Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Desalter
Uploaded by
shyam_anupOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Desalter
Uploaded by
shyam_anupCopyright:
Available Formats
DR.
Hemdan 1
DESALTING
DR.Hemdan 2
CRUDE OIL
DESALTING
DR.Hemdan 3
Crude Oil Desalting:-
Salts are distributed in crude oil as brine (Nacl)
Defects of Salts are:
-Cause plugging of heat exchangers tubes.
-Cause deposits in pipe still tubes (furnaces)
and consequently cause .
-Decrease in heat transfer coefficient.
-Create pressure drop which affects on
pumps.
Salts may reach up to 260 PTb each 100 PTb cause
deposits of about 3 ft/day .
Salts should be removed before distillation tower where
these salts liberate HCL gas which cause many
corrosion problems .
DR.Hemdan 4
DR.Hemdan 5
Problems of oleophobics
-Corrosion due to hydrolysis of salts .
-Increase consumption of NH3 to
neutralize HCL
-Erosion .
-Plugging of Equipment and fouling .
-Trace metals in distillates which acts as
catalyst poisoning
DR.Hemdan 6
Crude desalting is the first processing step in a refinery .
The objectives of crude desalting are :
1-the removal of salts and solids
2- the formation water from unrefined crude oil before
the crude is introduced in the crude distillation unit .
3-removal of suspended solids from the crude oil.
4-Reduced equipment fouling and corrosion and
5-longer catalyst life
DR.Hemdan 7
DR.Hemdan 8
DR.Hemdan 9
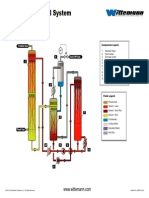
SINGLE-STAGE DESALTER
..
Mix
Valve
Heat
Exchangers
Demulsifier
Water
Feed Oil
Desalter
Effluent Water
Desalted
Crude
DR.Hemdan 10
1st Stage Crude Outlet
(5.0 PTB, 0.2% BS&W)
Two-Stage Desalter Example
2nd Stage Effluent Water
is 1st Stage Wash Water
1st Stage Desalter
Mix
Valve
Crude Charge
(100 PTB, 1% BS&W)
Desalted Crude
(0.5 PTB, 0.2% BS&W)
Wash Water
Effluent Water
2nd Stage Desalter
5.0% 5.0%
5.8%
Figure 2
Mix
Valve
Counter-current flow
DR.Hemdan 11
SERIES: Maximize Desalting Efficiency
Water
Feed
Oil
Heat
Exchangers
1
st
Stage
2
nd
Stage
Mix Valve
Mix Valve
Effluent
Water
Desalted
Crude
100ppm
salt in
10ppm
salt out
1ppm
salt out
Overall Efficiency = (100 - 1) / 100 = 99%
MULTI-STAGE DESALTING
DR.Hemdan 12
PARALLEL:
Maximize Throughput
Feed Oil
Heat
Exchangers
Mix Valves
Effluent Water
Desalted
Crude
Water
MULTI-STAGE DESALTING
DR.Hemdan 13
Pure water and NaOH is added to the
desalter
Some deemulsifier may be added to break
forces between salts and the oil
In electrostatic precipitator applied voltage
up to 30KV
Salt drops coalesce together and form
larger drops which separated down to the
bottom of desalter
Salt removal reach to about 90%
DR.Hemdan 14
It is necessary to adjust the pH of the brine to
obtain a value of 7 or less.
If the pH of the brine exceeds 7, emulsions are
formed because of the presence of sodium
naphthenate and sodium sulfide.
For most crude oils, it is desirable to keep the
pH below 8.
Better dehydration is obtained in electrical
desalters when they are operated at a pH of 6.
The pH is controlled by the addition of acid to
the incoming or recycle water.
DR.Hemdan 15
The trend toward running heavier crude
oils has increased the importance of
efficient desalting of crudes. Until recently,
the criterion for desalting crude oils was 10
lb salt/1000 bbl (expressed as NaCl) or
more, but now many companies desalt all
crude oils.
DR.Hemdan 16
Salt in the crude oil is in the form of
dissolved or suspended salt crystals in
water emulsified with the crude oil.
The basic process of desalting is to wash
the salt from crude oil with water.
