Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Communication
Uploaded by
makalettinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 Communication
Uploaded by
makalettinCopyright:
Available Formats
Communication
Functions of Communication
Communication
The transference and understanding of meaning
Communication Functions
Control member behavior
Foster motivation for what is to be done
Provide a release for emotional expression
Provide information needed to make decisions
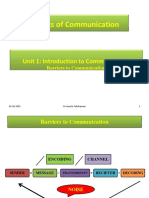
The Communication Process
Communication Process
The steps between a source and a receiver
that result in the transference and
understanding of meaning
Key Parts of Communication Process
The Sender initiates message
Encoding translating thought to message
The Message what is communicated
The Channel the medium the message travels
through
Decoding the receivers action in making sense of
the message
The Receiver person who gets the message
Noise things that interfere with the message
Feedback a return message regarding the initial
communication
Communication Channels
Channel
The medium selected by the sender through which
the message travels to the receiver
Types of Channels
Formal Channels
Are established by the organization and transmit
messages that are related to the professional
activities of members
Informal Channels
Used to transmit personal or social messages in
the organization. These informal channels are
spontaneous and emerge as a response to
individual choices
Interpersonal Communication
Oral Communication
Advantages: Speed and feedback
Disadvantage: Distortion of the message
Written Communication
Advantages: Tangible and verifiable
Disadvantages: Time consuming and lacks feedback
Nonverbal Communication
Advantages: Supports other communications and
provides observable expression of emotions and feelings
Disadvantage: Misperception of body language or
gestures can influence receivers interpretation of
message
Direction of Communication
CEO
VP
Mgr Mgr
VP
Mgr Mgr
D
O
W
N
W
A
R
D
U
P
W
A
R
D
LATERAL
Three Common Formal Small-Group Networks
Chain:
Rigidly follows the chain of
command
Wheel:
Relies on a central figure to
act as the conduit for all
communication
Team with a strong leader
All Channel:
All group members
communicate actively with
each other
Self-managed teams
Small Group Network Effectiveness
Small group effectiveness depends on the
desired outcome variable
TYPES OF NETWORKS
Criteria Chain Wheel All Channel
Speed Moderate Fast Fast
Accuracy High High Moderate
Emergence of a leader Moderate High None
Member satisfaction Moderate Low High
The Grapevine
The informal communication network in a group or
organization is called the grapevine. Main Grapevine
Characteristics
1. Informal, not controlled by management
2. Perceived by most employees as being more
believable and reliable than formal communications
Results from:
Desire for information about important situations
Ambiguous conditions
Conditions that cause anxiety
Serves employees social needs
Reducing Rumors
1. Announce timetables for making important
decisions
2. Explain decisions and behaviors that may
appear inconsistent or secretive
3. Emphasize the downside, as well as the
upside, of current decisions and future
plans
4. Openly discuss worst-case possibilities
Electronic Communications: E-mail
E-mail
Advantages: quickly written, sent, and stored; low
cost for distribution
Disadvantages:
Messages are easily and commonly misinterpreted
Not appropriate for sending negative messages
Overused and overloading readers
Difficult to get emotional state understood
Non-private: e-mail is often monitored and may be
forwarded to anyone
Electronic Comms: Instant/Text
Messaging
Instant Messaging
Immediate e-mail sent to receivers desktop or device
Text Messages
Short messages typically sent to cell phones or other
handheld devices
Explosive growth in business use
Fast and inexpensive means of communication
Can be intrusive and distracting
Easily hacked with weak security
Can be seen as too informal
Electronic Comms: Networking Software
Linked systems organically spread throughout
the nation and world that can be accessed by a
PC
Includes:
Social networks like MySpace and Facebook
Professional networks like Ziggs
Corporate networks such as IBMs BluePages
Key Points:
These are public spaces anyone can see what you post
Can be used for job application screening
Avoid overstimulating your contacts
Electronic Comms: Blogs and
Videoconferencing
Blogs: Web sites about a single person (or entity)
that are typically updated daily
A popular, but potentially dangerous activity:
Employees may post harmful information
Such comments may be cause for dismissal
Can be against company policy to post in a blog during
company time and on company equipment/connections
Videoconferencing: uses live audio and video Internet
streaming to create virtual meetings
Now uses inexpensive webcams and laptops in place of
formal videoconferencing rooms
Choice of Communication Channel
The model of media richness helps explain an
individuals choice of communication channel
Channels vary in their capacity to convey information
A rich channel is one that can:
Handle multiple cues simultaneously
Facilitate rapid feedback
Be very personal
Choice depends on whether the message is
routine
Media Richness Model
Low channel richness High channel richness
Persuasive Communication
The attempt by one person or group to transmit
and share information with another person or
group to get them to accept, agree with, follow,
and seek to achieve the formers goals and
objectives.
