Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Chain Management Strategy and Design
Uploaded by
suresh_prk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views36 pagesSupply Chain Management
Original Title
supplychainmanagementpptdoms-120129230629-phpapp01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSupply Chain Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views36 pagesSupply Chain Management Strategy and Design
Uploaded by
suresh_prkSupply Chain Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 36
Supply Chain Management
Strategy and Design
1
Lecture Outline
The Management of Supply Chains
Green Supply Chains
Information Technology: A Supply Chain
Enabler
Supply Chain Integration
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
Measuring Supply Chain Performance
10-2
Supply Chains
10-3
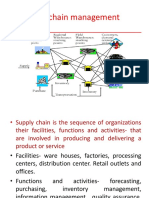
All facilities, functions, and activities associated
with flow and transformation of goods and
services from raw materials to customer, as well
as the associated information flows
An integrated group of processes to source,
make, and deliver products
The Supply Chain Figure10.1
10-4
Supply Chain for Denim Jeans
Figure 10.2a
10-5
Supply Chain for Denim Jeans (cont.)
Figure 10.2b
10-6
Supply Chain Processes
10-7
Supply Chain for Service Providers
More difficult than manufacturing
Does not focus on the flow of physical goods
Focuses on human resources and support services
More compact and less extended
10-8
Value Chains
Value chain
every step from raw materials to the eventual end user
ultimate goal is delivery of maximum value to the end
user
Supply chain
activities that get raw materials and subassemblies into
manufacturing operation
ultimate goal is same as that of value chain
10-9
Value Chains
Demand chain
increase value for any part or all of chain
Terms are used interchangeably
Value
creation of value for customer is important aspect of
supply chain management
10-10
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Managing flow of information through supply chain in
order to attain the level of synchronization that will
make it more responsive to customer needs while
lowering costs
Keys to effective SCM
information
communication
cooperation
trust
10-11
Supply Chain
Uncertainty and Inventory
A major objective of SCM:
respond to uncertainty in customer demand without
creating costly excess inventory
Negative effects of uncertainty
lateness
incomplete orders
Inventory
insurance against supply chain uncertainty
10-12
Supply Chain
Uncertainty and Inventory
Factors that contribute to uncertainty
inaccurate demand forecasting
long variable lead times
late deliveries
incomplete shipments
product changes
batch ordering
price fluctuations and discounts
inflated orders
10-13
Bullwhip Effect
Occurs when slight demand variability is
magnified as information moves back
upstream
10-14
Risk Pooling
Risks are aggregated to reduce the impact of
individual risks
Combine inventories from multiple locations into one
Reduce parts and product variability, thereby reducing the
number of product components
Create flexible capacity
10-15
Green Supply Chains
Sustainability
Meeting present needs without compromising
the ability of future generations to meet their
needs
Sustaining human and social resources
It can be cost effective and profitable
Can provide impetus for product and process
innovations
Impetus comes from downstream in the supply
chain and moves upstream to suppliers 10-16
Sustainability and Quality
Management
Reducing waste through quality programs
helps achieve sustainability goals
Improving fuel efficiency of vehicles
Telecommuting
Eco-friendly packing materials
Energy-efficient facilities
10-17
Information Technology:
A Supply Chain Enabler
Information links all aspects of supply chain
E-business
replacement of physical business processes with electronic
ones
Electronic data interchange (EDI)
a computer-to-computer exchange of business documents
Bar code and point-of-sale
data creates an instantaneous computer record of a sale
10-18
IT: Supply Chain Enabler
Radio frequency identification (RFID)
technology can send product data from an item to a reader