Problems occur are:
1-inefficient and economical water/oil mixing,
2-water wetting of suspended solids, and
3-separation of oil from wash water
DR.Hemdan 17
The separation of oil and washwater i.e
desalter performance is affected by :
1-the gravity
2-viscosity
3-pH of the crude oil
4-the ratio of water/crude used for washing.
5-temperature
6-pressure drop
7-chemicals additions
DR.Hemdan 18
Desalting is carried out by emulsifying the
crude oil with 3 to 10 vol% water at a
temperature of 200-300F. Both the ratio of
water to oil and the operating temperature
are functions of the gravity of the crude oil.
Typical operating conditions are :
DR.Hemdan 19
DR.Hemdan 20
Trouble shooting
You might also like
- A Quick Look at DesaltingDocument12 pagesA Quick Look at Desaltingananth2012No ratings yet
- Eletrochemicaldesalter 191231094907Document6 pagesEletrochemicaldesalter 191231094907ShakerMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil DesaltingDocument2 pagesCrude Oil Desaltinghassan zakwanNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil DesaltingDocument14 pagesCrude Oil DesaltingDucViking100% (1)
- Desalter EfficiencyDocument3 pagesDesalter Efficiencykronos39zeusNo ratings yet
- Desalter Start Up ProcedureDocument2 pagesDesalter Start Up Procedureesakkiraj1590No ratings yet
- DesalterDocument2 pagesDesalterHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Oil and Gas Separation - LectDocument62 pagesModule 2 - Oil and Gas Separation - LectmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Desalter OperationDocument19 pagesDesalter OperationmohammedNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Design of Dehydration Unit and NGL ProcessDocument51 pagesOptimization and Design of Dehydration Unit and NGL ProcessHoracio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Introduction For Test Separator: CNPCIC Field ProductionDocument18 pagesIntroduction For Test Separator: CNPCIC Field Productionsalahadine maideNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument26 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionRozh SartipNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Desalting ProcessDocument24 pagesCrude Oil Desalting ProcessamirejazNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Separators ( Separators') - Ascom SeparationDocument5 pages3 Phase Separators ( Separators') - Ascom Separationnaveenbaskaran1989No ratings yet
- Acid Gas Removal Flow PDFDocument1 pageAcid Gas Removal Flow PDFHIPAPNo ratings yet
- BTEX in GDUDocument19 pagesBTEX in GDUAnonymous QSfDsVxjZNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Separators Sizing Parameter MM083015Document42 pagesGas Liquid Separators Sizing Parameter MM083015Mubarik AliNo ratings yet
- 04 Solid Bed DehydrationDocument23 pages04 Solid Bed DehydrationMohamed SahnounNo ratings yet
- Scrubber NATCODocument22 pagesScrubber NATCOkalikamalaNo ratings yet
- Equipment Catalogue API Oil SeparatorDocument2 pagesEquipment Catalogue API Oil Separatorbesant vargheesNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem StatementDocument2 pagesSample Problem Statementsunildubey02No ratings yet
- 2 Phase Seperator PDFDocument66 pages2 Phase Seperator PDFKanthan DevanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Oil - Water Treater & Desalter: Calculated AnswersDocument2 pagesElectrostatic Oil - Water Treater & Desalter: Calculated AnswersLeonardo ChávezNo ratings yet
- How Is Nitrogen Used in Oil and Gas FieldsDocument4 pagesHow Is Nitrogen Used in Oil and Gas FieldsrajasekharboNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Crude Oil Electrostatic Desalters PerformanceDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Crude Oil Electrostatic Desalters PerformanceAlvaro Andres Blanco GomezNo ratings yet
- Separator SizingDocument3 pagesSeparator SizingMaryJane Ayisha Sado-ObahNo ratings yet
- ETI Electrostatic BrochureDocument6 pagesETI Electrostatic BrochureHector RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Calculate Gas Rate Using Choke Equation Texas A & I ModelDocument6 pagesCalculate Gas Rate Using Choke Equation Texas A & I ModelJunaid MateenNo ratings yet