Automatic processing
Controlled processing
Factors in processing ,
Interest level
Prior knowledge
Personality
Message characteristics
Barriers to Effective Communication
Wrong choice of medium
Filtering
A senders manipulation of information so that it will be seen
more favorably by the receiver
Physical Barriers
Selective Perception
People selectively interpret what they see on the basis of their
interests, background, experience, and attitudes
Information Overload
A condition in which information inflow exceeds an individuals
processing capacity
Emotions
How a receiver feels at the time a message is received will
influence how the message is interpreted
More Barriers to Effective
Communication
Language
Words have different meanings to different
people
Communication Apprehension
Undue tension and anxiety about oral
communication, written communication, or
both
Gender Differences
Men tend to talk to emphasize status while
women talk to create connections
Guidelines for Effective Listening
1. Eye contact
2. Bodily exhibitions
3. Avoid distracting actions or gestures
4. Ask question
5. Put the speaker at ease
6. Avoid premature arguments
6. Listen patiently
7. No personal bias
8. Observe non-verbal cues
9. Avoid fake attention
Global Implications
Cross-cultural factors increase communication
difficulties
Cultural Barriers:
Semantics: some words arent translatable
Word Connotations: some words imply multiple meanings
beyond their definitions
Tone Differences: the acceptable level of formality of
language
Perception Differences: language affects worldview
Cultural Context:
The importance of social context to meaning
Low-context cultures (like the U.S.) rely on words for meaning
High-context cultures gain meaning from the whole situation
A Cultural Guide
To reduce your chance of making a faux
pas in another culture:
Assuming differences until similarity is proven
Emphasizing description rather than
interpretation or evaluation
Practicing empathy in communication
Treating your interpretations as a working
hypothesis
Body Language
Appearance
Body Language
Facial
Expressions
Eye contact
Body Language
Body Language
Smile
You are never fully
dressed unless you wear
a smile.
Body Language
Posture (Body Position)
Body Language
Posture (Body Position
Body Language
Posture (Body Position
Body Language
Gestures
Body Language
Space Distance
You might also like
- Ders 10 (2116)Document22 pagesDers 10 (2116)Dilara ŞimşekNo ratings yet
- CommuniDocument20 pagesCommuniAnand ReddyNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument26 pagesCommunicationPratyum PradhanNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument21 pagesCommunicationDhanya DasNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To CommunicationDocument32 pagesCH1 - Introduction To CommunicationBarkhad HassanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Managing CommunicationDocument32 pagesImportance of Managing CommunicationMaruf ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument56 pagesBusiness Communicationvicky181089No ratings yet
- Funda Com Non VerbalDocument19 pagesFunda Com Non Verbalfriend_foru2121No ratings yet
- Mba 552 Lecture FourDocument76 pagesMba 552 Lecture FourKamran NaeemNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Chapter Five CommunicationDocument24 pagesLecture of Chapter Five CommunicationAwetNo ratings yet
- Project Comms GuideDocument37 pagesProject Comms GuideJohn Ray CuevasNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Communication2023nDocument37 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Communication2023nHANA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Group HDocument39 pagesGroup HzubinpujaraNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills - Dr. Sanjay KeharDocument134 pagesCommunication Skills - Dr. Sanjay KeharNeeřąj ĶúmąřNo ratings yet
- Communication (Unit II)Document11 pagesCommunication (Unit II)aniket yadav0006No ratings yet
- Business+Communication 1,2Document52 pagesBusiness+Communication 1,2Emily PhilipNo ratings yet
- Gateways To CommunicationDocument32 pagesGateways To Communicationthakur_neha20_903303100% (1)
- Communication: Presented byDocument21 pagesCommunication: Presented byRadHika GaNdotraNo ratings yet
- Importance of ManagingDocument32 pagesImportance of ManagingMaruf ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Managers and CommunicationDocument33 pagesChapter 15 - Managers and Communicationremino1100% (1)
- 5 Types of Communication BarriersDocument15 pages5 Types of Communication BarriersMaria Angelica MandarioNo ratings yet
