Professional Documents
Culture Documents
f4 SC Chapter 3
Uploaded by
Jessica StewartOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
f4 SC Chapter 3
Uploaded by
Jessica StewartCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Cells
Chromosomes
DNA Genes
Characteristics
/ traits
Built up of containing
determining
containing
containing
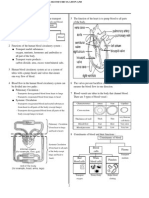
3.1 CELL DIVISION
Chromosomes, genes and DNA
Life cycle and cell division
Mitosis: growth
Meiosis: sexual reproduction
Cik Emy
NUCLEUS
CHROMOSOMES
-threadlike structure
-human beings have 46 (23 pairs
-contain protein and DNA
DNA
-Double helix structure
--Made up of series of genes
GENE
-Segment of DNA
-Genetic codes which
determine an organism
characteristics
Definition:
A cell division process in which a parent cell
(original cell) divides into two identical
daughter cells (new cells)
Occurs in:
Human and animal : somatic cells
Plants: tips of roots and shoots
Chromosomes in the nucleus shorten,
thicken and more visible.
Replication of chromosomes occur.
Each strand of chromosome is called
chromatid.
chromatid
centromere
nucleus membrane
The nucleus membrane forms again.
Two daughter cells are formed.
Each daughter cell has the same number of
the chromosomes as the parent cell.
Spindle fibres emerge.
Chromosomes align themselves in the centre
of the cell.
The nucleus membrane disappears.
Chromatids divide and separate to the
opposite ends of the cell.
At the same time the cell starts to divide.
spindle fibres
Produce new cells for
growth unicellular zygote
to multicellular organism
Asexual reproduction for
simple organism like amoeba
Regenerate body parts
such as lizard grows a
new tail
Vegetative reproduction
such as rhizomes, tubers,
leaves
Produce new cells for
replacing dead
cells/repairing tissues
Definition:
A process in which a nucleus of a parent cell
divides into four daughter cells through two
divisions.
The daughter cells will have half the number of
chromosomes in parent cell.
Occurs in reproductive organs to produce
gametes (ovum and sperms):
Human and animals: testes (male) and ovary (female)
Plants : anthers and ovaries
Chromosomes in the nucleus
shorten, thicken and more visible.
Crossing over and replication
process occur on chromatids.
Meosis 1
Chromosomes align themselves in the
centre of the cell.
The nucleus membrane disappears.
Chromatids separate and move to the
opposite ends of the cell.
The cell begins to divide into two.
Two daughter cells are produced.
The nucleus membrane reforms.
The nucleus membrane is formed again.
Four daughter cells are formed.
Each daughter cell has half of the
number of chromosomes in the parent
cell.
Spindle fibres emerge.
Chromosomes align themselves in the
centre of the cell.
The nucleus membrane disappears.
Chromatids divide and separate to the
opposite ends of the cell.
The cell starts to divide.
Meosis 2
Crossing over
process
Independent
assortment of
chromosomes
(characteristics are separated during
formation of gamete and randomly
combined during fertilization)
1. To produce
gametes
2. To allow
variation
through :
Meiosis
Fertilisation
Mitosis
Male
(46 chromosomes)
Female
(46 chromosomes)
Sperm
(23 chromosomes)
Ovum
(23 chromosomes)
Zygote
(46 chromosomes)
Baby
(46 chromosomes)
SIMILARITIES
Replication
of DNA
takes place
Involves
division of
nucleus and
cytoplasm
Cell division
occurs
DIFFERENCES
MITOSIS MEIOSIS
Replication process
Number of division
Number of daughter
cells produced
Number of
chromosomes in
daughter cell
Combination of gene
Occur
One only
Four
Same as in parent cell
Same as parent cell
Occur in the first
division
Two times
Two
Half of parent cell
Different from parent cell
Crossing over process Does not occur Occur
3.2 THE PRINCIPLES AND MECHANISM OF
INHERITANCE
Gene
Exist in pair
Dominant gene
-A gene which expresses the trait
when paired with a dominant or
recessive gene
-Denote as capital letter, eg
T (tall)
Dominant trait
Characteristics controlled by
dominant genes
Recessive gene
-A gene which expresses the trait
when paired with a recessive gene
only (in the absence of a dominant
gene)
-Denote as small letter, eg t (short)
Recessive trait
Characteristics controlled by
recessive genes
Chromosomes are in pair. One from the
father while the other one from the
mother.
