Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organizational Structure
Uploaded by
jaffnaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organizational Structure
Uploaded by
jaffnaCopyright:
Available Formats
LOGO
THE ORGANIZATION
CHAMARA DE ZOYSA
6/10/2014
1
Contents
The Introduction to organization
Organizational Structure
Organizational Functions
Organizational Strategy
1
2
4
3 3
6/10/2014 2
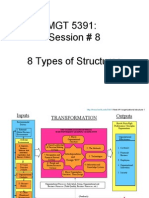
Designing Organizational Structure
Organizing
The process by which managers establish
working relationships among employees to
achieve goals.
Organizational Structure
Formal arrangement of jobs within an
organization.
Organizational design
The process by which managers make specific
choices that result in a particular kind of
organizational structure.
11-3
6/10/2014
4
Purposes of Organizing
Divides work to be done into specific jobs and
departments.
Assigns tasks and responsibilities associated with
individual jobs.
Coordinates diverse organizational tasks.
Clusters jobs into units.
Establishes relationships among individuals,
groups, and departments.
Establishes formal lines of authority.
Allocates and deploys organizational resources.
6/10/2014
5
Defining Organizational Structure
Organizational Structure
The formal arrangement of jobs within an
organization.
Organizational Design
A process involving decisions about six key
elements:
Work specialization
Departmentalization
Chain of command
Span of control
Centralization and decentralization
Formalization
6/10/2014
6
Organizational Structure
Work Specialization
The degree to which tasks in the organisation
are divided into separate jobs with each step
completed by a different person.
Over specialization can result in human
diseconomies from boredom, fatigue, stress,
poor quality, increased absenteeism, and
higher turnover.
6/10/2014
7
Departmentalization by Type
Functional
Grouping jobs by
functions performed
Product
Grouping jobs by
product line
Geographical
Grouping jobs on the
basis of territory or
geography
Process
Grouping jobs on the
basis of product or
customer flow
Customer
Grouping jobs by type
of customer and needs
An organizational structure composed of separate
business units within which are the functions that work
together to produce a specific product for a specific
customer.
6/10/2014
Functional Structure
An organizational structure composed of all
the departments that an organization
requires to produce its goods or services.
Advantages
Encourages learning from others doing
similar jobs.
Easy for managers to monitor and
evaluate workers.
Possible Disadvantages
Difficult for departments to communicate
with others.
Preoccupation with own department and
losing sight of organizational goals.
11-8
6/10/2014
FIGURE 11.5
Functional Structure
11-9
6/10/2014
Product Structure
11-10
Divisions by the product group or category
6/10/2014
11
Chain of Command
Chain of Command
The continuous line of authority that
extends from upper levels of an
organization to the lowest levels of the
organization and clarifies who reports to
who.
6/10/2014
12
Authority
The rights inherent in a managerial
position to tell people what to do and to
expect them to do it.
Responsibility
The obligation or expectation to
perform.
Unity of Command
The concept that a person should have
one boss and should report only to that
person.
6/10/2014
13
Organisation Structure (contd)
Span of Control
The number of employees who can be effectively
and efficiently supervised by a manager.
Width of span is affected by:
Skills and abilities of the manager
Employee characteristics
Characteristics of the work being done
Similarity of tasks
Complexity of tasks
Physical proximity of subordinates
Standardization of tasks
6/10/2014
Flat structures
Few organizational levels
Wide spans of control
Tall structures
Many organizational levels
Narrow spans of control
11-14
6/10/2014
15
Organisation Structure
Centralization
The degree to which decision-making is
concentrated at a single point in the
organizations.
Decentralization
Organizations in which decision-making
is pushed down to the managers who
are closest to the action.
Employee Empowerment
Increasing the decision-making authority
(power) of employees.
6/10/2014
16
The degree to which jobs within the
organization are standardized and the extent
to which employee behavior is guided by rules
and procedures.
High: formalization: Formal rules and procedures
used to standardize operations (Do it by the
book)
Usually associated with centralized authority
Low : formalization: Coordination by mutual
adjustment rather than formal rules & procedures
Usually associated with decentralized
authority
Formalization
6/10/2014
Organizational Strategy
Johnson and Scholes (Exploring
Corporate Strategy) define strategy as
follows:
"Strategy is the direction and scope
of an organization over the long-term:
which achieves advantage for the
organization through its configuration
of resources within a challenging
environment, to meet the needs of
markets and to fulfill stakeholder
expectations".
6/10/2014 17
In other words, strategy is about:
Where is the business trying to get to
in the long-term (direction)
Which markets should a business
compete in and what kind of activities
are involved in such markets?
(markets; scope)
How can the business perform better
than the competition in those
markets? (advantage)?
6/10/2014 18
What resources (skills, assets,
finance, relationships, technical
competence, facilities) are required in
order to be able to compete?
(resources)?
What external, environmental factors
affect the businesses' ability to
compete? (environment)?
What are the values and expectations
of those who have power in and
around the business? (stakeholders)
6/10/2014 19
Strategy at Different Levels of a Business
Strategies exist at several levels in any organization -
ranging from the overall business (or group of businesses)
through to individuals working in it.
Corporate Strategy - is concerned with the
overall purpose and scope of the business to
meet stakeholder expectations. This is a crucial
level since it is heavily influenced by investors in
the business and acts to guide strategic
decision-making throughout the business.
Corporate strategy is often stated explicitly in a
"mission statement".
6/10/2014 20
Business Unit Strategy - is
concerned more with how a business
competes successfully in a particular
market. It concerns strategic
decisions about choice of products,
meeting needs of customers, gaining
advantage over competitors,
exploiting or creating new
opportunities etc.
6/10/2014 21
Operational Strategy - is concerned
with how each part of the business is
organized to deliver the corporate
and business-unit level strategic
direction. Operational strategy
therefore focuses on issues of
resources, processes, people etc.
6/10/2014 22
How is Strategy Managed?
6/10/2014 23
Strategic Analysis
PEST Analysis - a technique for
understanding the "environment" in
which a business operates
Scenario Planning - a technique that
builds various plausible views of
possible futures for a business
Five Forces Analysis - a technique for
identifying the forces which affect the
level of competition in an industry
Market Segmentation - a technique
which seeks to identify similarities and
differences between groups of
customers or users
6/10/2014 24
Competitor Analysis - a wide range of
techniques and analysis that seeks to
summaries a businesses' overall
competitive position
Critical Success Factor Analysis - a
technique to identify those areas in
which a business must outperform the
competition in order to succeed
SWOT Analysis - a useful summary
technique for summarizing the key
issues arising from an assessment of a
businesses "internal" position and
"external" environmental influences.
6/10/2014 25
Strategic Choice
This process involves understanding the
nature of stakeholder expectations (the
"ground rules"), identifying strategic
options, and then evaluating and
selecting strategic options.
Strategy Implementation
Often the hardest part. When a strategy
has been analyzed and selected, the
task is then to translate it into
organizational action.
6/10/2014 26
You might also like
- The Importance of Strategic Management To Business OrganizationDocument11 pagesThe Importance of Strategic Management To Business Organizationrival pahlepiNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The External Environment of The FirmDocument16 pagesAnalyzing The External Environment of The FirmPrecious JirehNo ratings yet
- Expansion JointsDocument35 pagesExpansion Jointsjaffna100% (2)
- Bridge Bearing Types and DesignDocument53 pagesBridge Bearing Types and DesignReemALMousawiNo ratings yet
- Bituminous Mix Design & Superpave MixesDocument53 pagesBituminous Mix Design & Superpave Mixesjaffna100% (9)
- Earthing HandoutDocument18 pagesEarthing Handoutjaffna100% (1)
- Organizational Structure Design & Components ExplainedDocument38 pagesOrganizational Structure Design & Components Explainedacemave100% (1)
- Inroduction To Consumer BehaviorDocument34 pagesInroduction To Consumer BehaviorSehrish AnsariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bridge EngineeringDocument125 pagesIntroduction To Bridge Engineeringjaffna100% (1)
- Building Management System - BMS 1Document31 pagesBuilding Management System - BMS 1jaffna100% (1)
- Event MnagementDocument5 pagesEvent MnagementMary Rapunzel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- The 4ps of MarketingDocument15 pagesThe 4ps of MarketingJustin David Sanduco100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Strategy and Competitive AdvantageDocument157 pagesChapter 1 Strategy and Competitive AdvantageMeha DaveNo ratings yet
- Developing A Strategic Business PlanDocument75 pagesDeveloping A Strategic Business Planearl58No ratings yet
- Nursing Hospital Staff Job Description AimsDocument20 pagesNursing Hospital Staff Job Description AimsSanthu Su100% (1)
- Introduction to Levelling ProceduresDocument58 pagesIntroduction to Levelling Proceduresjaffna100% (1)
- Mobilisation With Movement - Vicenzino 25pDocument25 pagesMobilisation With Movement - Vicenzino 25pMauricio Castillo11% (9)
- Performance management conceptsDocument204 pagesPerformance management conceptsJacob Mathew PulikotilNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Analysis BCG and AnsoffDocument22 pagesPortfolio Analysis BCG and AnsoffV.J. NagyNo ratings yet
- Mergers and AcquisitionDocument14 pagesMergers and AcquisitionKaushik Thacker100% (2)
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit 1Document60 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit 1A.R. Pradeep Kumar91% (11)
- Traverse ComputationsDocument42 pagesTraverse Computationsjaffna100% (3)
- CRM PPT 1Document101 pagesCRM PPT 1Saket Sharma100% (1)
- The NEC Compared and ContrastedDocument114 pagesThe NEC Compared and Contrastedqatarstructz30No ratings yet
- Concrete Making MaterialsDocument55 pagesConcrete Making Materialsjaffna100% (1)
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument11 pagesSewage Treatment Plantjaffna86% (7)
- Perdev-Midterm 2nd SemDocument3 pagesPerdev-Midterm 2nd SemEmerson Biclar Golipardo100% (3)
- Understanding RBVDocument12 pagesUnderstanding RBVJEMIMAH MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- Leveling Fundamentals GuideDocument33 pagesLeveling Fundamentals Guidejaffna100% (2)
- Building Management System - BMS 2Document44 pagesBuilding Management System - BMS 2jaffna100% (3)
- Marketing Management Chapter 14Document42 pagesMarketing Management Chapter 14Soumya Jyoti BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Hot Mix Plant Calibration, Laying & TestingDocument55 pagesHot Mix Plant Calibration, Laying & Testingjaffna88% (17)
- Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyDocument69 pagesCustomer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyMUHAMMAD HAMZA JAVEDNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure and Design FundamentalsDocument27 pagesOrganizational Structure and Design Fundamentalskary2907900% (1)
- Cambridge International AS - A Level Accounting Executive Preview-1Document63 pagesCambridge International AS - A Level Accounting Executive Preview-1Shingirayi MazingaizoNo ratings yet
- PERIOD: 01 - INTRODUCING YOURSELFDocument79 pagesPERIOD: 01 - INTRODUCING YOURSELFKhanh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Strategic Plan Format - Case AnalysisDocument6 pagesStrategic Plan Format - Case AnalysisProudmoore KunkkaNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7S ModelDocument6 pagesMcKinsey 7S Modelpriyank1256No ratings yet
- P Pretest and Posttest Phoenetic and MarungkoDocument25 pagesP Pretest and Posttest Phoenetic and MarungkoJellie Tamonan BarbajoNo ratings yet
- Vision, Mission, Values and ObjectivesDocument28 pagesVision, Mission, Values and ObjectivesGobind KohliNo ratings yet
- The Ten Ps of Tourism MarketingDocument18 pagesThe Ten Ps of Tourism MarketingSalah FerdiaNo ratings yet
- Marketing - 2: Debasish Nayak PGDM 2 Year Krupajal Business SchoolDocument14 pagesMarketing - 2: Debasish Nayak PGDM 2 Year Krupajal Business SchoolDebasish NayakNo ratings yet
- Section 4: Science, Technology, and Nation-BuildingDocument50 pagesSection 4: Science, Technology, and Nation-Buildingelizabeth bernales100% (4)
- A Review On Value Creation in Tourism IndustryDocument10 pagesA Review On Value Creation in Tourism IndustryPablo AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Mall Management: 5 Key Components of Mall ManagementDocument6 pagesMall Management: 5 Key Components of Mall ManagementHEMANTA KUMAR SAHOO100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet: English 8Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: English 8Sandra QS Membrere100% (1)
- Introduction To Business Model InnovationDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Business Model InnovationDuong Chi ThanhNo ratings yet
- Thesis GuidelinesDocument18 pagesThesis GuidelinesAsad HamidNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Competitor AnalysisDocument26 pagesSession 5 Competitor AnalysisAhmed MunawarNo ratings yet
- Writing A Business Plan: Bruce R. Barringer R. Duane IrelandDocument35 pagesWriting A Business Plan: Bruce R. Barringer R. Duane IrelandDawood HusainNo ratings yet
- Five Generic Competitive StrategiesDocument18 pagesFive Generic Competitive StrategieskennetholayvarNo ratings yet
- 11 Organizational StructureDocument115 pages11 Organizational Structureabhishek ibsar50% (2)
- An Entrepreneur Is A Person Who Has Possession of A New EnterpriseDocument12 pagesAn Entrepreneur Is A Person Who Has Possession of A New EnterpriseJose ThomasNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Management and LeadershipDocument4 pagesDifference Between Management and LeadershiplibertadmasNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument2 pagesCompetitive AdvantageShipra SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BRM CityCell Marketing PromotonDocument31 pagesBRM CityCell Marketing PromotonSamiul RikthNo ratings yet
- List of Case Studies On Strategy (Catalogue IV)Document53 pagesList of Case Studies On Strategy (Catalogue IV)Sushil Agrawal0% (1)
- Developing an understanding of leadership traits and theoriesDocument12 pagesDeveloping an understanding of leadership traits and theoriesShubham GoelNo ratings yet
- AIESEC Balanced ScorecardDocument29 pagesAIESEC Balanced ScorecardCarl ChiangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Module 1: Introduction To ManagementDocument32 pagesPrinciples of Management: Module 1: Introduction To Managementnaman khan satnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To STP ModelDocument6 pagesIntroduction To STP ModelArushi SinghNo ratings yet
- Managing Change and InnovationDocument23 pagesManaging Change and InnovationDimitri Elitist BlessNo ratings yet
- Vision, Mission & ObjectivesDocument23 pagesVision, Mission & Objectivesnightriders59No ratings yet
- Business-Strategic Management Study GuideDocument96 pagesBusiness-Strategic Management Study GuideNokuthula PearlNo ratings yet
- Operations Strategy and CompetitivenessDocument3 pagesOperations Strategy and CompetitivenessMuneera Al Hassan0% (1)
- Forest Resources in IndiaDocument4 pagesForest Resources in Indiaahemad_ali10No ratings yet
- Defining The New Marketing ConceptDocument11 pagesDefining The New Marketing ConceptJen Beilfuss ScullyNo ratings yet
- 10 Green Business IdeasDocument26 pages10 Green Business Ideasa_hamzaNo ratings yet
- Building Brand AwarenessDocument15 pagesBuilding Brand AwarenessAnthon MendezNo ratings yet
- A Study On Existing Talent Management Practice and PDFDocument14 pagesA Study On Existing Talent Management Practice and PDFS- AjmeriNo ratings yet
- Business Model Value Proposition PDFDocument5 pagesBusiness Model Value Proposition PDFSamaritanFahadNo ratings yet
- Bachelor Reflective JournalDocument14 pagesBachelor Reflective JournalduchesslizNo ratings yet
- Business Environment NotesDocument4 pagesBusiness Environment NotesAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Principles of Management (Bpmn1013) Group GDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 Principles of Management (Bpmn1013) Group GEvon TohNo ratings yet
- Startup VentureDocument45 pagesStartup VentureMAA KI AANKH0% (1)
- 6W2X - Business Model Canvas With ExplanationsDocument2 pages6W2X - Business Model Canvas With ExplanationstorqtechNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis: Submitted To: Submitted By: Pooja Seth (UB2784596)Document12 pagesCompetitive Analysis: Submitted To: Submitted By: Pooja Seth (UB2784596)aaservices100% (1)
- Unit 3 PlanningDocument52 pagesUnit 3 PlanningPreeti BhaskarNo ratings yet
- StrategyDocument5 pagesStrategyIFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Management by ExceptionDocument9 pagesManagement by Exception2K20DMBA158 Prabhakar MallikNo ratings yet
- Competitiveness Strategy and ProductivityDocument34 pagesCompetitiveness Strategy and ProductivityRaymuel BelarminoNo ratings yet
- Planning and OrganizingDocument27 pagesPlanning and OrganizingOwais ShiekhNo ratings yet
- Pre-cast Girder Construction Process Step-by-StepDocument19 pagesPre-cast Girder Construction Process Step-by-StepjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Grillage Method of Superstructure Analysis: Dr. Shahzad Rahman NWFP University of Engg & Technology, PeshawarDocument59 pagesGrillage Method of Superstructure Analysis: Dr. Shahzad Rahman NWFP University of Engg & Technology, PeshawarpotharajudvnagaNo ratings yet
- LevellingDocument42 pagesLevellingjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Surveying: Basics of TraversingDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Surveying: Basics of Traversingjaffna100% (1)
- Multiview SketchesDocument28 pagesMultiview SketchesjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Fusion WeldingDocument31 pagesFusion WeldingjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Mix DesignDocument15 pagesMix DesignjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Management AccountingDocument21 pagesManagement AccountingbelladoNo ratings yet
- CulvertsDocument46 pagesCulvertsjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Ingredients of Bituminous Mixes & Introduction To ModifiersDocument69 pagesIngredients of Bituminous Mixes & Introduction To ModifiersjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Chain SurveyDocument21 pagesChain SurveyjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Product SpecificationDocument39 pagesEngineering Product SpecificationjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Bituminous MixesDocument56 pagesBituminous MixesjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Basics of SurveyingDocument48 pagesBasics of SurveyingjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument25 pagesEvolution of Management TheoriesjaffnaNo ratings yet
- Digital Storytelling Night Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDigital Storytelling Night Lesson Planapi-397843699No ratings yet
- Introduction To BQ2Document10 pagesIntroduction To BQ2Emir KandemirNo ratings yet
- Class 10 SSTDocument2 pagesClass 10 SSTSurinder PalNo ratings yet
- Port City International University Is One of The Leading Universities in BangladeshDocument2 pagesPort City International University Is One of The Leading Universities in BangladeshSadia FarjanaNo ratings yet
- Audio Essay ReflectionDocument2 pagesAudio Essay ReflectionSarah LineschNo ratings yet
- Science TeachersDocument16 pagesScience TeachersNashwaNo ratings yet
- Assignment/ Tugasan - Introductory Business CommunicationDocument6 pagesAssignment/ Tugasan - Introductory Business CommunicationKhai LimNo ratings yet
- Uni 1 gw5 - TestDocument3 pagesUni 1 gw5 - TestDebora AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- STPM Literature SyllablesDocument52 pagesSTPM Literature SyllablesSheng Yuan SooNo ratings yet
- FINAL Project-Proposal-Rubric-2021Document3 pagesFINAL Project-Proposal-Rubric-2021Kurt AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Certificate - Online FormatDocument4 pagesProject Management Certificate - Online FormatAhmedNo ratings yet
- BOW - ENTREP9 - 1st QTRDocument2 pagesBOW - ENTREP9 - 1st QTREdgardo De Mesa MalaitNo ratings yet
- DepEd Moises Padilla Variety Show RulesDocument2 pagesDepEd Moises Padilla Variety Show RulesFrankie Snook Bravo IIINo ratings yet
- Department of FoodDocument2 pagesDepartment of FoodBhushan DevraniNo ratings yet
- Guide For Applicants For Admission - Version 3.1 - Issued 26 June 2020Document61 pagesGuide For Applicants For Admission - Version 3.1 - Issued 26 June 2020seunidowu7668No ratings yet
- Universityies Email ID - PreDocument10 pagesUniversityies Email ID - PreMuhammad Waris HarganNo ratings yet
- W1. Ucsp Unit 6, Lesson 5 - EducationDocument3 pagesW1. Ucsp Unit 6, Lesson 5 - EducationPrince Ariean Songcuan PinedaNo ratings yet
- Aiden Tenhove - ResumeDocument1 pageAiden Tenhove - Resumeapi-529717473No ratings yet
- Daily Report: Canteen Renovation ProjectDocument1 pageDaily Report: Canteen Renovation ProjectSulistiyo PutraNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On The Bond For Training Public Servants July 2018Document30 pagesGuidelines On The Bond For Training Public Servants July 2018Jan TangNo ratings yet
- DLP 10 -4.3 Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesDLP 10 -4.3 Literature ReviewShela TupagNo ratings yet
- Guinto, Critique PaperDocument4 pagesGuinto, Critique PaperReanne GuintoNo ratings yet