahabCopyright:
Available Formats
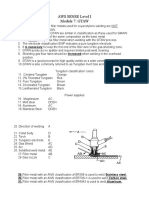
Acidic saline sodic soil ALKALIN
Problem soils
(Chemical)
These soils are called as problem soils
Occur in different parts of India, especially in
the coastal regions of low lying areas.
They contain different proportion of salts
including NaCl. They are harmful and do not
permit normal crop growth.
Resistant Crops like coconut, ragi, rice
(varieties) are cultivated in these soils.
Punjab and Haryana also contain saline and
alkali soil.
Saline soils will have pH <8.5
PROBLEM
SOILS
(physical)
Fluffy
paddy
soils
Sandy
soils
HARD
PAN
Surface
crusted soils
Heavy
textured clay
soils
Acid soil with < 5 pH deficient in Ca, Mg & K
which are leached beyond root zone
Occur in regions with high rainfall
Also deficient in sulphur and boron
Excessive amount of soluble Al, Fe and Mn which
are harmful to plant growth
Also contain toxic amount of copper and zinc.
Deficient in available P as precipated in insoluble
hydroxyl phosphate
Bacteria and actinomycetes will be ineffective and
fungi dominate
Suitable crops : acedophytes potato, rice, tea,
coffee and cotton
Acid soils are characteristically low in pH ( < 6.0). Predominance
of H + and Al3+ cause acidity resulting in deficiency of P, K, Ca,
Mg , Mo and B.
These soils are prevalent in
a) Hilly tracts of Ooty, Kodaikkanal and Yercaud
b) Laterite soils of Pudukkottai, Kanyakumari etc
Application of lime as per the lime requirement test uniformly by
broadcast and incorporation is recommended.
The alternate amendments like dolomite, basic slag, flue dust,
wood ash, pulp mill lime may also be used on lime equivalent
basis.
Lime Requirement (tons of CaCO3/acre)
pH of soil buffer suspension Lime requirement to bring the
soil to indicated pHpH 6.0pH 6.4pH 6.8
Saline soils are characterised by higher amount of
water soluble salt, due to which the crop growth is
affected.
For these soils with electrical conductivity of more
than 4 dS m-1, provision of lateral and main
drainage channels of 60 cm deep and 45 cm wide
and leaching of salts could reclaim the soils.
Application of farm yard manure at 5 t ha-1 at 10 -
15 days before transplanting in the case of paddy
crop and before sowing in the case of garden land
crops can alleviate the problems of salinity.
Sodic soils
Sodic soils are characterised by the predominance of sodium in
the complex with the exchangeable sodium percentage
exceeding 15 per cent and the pH more than 8.5.
Reclamation of sodic soils
Plough the soil at optimum soil moisture regime
Gypsum requirement based gypsum application
Impound water
Provision of drainage for leaching out the soluble salts
In situ incorporation of green manure at 5 t ha-1
The ESP > 15% and the pH between
8.5 -10
Leaching of saline alkali soil in the
absence of Gypsum in soil leads to
formation of alkali soil
NaOH formed due to hydrolysis
dissolves the OM present in the soil
and dispersed
and is deposited on the surface by
evaporation causing darkening of the
soil called as black alkali
They are characterised by low bulk density
of the topsoil resulting in the sinking of
farm animals and labourers as well as
poor anchorage to paddy seedlings.
Such soils can be reclaimed by, passing of
400 kg stone roller or oil drum with sand
inside eight times when the soil is in semi
dry condition along with addition of lime @
2t ha-1 once in three years.
The size of the particles are the largest. It is
granular and consists of rock and mineral
particles that are very small. The texture is
coarse. It is easier to cultivate if the soil is rich in
organic material but either it might quickly drain
water out, resulting in dehydrating of the plants
in summer or too wet in winters and rainy
season. Sandy soil is composed of 60-70%
sand, 20-25% silt and 10-15% clay.
7. Hard pan soils
Hard pan occurs in red soil areas below 15 cm depth due to the
movement of clay and iron hydroxides and settling at shallow
depth, preventing the root proliferation.
