Professional Documents
Culture Documents
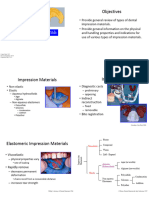
Impression Materials: by Bibin Bhaskaran
Uploaded by
Priyanka SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impression Materials: by Bibin Bhaskaran
Uploaded by
Priyanka SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Impression materials
by
Bibin bhaskaran
Impression materials
Definition :- (GPT):
1) A negative likeness or copy in reverse of the
surface or object.
2) An imprint of the teeth and adjacent
structures for use in dentistry
Impression material:-
Any substance or combination of substances
used for making an impression or negative
reproduction.
Impression technique:-
A method and manner used in making a
negative likeness.
inelastic or
rigid
elastic
material use material use
Chemical
reaction
(irreversible)
plaster of Paris Edentulous
ridge
Alginate
hydrocolloid
Teeth and
soft tissues
zinc oxide-eugenol Interocclusal
records
Non aqueous
elastomers
Polysulfide,polyet
her
Condensation
silicone
Addition silicones
classification
Thermally
induced
Physical
reaction
(reversible)
Compound wax
Preliminary
impression
Agar
TEETH &
SOFT
TISSUES
Classification
Based on rigidity : Rigid
eg Plaster,Zincoxide eugenol
impression compound
Elastic
eg Alginate,polyether,silicone
Based on setting of the material: 1.) Chemical reaction(irreversible)
eg plaster of paris,zincoxide eugenol
alginate,additon and condensation silicones
2 ) Physical change of state(reversible)
eg agar
Based on viscosity : Mucostatic
eg impression plaster,agar,
light body elastomer
Mucocompressive
eg Impression compound,alginates
Pseudoplastic
eg addition silicones
Based on interaction with saliva
and water : Hydrophobic
eg polysulfide ,condensation
silicones
Hydrophilic
eg putty,impression plaster
Based on use :
Primary
impression material
eg impression compound,alginate
Secondary
Impression material
eg Zoe,medium bodied elastomers
Duplicating
material
eg agar
Based on
Chemical composition : impression plaster
impression compound
metal oxide(zinc oxide eugenol)
pastes
agar hydrocolloid
alginate hydrocolloid
polysulfides
condensation silicones
addition silicones
polythers
light curing polyether
(urethane dimethacrylate)
Desirable qualities
Pleasant odor taste and color
Absence of toxic irritants
Adequate shelf life
Economical
Easy to use
Setting that meet clinical requirements
Satisfactory consistency
Readily wet oral tissues
Elastic
Adequate strenght
Dimensional stability
Compatiblity with cast and die materials
Accuracy
Disinfection
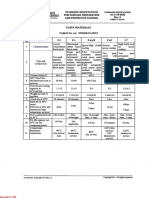
Impression plaster
ADA
specificat
ion
Composit
ion
Uses Mixing
time
Working
time
Setting
time
Advanta
ges
Disadvan
tages
No 25 Calcined
caso4
Anti
expansio
n agents
k2so4
Accelera
tors
k2so4
Retarder
borax
Gelatin
Gum
tragnath
Starch
Alizarin
red
Primary
impressio
n material
Seconda
ry
impressio
n material
60 sec Altered
by use of
additives
same Good
deatail
reproduct
ion
Inexpens
ive
Easy to
handle
Non
toxic
Increase
d shelf
life
Setting
time can
be
controlle
d.
Requires
separatin
g medium
Dry
sensation
to
patients
mouth
Impression plaster
The impressions are very accurate
Being hydrophilic it has got intimate contact with oral
tissues by absorbing surface moisture
Impression compound
ADA
specificatio
n
Compositi
on
Uses Flow Advantage
s
Disadvanta
ges
Disinfectio
n
No 3
Type 1-
Impression(
low fusing)
Type 2-
Tray(high
fusing)
Rosin
Copal
resin
Carnauba
wax
Stearic
acid
Talc
Coloring
agent
Type 1-
primary
impression,
peripheral
tracing
Type 2-As
a tray to
support
other
materials
Type 1
flow at
mouth
temp is 6%
Type 2
flow at
mouth
temp is 2%
Non toxic
and non
irritant
Hardens in
reasonably
acceptable
time
Compatibl
e with
gypsum
products
No
separating
medium
required
Although
plastic not
fluid
enough to
record fine
detail
Distorts
over
undercuts
Shrinkage
on cooling
Dimension
al change
on storage
2%alkaline
glutarldehy
de
Impression compound
Fusion temperature of impression compound is 43.5 degree
celesius
Zinc oxide eugenol impression material
ADA
specificat
ion
Composit
ion
Uses Mixing
time
Setting
time
Advanta
ges
Disadvan
tages
Disinfecti
on
No 16
Type1
(hard)
Type 2
(soft)
2 tubes
Tube 1-
ZnO
Veg or
mineral
oil
Tube 2-
Clove oil
or
eugenol
Gum/pol
ymerised
rosin
Filler
silica
Lanolin
Accelera
tors
cacl2,mgc
l2
Impressi
on pastes
Cement
Tempora
ry filling
Root
canal
filling
Bite
registrati
on paste
Tempora
rly reline
material
Surgical
dressing
1 min/30-
40 sec
Type 1-
Initial
3-6min
Final-
10 min
Type 2-
Initial-
3-6min
Final
15 min
Adheres
well to
tray
Sufficien
tly fluid to
record
fine detail
No
dimensio
nal
change in
setting
process
Hard
when set
No
separatin
g medium
required
Non
toxic
Burning
of
eugenol
Persisten
t taste
Adheres
to tissue
Rigid
material
cant be
used
2%
glutarlde
hyde
Zincoxide eugenol impression material
Non eugenol pastes-
One of the chief disadvantages of Zoe pastes is the possible
burning sensation caused by
eugenol.orthoethoxybenzoic acid (EBA) is a valuable
substitute for eugenol in this regard.
Alginate
ADA
specificat
ion
Composi
tion
Uses Mixing
time
Working
time
Setting
time
Advanta
ges
Disadvan
tages
Disinfecti
on
No 18
Type 1
(Fast)
Type 2
(Slow)
Soluble
alginates
Na,K,
Ammonia
Calcium
sulphate
dihydrate
Trisodiu
m
phosphat
e
Diatoma
ceous
earth
Potassiu
m
titanium
fluoride
Flavouri
n agent.
To
record
impressio
ns of
dental
arches
Premilin
ary
impressio
n
Duplicati
ng cast
and
models
Type 1-
45sec
Type 2-
1min
Type 1-
1.25-
2min
Type 2-
3-4.5min
Type 1-
1-2min
Type2
2-4.5min
Non
toxicand
non
irritant
Accepta
ble odor
Compati
ble with
gypsum
Elastic
Sufficien
tly fluid
Dimensi
onally
unstable
Tears if
undercut
s severe
Difficult
to
sterilize
Poor
shelf life
10 min in
sodium
hypochlo
rite
solution
10 min in
iodophor
solution
10 min in
glutarald
ehyde
solution
Alginate
Gelation reaction-
2Na3P04 + 3CaSo4----- Ca3(Po4)2+3 Na2SO4
Recent advances in alginates
Dust free alginates-
De-dusting agent (glycerin or glycol)
Siliconized alginates-
silicon polymers are added to strengthen the material
Alginates containing disinfectants-
eg quaternary ammonium salts or chlorohexamine are added to
alginate powder.
Hard and soft set alginates-
by adjusting the amount of fillers
Reversible hydrocolloid-AGAR
ADA
specificatio
n
Compositi
on
Gelation
temperatu
re
Liquefactio
n
temperatu
re
Advantage
s
Disadvanta
ges
Disinfectio
n
No 11 Agar
Sulfates
(k2so4)
Borax
Alkyl
benzoate
Water
Fillers
(silica)
Plasticizer(
glycerine)
Bactericid
e
(thymol)
colors
37 degree
celesius
To
45 degree
celesius
60 to 70
Degree
celesius
No custom
tray
required
Clean and
pleasant
Easy to
pour
Inexpensiv
e
Good shelf
life
High
accuracy
Re-usable
Requires
conditionin
g unit
Decreased
dimensiona
l stability
Weak inn
deep sulcus
Iodophor
/bleach/glut
arldehyde
Agar
Gelation-
Gelation is accomplished by circulating cold water of
approximately 18-23 degree for not less than 5 min.
Elastomeric impression materials
Classification :-
Based on viscosity-
Class 1 heavy body heavy viscosity
Class 2 regular body or medium body
Class 3 light body or low viscosity
Based on chemistry-
Polysulfides
Condensation silicones
Additional slilicones
Polythers
Visible light curable polyether
POLYSULFIDES
ADA
Specific
ation
Composition
Mixing
time
Working
time
Setting
time
Advanta
ges
Disadv
antage
s
Disinfe
ction
No 19
1,Base paste
Liquid polymer
containing
thiol,mercaptan or
polysulfide
polymer.
