Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometric Tolerancing - Definitions
Uploaded by
Sergio Boillos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
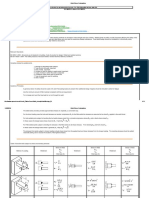
105 views23 pagesMaximum material condition (MMC) - the condition in which a feature of size contains the maximum amount of material with the stated limits of size. Least Material Condition (LMC) is the condition in which the feature contains the least amount of material. A feature must be parallel to Datum B within.007 at MMC (largest cylinder) as measured on the diameter.007 Tolerance Zone This cylinder must be straight within 0.03 mm.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMaximum material condition (MMC) - the condition in which a feature of size contains the maximum amount of material with the stated limits of size. Least Material Condition (LMC) is the condition in which the feature contains the least amount of material. A feature must be parallel to Datum B within.007 at MMC (largest cylinder) as measured on the diameter.007 Tolerance Zone This cylinder must be straight within 0.03 mm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views23 pagesGeometric Tolerancing - Definitions
Uploaded by
Sergio BoillosMaximum material condition (MMC) - the condition in which a feature of size contains the maximum amount of material with the stated limits of size. Least Material Condition (LMC) is the condition in which the feature contains the least amount of material. A feature must be parallel to Datum B within.007 at MMC (largest cylinder) as measured on the diameter.007 Tolerance Zone This cylinder must be straight within 0.03 mm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
Geometric Tolerancing - Definitions
Maximum Material Condition (MMC) The condition
in which a feature of size contains the maximum
amount of material with the stated limits of size, -
fore example, minimum hole diameter and maximum
shaft diameter
Least Material Condition (LMC) Opposite of MMC,
the feature contains the least material. For example,
maximum hole diameter and minimum shaft diameter
Virtual Condition The envelope or boundary that
describes the collective effects of all tolerance
requirements on a feature (See Figure 7-25 TG)
Virtual Condition Envelope
All Required Tolerances
20.06 Maximum
Envelope
20.00
Maximum
Allowable
Diameter
0.06
Maximum
Allowable
Curvature
Feature Control Frame
This feature must be parallel to Datum B within .007 at MMC
(largest cylinder) as measured on the diameter
.007 M B
Geometric
Characteristic
Symbol
Tolerance
Material condition
Datum
Reference
B
.007
Tolerance of Form - Straightness
19.89
19.76
0.03
0.03 Tolerance Zone
This cylinder must be straight
within 0.03 mm.
What it means -
Concentricity Tolerance Note
XX
A
YY
.007 A
This cylinder (the right cylinder) must be concentric
within .007 with the Datum A (the left cylinder)
as measured on the diameter
.007 Tolerance
Zone
What It Means
DIMENSIONING
Requirements
1. Unambiguous
2. Completeness
3. No redundancy
0.83 ' 0.95 ' 1.22 '
3.03 '
Redundant dimensioning
0.83 ' 1.22 '
3.03 '
1.72 '
0.86 '
Adequate dimensioning
Incomplete
dimensioning
TOLERANCE
unilateral
bilateral
1.00 0.05
+
-
nominal dimension
tolerance
0.95
+ 0.10
- 0.00
1.05
+ 0.00
- 0.10
1.00 0.05
+
-
0.95 - 1.05 means a range
"TOLERANCE IS ALWAYS ADDITIVE"
What is the expected dimension and tolerances?
d = 0.80 +1.00 + 1.20 = 3.00
t = (0.01 + 0.01 + 0.01) = 0.03
0.80 ' 0.01 1.20 ' 0.01
1.00 ' 0.01
?
Maximum x length = 3.01 - 0.79 - 1.19 = 1.03
Minimum x length = 2.99 - 0.81 - 1.21 = 0.97
Therefore x = 1.00 0.03
0.80 ' 0.01 1.20 ' 0.01
3.00 ' 0.01
?
x
SURFACE FINISH
w a v i n e s s w i d t h
r o u g h n e s s w i d t h
w a v i n e s s
r o u g h n e s s
STRAIGHTNESS
Value must be smaller
than the size tolerance.
1.000 ' 0.002
0 . 0 0 1
M e a s u r e d e r r o r 0 . 0 0 1
1.000 ' 0.002
0 . 0 0 1
0 . 0 0 1
Design Meaning
Tolerance zone between two straightness lines.
FLATNESS
1.000 ' 0.002
0 . 0 0 1
0 . 0 0 1
p a r a l l e l
p l a n e s
Tolerance zone defined by two parallel planes.