These soils can be reclaimed by
Chiselling the soils with chisel plough at 0.5 m interval first in one
direction and then in the direction perpendicular to the previous
one, once in three years.
Application of FYM or composted coir pith at 12.5 t ha-1could
bring additional yield apart from getting longer residual effect.
The soils are weakly aggregated soil structure are
easily broken by the impact of rain drops resulting in
the formation of clay crust at the soil surface.
The clay pan prevent the emerging seedlings and
arrest the free exchange of gasses between the soil
and atmosphere
Heavy textured clay soils
Soils containing major amounts of clay resulting in
the poor permeability and nutrient fixation
Surface crusted soils
The soils having weakly aggregated soil structure are easily
broken by the impact of rain drops resulting in the formation of
clay crust at the soil surface.
The clay pan prevents the emerging seedlings and arrest the free
exchange of gases between the soil and atmosphere.
The surface crust can be easily broken by harrowing or cultivator
ploughing.
Surface crust formation can be prevented by improving the
aggregate stability by the application of lime or gypsum at 2 t ha-
1 and FYM at 12.5 t ha-1.
Retaining crop residues on the surface as a protective cover.
Heavy textured clay soils
The clay soils are containing major amounts of clay fraction
resulting in the poor permeability and nutrient fixation.
Such soils can be reclaimed by
Addition of river sand at 100 t ha 1.
Managed by deep ploughing the field with mould board plough or
disc plough during summer to enhance the infiltration and
percolation.
Low permeable black soils
Application of 100 cart loads of red loam soil.
Deep ploughing the field with mould board plough or disc plough
during summer enhances the infiltration and percolation .
Application of FYM , composted coir pith or pressmud at 25 t ha-
1 per year will improve the physical properties and internal
drainage of the soil
Application of tank silt or black soil at 25 t
ha-1 per year along with FYM , composted
coir pith or pressmud at 25 t ha-1.
Deep ploughing the field with mould board
plough or disc plough during summer to
improve the water holding capacity of the soil
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- CompetenciesDocument1 pageCompetenciesHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Item list with part details for various vehiclesDocument18 pagesItem list with part details for various vehiclesHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Land Reforms Act, 1977Document13 pagesLand Reforms Act, 1977Awami Awaz Sunday MagNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Revenue Recovery Act, 1890Document6 pagesRevenue Recovery Act, 1890Haseeb HassanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Profile Member BalochistanDocument1 pageProfile Member BalochistanHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Revised Syllabus CE-2016 10 Jul 2015Document158 pagesRevised Syllabus CE-2016 10 Jul 2015Muhammad Faisal TahirNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Land Dispositions Saving of Shamilat Ordinance 1959Document3 pagesLand Dispositions Saving of Shamilat Ordinance 1959Haseeb HassanNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Profile Member PunjabDocument1 pageProfile Member PunjabHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Land Acquisition Act 1894Document25 pagesThe Land Acquisition Act 1894Shahid Jamal TubrazyNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Abolition of Jagirs Act, 1952Document3 pagesAbolition of Jagirs Act, 1952Haseeb HassanNo ratings yet
- Political and Administrative Structure of Local Bodies in Pakistan A Case Study of City District Government FaisalabadDocument15 pagesPolitical and Administrative Structure of Local Bodies in Pakistan A Case Study of City District Government FaisalabadMuhammad Ahmad WarraichNo ratings yet
- Punjab Civil Administration Ordinance 2016Document10 pagesPunjab Civil Administration Ordinance 2016Hafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 27361pay Revision RulesDocument136 pages27361pay Revision Rulesguddu_bhai100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Advertisement 27-7-2016Document9 pagesAdvertisement 27-7-2016Hafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- 1777 FullDocument37 pages1777 FullHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 02Document10 pages02Hafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 016788099290151Z Main PDFDocument26 pages1 s2.0 016788099290151Z Main PDFHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Saline Agriculture: Promises and Prospects For