- Managing communication techniquesDocument52 pagesManaging communication techniquesMaje BojoNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument50 pagesBarriers To CommunicationjayshreeNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument23 pagesBarriers To CommunicationAshraf FawmeyNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument62 pagesCommunicationSai GaneshNo ratings yet
- Executive Diploma in Apparel Management and TechnologyDocument33 pagesExecutive Diploma in Apparel Management and TechnologyMadawa MaduwanthaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Effective Communication Aboard and AshoreDocument159 pages3.1 Effective Communication Aboard and AshoreX SxUxGxAxR X50% (2)
- Business Communication - An IntroductionDocument31 pagesBusiness Communication - An IntroductionVital TejaNo ratings yet
- What Is Communication: by Archana BhattDocument25 pagesWhat Is Communication: by Archana BhattArchana Subahu Bhatt0% (1)
- POM Chapter11Document4 pagesPOM Chapter11indie01No ratings yet
- Communication: Dr. Monica ShrivastavaDocument49 pagesCommunication: Dr. Monica ShrivastavaanjiwritesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 & 11 (Unit 1 - Barriers To Communication)Document23 pagesLecture 10 & 11 (Unit 1 - Barriers To Communication)siddharthaNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication SkillsDocument39 pagesEffective Communication SkillsNur IzzahNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Chapter 9Document25 pagesWeek 7 Chapter 9Dhruvi RajNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication at WorkDocument28 pagesEffective Communication at WorkLeoreyn Faye MedinaNo ratings yet
- Communication ChapterDocument43 pagesCommunication ChapterSuchismita Sen100% (2)
- CH 1Document33 pagesCH 1Neha HittooNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument26 pagesCommunicationghenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Communication ProcessDocument41 pagesLesson 1-Communication ProcessAnagirl LynNo ratings yet
- 2 Fundamentals, Barriers, GatewaysDocument26 pages2 Fundamentals, Barriers, GatewaysNeeraj SahuNo ratings yet
- 8Comm-Barriers&OvercomeDocument37 pages8Comm-Barriers&OvercomeWAN DANISH HAIKAL WAN JASRULKHIRINo ratings yet
- Boost Business Communication with 7Cs and 4SsDocument30 pagesBoost Business Communication with 7Cs and 4SsKiran GurrapuNo ratings yet
- Communication in OrganizationsDocument9 pagesCommunication in Organizationsfareha riazNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication is Key to SuccessDocument22 pagesEffective Communication is Key to SuccessJaskaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication SkillsDocument18 pagesAdvanced Communication Skillssubramani muthusamyNo ratings yet
- Project Communications PrimerDocument25 pagesProject Communications PrimerLucas Mendes PereiraNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS COMMUNICATION - Unit 1 - Business Communication BasicsDocument26 pagesBUSINESS COMMUNICATION - Unit 1 - Business Communication BasicsKeshalini Perambalam0% (1)
- Communication Skills 1 634Document57 pagesCommunication Skills 1 634DrPoonam ValviNo ratings yet
- Communication: by Kamil Shahzad Assistant Professor Balochistan Institute of TechnologyDocument23 pagesCommunication: by Kamil Shahzad Assistant Professor Balochistan Institute of Technologysania awanNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument38 pagesCommunicationNamrata PathakNo ratings yet
- Communication and Organization StructureDocument23 pagesCommunication and Organization StructureFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument30 pagesCommunicationromeojrNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION NotesDocument10 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION NotesMicah Joy JuliandaNo ratings yet
- BC (S1&2)Document23 pagesBC (S1&2)shahramliveNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument63 pagesBusiness CommunicationMark RiveraNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills May 12 2022Document41 pagesCommunication Skills May 12 2022Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication PrinciplesDocument30 pagesPurposive Communication PrinciplesMikylla Paula BelarminoNo ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument41 pagesCommunication Barrierskabibhandari100% (1)
- Leadership Language: Executive Top Ten Lists for Communication SuccessFrom EverandLeadership Language: Executive Top Ten Lists for Communication SuccessNo ratings yet
