Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Total Quality Management & Cost of Quality
Uploaded by
D Nitins SharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Total Quality Management & Cost of Quality
Uploaded by
D Nitins SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
TOTAL QUALITY
MANAGEMENT &
COST OF QUALITY
What is Quality?
Quality is fitness for use
(Joseph Juran)
Quality is conformance to requirements
(Philip B. Crosby)
Quality of a product or services is its ability to
satisfy the needs and expectations of the
customer
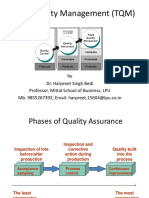
Evolution of Quality Management
Inspection
Quality
Control
Quality
Assurance
TQM
Salvage, sorting, grading, blending, corrective
actions, identify sources of non-conformance
Develop quality manual, process performance
data, self-inspection, product testing, basic
quality planning, use of basic statistics,
paperwork control.
Quality systems development, advanced quality
planning, comprehensive quality manuals, use of
quality costs, involvement of non-production
operations, failure mode and effects analysis, SPC.
Policy deployment, involve supplier & customers,
involve all operations, process management,
performance measurement, teamwork, employee
involvement.
Why care about quality
Increase productivity
Expand market share
Raise customer loyalty
Enhance competitiveness of the firm
At a minimum, serve as a price of entry
Why Quality is so difficult to do?
Quality can only be defined in terms of an
agent (a judge of quality).
One has to translate future needs of the user
into measurable characteristics
Service Industries are
particularly Difficult
Reasons:
High volume of transaction
Immediate consumption
Difficult to measure and control
More labor intensive
High degree of customization required
Image is a quality characteristic
Behavior is a quality characteristic
Quality Gurus
Deming: The father of the quality movement.
Scientific approach to quality
Joseph M. Juran: Quality by design/fitness for
use
Philip B.Crosby: Quality is free
Karou Ishikawa : Participative approach,
Quality circle
Shigeo Shingo : Poka Yoke Mistake proofing
Genichi Taguchi Three Stage Design Process
8
Application of quantitative methods and human
resources to improve all the processes within an
organization and exceed customer needs now
and in the future.
Total Quality Management
What is TQM?
Constant drive
for continuous
improvement
and learning.
Concern for
employee
involvement and
development
Management
by Fact
Result Focus
Passion to deliver
customer value /
excellence
Organisation
response -
ability
Actions not just
words
(implementation)
Process
Management
Partnership
perspective
(internal /
external)
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF TQM
Approach Management Led
Scope Company Wide
Scale Everyone is responsible for Quality
Philosophy Prevention not Detection
Standard Right First Time
Control Cost of Quality
Theme On going Improvement
Elements of Total Quality
Management
Commitment
of
Top
Management
Employee
Involvement
Training
Requirement
Quality
managements
Tools
Quality Management Tools Tools
Highlighting
Quality
Problems
Control
Charts
Identifying
Improvement
Opportunities
Histogram
Check Sheets
Scatter Diagram
Pareto Diagram
Graphs
Analyzing
Problems and
Their Root
cause
Fishbone
Diagram
Cause and
Effect Diagram
with Action card
(CEDAC)
Tools for
Operational
Planning
Tree
Diagram
Matrix
Diagram
Process
decision
program
Chart
Poka Yoka
Arrow
diagram
Tools For
Strategic
Planning
PDCA
Quality
Function
Deployment
(QFD )
Quality Cost
PLAN
CHECK
DO
ACT
The Deming Cycle or PDCA Cycle
Plan a change to the process. Predict the effect
this change will have and plan how the effects
will be measured
Implement the change on a
small scale and measure the
effects
Adopt the change as a
permanent modification to
the process, or abandon it.
Study the results to learn
what effect the change had,
if any.