Same genes:
Dominant gene and
recessive gene are placed
opposite to each other
Homologous chromosomes
t T
Trait Dominant Recessive
Earlobes
Free earlobes
Attached earlobes
Tounge
Ability to roll Inability to roll
Dimples
Presence
Absence
Hair
Curly Straight
Iris colour
Brown Blue
Height
Tall Dwarf
Gregory Mendel was the first person who
discovered the principles of heredity.
Genotype
Phenotype
The genetic information of
an organism
The physical characteristics
of an organism
TT tt
Tall (pure breed) Dwarf (pure breed)
T T t t
T t t T
Tall Tall Tall Tall
Tall Tall Tall Dwarf
Phenotype :
Genotype :
Phenotype :
Genotype :
Phenotype :
Genotype :
F2 Generation
F1 Generation
Gametes
Gametes
T t
T t
T t
T t
T t T t
T T
t t
Key:
Homozygous: both genes are
same
Eg: TT, tt
Heterozygous: genes are
different
Eg: Tt
In the pea plant, the gene for round seed(R) is
dominant to the gene for wrinkled seed(r).
a) If a homozygous round-seeded pea plant is
crossed with a homozygous wrinkled-seeded
plant, what will be the phenotype of F1 plants?
b) If the F1 plants are self-pollinated, what will be
the genotype and phenotype ratios of the F2
plants?
RR rr
Round seed Wrinkled seed
R R r r
Round Round Round Round
Parental Phenotype :
Parental Genotype :
F1 Generation
Gametes
R r
R r
R r
R r
Hence all the F1 plants have round seeds.
a)
Key:
R: round seeded
r : wrinkled seeded
b)
R r r R
Round Round Round Wrinkled
F2 Phenotype :
F2 Genotype :
F1 Generation
Gametes
R r
R r
R r R r
R R
r r
Genotype ratio is 1 RR:2 Rr: 1rr
Phenotype ratio is 3 plants with round seeds : 1 plant with wrinkled seed
B represents the dominant gene for black cat,
and b represents the recessive gene for a
white cat.
What is the phenotype ratio of the number of
black cats to the number of white cats if black
fur cat (Bb) is crossed with another black fur
cat (Bb)?
B b b B
Black Black Black White
F1 Phenotype :
F1 Genotype :
Parents
Gametes
B b
R b
B b B b
B B
b b
Phenotype ratio is 3 black fur cats: 1 white fur cat
Key:
R: black cat
r: white cat
Answer:
In the pea plant, the gene for purple flowers
(P) is dominant to the gene for white flowers
(p). A cross between a heterozygous pea plant
with purple flowers and a homozygous pea
plant with white flowers is done.
What are the genotypes of the offsprings?
P p p p
Purple White Purple White
F1 Phenotype :
F1 Genotype :
Parents
Gametes
P p
p p
p p P p
P p
p p
Genotype ratio is 2 Pp : 2 pp
Key:
Pp: heterozygous , purple flower
pp: homozygous , white flower
Answer:
3.3 SEX DETERMINATION AND THE
OCCURRENCE OF TWINS IN HUMAN BEINGS
Sex chromosomes: the last pair in human chromosomes
Male: 22 pairs of autosomes and a
pair of sex chromosomes XY.
Female: 22 pairs of autosomes and
a pair of sex chromosomes XX.
