Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 3
Uploaded by
vrajan19880 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views47 pagesC)Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures IIT Madras, SERC madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG 1 ROLE OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEER IN THE 21 st CENTURY CONTENTS INTRODUCTION the CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER DURABILITY and LIFE CYCLE COST ISSUES the EVERYDAY LIFE of STRUCTURAL ENGINEER design REQUIREMENTS CONCLUDING remarks.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ch3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentC)Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures IIT Madras, SERC madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG 1 ROLE OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEER IN THE 21 st CENTURY CONTENTS INTRODUCTION the CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER DURABILITY and LIFE CYCLE COST ISSUES the EVERYDAY LIFE of STRUCTURAL ENGINEER design REQUIREMENTS CONCLUDING remarks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views47 pagesCH 3
Uploaded by
vrajan1988C)Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures IIT Madras, SERC madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG 1 ROLE OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEER IN THE 21 st CENTURY CONTENTS INTRODUCTION the CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER DURABILITY and LIFE CYCLE COST ISSUES the EVERYDAY LIFE of STRUCTURAL ENGINEER design REQUIREMENTS CONCLUDING remarks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 47
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
1
ROLE OF STRUCTURAL
ENGINEER IN THE 21
st
CENTURY
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
2
ROLE OF STRUCTURAL ENGINEER IN THE 21
st
CENTURY
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
THE CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER
DURABILITY AND LIFE CYCLE COST
ISSUES
THE EVERYDAY LIFE OF STRUCTURAL
ENGINEER
DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
3
INTRODUCTION
Engineers - Creators of artefacts, using their ingenuity
and capacity for original thinking within the
constraints of affordability and practicability
- Understand the role of financing, project
management and information technology in
improving the quality of designs
- Full and on-going interaction between other
members of the design team is essential to
maintain effective communication across
professional boundaries
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
4
INTRODUCTION
Besides principal role as an innovator, the designer
of constructed facility has to ensure that his plan is
Fit for its purpose
Economical and durable
Safe, both for the users and for the environment
Buildable, without inconveniencing the community
Aesthetically pleasing.
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
5
CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER
There is no single correct solution to design
problem. There are many correct solutions due to
Designs are subjective to individual taste
Solutions are different according to specific
requirement
Designers own individual bias
Design problems are open ended
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
6
Goals of the design project are
Safety of the structure and human beings
Timely completion of the project
Cost within the budgeted estimate
Engineering design:
A creative activity of building a new artefact which
provides an optimum solution to satisfy a defined
requirement or need without endangering the
environment.
CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
7
Herbert Hoover, a former President of the United
States of America - described the Engineering
profession as follows (1961):
It is a great profession. There is the fascination of
watching the figment of the imagination emerge
through the aid of Science to a plan on paper. Then
it moves to realisation in stone or metal or energy.
Then it brings jobs and homes to men. Then it
elevates the standards of living and adds to the
comforts of life. That is the Engineers high
privilege. The great liability of the engineer
compared to men of other professions is that his
works are out on the open, where all can see them.
CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
8
His acts, step by step, are in hard substance. He
cannot bury his mistakes in the grave like
physicians. He cannot argue them into thin air or
blame the judge like the lawyers. He cannot, like the
architects, cover his failures with trees and vines.
He cannot, like the politicians, screen his
shortcomings by blaming his opponents and hope
that the people will forget. The engineer simply
cannot deny that he did it. If his works do not work,
he is damned forever.
CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
9
On the other hand, unlike the doctor, his is not a
life among the weak. Unlike the soldier, destruction
is not his purpose. Unlike the lawyer, quarrels are
not his daily bread. To the engineer falls the job of
clothing the bare bones of science with life comfort
and hope. No doubt, as the years go by, the people
forget which engineer did it, even if they ever knew.
Or some politician puts his name on it. Or they
credit it to some promoter, who used other peoples
money But the engineer himself looks back at the
unending stream of goodness which flows from his
success with satisfaction that few other
professions may know. And the verdict of his
fellow professionals is all the accolade he wants.