via radio waves
Internet
allows companies to communicate with suppliers,
customers, shippers and other businesses around the world
instantaneously
Build-to-order (BTO)
direct-sell-to-customers model via the Internet; extensive
communication with suppliers and customer
10-19
Supply Chain Enablers
10-20
E-Business & Supply Chain
Management
Savings due to lower transaction costs
Reduction of intermediary roles
Shorter supply chain response times
Wider presence and increased visibility
Greater choices & more info for customers
Improved service
Collection & analysis of huge amounts of customer data
& preferences
Access to global markets, suppliers & distribution
channels
10-21
Electronic Data Interchange
Computer-to-computer exchange of documents
in a standard format
Purchasing, shipping and receiving
Improve customer service
Reduce paperwork
Increase productivity
Improve billing and cost efficiency
Reduce bullwhip effect through information
sharing
10-22
Bar Codes
Automated data collection system
Bar code contains identifying information
Provide instantaneous tracking information
Checkout scanners create point-of-sale data
Update inventory records
Identify trends
Order material
Schedule orders
Plan deliveries
10-23
Radio Frequency Identification
(RFID)
Use radio waves to transfer data from chip to
a reader
Provides complete visibility of product
location
Continuous inventory monitoring
Reduce labor to manage inventory
Reduce inventory costs
RFID is not standardized yet
Difficult to track between systems
10-24
RFID Capabilities
10-25 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
RFID Capabilities
10-26
Supply Chain Integration
Share information among supply chain members
Reduced bullwhip effect
Early problem detection
Faster response
Builds trust and confidence
Collaborative planning, forecasting,
replenishment, and design
Reduced bullwhip effect
Lower costs (material, logistics, operating, etc.)
Higher capacity utilization
Improved customer service levels
10-27
Supply Chain Integration
Coordinated workflow, production and
operations, procurement
Production efficiencies
Fast response
Improved service
Quicker to market
Adopt new business models and technologies
Penetration of new markets
Creation of new products
Improved efficiency
Mass customization
10-28 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and
Replenishment (CPFR)
Two or more companies in a supply chain to
synchronize their demand forecasts into a single plan
to meet customer demand
Parties electronically exchange
past sales trends
point-of-sale data
on-hand inventory
scheduled promotions
forecasts
10-29
SCM Software
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
software that integrates the components of a
company by sharing and organizing information
and data
10-30
Measuring Supply Chain
Performance
Metrics used to measure supply chain performance
inventory of value aggregate Average
sold goods of Cost
turns Inventory
10-31
) item e (unit valu ) item for inventory (average
inventory of value aggregate Average
i i
Inventory turnover
Total value (at cost) of inventory
Measuring Supply Chain
Performance
10-32
Days of supply
Fill rate: fraction of orders filled by a distribution center
within a specific time period
days) sold)/(365 goods of (Cost
inventory of value aggregate Average
supply of Days
Computing Key Performance
Indicators
10-33
Process Control and SCOR
Process Control
not only for manufacturing operations
can be used in any processes of supply chain
Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR)
a cross industry supply chain diagnostic tool
maintained by the Supply Chain Council
10-34 Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
SCOR Model Processes
10-35
SCOR Performance Metrics
10-36
You might also like
- An Introduction to SDN Intent Based NetworkingFrom EverandAn Introduction to SDN Intent Based NetworkingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bonus and FundingDocument19 pagesBonus and FundingBharti GoyalNo ratings yet
- BJMP2033 Chapter 4 SCMDocument37 pagesBJMP2033 Chapter 4 SCM邱励聪No ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Operations Management (FLX) CH 10Document33 pagesLecture 8 Operations Management (FLX) CH 10Felix LukmanNo ratings yet