CIRCULARITY (ROUNDNESS)
1.00 ' 0.05
0 . 0 1
At any section along the cylinder
Tolerance zone bounded by two concentric circles.
CYLINDRICITY
1.00 ' 0.05
0 . 0 1
0 . 0 1
Rotate in a V
Rotate between points
Tolerance zone bounded by two concentric cylinders
within which the cylinder must lie.
PERPENDICULARITY
A surface, median plane, or axis at a right angle to the datum plane
or axis.
0.500 ' 0.005
1.000 ' 0.005
. 0 0 2 A
2.000 ' 0.005
A
. 0 0 2 T A
ANGULARITY
A surface or axis at a specified angle (orther than 90) from a datum
plane or axis. Can have more than one datum.
3.500 ' 0.005
1 . 5 0 0 0 . 0 0 5
4 0
0 . 0 0 5 A
A
PARALLELISM
1.000 " 0.005
2.000 " 0.005
. 0 0 1 A
A
The condition of a surface equidistant at all points from a datum plane,
or an axis equidistant along its length to a datum axis.
0 . 0 0 1
PROFILE
A uniform boundary along the true profile within whcih
the elements of the surface must lie.
A
B
0 . 0 0 5 A B
0 . 0 0 1
RUNOUT
0.361 " 0.002
1.500 " 0.005
A
0.005 A
A composite tolerance used to control the functional relationship
of one or more features of a part to a datum axis. Circular runout
controls the circular elements of a surface. As the part rotates
360 about the datum axis, the error must be within the tolerance
limit.
D a t u m
a x i s
D e v i a t i o n o n e a c h
c i r c u l a r c h e c k r i n g
i s l e s s t h a n t h e
t o l e r a n c e .
TOTAL RUNOUT
D a t u m
a x i s
D e v i a t i o n o n t h e
t o t a l s w e p t w h e n
t h e p a r t i s r o t a t i n g
i s l e s s t h a n t h e
t o l e r a n c e .
0.361 " 0.002
1.500 " 0.005
A
0.005 A
TRUE POSITION
1.20
0.01
1.00 0.01
1 . 2 0
1 . 0 0
T o l e r a n c e z o n e
0 . 0 1 d i a
O 0 . 0 1 M A B
O . 8 0 0 . 0 2
Dimensional
tolerance
True position
tolerance
Hole center tolerance zone
A
B
TOLERANCE VALUE MODIFICATION
Produced True Pos tol
hole size
0.97 out of diametric tolerance
0.98 0.01 0.05 0.01
0.99 0.02 0.04 0.01
1.00 0.03 0.03 0.01
1.01 0.04 0.02 0.01
1.02 0.05 0.01 0.01
1.03 out of diametric tolerance
1.20
1.00
O 0.01 M A B
O 1.00 0.02
M L S
The default modifier for
true position is MMC.
MMC
LMC
For M the allowable tolerance = specified tolerance + (produced hole
size - MMC hole size)
A
B
MMC HOLE
Given the same peg (MMC peg), when the produced hole size
is greater than the MMC hole, the hole axis true position
tolerance zone can be enlarged by the amount of difference
between the produced hole size and the MMC hole size.