Sex determination : the sex of baby is determined by
the fathers sperm (XY)
44 + XY 44 + XX
Y
X
Gamete cells:
or
X
Fertilisation
Baby girl
44+XX
Baby boy
44+ XY
44 + XX 44 + XY
22 + X 22 + X
44 + XX 44 + XY
22 + Y 22 + X
44 + XX 44 + XY
Mother
Father
Gametes :
Parents :
Offsprings:
Ratio of daughter : son is 1:1
Therefore , the chance to get daughter or son is 50:50.
Daughter Daughter Son Son
An ovum is fertilised by a
sperm to form a zygote.
Zygote undergoes mitosis
and separates into two to
develop into two embryos.
Genetically identical.
Share the same placenta.
Same sex.
IDENTICAL TWINS
Two different ova fertilised
by two different sperms at the
same time.
Two different zygotes are
formed and develop into two
embryos.
Genetically different.
Each has own placenta.
Same sex or different sex.
Known as fraternal twins.
NON-IDENTICAL
TWINS
IDENTICAL TWINS
NON-IDENTICAL
TWINS
Zygote
undergoes
mitosis
Two
embryos
Foetus
share the
same
placenta
Two ova
are
fertilised
Two different
zygotes are
formed
Two
separate
embryos
Each foetus
has his own
placenta
Siamese twins
Identical twins that are joined at some parts of the
bodies.
Formed when zygote fails to divide completely in
the course of formation.
IDENTICAL TWINS
NON-IDENTICAL
TWINS
Similarities:
The twins are formed in the uterus.
Two babies are formed.
One
One
Same sex
Yes
Same / identical
Yes / sharing placenta
Two
Two
Same or different sex
No
Different
No / separate placenta
Number of sperms
Fertilised ovum splits
into two
Genetic make up
Sharing of placenta
Sex
Number of ova
Differences
3.4 MUTATION
Mutation: the spontaneous change to the
structure of genes or chromosomes
Occurs in
Somatic/body cells
(can be passed down
through mitosis)
Gametes/reproductive
cells
(inherited)
TYPES OF MUTATION
Gene mutation
Change in the structure
of DNA
Chromosome mutation
A change in the number
of chromosomes or in
the structure
Downs syndrome: an extra chromosome in
autosome 21 (47 chromosomes)
Klinefelters syndrome: a male with extra X
chromosome (XXY)
Turners syndrome: a female with one less X
chromosome (XO)
Polyploidy: having one or more chromosomes in
a set of chromosome
Colour blindness: a mutated gene in the X
chromosome
Sickle cell anemia: mutation in gene that
produces haemoglobin; inefficient in transporting
oxygen in the blood
Albinism: the gene for skin colour is mutated;
unable to produce black pigment (melanin)
Haemophilia: mutation in gene that is important
for blood-clotting
Downs syndrome
Additional chromosome at autosome 21.
Physical retardation
Thick neck
Slanted eyes
Protuding tounge
Reduced resistance to diseases
Klinefelters syndrome
A male with extra X chromosomes
(having XXY)
Infertile
Underdeveloped testes
Narrow shoulder
Enlarged breasts
Turners syndrome
A female having one less X
chromosome (XO)
Infertile
Short
Mentally retarded
Has no ovaries
Small breasts
Folded skin on neck
No menstrual cycle
Polyploidy
The number of chromosomes is increased by one
or more sets.
More common in plants.
Colour blindness
Mutant gene (recessive gene) on the X
chromosome.