CHALLENGE FACING THE DESIGNER
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
10
DURABILITY AND
LIFE CYCLE COST ISSUES
Traditionally the Professional Structural Engineer is
responsible for the complete process from the
conceptual stages to the finished structure
Structural Engineer in the 21st century will not be
confined to immediate economic and environmental
impact and also responsible for the long-term
environmental effects on the community by
considering the life cycle costs
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
11
THE INFRASTRUCTURE CRISIS
Advances in Science and Technology in last 50
years plunged the world into a number of crises,
which have impacted directly on the construction
industry. Global effect of these dramatic changes
can be collectively termed the Infrastructure Crisis
Problem is enhanced by
Uncontrolled population growth
Industrialisation that resulted in global urbanisation
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
12
THE INFRASTRUCTURE CRISIS
Housing sector
Land contamination by sub-structures.
Water pollution
Environmental degradation , for instance in the form
of climate change, ozone depletion, deforestation
and acid rain
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
13
THE DURABILITY CRISIS
Is it better to spend (say) 40% more initially, in order
that the life of a structure could be doubled? What
is better value to the client? Spend less initially or
opt for a longer life?
Total neglect of durability considerations in all the
infrastructure projects undertaken so far combined
with primitive construction practices have resulted
in a durability crisis
It is costing billions of rupees annually for repair
and rehabilitation of structures all over the world.
Hence, life cycle costing is now a mandatory
requirement in the planning process in West
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
14
TIME WASTED IS MONEY WASTED AND
OPPORTUNITIES LOST
When a constructed facility is completed early, it will
result in an early return on the capital employed
Delays in the completion of a project would
therefore represent a delay in the return on capital
invested, besides the loss of interest, which that
sum would have earned otherwise
This essential relationship between time and money
is well understood in the Western world but
unfortunately this is not the case in India
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
15
COST COMPETETIVENESS BY USING
ALTERNATIVE MATERIALS
In India, the designs are invariably limited to
concrete-intensive structures
Often the best optimal design solution will be a
sensible combination of reinforced and/or
prestressed concrete elements with structural steel
elements
There is a direct link between GNP per capita and
the per capita consumption of steel
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
16
LIFE CYCLE COST ISSUES
ASTM E917- 83 (1983) describes standard practices
for evaluating LCC of buildings and building systems
Motivation for LCC is that on any investment
decision, all costs arising from decision, both
immediate and in future are potentially important
Fast track methods in construction in western world
triggered the wide spread implementation of LCC
study that ensure enhanced productivity and efficient
utilisation of the capital.
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
17
LIFE CYCLE COST ISSUES
Life cycle cost of a structure can be regarded as
being made up of
INITIAL COST
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE COST
COST OF DISMANTLING THE STRUCTURE
LESS THE SALVAGE VALUE
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
18
INITIAL COST
Actual Cash Cost
Cost of the Investment Lock-Up without Returns
(The Time Cost)
Cost penalty to the Community due to
inappropriate Construction (Hidden Penalty
Cost)
Cost of damage to the Environment due to
Pollution (The Environment Cost)
Total Initial Cost
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
19
Flyover construction - The Indian way
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
20
Flyover construction - The Indian way
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
21
Do the business need roads?
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
22
Do the business need roads?
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
23
Where else do we store junk?
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
24
Where else do we store junk?
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
25
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE COST
Contributes to the longevity of structure
Economising this cost results in increased
expenditure later date
Most neglected activity in India
Problem is compounded by several myths
prevailing in Engineers and Architects
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
26
Myths
Concrete lasts forever without maintenance
Concrete bridges outlast steel bridges
Concrete bridges last forever without
maintenance
Structural steel can not be adequately protected
from corrosion
A steel structure is less safe in a fire than other
types of structures
Maintenance of Concrete intensive structures is
significantly cheaper than that of Steel
intensive Structures
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
27
COST OF DISMANTLING THE STRUCTURE
AT THE END OF ITS LIFE
Cost of dismantling steel structure is well below
R.C. structure
SALVAGE VALUE OF CONSTRUCTION
PRODUCTS
Cost of material recovered from steel-intensive
construction is almost equal to the original cost
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
28
EVERYDAY LIFE OF A
STRUCTURAL ENGINEER
Structural engineer designs structural systems for
buildings, bridges, dams, offshore platforms etc.
System - An assemblage of components with
specific objectives and goals and subject to certain
constraints.