hole axis t olerance zone
MMC hole
LMC hole
MMC peg will f it in t he hole
axis must be in t he t olerance zone
,
You might also like
- Weld Stress CalculationsDocument13 pagesWeld Stress Calculationsmih1No ratings yet
- ch01,2,6,8,9 HandoutsDocument138 pagesch01,2,6,8,9 HandoutsManish ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To High Energy Physics by Dan KabatDocument235 pagesIntroduction To High Energy Physics by Dan KabatAtanu GayenNo ratings yet
- Astm A877.a877mDocument5 pagesAstm A877.a877mOS Laboratory100% (1)
- E02 - Bridge CraneDocument13 pagesE02 - Bridge CraneLenin Pardo SalazarNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Test Code For Machine Tools - Determination of The Noise EmissionDocument11 pagesInternational Standard: Test Code For Machine Tools - Determination of The Noise EmissionAnonymous 2SQDbt2No ratings yet
- Design of Crane Track GirdersDocument30 pagesDesign of Crane Track GirdersSeifeldinNo ratings yet
- Wilson Hardness Conversion Chart - ShortDocument1 pageWilson Hardness Conversion Chart - ShortwellbeingempireNo ratings yet
- Wedling ModelingDocument32 pagesWedling ModelingManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Calypso: Option 6 Characteristic INDocument34 pagesCalypso: Option 6 Characteristic INGabriel TelepteanNo ratings yet
- Crane runway girder design and forcesDocument23 pagesCrane runway girder design and forcesVignesh RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Plug and Slot Welds V.1Document3 pagesPlug and Slot Welds V.1sboergertNo ratings yet
- 7 Die Maintenance Handbook Chapter 12 PDFDocument17 pages7 Die Maintenance Handbook Chapter 12 PDFAtthapol YuyaNo ratings yet
- Microstructural and Mechanical Properties Analysis of Plasma ARC Welded 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Joints Without Addition of Filler MaterialDocument17 pagesMicrostructural and Mechanical Properties Analysis of Plasma ARC Welded 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Joints Without Addition of Filler MaterialEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Tungsten CarbideDocument47 pagesTungsten CarbideAmit DhekaleNo ratings yet
- Mil F 5509Document18 pagesMil F 5509RwilcoNo ratings yet
- SI Base UnitsDocument11 pagesSI Base UnitsHasan BashoriNo ratings yet
- Toughness - WikipediaDocument3 pagesToughness - WikipediaaliNo ratings yet
- Testing Metallic Materials Lab HardnessDocument11 pagesTesting Metallic Materials Lab HardnessJaymin PatelNo ratings yet
- Yield Stress Von MIses Stress Strength of Materials - Mechanics of MaterialsDocument3 pagesYield Stress Von MIses Stress Strength of Materials - Mechanics of MaterialsGnabBangNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Electrical Harness DesignDocument3 pagesSpacecraft Electrical Harness Designe1094739No ratings yet
- Manual Técnico de Parafusos - BOSSARDDocument85 pagesManual Técnico de Parafusos - BOSSARDRenato Caldas100% (1)
- An Introduction to MIG WeldingDocument16 pagesAn Introduction to MIG WeldingHtet MyatNo ratings yet
- Aluminum 2024-T6 PropertiesDocument4 pagesAluminum 2024-T6 PropertiesThiru Kumaran0% (1)
- Introduction To Datums: Datums Tell Us Where To Measure From. Calling Them Out Clearly and Labelling EachDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Datums: Datums Tell Us Where To Measure From. Calling Them Out Clearly and Labelling Eachmanikantar15No ratings yet
- Welding PDFDocument6 pagesWelding PDFNavneet ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Vibratory Stress ReliefDocument7 pagesVibratory Stress ReliefSteve HornseyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cemented Carbide MaterialsDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Cemented Carbide MaterialsIrfan Yahya IkhsanudinNo ratings yet
- Lacey Thacker TutorialDocument10 pagesLacey Thacker TutorialWilliam Pinto HernándezNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual Snow Blower Models GuideDocument20 pagesOperator's Manual Snow Blower Models Guidefred_koehlerNo ratings yet
- GS52Document3 pagesGS52S.Hasan MirasadiNo ratings yet
- Stud Welding Capacitive Discharge WeldingDocument30 pagesStud Welding Capacitive Discharge WeldingwenigmaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Part1 Static AnalysisDocument10 pagesSimulation of Part1 Static AnalysisChaitanya Sai TNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets - Different StylesDocument3 pagesData Sheets - Different Stylesרונן לבNo ratings yet
- MIG Welding Basics On MIG Welding Machines.20121010.095920Document2 pagesMIG Welding Basics On MIG Welding Machines.20121010.095920anon_516042600No ratings yet