Not able to differentiate colours
especially green and red
More common in males because male
has only one X chromosome
Albinism
The gene for skin colour is mutated
(recessive gene)
Unable to produce melanin (black
pigment)
White hair
Pink eyes and pinkish skin
Skin is sensitive to sunlight
Sickle-cell anemia
Mutation in gene that produce
haemoglobin
Sickle-cell shaped of red blood cells
Not efficient in transporting oxygen
Facing painful crises such as chest pain,
fatigue, bone pain,
Yellowing of eyes
Inherited from both parents
Haemophilia
Mutation in chromosome X (for blood
clotting)
Have problem in blood clotting
May bleed continuously or for a longer
period
A woman carrier may inherit the
disease to a son
Spontaneous changes
during cell division
Exposure to physical
mutagens: UV radiation,
X-rays, radioactive
radiation
Environmental change: the
change of temperature for a
long period causes genetic
evolution in organism
Exposure to chemical
mutagens: Benzene,
formaldehyde, nicotine,
sodium nitrite, pesticides
Give rise to variation
which leads to
differences in traits
Better chance of
survival when new
species are more
resistant to diseases
Advantages
Cause physical
defects
Causes genetic
diseases
Some chromosome
mutations and gene
mutation are lethal
(fatal)
Causes mental
defects
Disadvantages
3.5 THE EFFECTS OF GENETIC RESEARCH
ON HUMAN LIFE
Gene therapy: to replace
damaged/faulty genes during
the foetal stage
Genetic screening: to predict
diseases likely to develop
Gene test: to screen unborn
children for diseases
Genetic engineering: to
transfer DNA from one
organism to another
Human genome project:
maps all human genes to
determine genes which
causes diseases
Field of Medicine
To produce plants which are
resistant to diseases and
infections
To produce engineered plants
which are able to live in
unfavourable conditions
To produce plants which grow
and mature fast
To produce higher yields
To produce high quality of
crops and livestock
Field of Agriculture
A process which involves cross
breeding and cloning of plants or
animals
Advantages
New varieties with
desired characteristics
can be produced
To produce new and
high quality crops
More resistant to
diseases
Disadvantages
May produce new
varieties with
undesirable
characteristics
Example 1: Cow
is cross bred
with
Friesian Cow Sahiwal Cow
Mafriwal Cow
-Grow faster -Bigger in size
-More milk -High resistant to disease
Example 2: Palm oil
is cross bred
with
Dura
Pisifera
Tenera
-Thick mesocarp and large kennel :much oil
-Thin shell: easier to extract
Thin
mesocarp
Large
kennel
Thick
mesocarp
Small
kennel
A process of cloning a plant by using a
plant part or single cell in a test tube
under a controlled condition
Advantages
To produce many
copies of the same
plants in a short time
To produce plants
anytime we want
Shorter maturation
time
No variation
Disadvantages
Complete wipe-out of
crops if there is spread
of diseases
a) Explant:
b) Multiplication:
c) Transplanting:
The process of producing an organism
that is an exact genetic copy of
another
Process:
Foods from plants and animals which
have had their genetic information
changed by adding genes from
another organisms
Advantages:
For crops: enhanced
taste and quality,
increased yields,
matures faster, better
resistance to diseases,
remain fresh longer
For livestock:
increased resistance
to infections and
diseases, higher yield
of milk, meat and eggs
Cause allergies and side effects to
human beings
Milk of genetically modified animals
may be unsafe
Antibiotic-resistant genes in GM
organisms may be pass on to bacteria;
difficult to kill them
Genetic research is expensive, poor
farmers cannot afford
3.6 VARIATION AMONG LIVING THINGS
Variation:
The differences among individuals
of the same species
Continuous
variation
Discontinuous
variation
-Characteristics among
individuals which do not show
distinct differences
-Quantitative and can be
measured
-Determined by genes and can
be influenced by environmental
factors
-Characteristics among
individuals which show distinct
differences
-Qualitative and cannot be
measured
-Determined by a single gene
and is not influenced by
environmental factors
Continuous
variation
Discontinuous
variation
Height
Skin
colour
Length of
foot
Intelligence
Weight
Earlobes
Iris colour
Colour
blindness
Tongue
rolling
Blood
group
Genetic factors
Crossing over during meiosis: genetic
material is exchanged
Random fusion of male and female
gametes during fertilisations
Chromosome and gene mutation:
creates new phenotypes
Independent assortment of
chromosomes: different gametes
Environmental
factors
Sunlight exposure: will have darker
complexion
Water climate, temperature
pH: the Hydrangea flower is blue in
acidic soil and pink in alkaline soil
Diet: a person who eats a lot will be
fatter
IMPORTANCE
Ensures the survival of a
species under changing
environment
Enable any species
to occupy a wider
range of habitat
Enable natural selection:
species with favourable
characteristics will be
selected by nature
Enable us to
distinguish
individuals of the
same species
CONTINUOUS
VARIATION
DISCONTINUOUS
VARIATION
Similarity:
Show differences in characteristics among
individuals of the same species
Yes
Not distinct
If it is influenced by
environmental factors
cannot be inherited
Two or more genes for
the same character
Quantitative/ can be
measured
No
Distinct
Can be inherited
Single gene
Qualitative/ cannot be
measured
Influenced by
environmental factors?