Cost of Quality
Quality
Cost
Control
Cost
Prevention Appraisal
Failure
Cost
Internal External
Quality Certifications and
Awards
The Deming Prize
The Malcom Baldrige national Quality
Awards
European Quality Award
CII- EXIM Business Excellence award
Rajeev Gandhi National Quality
Award
Quality
Awards
ISO9000 Series
ISO14000 Series
QS9000 Series
TL9000 Series
OHSAS 18001
Quality
Certifications
You might also like
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument17 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsAnkeshNo ratings yet
- Methods of Quality Management: College of Nursing Meng Qinghui 2007-4Document31 pagesMethods of Quality Management: College of Nursing Meng Qinghui 2007-4s_jithsreeNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument30 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsMd. Mizanur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument36 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsMuhannad AbdulRaoufNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument36 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- 1 TQMDocument24 pages1 TQMLakky ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: Aireen Y. CloresDocument51 pagesTotal Quality Management: Aireen Y. CloresaireencloresNo ratings yet
- TQM IntroductionDocument32 pagesTQM Introductionshivashankar sgNo ratings yet
- Value Creation Strategies: Quality Concepts and ToolsDocument87 pagesValue Creation Strategies: Quality Concepts and ToolsAjay PadhiNo ratings yet
- Second ClassDocument48 pagesSecond ClassMartinus Golden SiteketaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - TQMDocument37 pagesUnit 8 - TQMAshutosh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14tqmDocument24 pagesLecture 14tqmapi-3754041No ratings yet
- Modern History of Quality ManagementDocument29 pagesModern History of Quality ManagementnalinijevalNo ratings yet
- IE E1-111 (QM Principles)Document12 pagesIE E1-111 (QM Principles)Dave AlberoNo ratings yet
- Quality and InnovationDocument61 pagesQuality and InnovationahyaniluthfianasariNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System: NotesDocument17 pagesQuality Management System: NotesJenine BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 QMDocument60 pagesUnit 5 QMAshlay BaichooNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: P. M. SagareDocument32 pagesTotal Quality Management: P. M. SagareDeep UmradiyaNo ratings yet
- TQM - HandoutDocument11 pagesTQM - Handoutrdx216No ratings yet
- Otal Quality ManagementDocument53 pagesOtal Quality ManagementdrrajputNo ratings yet
- 17 Quality ManagementDocument45 pages17 Quality ManagementAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1tqmDocument16 pagesLecture 1tqmapi-3754041No ratings yet
- Module 2 TQMDocument58 pagesModule 2 TQMkavyashreembNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument31 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsbhattacharjeesomnathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document33 pagesChapter 9Denise BaterinaNo ratings yet
- PPT3-Managing QualityDocument29 pagesPPT3-Managing QualityIka FitriNo ratings yet
- The Total Quality Management: Prof: Mohammad Al NuaimiDocument53 pagesThe Total Quality Management: Prof: Mohammad Al NuaimiRaghad MasarwehNo ratings yet
- OM Chapter FiveDocument67 pagesOM Chapter FiveLakachew GetasewNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management Unit I GE2022Document52 pagesTotal Quality Management Unit I GE2022standalonembaNo ratings yet
- Revisi PPT3-Managing QualityDocument28 pagesRevisi PPT3-Managing QualityAbdul GhoniNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Mutu: (Heizer/Render - Operations Management, 8e - © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc)Document72 pagesManajemen Mutu: (Heizer/Render - Operations Management, 8e - © 2006 Prentice Hall, Inc)FrankyLinkNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management (TQM)Document46 pagesTotal Quality Management (TQM)Harsimran SinghNo ratings yet
- Deming Crosby JuranDocument93 pagesDeming Crosby Juranmannarmannan2No ratings yet
- 2 Total Quality ManagementDocument33 pages2 Total Quality Managementzenia thea dulayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Approaches To Total Quality Management PDFDocument35 pagesLecture 3 Approaches To Total Quality Management PDFAnnerose GaleraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Total Quality ManagementDocument88 pagesTopic 1 Total Quality ManagementncubemellonNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument175 pagesTotal Quality Managementimad83% (6)
- TQM2Document51 pagesTQM2Aboody AlzeeerNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument47 pagesQuality ManagementDora LimNo ratings yet
- Operations & Productions Management: Bahria UniversityDocument16 pagesOperations & Productions Management: Bahria UniversityFareed khan ZKNo ratings yet
- Mce 6221 Total Quality ManagementDocument26 pagesMce 6221 Total Quality ManagementMohammad Muhtasim Mashfy, 170011054No ratings yet
- Operations Manager: - Deliver A Quality Product/service ToDocument23 pagesOperations Manager: - Deliver A Quality Product/service ToakshaynnaikNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management (TQM) - Philosophy & ImplementationDocument181 pagesTotal Quality Management (TQM) - Philosophy & Implementationmayank patelNo ratings yet
- Assighment by Anurag KumarDocument6 pagesAssighment by Anurag Kumarkapil gargNo ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement Strategy T Q M: Definition, Concept & Pillars of TQM Breakthrough Improvement Strategy Business Process Reengineering (BPR)Document25 pagesContinuous Improvement Strategy T Q M: Definition, Concept & Pillars of TQM Breakthrough Improvement Strategy Business Process Reengineering (BPR)Sam DreamNo ratings yet
- QualityDocument25 pagesQualitygsidhu156276No ratings yet