- Extending The Organization - Supply Chain Management (SCM)Document35 pagesExtending The Organization - Supply Chain Management (SCM)rizcst9759No ratings yet
- Basics of Supply Chain ManagementDocument34 pagesBasics of Supply Chain ManagementBhuvanes KumarNo ratings yet
- Dreamorbit Softech Private LimitedDocument54 pagesDreamorbit Softech Private LimitedjayeshNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagmentDocument22 pagesSupply Chain ManagmentDesdoHexNo ratings yet
- Operations MGMTDocument77 pagesOperations MGMTDinesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10 Morern Concept in Supply ChainDocument14 pages10 Morern Concept in Supply ChainHello WorldNo ratings yet
- SCM & LogisticsDocument27 pagesSCM & LogisticsPratik Awari100% (1)
- Supply ChainmanagementDocument37 pagesSupply Chainmanagementharini yaraganiNo ratings yet
- Revised - Week6 - ch11Document49 pagesRevised - Week6 - ch11吃芦娃了三地说No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Prof.G.Purandaran M.Tech (I.I.T-Madras) PGDM (I.I.M-Bangalore)Document63 pagesSupply Chain Management: Prof.G.Purandaran M.Tech (I.I.T-Madras) PGDM (I.I.M-Bangalore)pura_malliNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: by Ajit Kumar Seth Una Chittaranjan Syed Md. KarimDocument25 pagesSupply Chain Management: by Ajit Kumar Seth Una Chittaranjan Syed Md. Karimajitseth10No ratings yet
- E-Commerce 2017 Business. Technology. Society.: 13 EditionDocument45 pagesE-Commerce 2017 Business. Technology. Society.: 13 EditionFahim RezaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Supply Chain ManagementDocument43 pagesBasics of Supply Chain ManagementsriramNo ratings yet
- Russell and Taylor Operations and Supply Chain Management, 8th EditionDocument34 pagesRussell and Taylor Operations and Supply Chain Management, 8th EditionMichael Christensen100% (1)
- Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Supply Chain ManagementSneha Karpe100% (1)
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument124 pagesSupply Chain ManagementLeena SharmaNo ratings yet
- IS6006 - IT and Supply Chain ManagementDocument69 pagesIS6006 - IT and Supply Chain ManagementAnonymous vULUCMuoNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarDocument54 pagesSupply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. Vedpuriswarramasb4uNo ratings yet
- E Supply ChainDocument35 pagesE Supply ChainSara JohnstonNo ratings yet
- Ses11 GSLC Chap11 Supply Chain ManagementDocument27 pagesSes11 GSLC Chap11 Supply Chain ManagementRonan WisnuNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument51 pagesSupply Chain Managementgubdia100% (1)
- Oracle ASCP Success StoriesDocument31 pagesOracle ASCP Success Storiesboddu2450% (2)
- ITin SCDocument36 pagesITin SCChirag PrabhudessaiNo ratings yet
- St. Gonsalo Garcia College: Logistics ManagementDocument22 pagesSt. Gonsalo Garcia College: Logistics Managementk_suryaNo ratings yet
- E SCMDocument37 pagesE SCMindu296100% (2)
- Chap010.ppt Supply Chain Management 000Document27 pagesChap010.ppt Supply Chain Management 000Saad Khadur EilyesNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument67 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAvijit DindaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Supply Chain ManagementDocument42 pagesChapter Seven: Supply Chain ManagementYaredNo ratings yet
- 04 Achieving Operational Excellence & CustomerDocument29 pages04 Achieving Operational Excellence & CustomerAlvi KabirNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarDocument54 pagesSupply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarAkhmadRifaniNo ratings yet
- Information System For Supply Chain ManagementDocument18 pagesInformation System For Supply Chain ManagementashishlordNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarDocument54 pagesSupply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarSatish Kumar SatishNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarDocument54 pagesSupply Chain Management: A Presentation by A.V. VedpuriswarharivanshvermabbaNo ratings yet