- 2012 Sayistay ElemeDocument37 pages2012 Sayistay ElemeAli KoseogluNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Organizational Behavior (OBDocument22 pagesIntroduction to Organizational Behavior (OBmakalettinNo ratings yet
- 3-Personality Theories and Personality DisorderDocument47 pages3-Personality Theories and Personality DisordermakalettinNo ratings yet
- 5 Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument22 pages5 Attitudes and Job SatisfactionmakalettinNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Group BehaviorDocument29 pagesFoundations of Group BehaviormakalettinNo ratings yet
- Brain Chip ReportDocument30 pagesBrain Chip Reportsrikanthkalemla100% (3)
- Food Product Development - SurveyDocument4 pagesFood Product Development - SurveyJoan Soliven33% (3)
- Marrickville DCP 2011 - 2.3 Site and Context AnalysisDocument9 pagesMarrickville DCP 2011 - 2.3 Site and Context AnalysiskiranjiNo ratings yet
- Overlord Volume 1 - The Undead King Black EditionDocument291 pagesOverlord Volume 1 - The Undead King Black EditionSaadAmir100% (11)
- Preparation For Exercise1-1 CompleteDocument28 pagesPreparation For Exercise1-1 CompleteSimon GranNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Math 10 Module 2Document1 pageWeekly Home Learning Plan Math 10 Module 2Yhani RomeroNo ratings yet
- Tes 1 KunciDocument5 pagesTes 1 Kuncieko riyadiNo ratings yet
- Compound SentenceDocument31 pagesCompound Sentencerosemarie ricoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Adverb Phrase (Advp)Document2 pages1.1.1 Adverb Phrase (Advp)mostarjelicaNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Students Pronounciation Errors Made by Ninth Grade of Junior High School 1 TengaranDocument22 pagesAn Analysis of Students Pronounciation Errors Made by Ninth Grade of Junior High School 1 TengaranOcta WibawaNo ratings yet
- The Serpents Tail A Brief History of KHMDocument294 pagesThe Serpents Tail A Brief History of KHMWill ConquerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The Incredible Story of How The Great Controversy Was Copied by White From Others, and Then She Claimed It To Be Inspired.Document6 pagesChapter 12 The Incredible Story of How The Great Controversy Was Copied by White From Others, and Then She Claimed It To Be Inspired.Barry Lutz Sr.No ratings yet
- Resarch Paper On Franchising Business MacobDocument8 pagesResarch Paper On Franchising Business MacobAngelika Capa ReyesNo ratings yet
- Leku Pilli V Anyama (Election Petition No 4 of 2021) 2021 UGHCEP 24 (8 October 2021)Document52 pagesLeku Pilli V Anyama (Election Petition No 4 of 2021) 2021 UGHCEP 24 (8 October 2021)Yokana MugabiNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court declares Pork Barrel System unconstitutionalDocument3 pagesSupreme Court declares Pork Barrel System unconstitutionalDom Robinson BaggayanNo ratings yet
- Trang Bidv TDocument9 pagesTrang Bidv Tgam nguyenNo ratings yet
- Edition 100Document30 pagesEdition 100Tockington Manor SchoolNo ratings yet
- What Is Love? - Osho: Sat Sangha SalonDocument7 pagesWhat Is Love? - Osho: Sat Sangha SalonMichael VladislavNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - G10 Workbook - Docx 7Document88 pagesMicrosoft Word - G10 Workbook - Docx 7Pax TonNo ratings yet
- Offer Letter for Tele Sales ExecutiveDocument3 pagesOffer Letter for Tele Sales Executivemamatha vemulaNo ratings yet
- Write a composition on tax evasionDocument7 pagesWrite a composition on tax evasionLii JaaNo ratings yet
- AI Capstone Project Report for Image Captioning and Digital AssistantDocument28 pagesAI Capstone Project Report for Image Captioning and Digital Assistantakg29950% (2)
- MinePlan Release NotesDocument14 pagesMinePlan Release NotesJuanJo RoblesNo ratings yet
- 11th AccountancyDocument13 pages11th AccountancyNarendar KumarNo ratings yet
- AVK Butterfly Valves Centric 75 - TADocument1 pageAVK Butterfly Valves Centric 75 - TANam Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Casey at The BatDocument2 pagesCasey at The BatGab SorianoNo ratings yet
- Earth Drill FlightsDocument2 pagesEarth Drill FlightsMMM-MMMNo ratings yet
- Search Inside Yourself PDFDocument20 pagesSearch Inside Yourself PDFzeni modjo02No ratings yet
- Developing An Instructional Plan in ArtDocument12 pagesDeveloping An Instructional Plan in ArtEunice FernandezNo ratings yet
- HERBAL SHAMPOO PPT by SAILI RAJPUTDocument24 pagesHERBAL SHAMPOO PPT by SAILI RAJPUTSaili Rajput100% (1)