Any constructed facility is a system; Structural
system is one of its major sub systems.
Components of the structural system have to meet
design requirements of strength and stiffness while
satisfying economy, buildability and durability
criteria.
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
29
Examples of Steel Framed Structures
Braced frame Moment resisting
frame
Core and suspended
floors
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
30
Examples of Steel Framed Structures
Saw tooth roof Space frame roof
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
31
Examples of Steel Framed Structures
Pylon
Lattice girder
Tapered portal
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
32
GOALS
Every system will have goals and specify what
the system is to accomplish and how it will effect
the environment and other systems
They are made in statements of specific design
objectives such as
purpose
time limitation
cost limitation
environmental constraints
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
33
SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
Objectives explain in detail the requirements that the
system must satisfy to attain the goals.
Some essential objectives are
Health, safety and welfare of occupants of the structure
Minimization of initial cost
Life cycle cost
Construction time
One criterion must be associated with each objective;
it helps to evaluate alternative systems for the
structure.
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
34
CONSTRAINTS AND STANDARDS
Constraints: Restrictions on the values of design
variables that represent properties of the system,
which are under the control of the designer. (For
example, an I-beam section of 200 mm depth may
be desirable, but not available.)
Standard: Value or range of values associated
with each constraint
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
35
CODES AND SPECIFICATIONS
Structural engineer uses relevant codes and
specifications in design of structures
A detailed set of rules and suggestions for design
of a class of structures is called an engineering
specification. Interested party prepares these
specifications and they have no legal or official
sanction.
Codes are frequently formulated by a group of
professionals with a view to their adoption by the
profession as a whole. Revised at regular
intervals.
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
36
DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
Principal design requirement of a structure is
that it should be both buildable and fit for its
purpose.
Fitness for purpose requirement of the
constructed facility depends on the satisfaction
of its structural and other requirements.
Other design requirements include those of
economy and harmony.
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
37
MULTI - DISCIPLINE PROJECT ORGANISATION
Owners
representative
Design Team
Management
Lead disciplines
Principal
disciplines
Support
disciplines
THE PROJECT MANAGER Engineer or Architect
DESIGN PROFESSIONAL
Engineer or Architect
Lead design team leader
Engineer or Architect
Struct.
Engg
Electrical
Engg.
Architecture
Mech
Engg.
Civil
Engg.
Geotech.
.Engg
Survey-
ing
Space
planning
Land
Scaping
Scheduling,
Estimating
Urban
planning
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
38
THE OVERALL
DESIGN PROCESS
Definition of the
problem
Use
Consideration of
alternative designs
Primary design
Selection
Modification
Final design
Final evaluation
Documentation
Execution
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
39
The structural design process
Design Criteria
Design Codes
Design criteria
Design codes
Knowledge
Experience
Imagination
Intuition
Creativity
Invention or modification of
structural system
Preliminary analysis
Approximation
Loads
Behaviour
Proportioning Members and Joints
Analysis
Loads
Behaviour
Evaluation
Final Design
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
40
DESIGN VERSUS ANALYSIS
In an analysis problem, all the parameters
are known - a unique solution can be
arrived.
Designer has to make several decisions,
each of which could affect the final result.
As a consequence, no unique solution can
be offered
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
41
DESIGN ALTERNATIVES
Design for strength
Specifies that the design resistance of a structural
component is greater than the required strength to
transmit the loads safely
Design for serviceability
In the serviceability design criteria for structures, the
designer seeks to make the structure sufficiently stiff so
that its deflections under the most adverse working
loads will not affect its serviceability
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
42
FACTORS CONSIDERED IN THE
DESIGN COMPARISON
Materials to be used
Arrangement and structural system and flooring
system to be adopted
Fabrication and type of jointing
Method of erection of the framework to be used
Type of construction for floor, walls, cladding and
finishes
Installation of ventilating/ heating plant, lifts,
water supply, power etc.
