Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orifice Meter
Uploaded by
Nur Dahlia100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views16 pagesAn orifice meter works by placing a restriction (orifice plate) inside a pipe to cause a pressure drop in the fluid flowing through it. Pressure taps upstream and downstream of the orifice plate measure the differential pressure, which correlates to flow rate according to Bernoulli's principle. The flow rate can be calculated based on the pressures, the orifice and pipe diameters, and other parameters. Orifice meters are inexpensive, have predictable characteristics, and can measure flow in large pipes, though they cause more friction loss than some other flow meter types.
Original Description:
powerpoint brief description of orifice meter
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn orifice meter works by placing a restriction (orifice plate) inside a pipe to cause a pressure drop in the fluid flowing through it. Pressure taps upstream and downstream of the orifice plate measure the differential pressure, which correlates to flow rate according to Bernoulli's principle. The flow rate can be calculated based on the pressures, the orifice and pipe diameters, and other parameters. Orifice meters are inexpensive, have predictable characteristics, and can measure flow in large pipes, though they cause more friction loss than some other flow meter types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views16 pagesOrifice Meter
Uploaded by
Nur DahliaAn orifice meter works by placing a restriction (orifice plate) inside a pipe to cause a pressure drop in the fluid flowing through it. Pressure taps upstream and downstream of the orifice plate measure the differential pressure, which correlates to flow rate according to Bernoulli's principle. The flow rate can be calculated based on the pressures, the orifice and pipe diameters, and other parameters. Orifice meters are inexpensive, have predictable characteristics, and can measure flow in large pipes, though they cause more friction loss than some other flow meter types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Flow Rate With Orifice Meter
Background and Theory
Flow meters are used in the industry to measure the volumetric flow
rate of fluids.
Differential pressure type flow meters (Head flow meters) measure
flow rate by introducing a constriction in the flow.
The pressure difference caused by the constriction is correlated to
the flow rate using Bernoulli's theorem.
Rate of discharge from the constriction can be calculated by
knowing this pressure reduction, the area available for flow at the
constriction ,the density of the fluid and the coefficient of discharge
Cd.
What is orifice meter?
Orifice meter is a flow measuring device used for calculating
the pressure drop,flow rate and behaviour of the fluid moving
through the pipe.
What is an orifice meter?
A restriction in a pipe between two pressure taps; by attaching
a pressure gauge the airflow can be determined.
Figure of orifice meter for lab test
Figure of orifice meter in field
Orifice plates and flanges
Description of Orifice Meter
The main parts of an orifice flow meter
are as follows:
A stainless steel orifice plate which is
held between flanges of a pipe carrying
the fluid whose flow rate is being
measured.
The pipe carrying the fluid should be
straight in order to maintain laminar
flow conditions.
Openings are provided at two places 1
and 2 for attaching a differential
pressure sensor (U-tube manometer,
differential pressure gauge etc.) as
shown in the diagram.
Working principles of the orifice
meter
An obstruction (orifice) is placed in a pipe filled with fluid. The
pressure of the fluid is measured at two different points.
At the upstream of the orifice, before the converging of the fluid
takes place, the pressure of the fluid (P1) is maximum. As the fluid
starts converging, to enter the orifice opening its pressure drops.
When the fluid comes out of the orifice opening, its pressure is
minimum (p2) and this minimum pressure remains constant in the
minimum cross section area of fluid flow at the downstream.
The differential pressure sensor attached between points 1 and 2
records the pressure difference (P1 P2) between these two points
which becomes an indication of the flow rate of the fluid through
the pipe when calibrated
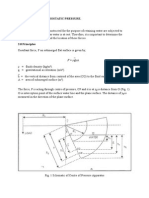
Basic Principle of Orifice Meter
Where,
Qa = Flow rate
Cd = Discharge coefficient
A1 = Cross sectional area of pipe
A2 = Cross sectional area of orifice
P1, P2 = Static Pressures
The orifice plate causes a pressure drop which varies with the
flow rate.
Orifice Plate / Restriction Orifice
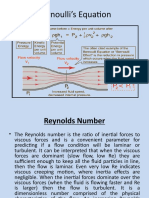
Orifice plate works based on Bernoullis principle.
Bernoullis equation states that pressure drop across the
orifice plate is directly proportional to the volumetric flow rate
passing through the orifice plate.
The main difference between orifice plate and restriction
orifice is their usage. Restriction orifice is used for killing
pressure in a pipe by increasing fluid velocity. Restriction
orifice and orifice plates are similar in structure and both are
based on Bernoullis equation.