Future Agriculture in Degraded Saline LandsDocument8 pagesSaline Agriculture: Promises and Prospects For Future Agriculture in Degraded Saline LandsHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Saline Agriculture: Promises and Prospects For Future Agriculture in Degraded Saline LandsDocument8 pagesSaline Agriculture: Promises and Prospects For Future Agriculture in Degraded Saline LandsHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- JH student paper submission analysisDocument10 pagesJH student paper submission analysisHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Giri Et AlDocument6 pagesGiri Et AlHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- 71 Potassium Dynamics in The SoilDocument12 pages71 Potassium Dynamics in The SoilHafiz Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Recycling of Pad-Batch Washing Textile Wastewater Through Advanced Oxidation Processes and Its Reusability Assessment For Turkish Textile IndustDocument7 pagesRecycling of Pad-Batch Washing Textile Wastewater Through Advanced Oxidation Processes and Its Reusability Assessment For Turkish Textile IndustGizem D.No ratings yet
- Comenius - CodDocument13 pagesComenius - CodsridharancNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Reservoir Drive Mechanisms PDFDocument28 pagesReservoir Drive Mechanisms PDFWassef MB100% (1)
- Tea Processing: How Leaves Become Black Tea in 4 StepsDocument27 pagesTea Processing: How Leaves Become Black Tea in 4 StepsSaidur Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, Mathematics & Physics: All India Internal Test SeriesDocument15 pagesChemistry, Mathematics & Physics: All India Internal Test Seriesmadhav aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 4Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise 4dennise reyesNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Lab 6-The Silver GroupDocument6 pagesLab 6-The Silver Groupsteph002100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Gas Flowmeters For Permanent Installation in Hazardous AreasDocument31 pagesUltrasonic Gas Flowmeters For Permanent Installation in Hazardous AreasrudrakrNo ratings yet
- Rongalit ST LiqDocument11 pagesRongalit ST LiqMayank DhawanNo ratings yet
- Mech-HT 15.0 WS05 SolenoidDocument16 pagesMech-HT 15.0 WS05 SolenoidAndres Felipe Salas VillalvaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rate of EvaporationDocument22 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of EvaporationShimnu MoneNo ratings yet
- 2 MS ElectrochemistryDocument7 pages2 MS ElectrochemistrysachinNo ratings yet
- Lobo and Evans PDFDocument6 pagesLobo and Evans PDFSong HoeNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Liquid Oxygen BleachDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of Liquid Oxygen BleachSingh GurleenNo ratings yet
- Airborne Oil and Gas TCP Flowline Brochure 2017Document4 pagesAirborne Oil and Gas TCP Flowline Brochure 2017Aaron Vazquez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Applied Physics, Sem-1, BS-105Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Applied Physics, Sem-1, BS-105Kartik AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics-Rayleigh FlowDocument26 pagesGas Dynamics-Rayleigh FlowRahul100% (4)
- Chapter 11 Physical and ChemicalDocument49 pagesChapter 11 Physical and ChemicalJJ Almagro100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 12 Amadi TEOP Master-Ed2013-14 PDFDocument25 pages12 Amadi TEOP Master-Ed2013-14 PDFluis_seczonNo ratings yet
- UOP Polybed PSA System For Gas Extraction PurificationDocument2 pagesUOP Polybed PSA System For Gas Extraction PurificationchemiafNo ratings yet
- Convection and Conduction Heat TransferDocument406 pagesConvection and Conduction Heat Transfertfemilian100% (2)
- Air PollutionDocument2 pagesAir PollutionBarani KingNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange PDFDocument18 pagesIon Exchange PDFSarah LimaNo ratings yet
- Aws Gtaw Study GuideDocument2 pagesAws Gtaw Study GuideTouil HoussemNo ratings yet
- XY-6S-10 English ManualDocument28 pagesXY-6S-10 English ManualShishir Kumar100% (1)
- Polymer CharacterizationDocument29 pagesPolymer CharacterizationCarlos Miguel Dacaimat0% (1)
- 12.elastic ConstantsDocument18 pages12.elastic ConstantsaderancNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document6 pagesExperiment 6Sobana Kanthi33% (3)
- Plasmid Curing in BacteriaDocument3 pagesPlasmid Curing in BacteriaPayel BoseNo ratings yet
- Quantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Document4 pagesQuantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Bezverkhniy VolodymyrNo ratings yet
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet