Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Reproduction1
Uploaded by
Wilson HindartoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Reproduction1
Uploaded by
Wilson HindartoCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproduction of Cells
The DNA
Molecule
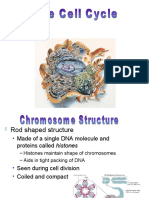
Chromosome Structure
Rod shaped structure
Made of a single DNA molecule and
proteins called histones
Histones maintain shape of chromosomes
Aids in tight packing of DNA
Seen during cell division
Coiled and compact
DNA and Chromosomes
double-stranded
DNA molecule
A Pair of Homologous
Chromosomes
centromere
homologous
chromosomes
DNA
Replication
Chromosome structure
Chromosome consists of two
identical halves
Each half is a chromatid
Formed when DNA makes a copy of itself
before cell division
Each new cell will receive one chromatid
from each chromosome
Chromatids are held together by a
centromere
Chromosomal Replication
sister chromatids
DNA replication
A Chromosome After Replication
QuickTime and a
Cinepak Codec by Radius decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
sister chromatids
Human Chromosomes
Human Chromosomal Pairs
23 pairs
Sex
chromosomes
autosomes
Cell Cycle
The Cell Cycle
The Cell Cycle
Interphase- 75% of cell life cycle
G
1
: rapid growth; centrioles
replicate.
S: DNA replicates
G
2
: cell prepares for cell
division; microtubular structures
form.
The Cell Cycle
Cell Division
Mitosis: cell divides its nuclear
components (chromosomes).
Cytokinesis: cell divides its
cytoplasmic components.
Stages of Mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
centrioles
chromatin
plasma
membrane
nucleolus
nuclear
envelope
Interphase
Prophase
Chromosomes shorten and become
visible (early prophase)
Chromosomes made up of 2 identical
chromatin threads called chromatids
Centrioles migrate toward opposite pole
pulled by kinetochore
Nuclear envelope disintegrates (late
prophase).
Prophase
centromere
chromosome
aster
centrioles
aster
polar fiber
chromosomal
fiber
fragmenting
nuclear
envelope
Prophase
Centrioles
During
Prophase
centrioles
nucleus
Metaphase
Chromosomes lined up in the
middle
Mitotic spindle complete.
metaphase plate
spindle
Metaphase
polar fibers
chromosomal
fibers
sister chromatids
Metaphase
Chromosome at Metaphase
Anaphase
Sister chromatids (= identical strands of
DNA) split from each other to form divided
identical chromosomes.
Kinetochore fibers shorten and pull divided
identical chromosomes to opposite sides of
the dividing cell.
Polar microtubules slide past each other,
lengthening and pushing the cell apart
daughter
chromosomes
Anaphase
Telophase
Divided chromosomes reach opposite
sides of cell and begin to disperse as
chromatin.
Nuclear envelopes reforms around
separated collections of chromosomes to
form two nuclei.
Cytokinesis- completion of cell division
Telophase
Spindle apparatus disintegrates.
Cytokinesis usually begins near the
end of telophase.
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Separation of cytoplasmic
components to yield two daughter
cells
Microfilaments form a contracting
ring that pinches the plasma
membrane inward between the
forming daughter cells
Cytokinesis
cleavage furrow
Cytokinesis
Cancer
Rapid and uncontrollable
development and production of cells.
Development of Cancer Cells
1. Inheritance may increase risk
2. Proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor
genes mutate or become damaged by
carcinogens
3. Known carcinogens:
Viruses and bacteria
Environmental chemicals
Tobacco
Radiation
Dietary factors
Conversion
Conversion begins with a mutation
(a change in DNA) by:
1. Chemical
2. Physical
3. Biological
Conversion
Production of Cancer Cells
Development and Progression
Development &
Progression of Cancer
Begins when a chemical substance
stimulates growth of a mutated cell
Those chemical substances
influence a 2
nd
stage of
carcinogens called promoters.
Promoters stimulate cell to divide
uncontrollably
Metastasis- cancer traveling to
other sites; like a forest fire
Development of a
Benign Tumor
Development of a
Malignant Tumor
Overview of the
Development Cancer
Ultraviolet Radiation
and Skin Cancer
ozone
Ozone:
Screens out 99% of harmful UV light
Ozone produced by lightening
1% in ozone will result in a 2% in
skin cancer
Holes in ozone:
Dupont- CFCs: hairspray, refrigerators,
air conditioning
Which country has the highest rate of
skin cancer?