What is the Calibration curve of
orifice meter ?
The calibration curve for an orifice meter will
depend on the size of the orifice, the size of
the pipe and the pressure loss over the meter.
Typical calibration curves have pressure (or
head) loss on the vertical (y) axis and flow rate
on the horizontal (x) axis.
Calibration Calculation
C - Orifice coefficient
D1 - Pipe diameter
D - Orifice diameter
P1,P2 - Pressure drop
V - Orifice volume
- density
Applications of Orifice Meter
To measure the flow rate of gases and fluids
The concentric orifice plate is used to measure flow rates of
pure fluids and has a wide applicability as it has been
standardized.
The eccentric and segmental orifice plates are used to
measure flow rates of fluids containing suspended materials
such as solids, oil mixed with water and wet steam.
Orifice Meter
Advantages
It is very cheap and easy method
to measure flow rate.
It has predictable characteristics
and occupies less space.
Can be used to measure flow
rates in large pipes.
Limitations
The vena-contracta length
depends on the roughness of the
inner wall of the pipe and
sharpness of the orifice plate.
In the upstream straightening
vanes are a must to obtain
laminar flow conditions.
Gets clogged when the
suspended fluids flow.
The coefficient of discharge is
low.
Adds on information
Many factors associated with the pipe, orifice and fluid affect the
measurement.
Satisfactory measurement requires steady-state, homogeneous,
turbulent flowing fluids.
Other properties which affect the measurement include: the ratio
of pipe diameter to orifice diameter and the density, temperature,
compressibility and viscosity of the fluid.
Conclusion
The largest contribution to the uncertainty in the measured
coefficient is due to the time measurement.
The main disadvantage of this meter is the greater frictional
loss it causes as compared with the other devices and hence
causes large power consumption.
Within the limit of the experimental uncertainty and the
Reynolds number range investigated, the result obtained for
the discharge coefficient through an orifice plate with the
empirical relation
You might also like
- Orifice MeterDocument15 pagesOrifice Metermurad67% (3)
- Orifice DischargeDocument12 pagesOrifice Dischargehammada1001100% (3)
- Flow Through A Pipe Orifice Meter LabDocument8 pagesFlow Through A Pipe Orifice Meter LabHenDricky MagosiNo ratings yet
- Orifice Plate Flow MetersDocument4 pagesOrifice Plate Flow Metersvilaschinke123100% (2)
- Venturimeter (Discharge Coefficient)Document16 pagesVenturimeter (Discharge Coefficient)saleemdbg76% (21)
- Exp 2 Friction LossesDocument15 pagesExp 2 Friction LossesDonna Mae Ramos Galaez0% (1)
- Fluid FrictionDocument18 pagesFluid Frictioncakhoa100% (2)
- Fluid Flow Measurement Lab: ObjectDocument9 pagesFluid Flow Measurement Lab: ObjectAboodNo ratings yet
- Flow Through An OrificeDocument7 pagesFlow Through An OrificeVinay Shenoy100% (1)
- Pressure MeasurementDocument16 pagesPressure MeasurementTheyvan T-van83% (6)
- Pressure MeasurementDocument22 pagesPressure MeasurementAshley_Rulzzzzzzz100% (1)
- Investigate Validity of Bernoulli's TheoremDocument26 pagesInvestigate Validity of Bernoulli's TheoremSaber Minato Azrul100% (1)
- Friction Losses in Pipes Consisting of Bends and ElbowsDocument11 pagesFriction Losses in Pipes Consisting of Bends and Elbowswhoelse_i86% (28)
- Experiment 4 - Flow MeasurementDocument24 pagesExperiment 4 - Flow MeasurementKhairil Ikram67% (6)
- Lab Report 2Document16 pagesLab Report 2Limmy Yingran0% (1)
- Fluids Lab ReportDocument19 pagesFluids Lab Reportdhruv100% (3)
- Lab Experiments Losses in PipeDocument14 pagesLab Experiments Losses in Pipesawmag123No ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Lab5Document18 pagesFlow Measurement Lab5Jérôme J. JeitanyNo ratings yet
- (Exp # 5) Energy Losses in BendsDocument16 pages(Exp # 5) Energy Losses in BendshamZA17% (12)
- Critical Reynolds Number in Pipe FlowDocument9 pagesCritical Reynolds Number in Pipe FlowStephen Mirdo100% (3)