- E Supply Chain ManagementDocument52 pagesE Supply Chain ManagementSubrata Halder100% (2)
- CH 09Document31 pagesCH 09Ammar YasserNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document31 pagesCH 09Ammar YasserNo ratings yet
- International Business: by Jafin Muneer Melita StephenDocument54 pagesInternational Business: by Jafin Muneer Melita Stephendeejayblog2114No ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument55 pagesSupply Chain ManagementGopikrishna S NairNo ratings yet
- Sampath SCM Unit 4 MBADocument58 pagesSampath SCM Unit 4 MBAd Vaishnavi OsmaniaUniversityNo ratings yet
- L2 Supply Chain Driver and MatrixDocument48 pagesL2 Supply Chain Driver and MatrixPrithvi GuhaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Supply Chain: Chapter-1 (Meindl - Chopra)Document55 pagesUnderstanding Supply Chain: Chapter-1 (Meindl - Chopra)Sanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Designing Distribution Networks and Application To Online SalesDocument20 pagesLecture 4 - Designing Distribution Networks and Application To Online SalesNadine AguilaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Supply Chain Management: E CommerceDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Supply Chain Management: E CommerceAnonymous K0ZhcHT2iu100% (1)
- Corporate Strategy and Its Connection To Supply Chain ManagementDocument22 pagesCorporate Strategy and Its Connection To Supply Chain ManagementTijado HewittNo ratings yet
- IT & Retail ReplenishmentDocument17 pagesIT & Retail ReplenishmentKristian TarucNo ratings yet
- IT in Supply Chain ManagementDocument62 pagesIT in Supply Chain Managementrohitsingh17No ratings yet
- IT in SCM - FinalDocument21 pagesIT in SCM - Finalrjrahulsrk100% (1)
- Lecture - Information Technology in Supply Chain ManagementDocument23 pagesLecture - Information Technology in Supply Chain Managementtimesave240No ratings yet
- Impact of Information Technology On Supply Chain ManagementDocument43 pagesImpact of Information Technology On Supply Chain ManagementAnoop Narayanan60% (5)
- Cadena de SuministrosDocument49 pagesCadena de SuministrosCristian LeonNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument26 pagesSupply Chain Managementzahid_497No ratings yet
- Logistics and S Chain ManagementDocument46 pagesLogistics and S Chain ManagementkeyarjpNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain 4.0: From Stocking Shelves to Running the World Fuelled by Industry 4.0From EverandSupply Chain 4.0: From Stocking Shelves to Running the World Fuelled by Industry 4.0Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Quantitative Assessments of Distributed Systems: Methodologies and TechniquesFrom EverandQuantitative Assessments of Distributed Systems: Methodologies and TechniquesDario BruneoNo ratings yet
- Learn C ProgrammingDocument169 pagesLearn C ProgrammingAamer100% (3)
- Ipv4 Subnetting PDFDocument2 pagesIpv4 Subnetting PDFsuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Address Classes PDFDocument2 pagesIpv4 Address Classes PDFAmol IngleNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typescut irnandaNo ratings yet
- Electronics For You+ - April 2016Document140 pagesElectronics For You+ - April 2016suresh_prk100% (2)
- Ipv4 AddressingDocument3 pagesIpv4 Addressingsuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Reserved AddressesDocument2 pagesIpv4 Reserved Addressessuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Rigveda SandhyaavandanamDocument10 pagesRigveda SandhyaavandanamShivprasad ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Tharpanam ProcedureDocument26 pagesTharpanam Proceduresuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- MPLS VPN TechnologyDocument136 pagesMPLS VPN TechnologyBehrooz GholamzadehNo ratings yet
- Mpls VPN BasicDocument13 pagesMpls VPN Basicsouly88No ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel 2010: Charts and Graphs TutorialDocument13 pagesMicrosoft Excel 2010: Charts and Graphs Tutorialsuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- 0101 - SQL Server 2005 ArchitectureDocument36 pages0101 - SQL Server 2005 Architecturesuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- SQL Server 2005 - Data MiningDocument27 pagesSQL Server 2005 - Data Miningsuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: What Is It?Document34 pagesCloud Computing: What Is It?suresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Mpls VPN BasicDocument13 pagesMpls VPN Basicsouly88No ratings yet