- Fcaw Welding Guide PDFDocument2 pagesFcaw Welding Guide PDFElizabethNo ratings yet
- SOM All Chapters With TimingsDocument376 pagesSOM All Chapters With TimingsSUMIT SUMANNo ratings yet
- Assembly of Screwed Fastenings: Preloads and Tightening Torque For Fasteners From SteelDocument1 pageAssembly of Screwed Fastenings: Preloads and Tightening Torque For Fasteners From SteelDani Quirante Flaaut EtcNo ratings yet
- SEO Optimized Product Data Sheet for OK Tigrod 316L TIG Welding RodDocument2 pagesSEO Optimized Product Data Sheet for OK Tigrod 316L TIG Welding Rodsoft4gsmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Material ScienceDocument42 pagesChapter 6 Material Science9al6oonNo ratings yet
- Parametric Study of A Dog Clutch Used in A Transfer Case For TrucksDocument46 pagesParametric Study of A Dog Clutch Used in A Transfer Case For TrucksCesar VasquesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing StandardDocument59 pagesEngineering Drawing StandardYuva Raj AnandNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Friction Weld (FRW) in Truck Axle ApplicationDocument4 pagesFailure Analysis of Friction Weld (FRW) in Truck Axle ApplicationVivekintenseCmNo ratings yet
- 1.0 TitleDocument10 pages1.0 TitlezackziffiNo ratings yet
- Fortress Timber & Metal SDS Screws 2017 WebDocument36 pagesFortress Timber & Metal SDS Screws 2017 WebGabriel MacedoNo ratings yet
- Torque and Tension RelationshipDocument23 pagesTorque and Tension RelationshipChris MedeirosNo ratings yet
- AWS Cluster Porosity in Fillet WeldDocument7 pagesAWS Cluster Porosity in Fillet WeldpktienNo ratings yet
- Von Mises Yield CriteriaDocument6 pagesVon Mises Yield CriteriaParikshit VermaNo ratings yet
- Sharp Lc-32d47 Sb27 c3237 SM LCDDocument128 pagesSharp Lc-32d47 Sb27 c3237 SM LCDRoosevelt Vega SanchezNo ratings yet
- SFD Csa S16 14Document110 pagesSFD Csa S16 14Ramon Toral BaezNo ratings yet
- PPD 199 - Lifting Fixture Engineering NoteDocument15 pagesPPD 199 - Lifting Fixture Engineering NoteWalterNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Magnetic Particle TestingDocument7 pagesIntroduction of Magnetic Particle TestingKhair Jamiulanwar100% (1)
- Induction Heat Treating: Richard E. HaimbaughDocument14 pagesInduction Heat Treating: Richard E. HaimbaughKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Magnesium-Alloy Sheet and Plate: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesMagnesium-Alloy Sheet and Plate: Standard Specification ForDanZel DanNo ratings yet
- Plate StandDocument6 pagesPlate Standmoseslugtu6324No ratings yet
- Materials and Fluid Properties ChartDocument2 pagesMaterials and Fluid Properties ChartBashu PoudelNo ratings yet
- Term Paper-Sheet Metal WeldingDocument6 pagesTerm Paper-Sheet Metal Welding11gargdinesh7No ratings yet
- Geometric Tolerancing - DefinitionsDocument23 pagesGeometric Tolerancing - DefinitionsKakoDaNo ratings yet
- 5dimensioning and TolerancingDocument43 pages5dimensioning and TolerancingPavan RaghavNo ratings yet
- Confidence IntervalsDocument12 pagesConfidence IntervalsDheerajNo ratings yet
- Building A Safety Case in Compliance With ISO 26262Document124 pagesBuilding A Safety Case in Compliance With ISO 26262Sergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- VDA Volume-Criteria For Car-Washes Conforming To VDA SpecificationsDocument57 pagesVDA Volume-Criteria For Car-Washes Conforming To VDA SpecificationsSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- Qs 9000Document152 pagesQs 9000cwbehNo ratings yet
- VDA Volume Field Failure AnalysisDocument22 pagesVDA Volume Field Failure Analysishmp90No ratings yet
- GM 1927-16a PWT Gear Commodity AuditDocument5 pagesGM 1927-16a PWT Gear Commodity AuditSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- VDA Volume Field Failure AnalysisDocument22 pagesVDA Volume Field Failure Analysishmp90No ratings yet
- VDA Minimizing Risks in The Supply ChainDocument0 pagesVDA Minimizing Risks in The Supply Chaintimkoid100% (1)
- Fmea 4 Edition PDFDocument93 pagesFmea 4 Edition PDFSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- Supplier Quality Global Launch Process ManualDocument11 pagesSupplier Quality Global Launch Process ManualSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Residual AnalysistopostDocument20 pagesCH 8 Residual AnalysistopostAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- ANSI Drafting Standards: ASME Y-14.5 2009Document9 pagesANSI Drafting Standards: ASME Y-14.5 2009Sergio Boillos100% (1)
- Introduction To Acceptance SamplingDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Acceptance Samplingjsalu_khanNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing and the Toyota Production System ExplainedDocument3 pagesLean Manufacturing and the Toyota Production System ExplainedSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- 4-GM1828 - Pre-Proto & PrototypeTagDocument1 page4-GM1828 - Pre-Proto & PrototypeTagSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- G DHS 1Document22 pagesG DHS 1Sergio Boillos100% (1)
- 3-GM1827 - Pre-Proto & Prototype LabelDocument1 page3-GM1827 - Pre-Proto & Prototype LabelSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- 3-GM1827 - Pre-Proto & Prototype LabelDocument1 page3-GM1827 - Pre-Proto & Prototype LabelSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- Control PlanDocument2 pagesControl PlanSergio BoillosNo ratings yet
- Comparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsDocument31 pagesComparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsJuan ManuelNo ratings yet
- Henderson - Historical Documents of The Middle AgesDocument536 pagesHenderson - Historical Documents of The Middle AgesVlad VieriuNo ratings yet
- Longman - New Total English Elementary Video BankDocument26 pagesLongman - New Total English Elementary Video Bankyuli100% (1)
- Silvianita - LK 0.1 Modul 2 English For Personal CommunicationDocument3 pagesSilvianita - LK 0.1 Modul 2 English For Personal CommunicationSilvianita RetnaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Blaise PascalDocument8 pagesBlaise PascalBosko GuberinicNo ratings yet
- ANTENATAL ASSESSMENT Form 13Document4 pagesANTENATAL ASSESSMENT Form 13Kaku ManishaNo ratings yet
- Sengoku WakthroughDocument139 pagesSengoku WakthroughferdinanadNo ratings yet
- BSC Part IiDocument76 pagesBSC Part IiAbhi SinghNo ratings yet
- My Perspective On Ayurveda-ArticleDocument2 pagesMy Perspective On Ayurveda-ArticleAaryan ParashuramiNo ratings yet
- VIII MKL Duet I Etap 2018 Angielski Arkusz Dla PiszącegoDocument5 pagesVIII MKL Duet I Etap 2018 Angielski Arkusz Dla PiszącegoKamilNo ratings yet
- Software Security Engineering: A Guide for Project ManagersDocument6 pagesSoftware Security Engineering: A Guide for Project ManagersVikram AwotarNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment K12Document88 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment K12Jardo de la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Analysing Context CluesDocument2 pagesAnalysing Context CluesSwathiNo ratings yet
- Jolly Phonics Teaching Reading and WritingDocument6 pagesJolly Phonics Teaching Reading and Writingmarcela33j5086100% (1)
- Mansabdari SystemDocument10 pagesMansabdari SystemSania Mariam100% (8)
- Origin and Development of Law of Sea PDFDocument135 pagesOrigin and Development of Law of Sea PDFkimmiahujaNo ratings yet
- Unpacking of StandardsDocument41 pagesUnpacking of StandardsJealf Zenia Laborada CastroNo ratings yet
- The Islam Question - Should I Become A Muslim?Document189 pagesThe Islam Question - Should I Become A Muslim?Aorounga100% (1)
- Christian Storytelling EvaluationDocument3 pagesChristian Storytelling Evaluationerika paduaNo ratings yet
- ARCH1350 Solutions 6705Document16 pagesARCH1350 Solutions 6705Glecy AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vitamin C, (Chemistry STPM)Document2 pagesIntroduction To Vitamin C, (Chemistry STPM)NarmeenNirmaNo ratings yet
- GII-07 Training MaterialDocument191 pagesGII-07 Training MaterialIris Amati MartinsNo ratings yet
- ET's and Aliens: Problems of Exopolitics - Dec 2009Document8 pagesET's and Aliens: Problems of Exopolitics - Dec 2009Alex KochkinNo ratings yet
- 7 Years - Lukas Graham SBJDocument2 pages7 Years - Lukas Graham SBJScowshNo ratings yet
- Extinction - WikipediaDocument14 pagesExtinction - Wikipediaskline3No ratings yet
- Vinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Document496 pagesVinzenz Hediger, Patrick Vonderau - Films That Work - Industrial Film and The Productivity of Media (Film Culture in Transition) (2009)Arlindo Rebechi JuniorNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Resistance and Unusual Phenotypes Tables v3.2 20200225Document12 pagesIntrinsic Resistance and Unusual Phenotypes Tables v3.2 20200225Roy MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Book Review Reclaim Your HeartDocument7 pagesBook Review Reclaim Your HeartShaheer KhanNo ratings yet
- Levenbach Causal2017Document15 pagesLevenbach Causal2017Jenna GrantNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument25 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive Educationmarjory empredoNo ratings yet