Skin Cancer
1. Avoid sun between 10am to 4pm.
2. Wear sunscreen w/ SPF 40+.
3. Wear appropriate clothing.
Testing
Genetic testing
Biopsy
Blood test
X-rays, PET, MRI
Visual & tactile observation
Treatments
Surgery
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Homeopathy
Prevention
Know family history
Get regular medical screenings
Learn self-exam techniques
Avoid direct sunlight
Watch your diet and weight
Dont smoke
Drink alcohol in moderation (alcohol
decrease heart disease, but increases
risk of certain cancers)
Become educated
You might also like
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Bio ReportDocument53 pagesBio ReportMichaelmr ArnozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - 23.12.2022Document30 pagesLecture 7 - 23.12.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument85 pagesCell DivisionGlendel DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument24 pagesMitosisapi-202349222No ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 7Document40 pagesBIOL223-Lab 7chicken fries100% (2)
- Cell DIVISIONDocument33 pagesCell DIVISIONSharifah NurainNo ratings yet
- Structure of Chromosomes XRDocument16 pagesStructure of Chromosomes XRhrishikeshanil123No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document14 pagesChapter 9alaskamofoNo ratings yet
- 3- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument33 pages3- Cell Cycle and MitosisAmany SaifNo ratings yet
- Mitosis 1Document27 pagesMitosis 1USAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument48 pagesCell DivisionMichaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Document42 pagesChapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Nehjoy GerangueNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis: Biology 1Document19 pagesCell Division: Mitosis: Biology 1vijauNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & MitosisDocument30 pagesCell Cycle & MitosisRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ChromosomeDocument28 pagesChromosomeSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 MitosisDocument36 pagesLesson 7 MitosisMobileLegends SbNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument13 pagesMitosisIshwar singh DhamiNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument16 pagesMitosisAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- Izat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmDocument18 pagesIzat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmSuhailina Mohd IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - DiscussionDocument30 pagesMitosis - DiscussionTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument20 pagesMitosis and The Cell CycleJustyna DończykNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleMitosis - ElisaDocument40 pagesCell CycleMitosis - ElisabenjaNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Chap 6Document53 pagesBio F4 Chap 6Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument39 pagesMITOSISEmmalyn VillosoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesUnit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionTeo PhiriNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Mitosis ExplainedDocument29 pagesCell Division and Mitosis ExplainedEL PEPENo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Division ProcessDocument48 pagesCell Cycle & Division ProcessCham RosarioNo ratings yet
- Bio Cell Division 100106220037 Phpapp01Document35 pagesBio Cell Division 100106220037 Phpapp01PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Cell.7Document14 pagesReproduction in Cell.7Soha Ch100% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument86 pagesCell DivisionaliNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument28 pagesMeiosisPari ValechaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument40 pagesThe Cell Cycle and MitosisStifany Dianne VillasNo ratings yet
- Mitosis (Cytogenetics)Document20 pagesMitosis (Cytogenetics)Via Gail CanlasNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Document96 pagesMitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesANnur RAshidNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four.. 2022-10-12 11 - 31 - 55Document34 pagesChapter Four.. 2022-10-12 11 - 31 - 55Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: ObjectivesDocument56 pagesMitotic Cell Division - Exercise 7: Objectiveskaran79No ratings yet
- Cell Division NoteDocument12 pagesCell Division NoteAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: MitosisDocument36 pagesThe Cell Cycle: MitosisEllen Jane RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell Division: - Biology - Form 4 - 2021Document46 pagesChapter 6 Cell Division: - Biology - Form 4 - 2021Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument27 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 Icse Boards!Document10 pagesBiology Class 10 Icse Boards!nark.jf4No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument55 pagesCell DivisionjohnpenielmontalesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PDFDocument30 pagesMitosis PDFPankaj MalikNo ratings yet
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument27 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsYecid Rojas-MolinaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument30 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionamitNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument36 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionHeart VidalNo ratings yet
- Cell Diviosin For CCDocument27 pagesCell Diviosin For CCmiss HalaNo ratings yet
- LAS 36 MitosisDocument27 pagesLAS 36 MitosisAls Centre A OpolNo ratings yet