- Ipaddr 1217448089978438 9Document62 pagesIpaddr 1217448089978438 9suresh_prkNo ratings yet
- IT Networking For Application Developers: Presenter: Roy KimDocument22 pagesIT Networking For Application Developers: Presenter: Roy Kimsuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About Cloud ComputingDocument26 pagesEverything You Need To Know About Cloud ComputingDarrell Jordan-Smith100% (2)
- Routing Protocols ConceptsDocument14 pagesRouting Protocols Conceptssuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Advantages of ScsiDocument2 pagesAdvantages of Scsisuresh_prkNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Planning With SAPDocument46 pagesSupply Chain Planning With SAPPrakash MandaviaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Session 24Document39 pagesOperations Management: Session 24JojoPANGNo ratings yet
- DHL Supply ChainDocument28 pagesDHL Supply ChainJohn Chauca100% (1)
- Barge ContainerDocument6 pagesBarge Containerrahmat100% (1)
- Post (Rti Stamp) CompleteDocument16 pagesPost (Rti Stamp) CompleteLive LawNo ratings yet
- Distribution Centre - Roles & FunctionDocument4 pagesDistribution Centre - Roles & FunctionHarzamir BamoreNo ratings yet
- Inventory & Risk PoolingDocument64 pagesInventory & Risk PoolingMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Resume 2011Document2 pagesResume 2011Jose Kiko RomeroNo ratings yet
- Materials ManagementDocument3 pagesMaterials ManagementDignityboyNo ratings yet
- Green Shipping LineDocument24 pagesGreen Shipping LineyashurockuNo ratings yet
- Freight Forwarding Chapter 1Document12 pagesFreight Forwarding Chapter 1Ajeet KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- ACS NZ Stamps 2017 PDFDocument132 pagesACS NZ Stamps 2017 PDFpeter smithNo ratings yet
- Expenditure Cycle Business ActivitiesDocument23 pagesExpenditure Cycle Business ActivitiesBear CooporNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Logistic System in DHLDocument57 pagesProject Report On Logistic System in DHLManas Khanna77% (13)
- 01 Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementDocument110 pages01 Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementSudhir Patel100% (4)
- Canadian Tire EL Commented GOODDocument10 pagesCanadian Tire EL Commented GOODDavid TanNo ratings yet
- Bullwhip Effect - Supply Chain Management Encyclopedia PDFDocument7 pagesBullwhip Effect - Supply Chain Management Encyclopedia PDFUDAYAN BIPINKUMAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Telengtan Brothers Vs CADocument9 pagesTelengtan Brothers Vs CALeft Hook OlekNo ratings yet
- Case Study Report Empty Container LogisticsDocument0 pagesCase Study Report Empty Container LogisticsChetan AdsulNo ratings yet
- Chart of Responsibility: Any Transport Mode Sea/Inland Waterway Transport Any Transport ModeDocument1 pageChart of Responsibility: Any Transport Mode Sea/Inland Waterway Transport Any Transport ModeBhayaniNo ratings yet
- ICD Visit ReportDocument18 pagesICD Visit ReportpankajdesardaNo ratings yet
- Section 901Document3 pagesSection 901Mark AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Case Study U.S. StrollersDocument4 pagesCase Study U.S. StrollersAnonymous LW8Q1Xq3TH50% (2)
- DHL-Distribution NetworkDocument18 pagesDHL-Distribution NetworkRaghaw Mundhra50% (2)
- Amazon DataDocument29 pagesAmazon DataSangeeta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mini CaseDocument3 pagesMini CaseAlgus DarkNo ratings yet
- SCM Unit 1Document17 pagesSCM Unit 1syedluqman1100% (1)
- Toqeer Moazzam CVDocument4 pagesToqeer Moazzam CVToqeer MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Inventory Management Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesSolutions To Inventory Management Practice Problemsmanjeet39100% (1)
- MT Tradewind v-15 - BL Draft Angola PortDocument1 pageMT Tradewind v-15 - BL Draft Angola PortNoel Fajardo Domingo100% (1)