- DesalterDocument23 pagesDesalterkishoreprithika100% (1)
- MSDS aMDEA TamincoDocument10 pagesMSDS aMDEA TamincoIlham Dwi ShaputraNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Quality Enhancement: Training Report ONDocument20 pagesNatural Gas Quality Enhancement: Training Report ONRajkishan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Line Sizing Criteria As Per Different StandardsDocument4 pagesLine Sizing Criteria As Per Different StandardsAMRUTA PATILNo ratings yet
- Gas Flowmeter SizingDocument1 pageGas Flowmeter SizingtungluongNo ratings yet
- What Is DistillationDocument25 pagesWhat Is DistillationashirNo ratings yet
- Desalting of Crude Oil in RefineryDocument3 pagesDesalting of Crude Oil in RefineryKmt_AeNo ratings yet
- Case 1. Gas Lift System DesignDocument10 pagesCase 1. Gas Lift System DesignDaniel ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Inject MethanolDocument9 pagesInject MethanolabdounouNo ratings yet
- Principles of Separation: Production and Test SeparatorsDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Separation: Production and Test SeparatorsهانيزايدNo ratings yet
- Two-Phase Flow - Condensate Drain Lines Design GuideDocument2 pagesTwo-Phase Flow - Condensate Drain Lines Design Guidec_nghiaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Stage Separator: For Production Conditions / The Process Can Be AchievedDocument5 pages2nd Stage Separator: For Production Conditions / The Process Can Be AchievedihsansepalmaNo ratings yet
- Flare SystemDocument60 pagesFlare Systemmmairaja100% (1)
- Chemical Injection SkidDocument6 pagesChemical Injection SkidRaheel SultanNo ratings yet
- Gas TreatingDocument36 pagesGas TreatingPradeep MunnaNo ratings yet
- B. Oil-Gas SeparatorsDocument74 pagesB. Oil-Gas SeparatorsalooookiNo ratings yet
- Treater Mohandesi Shimi 87-3-16 A SyDocument7 pagesTreater Mohandesi Shimi 87-3-16 A Syrahul84803No ratings yet
- Two Phase Horizontal Separator - Design ProcedureDocument24 pagesTwo Phase Horizontal Separator - Design ProcedurekennethmsorianoNo ratings yet
- Total - VESSELSDocument18 pagesTotal - VESSELSTala RamezaniNo ratings yet
- Gas Dehydration Solid AdsorptionDocument2 pagesGas Dehydration Solid Adsorptionachmadh_2010No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electrostatic DesalterDocument46 pagesUnit 1 Electrostatic Desalterkhalimn100% (4)
- Hydrocyclone SeparatorDocument2 pagesHydrocyclone Separatorgautam_96948069100% (1)
- Advances in Electrostatic Treatment of Crude OilDocument5 pagesAdvances in Electrostatic Treatment of Crude OilAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- Hydrate Inhibition With MethanolDocument11 pagesHydrate Inhibition With Methanolsachin2010No ratings yet
- Design Review of AbsorbersDocument46 pagesDesign Review of AbsorbersAngelik MoralesNo ratings yet
- Exploration & Production: TechnologyDocument36 pagesExploration & Production: Technologyidzham78No ratings yet
- Oil& Gas SeparationDocument9 pagesOil& Gas SeparationHomam MohammadNo ratings yet
- 1 DesalterDocument20 pages1 DesalterDucViking80% (5)
- 1 DesalterDocument20 pages1 Desalterbakhtyar21No ratings yet
- Pre-Treatment of Crude OilDocument25 pagesPre-Treatment of Crude OilAbhisek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Desalting Crude OilsDocument3 pagesDesalting Crude OilsEdgar YoveraNo ratings yet
- Birla SunlifeDocument104 pagesBirla Sunlifeshyam_anupNo ratings yet
- Capacity Control of Screw Compressor PDFDocument8 pagesCapacity Control of Screw Compressor PDFshyam_anupNo ratings yet
- What's New in API 610 11th EditionDocument4 pagesWhat's New in API 610 11th Editionshyam_anupNo ratings yet
- Desalter Test Run2004Document11 pagesDesalter Test Run2004shyam_anupNo ratings yet
- Pressure TransientDocument48 pagesPressure Transientshyam_anupNo ratings yet
- Afro Paper No 11Document60 pagesAfro Paper No 11shyam_anupNo ratings yet
- ISO-8859-1 Cadbury GoodDocument4 pagesISO-8859-1 Cadbury GoodIrshad SherwaniNo ratings yet