Inheritance
No of gene
Type of data
Characteristic
Differences
Similarities And Differences Between
Continuous And Discontinuous Variation
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Form 4 Timetable: Subject Time DurationDocument1 pageForm 4 Timetable: Subject Time DurationJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Airway Management 2018 - . - 2Document30 pagesAirway Management 2018 - . - 2Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Approach To Fever and SepsisDocument12 pagesApproach To Fever and SepsisJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- EEB1113 DC7 Mesh&SuperMeshAnalysisDocument13 pagesEEB1113 DC7 Mesh&SuperMeshAnalysisJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Seminar Cover PageDocument1 pageSeminar Cover PageJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- EEB1113 DC8 SuperpositionDocument14 pagesEEB1113 DC8 SuperpositionJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Seminar Abdominal InjuryDocument83 pagesSeminar Abdominal InjuryJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- What Is The Menstrual CycleDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Menstrual CycleJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 1 Cell StructureDocument41 pages1 Cell StructureIra MunirahNo ratings yet
- Trauma Care (ATLS) PICDocument37 pagesTrauma Care (ATLS) PICJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 9780198390183Document14 pages9780198390183Jessica Stewart100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Chap 2 PMR SC EditedDocument2 pagesChap 2 PMR SC EditedJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 0f F FDDocument12 pages0f F FDEnica RichardNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 0610 s16 QP 41Document20 pages0610 s16 QP 41Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Menstruation Is The Shedding of The Lining of The UterusDocument6 pagesMenstruation Is The Shedding of The Lining of The UterusJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- SalpingoDocument1 pageSalpingoJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Sym Physio To MyDocument1 pageSym Physio To MyJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- SalpingoDocument1 pageSalpingoJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case Presentation 3Document4 pagesPediatric Case Presentation 3Ramona Bratu78% (9)
- F3 Chapter 2 - Blood CirculationDocument2 pagesF3 Chapter 2 - Blood CirculationJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Body Coordination NotesDocument4 pagesBody Coordination NotescolorpencilgaloreNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell StructureDocument41 pages1 Cell StructureIra MunirahNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument11 pagesAnatomyJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter3 Chemical FormulaDocument10 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter3 Chemical FormulaAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- 2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersDocument27 pages2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Short Stature.Document77 pagesShort Stature.Jessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Suriati Bt A Rashid100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- APJ Abdul Kalam Success StoryDocument1 pageAPJ Abdul Kalam Success StorySanjaiNo ratings yet
- Essays of Warren Buffett - Lessons For Corporate America by Lawrence Cunningham - The Rabbit HoleDocument3 pagesEssays of Warren Buffett - Lessons For Corporate America by Lawrence Cunningham - The Rabbit Holebrijsing0% (1)