- Fluid Mechanics-I (LAB)Document12 pagesFluid Mechanics-I (LAB)Ahmad AwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment1 Orifice and Jet Flow Group1 A03Document6 pagesExperiment1 Orifice and Jet Flow Group1 A03Francis Aeron PabalanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 4 Flow MeasurementsDocument7 pagesExperiment No 4 Flow MeasurementsNathanian81% (16)
- Experiment 12 Fluid FrictionDocument4 pagesExperiment 12 Fluid FrictionHadoosh2786% (7)
- PIPE FLOW EXPERIMENTDocument7 pagesPIPE FLOW EXPERIMENTLance HernandezNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Venturimeter and OrificemeterDocument6 pagesCalibration of Venturimeter and Orificemeteranil chejara83% (6)
- Losses in Pipe Systems and FittingsDocument15 pagesLosses in Pipe Systems and FittingsMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in BendsDocument10 pagesEnergy Losses in BendsAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Bends and FittingsDocument11 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends and FittingsQuenneBelocura100% (1)
- Flow MeasurementDocument10 pagesFlow Measurementnirvan93No ratings yet
- Comparing Accuracy of Flow Measurement DevicesDocument23 pagesComparing Accuracy of Flow Measurement Devicesinterestingese100% (1)
- Experiment 7Document13 pagesExperiment 7Malik Ainuddin50% (2)
- Exp 5 Head Loss Due To FrictionDocument17 pagesExp 5 Head Loss Due To FrictionnileshNo ratings yet
- Friction Loss in PipeDocument12 pagesFriction Loss in Pipenextdarklord50% (2)
- Energy Losses in Bends I.: Experiment No. 9Document10 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends I.: Experiment No. 9Jemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Theorem ExperimentDocument4 pagesBernoulli's Theorem ExperimentT/ROX94% (18)
- Measuring Flow Rates Using an Orifice Meter Lab ReportDocument17 pagesMeasuring Flow Rates Using an Orifice Meter Lab ReportVerlon VincentNo ratings yet
- Bernaulli's Theorem FullDocument17 pagesBernaulli's Theorem FullBart KwanNo ratings yet
- Reynolds ReportDocument6 pagesReynolds ReportKiran Raj Veerappen100% (1)
- Work Sheet PneumaticDocument130 pagesWork Sheet PneumaticDimas WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Calibration of An Orifice and Venturi Meter PDFDocument20 pagesCalibration of An Orifice and Venturi Meter PDFjamaiiicaNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 - Lab Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesSem 3 - Lab Venturi MeterLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Determination of Coefficient of Discharge of A Venturi MeterDocument1 pageDetermination of Coefficient of Discharge of A Venturi MeterJoffer Gallamaso50% (2)
- Tutorial 2 Bending Stress With SolutionsDocument11 pagesTutorial 2 Bending Stress With SolutionsAbelBayartNo ratings yet
- Centre of Hidrostatic PressureDocument16 pagesCentre of Hidrostatic PressureVanithaa Ponnaiah0% (1)
- Flow Measurement Using Venturi and Orifice MetersDocument6 pagesFlow Measurement Using Venturi and Orifice Metersleo besaNo ratings yet
- EM201 FLUID MECHANICS LAB REPORT 2Document17 pagesEM201 FLUID MECHANICS LAB REPORT 2Limmy Yingran100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 - Suggested AnswerDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Suggested AnswerBárbara VictóriaNo ratings yet
- Student Code of Ethic (SCE)Document10 pagesStudent Code of Ethic (SCE)Rahim GenesisNo ratings yet
- Experiment To Verify Bernoulli's PrincipleDocument8 pagesExperiment To Verify Bernoulli's PrincipleKarishma JuttunNo ratings yet
- Darcy-Weisbach Equation PDFDocument5 pagesDarcy-Weisbach Equation PDFMihir Soni80% (10)
- Energy Losses in Bends & FittingsDocument7 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends & Fittingssamama khan100% (1)
- Experiment 4 Head Losses in PipesDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 Head Losses in PipesChristine Anne LatayanNo ratings yet
- Series & Parallel PumpDocument14 pagesSeries & Parallel PumpDivaan Raj Karunakaran100% (3)