- Concrete Drain Tile: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesConcrete Drain Tile: Standard Specification ForEligio Antonio CerdaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Che Study-Package-1 Set-1 Chapter-1 001Document26 pagesCLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Che Study-Package-1 Set-1 Chapter-1 001Mudit Goel97% (29)
- Wps (Gtaw & Smaw)Document3 pagesWps (Gtaw & Smaw)Ramadhan AdityaNo ratings yet
- Deep 4 ProcessDocument1 pageDeep 4 ProcessGeorge ChedraouiNo ratings yet
- WTP PST Estimation R310.06.21Document16 pagesWTP PST Estimation R310.06.21juliyet strucNo ratings yet
- Certificado de Análisis GN 20-1620-01Document3 pagesCertificado de Análisis GN 20-1620-01MaryNo ratings yet
- E300 List DatasetsDocument5 pagesE300 List Datasetsrezagholami870% (1)
- Water and Sediment in Crude Oil by The Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)Document13 pagesWater and Sediment in Crude Oil by The Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)Jeferson RosalesNo ratings yet
- 600MW Training Manual of Boiler 20110326 PDFDocument94 pages600MW Training Manual of Boiler 20110326 PDFReda NariNo ratings yet
- Burete EUR-I-PS-0045, RO-EN, V12 - Fisa Tehnica N2538Document1 pageBurete EUR-I-PS-0045, RO-EN, V12 - Fisa Tehnica N2538RizzoRo1No ratings yet
- COOL - 006 Advances in Liquid Coolant Technologies For Electronics Cooling 2005Document7 pagesCOOL - 006 Advances in Liquid Coolant Technologies For Electronics Cooling 2005Leslie Diaz JalaffNo ratings yet
- Toughened Glass Data SheetsDocument2 pagesToughened Glass Data SheetsAr Aayush GoelNo ratings yet
- Z-4 Air Washer BuildingDocument9 pagesZ-4 Air Washer BuildingShubham KothariNo ratings yet
- H B Anilox GuideDocument18 pagesH B Anilox GuideYasser BadrNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Laterally Loaded Drilled Shafts and Piles Using LpileDocument51 pagesAnalysis of Laterally Loaded Drilled Shafts and Piles Using LpileSudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- Aeration101 Scott Mulinix Presentation Rev1Document43 pagesAeration101 Scott Mulinix Presentation Rev1jvan migvelNo ratings yet
- Defects On Weld BEADDocument47 pagesDefects On Weld BEADarash59_4uNo ratings yet
- Burgess Vulcan Latest Publication 2014Document36 pagesBurgess Vulcan Latest Publication 2014jianglai2010No ratings yet
- Proraso Shaving Cream Common Ingredients of 3 TypesDocument2 pagesProraso Shaving Cream Common Ingredients of 3 Typeschimene madiNo ratings yet
- TDS - Emaco CP 60Document3 pagesTDS - Emaco CP 60Venkata RaoNo ratings yet
- Submersible Wastewater Pumps With Single Vane Impeller 3" Discharge - 2" SolidsDocument2 pagesSubmersible Wastewater Pumps With Single Vane Impeller 3" Discharge - 2" SolidsAdemir JúniorNo ratings yet
- Technical Sheet Polyester DiolsDocument8 pagesTechnical Sheet Polyester DiolsQuality Control AHPNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Natural Rubber Shock Attenuation DevicesDocument10 pagesExperimental Study of Natural Rubber Shock Attenuation DevicesMeyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- MR Lopez ExpensesDocument2 pagesMR Lopez ExpensesferrermaricelaustriaNo ratings yet
- Solid RocketsDocument14 pagesSolid Rocketskmanas153No ratings yet
- XNEM-program: Photo Lithography Sequence For Developing Micro Structure & Rie (Reactive Ion Etching)Document7 pagesXNEM-program: Photo Lithography Sequence For Developing Micro Structure & Rie (Reactive Ion Etching)baraniinstNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis of Doped Manganese Cobalt Ferrites by Autocombustion TehniqueDocument4 pagesThe Synthesis of Doped Manganese Cobalt Ferrites by Autocombustion TehniqueAlin DrucNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialsDocument16 pagesBuilding MaterialsCleo Buendicho100% (1)
- 01-SAMSS-043 2018 ASTM Carbon Steel and Low Alloy Pipes For On-Plot ApplicationsDocument18 pages01-SAMSS-043 2018 ASTM Carbon Steel and Low Alloy Pipes For On-Plot ApplicationsWHWEN100% (1)