- Blackbook 2Document94 pagesBlackbook 2yogesh kumbharNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection ActDocument34 pagesConsumer Protection ActshikhroxNo ratings yet
- Assignment November11 KylaAccountingDocument2 pagesAssignment November11 KylaAccountingADRIANO, Glecy C.No ratings yet
- Densha: Memories of A Train Ride Through Kyushu: By: Scott NesbittDocument7 pagesDensha: Memories of A Train Ride Through Kyushu: By: Scott Nesbittapi-16144421No ratings yet
- Final - Anarchy One-Sheet Sell SheetDocument2 pagesFinal - Anarchy One-Sheet Sell SheetMaddanie WijayaNo ratings yet
- Solutions DPP 2Document3 pagesSolutions DPP 2Tech. VideciousNo ratings yet
- TechBridge TCP ServiceNow Business Case - Group 6Document9 pagesTechBridge TCP ServiceNow Business Case - Group 6Takiyah Shealy100% (1)
- HangersSupportsReferenceDataGuide PDFDocument57 pagesHangersSupportsReferenceDataGuide PDFIndra RosadiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- National Insurance Mediclaim Claim FormDocument4 pagesNational Insurance Mediclaim Claim FormIhjaz VarikkodanNo ratings yet
- Tata NanoDocument25 pagesTata Nanop01p100% (1)
- Unit-Ii Syllabus: Basic Elements in Solid Waste ManagementDocument14 pagesUnit-Ii Syllabus: Basic Elements in Solid Waste ManagementChaitanya KadambalaNo ratings yet
- The Marriage of Figaro LibrettoDocument64 pagesThe Marriage of Figaro LibrettoTristan BartonNo ratings yet
- 2015 NSPC Proposed Changes Book PDFDocument268 pages2015 NSPC Proposed Changes Book PDFMichelle Pinohermoso JabatNo ratings yet
- Land CrabDocument8 pagesLand CrabGisela Tuk'uchNo ratings yet
- Agenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Document13 pagesAgenda - 2 - Presentation - MS - IUT - Thesis Proposal PPT Muhaiminul 171051001Tanvir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Exclusive GA MCQs For IBPS Clerk MainDocument136 pagesExclusive GA MCQs For IBPS Clerk MainAnkit MauryaNo ratings yet
- PRESENTACIÒN EN POWER POINT Futuro SimpleDocument5 pagesPRESENTACIÒN EN POWER POINT Futuro SimpleDiego BenítezNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Vol 3 - Application) PDFDocument479 pagesPower System Protection (Vol 3 - Application) PDFAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- MegaMacho Drums BT READ MEDocument14 pagesMegaMacho Drums BT READ MEMirkoSashaGoggoNo ratings yet
- 9701 Nos Ps 23Document5 pages9701 Nos Ps 23Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Springs: All India Distributer of NienhuisDocument35 pagesSprings: All India Distributer of NienhuisIrina DroliaNo ratings yet
- Joomag 2020 06 12 27485398153Document2 pagesJoomag 2020 06 12 27485398153Vincent Deodath Bang'araNo ratings yet
- ABBindustrialdrives Modules en RevBDocument2 pagesABBindustrialdrives Modules en RevBMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Oil Gas Accounting International Petroleum Accounting International Petroleum Operations MSC Postgraduate Diploma Intensive Full TimeDocument70 pagesAdvanced Oil Gas Accounting International Petroleum Accounting International Petroleum Operations MSC Postgraduate Diploma Intensive Full TimeMoheieldeen SamehNo ratings yet
- Institutions and StrategyDocument28 pagesInstitutions and StrategyFatin Fatin Atiqah100% (1)
- 1KHW001492de Tuning of ETL600 TX RF Filter E5TXDocument7 pages1KHW001492de Tuning of ETL600 TX RF Filter E5TXSalvador FayssalNo ratings yet
- OBOE GougerDocument2 pagesOBOE GougerCarlos GaldámezNo ratings yet
- Less Homework More TroubleDocument7 pagesLess Homework More Troubleg697a0mw100% (1)