- Flow Measurement Lecture 1Document37 pagesFlow Measurement Lecture 1Rahul KalraNo ratings yet
- flow_sensors (2)Document57 pagesflow_sensors (2)bhaihello015No ratings yet
- Orifice Meter (ANANDA)Document12 pagesOrifice Meter (ANANDA)Ramit PaulNo ratings yet
- AnandaDocument15 pagesAnandaAnkita JanaNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument62 pagesFlowbapita roy100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document96 pagesChapter 5MahainiIm RuzailyNo ratings yet
- Valves Grese NDocument92 pagesValves Grese NYair Alexis Muñoz Rojas100% (1)
- Prince Hydraulics - RD-500 Adjustable Flow Priority Divider Offered by PRC Industrial SupplyDocument2 pagesPrince Hydraulics - RD-500 Adjustable Flow Priority Divider Offered by PRC Industrial SupplyPRC Industrial SupplyNo ratings yet
- 5047-En Einzelne - Schaltplanseiten - Mischauftrag - Einseitiger - DruckDocument8 pages5047-En Einzelne - Schaltplanseiten - Mischauftrag - Einseitiger - DruckMihai PopescuNo ratings yet
- 199ASV Anti-Siphon ValveDocument1 page199ASV Anti-Siphon ValveChristian Ezeagu OsitaNo ratings yet
- 0751 VICTAULIC in Mechanical PipingDocument17 pages0751 VICTAULIC in Mechanical PipingsyafiqNo ratings yet
- S8 Xe-BDocument11 pagesS8 Xe-BmnraveeNo ratings yet
- 2a Compressor FundamentalsDocument49 pages2a Compressor FundamentalsFirman Ali Nuryanto0% (1)
- Pid of A Piping SystemDocument4 pagesPid of A Piping SystemBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel Pope PDFDocument20 pagesWind Tunnel Pope PDFKrmxl Tdre100% (1)
- Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings Product GuideDocument1 pageStainless Steel Pipe Fittings Product GuideRICHARDNo ratings yet
- EN2314 Hydraulics - Formula Sheet 30oct19Document3 pagesEN2314 Hydraulics - Formula Sheet 30oct19mohamedyahaiNo ratings yet
- FLOW THROUGH FLUIDIZED BED LABDocument2 pagesFLOW THROUGH FLUIDIZED BED LABJishnu JohnNo ratings yet
- Engineer's Sticker: Butterfly Valve SchematicsDocument4 pagesEngineer's Sticker: Butterfly Valve SchematicssartajNo ratings yet
- European Standards for Valve Sizing CalculationDocument11 pagesEuropean Standards for Valve Sizing CalculationleotvrdeNo ratings yet
- Eni Zubair Oil Field PSV Process Data SheetDocument2 pagesEni Zubair Oil Field PSV Process Data SheetSIVANo ratings yet
- MIB303 Alarm & Fault Finding PDFDocument10 pagesMIB303 Alarm & Fault Finding PDFCarls EstefanNo ratings yet
- Backflow Prevention Repair Kits: Description Features and BenefitsDocument4 pagesBackflow Prevention Repair Kits: Description Features and BenefitsCatalin StrugariuNo ratings yet
- Bomba DekkerDocument4 pagesBomba Dekkerjverdejop100% (1)
- InstructionDocument4 pagesInstructionHtunn Thu Thu UNo ratings yet
- 3.10.E.pv25G Pneumatic Control Valves DN15-100-EnDocument6 pages3.10.E.pv25G Pneumatic Control Valves DN15-100-EnSon Trinh PhuongNo ratings yet
- TP40 20 Water TransmissionDocument24 pagesTP40 20 Water TransmissionNestor Augusto OyarceNo ratings yet
- Pipe Sizes and ScheduleDocument2 pagesPipe Sizes and Schedulechupacid0% (1)
- Pilot Operated Relief Valve GuideDocument8 pagesPilot Operated Relief Valve GuideEsau LaHraNo ratings yet
- Study boiler mountings and accessoriesDocument10 pagesStudy boiler mountings and accessoriesShahedNo ratings yet
- HPLC Pump Spares Price List: January 2020Document20 pagesHPLC Pump Spares Price List: January 2020mardonioandradeNo ratings yet
- 0910sem2 Me2135Document6 pages0910sem2 Me2135brugelionNo ratings yet
- Control ValvesDocument38 pagesControl Valvesprathamesh.gangal999100% (1)
- Series 825Y and LF825Y Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesSeries 825Y and LF825Y Installation InstructionsFEBCONo ratings yet
- Solution For Chapter 4 Differential FlowDocument24 pagesSolution For Chapter 4 Differential Flowkombat13_708353334100% (3)
- P Prro Od Du Uc Ctts S: Supplying Superior Instrumentation Fittings & ValvesDocument1 pageP Prro Od Du Uc Ctts S: Supplying Superior Instrumentation Fittings & ValveskrishnakumarsistNo ratings yet