- Total QualitDocument18 pagesTotal QualitSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Understanding QualityDocument4 pages01 Understanding QualityGELO GARCIANo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Quality AssuranceDocument16 pagesQuality Control and Quality AssurancemuhibNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: Practices and PrinciplesDocument49 pagesTotal Quality Management: Practices and PrinciplesJoyce AnnNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument54 pagesTotal Quality ManagementKaushika Rajapaksha PereraNo ratings yet
- TQM Chapter 1Document41 pagesTQM Chapter 1Farah Al-MajaliNo ratings yet
- OM - Mod 2.6 - Total Quality ManagementDocument33 pagesOM - Mod 2.6 - Total Quality ManagementAyush KaushalNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman CH 5 Total Quality ManagementDocument5 pagesRangkuman CH 5 Total Quality ManagementMhd. Yhoga Ananta WijayaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management Chapter 1Document49 pagesTotal Quality Management Chapter 1Princess Ria Generalao OhinaNo ratings yet
- NOTADocument37 pagesNOTADuin Abd AzizNo ratings yet
- 7 Total QualityDocument47 pages7 Total QualityTejas BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy in A Developing Country 2014Document19 pagesFiscal Policy in A Developing Country 2014D Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- NaftaDocument3 pagesNaftaD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Work StudyDocument22 pagesWork StudyD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project ManagemntDocument34 pagesProject ManagemntD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEBI Investor Protection GuidelinesDocument1 pageSEBI Investor Protection GuidelinesD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- LayoutDocument18 pagesLayoutD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Companies Act Important DefinitionsDocument6 pagesCompanies Act Important DefinitionsD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- SIP Guidelines For Students 2014Document11 pagesSIP Guidelines For Students 2014D Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dainik Bhaskar - A Success Story - RediffDocument4 pagesDainik Bhaskar - A Success Story - RediffD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsDocument53 pagesMarketing: Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dainik Bhaskar - A Success Story - RediffDocument4 pagesDainik Bhaskar - A Success Story - RediffD Nitins SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management (Tp4)Document16 pagesIntroduction To Database Management (Tp4)Kalicia RodriquesNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 IntroDocument20 pagesLecture01 IntroRijy LoranceNo ratings yet
- WellheadDocument2 pagesWellheadRicardo Paz SoldanNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Software Test AutomationDocument20 pages5.1 Software Test Automationudhayan udhaiNo ratings yet
- Forage Compactor 7700: Part of The FC7000 Series of Hay PressesDocument4 pagesForage Compactor 7700: Part of The FC7000 Series of Hay PressesAbimelec TaipeNo ratings yet
- It Era Final ModuleDocument103 pagesIt Era Final ModuleLeonso Visto JrNo ratings yet
- Core EdifDocument2 pagesCore EdifOsama ElfadniNo ratings yet
- ATA ConfigurationDocument14 pagesATA ConfigurationsreedharNo ratings yet
- CV NguyenLamTruong EngNew PDFDocument1 pageCV NguyenLamTruong EngNew PDFhoa leNo ratings yet
- Approach of Image Processing in Diagnosis and Medication of Fungal Infections in Pet AnimalsDocument15 pagesApproach of Image Processing in Diagnosis and Medication of Fungal Infections in Pet AnimalsJohn SnowNo ratings yet
- Society of International Gas Tanker & Terminal Operators (Sigtto)Document8 pagesSociety of International Gas Tanker & Terminal Operators (Sigtto)Mohamed MekkyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document62 pagesChapter 01Rap JaviniarNo ratings yet
- MEM201 L6-Tolerance RCDocument31 pagesMEM201 L6-Tolerance RCKaliya PerumalNo ratings yet
- Omron G8P 114P FD US DC12 DatasheetDocument6 pagesOmron G8P 114P FD US DC12 DatasheetCorretaje ResidencialNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems by S Haykin PDFDocument2 pagesCommunication Systems by S Haykin PDFAmandaNo ratings yet
- Technology in The Construction IndustryDocument5 pagesTechnology in The Construction IndustryGiancarlo GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Kanban: CEN 4010 Intro To Software Engineering Professor Alex RoqueDocument25 pagesKanban: CEN 4010 Intro To Software Engineering Professor Alex RoquespringleeNo ratings yet
- Data Format For RFID Data Using A Data-on-Tag Approach: Sarita PaisDocument243 pagesData Format For RFID Data Using A Data-on-Tag Approach: Sarita PaisElectrifying SaurabhNo ratings yet
- Proposed Research Titles: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesProposed Research Titles: ObjectivesApril Danica BiernezaNo ratings yet
- XLP Interface V4.0Document3 pagesXLP Interface V4.0Anonymous PedQHSMNo ratings yet
- DROPS - Reliable Securing Rev 04Document67 pagesDROPS - Reliable Securing Rev 04Chris EasterNo ratings yet
- StrikerDocument228 pagesStrikerVictoria Vazquez PerezNo ratings yet
- Automatic Memory Management (AMM) On 11g & 12cDocument9 pagesAutomatic Memory Management (AMM) On 11g & 12cejgonzalezpNo ratings yet
- Module 7 CSS G11 2nd Sem Week 3 4 PDFDocument59 pagesModule 7 CSS G11 2nd Sem Week 3 4 PDFKenkenNo ratings yet
- RTO Office Admn DocumentDocument57 pagesRTO Office Admn DocumentBlixProjects0% (2)
- SCE-CNF-VAS VAS Configuration Document V1 1Document11 pagesSCE-CNF-VAS VAS Configuration Document V1 1fran0% (1)
- X1 Using VA01 With Digital Call Panel Quick Start ProgrammingDocument4 pagesX1 Using VA01 With Digital Call Panel Quick Start ProgrammingMos CraciunNo ratings yet
- Megger Limited Mit330 en Megohmmeter DatasheetDocument4 pagesMegger Limited Mit330 en Megohmmeter DatasheetCésar Ricardo Mamani RetamalesNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - Session 2 - TAFC FoundationDocument64 pagesDay 1 - Session 2 - TAFC FoundationEmmanuel Uchenna ChukwuNo ratings yet
- PHD 2021 Entrance and Admission NoticeDocument1 pagePHD 2021 Entrance and Admission Noticevivek soniNo ratings yet