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument21 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsCristina MariaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PowerpointDocument28 pagesMitosis PowerpointShairah LozanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument16 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Chromosomesmitoticcycle 160401133710Document40 pagesChromosomesmitoticcycle 160401133710Suzette AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- BBC1-K11-13 Cell ReplicationDocument81 pagesBBC1-K11-13 Cell Replicationirvan tpNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PowerpointDocument31 pagesMitosis PowerpointLeenfranzen MagadiaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideDocument63 pagesThe Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideTrisha Mae VelascoNo ratings yet
- Cell CommunicationDocument45 pagesCell CommunicationWilson HindartoNo ratings yet
- The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument69 pagesThe Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria: Powerpoint Lectures ForWilson HindartoNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument42 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Powerpoint Lectures ForWilson HindartoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument123 pagesNervous SystemDrGasnasNo ratings yet
- The Cell As The Fundamental Unit of Life:: Membrane Transport ProcessesDocument24 pagesThe Cell As The Fundamental Unit of Life:: Membrane Transport ProcessesWilson HindartoNo ratings yet
- Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of Life: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument25 pagesCarbon and The Molecular Diversity of Life: Powerpoint Lectures ForWilson HindartoNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic Relationships Between The Three KingdomsDocument5 pagesPhylogenetic Relationships Between The Three Kingdomsibadullah shah100% (1)
- An Analytical Essay On Sinovac VaccineDocument3 pagesAn Analytical Essay On Sinovac VaccineShanya Lameyna VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Cell CommunicationDocument4 pagesCH 11 Cell Communicationwil7ver100% (2)
- Sneha P Naik: Qualification College/ Institute Year of Passing PercentageDocument4 pagesSneha P Naik: Qualification College/ Institute Year of Passing PercentageLokeshNo ratings yet
- Shpa International Register of Drug Information ServicesDocument26 pagesShpa International Register of Drug Information ServicesdianmpsNo ratings yet
- 2023 07 03 547464v1 FullDocument36 pages2023 07 03 547464v1 FullasdfsoidjfoiqjwefNo ratings yet
- Microevolution and MacroevolutionDocument4 pagesMicroevolution and MacroevolutionMuhammad Qasim100% (1)
- Archaean GrowthDocument2 pagesArchaean Growthapi-518282432No ratings yet
- Animal Research The FactsDocument4 pagesAnimal Research The Factsapi-358009419No ratings yet
- Paper 4 InheritanceDocument15 pagesPaper 4 InheritanceIai TiatNo ratings yet
- The 12th International Trichoderma & Gliocladium WorkshopDocument59 pagesThe 12th International Trichoderma & Gliocladium Workshopamir-scribdNo ratings yet
- B14 Ci 2 Z XN NSDocument38 pagesB14 Ci 2 Z XN NSAnonymous BkmsKXzwyKNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Technology and Bioceramics: From Cell To Gene EngineeringDocument15 pagesStem Cell Technology and Bioceramics: From Cell To Gene Engineeringcobram1No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions on Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationLama AshiNo ratings yet
- Bioscience Catalogue 64p PDFDocument64 pagesBioscience Catalogue 64p PDFbkkbrazilNo ratings yet
- Exploiting DNA Replication Stress For Cancer Treatment: Tajinder Ubhi and Grant W. BrownDocument10 pagesExploiting DNA Replication Stress For Cancer Treatment: Tajinder Ubhi and Grant W. BrownJaganNo ratings yet
- Marine Enzymes: Production and Applications For Human HealthDocument17 pagesMarine Enzymes: Production and Applications For Human HealthJessica Asitimbay ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Important Features of Probiotic Microorganisms in Food and NutritionDocument9 pagesTaxonomy and Important Features of Probiotic Microorganisms in Food and NutritionDhayu Mart Hindrasyah PandiaNo ratings yet
- Animal CloningDocument17 pagesAnimal CloningKen Carlo LambojonNo ratings yet
- University of Bucharest Faculty of BiologyDocument17 pagesUniversity of Bucharest Faculty of BiologyNicoleta AnghelNo ratings yet
- Bio 200 Spring 2015 SyllabusDocument3 pagesBio 200 Spring 2015 SyllabusEllen YinNo ratings yet
- Key Terms and Technologies in Drug Discovery ScreeningDocument16 pagesKey Terms and Technologies in Drug Discovery Screeninguzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Inheritance and Genetic Variations EXPLORE 3 Activity Using A Punnett SquareDocument5 pagesInheritance and Genetic Variations EXPLORE 3 Activity Using A Punnett SquareHeff317No ratings yet
- Bacteria: Tiny Organisms with Major ImpactDocument28 pagesBacteria: Tiny Organisms with Major ImpactVINDHYA SHANKERNo ratings yet
- List of Cro in IndiaDocument3 pagesList of Cro in Indiajaykardani_20% (1)
- OMS 2009 Manual de Detección de Rotavirus y Métodos de Caracterización.Document156 pagesOMS 2009 Manual de Detección de Rotavirus y Métodos de Caracterización.Anonymous Se5IdneSpNo ratings yet
- 2144 Remaining Codes For Mapping - Final Consolidated - 4 August 2021Document386 pages2144 Remaining Codes For Mapping - Final Consolidated - 4 August 2021Hussain Zannun mobNo ratings yet
- FCPS-1 Schedule of PsychiatryDocument6 pagesFCPS-1 Schedule of Psychiatryahsan.naseer50% (2)
- Molecular GeneticsDocument18 pagesMolecular GeneticsJeremy SellersNo ratings yet
- Global Response of Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans ATCC 53993Document9 pagesGlobal Response of Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans ATCC 53993CRISTOBAL MARTINEZ BUSSENIUNo ratings yet