Corrosion protection required
Fire protection required
Operating and maintenance costs
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
43
MAJOR BUILDING STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS
Wall-bearing construction
Beam and column construction
Trusses
Rigid frames
Arches
Suspension cables and cable-stayed systems
Steel lamella roof
Dome
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
44
Beam and column construction
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
45
Single Bay, SingleStorey Structures
Knee brace 3 pin portal Flat
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
46
Cable stayed structures
Teaching Resource in Design of Steel Structures
IIT Madras, SERC Madras, Anna Univ., INSDAG
47
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Role of a structural engineer in designing
constructed facilities in 21
st
century is discussed.
Importance of life cycle costing and a rational
selection of appropriate materials for construction
is stressed .
A strong case is made to account for durability
and environmental considerations in the design
process.
Structural design process and structural systems
are described.
You might also like
- A B S S B P .: Iddle AST AtarDocument5 pagesA B S S B P .: Iddle AST Atarvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Built Up Box PlatesDocument9 pagesBuilt Up Box Platesvrajan1988No ratings yet
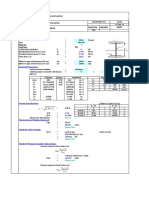
- Load Data:: VSL Middle East Qatar Date Sheet Albustan Street South, Qatar Design of Main Steel Beam Project: Document NoDocument4 pagesLoad Data:: VSL Middle East Qatar Date Sheet Albustan Street South, Qatar Design of Main Steel Beam Project: Document Novrajan1988100% (1)
- Built Up Box PlatesDocument16 pagesBuilt Up Box Platesvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Design of Column Tube1Document15 pagesDesign of Column Tube1vrajan1988No ratings yet
- GeometryDocument10 pagesGeometryvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Health PRO Brochure - 24-08-2020Document5 pagesHealth PRO Brochure - 24-08-2020vrajan1988No ratings yet
- Example Beam Column Design IS800 PDFDocument3 pagesExample Beam Column Design IS800 PDFvrajan1988No ratings yet
- 10 Combined Axial Compression and Bending Handout PDFDocument6 pages10 Combined Axial Compression and Bending Handout PDFtoliveira80No ratings yet
- Beam Express Pro TutorialDocument596 pagesBeam Express Pro Tutorialvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Load Data:: VSL Middle East Qatar Date Sheet Albustan Street South, Qatar Design of Main Steel Beam Project: Document NoDocument4 pagesLoad Data:: VSL Middle East Qatar Date Sheet Albustan Street South, Qatar Design of Main Steel Beam Project: Document Novrajan1988100% (1)
- CV610 Design of Flexural Member RajanDocument10 pagesCV610 Design of Flexural Member Rajanvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Built Up Box PlatesDocument16 pagesBuilt Up Box Platesvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Amount Water To DrinkDocument4 pagesAmount Water To Drinkvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresDocument43 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of Structuresajitgijare100% (1)
- Beam Design - 1 6mm Thick 14tk FlangeDocument7 pagesBeam Design - 1 6mm Thick 14tk Flangevrajan1988No ratings yet
- All Roof Load Criss Crossing and ParabolicDocument60 pagesAll Roof Load Criss Crossing and Parabolicvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Examples For Ductile Detailing RCC BuildingsDocument72 pagesExamples For Ductile Detailing RCC BuildingsVaidyanathan SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Pages From FinalReportContinuityDocument1 pagePages From FinalReportContinuityvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Amount Water To DrinkDocument2 pagesAmount Water To DrinkTamer El SaghirNo ratings yet
- Hwy STD Constr Details 100701 PDFDocument59 pagesHwy STD Constr Details 100701 PDFTony ZapantaNo ratings yet
- அழகிய தமிழ்ப் பெயர்கள் ஆயிரம்Document256 pagesஅழகிய தமிழ்ப் பெயர்கள் ஆயிரம்raattai100% (2)
- Drawing List Seb Typical Details: Drawing No. Drawing TitleDocument26 pagesDrawing List Seb Typical Details: Drawing No. Drawing Titlevrajan1988No ratings yet
- 2.barrier Reinforcement Details.: Detail ADocument1 page2.barrier Reinforcement Details.: Detail Avrajan1988No ratings yet
- Figure 4 PDFDocument1 pageFigure 4 PDFvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Pages From 177344845 Aashto LRFD 4th 2007Document2 pagesPages From 177344845 Aashto LRFD 4th 2007vrajan1988No ratings yet
- FinalReportContinuity PDFDocument139 pagesFinalReportContinuity PDFvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Pages From FinalReportContinuity 1 PDFDocument4 pagesPages From FinalReportContinuity 1 PDFvrajan1988No ratings yet
- Universal ColumnsDocument1 pageUniversal ColumnsAshish GalaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Ciria Report 108 Concrete Pressure On FormworkDocument1 pagePages From Ciria Report 108 Concrete Pressure On Formworkvrajan1988No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualElaineStewartieog100% (50)
- CHAPTER THREE-Teacher's PetDocument3 pagesCHAPTER THREE-Teacher's PetTaylor ComansNo ratings yet
- Film Interpretation and Reference RadiographsDocument7 pagesFilm Interpretation and Reference RadiographsEnrique Tavira67% (3)
- Code of Conduct For Public OfficialDocument17 pagesCode of Conduct For Public OfficialHaNo ratings yet
- 1941 Iraq and The IlluminatiDocument4 pages1941 Iraq and The IlluminatiZaneWeltonNo ratings yet
- Abbott 2021 ApJL 915 L5Document24 pagesAbbott 2021 ApJL 915 L5Manju SanthakumariNo ratings yet
- Review Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5Document4 pagesReview Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5XeniaNo ratings yet
- OSX ExpoDocument13 pagesOSX ExpoxolilevNo ratings yet
- Vialyn Group ResearchDocument17 pagesVialyn Group ResearchVial LynNo ratings yet
- LANY Lyrics: "Thru These Tears" LyricsDocument2 pagesLANY Lyrics: "Thru These Tears" LyricsAnneNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Construction of Concrete Batching Plant (Combined)Document72 pagesMethod Statement For Construction of Concrete Batching Plant (Combined)NP Dien100% (1)
- Weather Prediction Using Machine Learning TechniquessDocument53 pagesWeather Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniquessbakiz89No ratings yet
- Inglês - Advérbios - Adverbs.Document18 pagesInglês - Advérbios - Adverbs.KhyashiNo ratings yet
- 2017 Hu Spence Why Globalization Stalled and How To Restart ItDocument11 pages2017 Hu Spence Why Globalization Stalled and How To Restart Itmilan_ig81No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Sheet 5 Energy ADocument19 pagesHydraulics Sheet 5 Energy AMohamed H AliNo ratings yet
- Aa DistriDocument3 pagesAa Distriakosiminda143No ratings yet
- Angles, Bearings and AzimuthDocument10 pagesAngles, Bearings and AzimuthMarc Dared CagaoanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Text Book 61fb9947be91fDocument289 pagesGrade 8 Science Text Book 61fb9947be91fNadarajah PragatheeswarNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education. Academic Monitoring Department ProfileDocument14 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education. Academic Monitoring Department Profilevspd2010No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: ButterflyDocument4 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris: ButterflyRiyadi TeguhNo ratings yet
- Warranty FormDocument13 pagesWarranty FormEmpyrean Builders Corp.No ratings yet
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables: You Should LearnDocument8 pagesSolving Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables: You Should LearnTheodore JoaquinnNo ratings yet
- BPI - I ExercisesDocument241 pagesBPI - I Exercisesdivyajeevan89No ratings yet
- Super Gene 1201-1300Document426 pagesSuper Gene 1201-1300Henri AtanganaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Nurses' Knowledge of The Glasgow Coma Scale in Intensive Care and Emergency Departments at A Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh City, Saudi ArabiaDocument9 pagesExploring Nurses' Knowledge of The Glasgow Coma Scale in Intensive Care and Emergency Departments at A Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabianishu thapaNo ratings yet
- IBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Document80 pagesIBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Abubakar SidikNo ratings yet
- GMDSSDocument1 pageGMDSSRahul rajeshNo ratings yet
- Hssive-Xi-Chem-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Q & ADocument11 pagesHssive-Xi-Chem-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Q & AArties MNo ratings yet
- Imaging Anatomy Brain and Spine Osborn 1 Ed 2020 PDFDocument3,130 pagesImaging Anatomy Brain and Spine Osborn 1 Ed 2020 PDFthe gaangster100% (1)
- Heart Attack Detection ReportDocument67 pagesHeart Attack Detection ReportAkhil TejaNo ratings yet