Filler titanium
dioxide
Plasticizer-DI-n-
butyl phthalate
Sulfur
2,Reactor paste-
Pbo2 or organic
hydroperoxides or
inorganic
hydroxides
Inert oil/plasticizer
Filler -silica
Stearic acid
45 sec-
1min
5-7min 8min No
special
equipme
nt
Superior
strength
Pouring
can be
delayed
to 1 hr
Can be
electropl
ated
Adequat
e shelf
life
Custo
m trays
require
d
Hydro
phobic
Sensiti
ve to
heat
Long
setting
time
High
shrinka
ge
High
perman
ent
deform
ation
2%
glutarld
ehyde
polysulfides
Polysulfide is one of the least stiff or highly flexible of elastomeric
material
For accurate polysulfide impressions-
The cast should be poured immediately after taking impression
Minimise the amount of material used to take impression by using
custom made acrylic trays
ADA
Specific
ation
Composition
Mixing
itime
Workin
g time
Setting
time
Advant
ages
Disadva
ntages
Disinfec
tion
No 19
2 types-
1,Doubl
e mix
type
2,Putty
type
Base paste-
Polydimethyl
siloxane/liquid
silicone polymer
Filler silica
Reactor paste-
Tetra functional
silicates
Tin compound
45 sec Upto
5 min
10 12
min
No
special
equipme
nt
required
Modera
te
strenth
in deep
sulcus
Adequa
te shelf
life
Pleasan
t odor
Custom
tray
required
Difficul
t to
electropl
ated
hydrop
hobic
2%
glutalde
hyde
Condensation silicones
(Double mix type)
Condensation silicones
It is also called room temperature vulcanising silicones(RTV)
Uses
It is widely used in recording dentulous impressions in preparation of
crowns,bridges,inlays,onlays and to some extent for partial dentures
It is also used to record edentulous impressions in preparation of
complete denture
Putty type
Advantages
No custom tray required
No special equipment required
Moderate strength in deep sulcus
Pleasant odor
Adequate shelf life
Disadvantages
Should be poured shortly after removal
Hydrophobic
Difficult to electroplate
Easily distorted
Addition silicones
(Double mix type)
ADA
Specifica
tion
Composition
Mixing
itime
Working
time
Setting
time
Advantag
es
Disadvan
tages
No 19
2 types
1,Double
mix type
2, Putty
type
Polymer polyvinyl
siloxane,vinyl
polysiloxane,vinyl
silicones
Cross linking agent-
hydride silicone
Catalyst
chloroplatinic acid
30- 45 sec
Is greater
than
silicones
10-12min
No
special
equipment
Dimensio
naly stable
Good
shelf life
Pleasant
odor
Custom
tray
Hydroph
obic
Expensiv
e
Addition silicones
Addition polysilicones are the most stable of all the existing
materials
It has an excellent recovery of 99.93%
It exhibits pseudoplastic properties.it can be used both as syringe
and tray materials
Putty type
Advantages
No custom tray
No special equipment
Good shelf life
Can be poured more than once
Disadvantages
Extremely hydrophilic
More difficult to pour
Most expensive
Polyether materials
ADA
Specificati
on
Composition
Mixing
itime
Working
time
Setting
time
Advantag
es
Disadva
ntages
No 19
Base plate tube-
Pre polymer-
ethylene amine
Inert filler-silica
Plasticiser
glycolether
Catalyst paste-
Ester derivatives
of aromatic
sulphonic acid
Plasticiszer
phthalate
Thinner-octyl
phthalate
Methyl cellulose
30-45 sec
2-3min
5-6 min
No
special
equipment
Finish line
easily read
Pleasant
odor
Can be
poured
more than
once
Hydrophil
ic
Good
shelf life
Fast
setting
Custom
tray
Very
stiff
Least
tear
strength
More
expensiv
e
Polythers
Uses-
For recording impression in preparation of crowns and
bridges
Cavity preparation for inlays and onlays
For construction of partial and complete dentures
Visible light cured polyether
ADA
Specification
Composition
Advantages
Disadvantages
No 19
Introduced in
1988
Light bodied material=syringe
Heavy body=tubes
Contains
Polyurethane dimethacrylate
resin with sio2 +plasticizer
Polymerises in light
Complete control over
W.T/S.T
Curing time relatively
short
Excellent
physical/mechanical/clini
cal properties
Need for
transparent trays
If delay in
placement
material to be
stored in dark
place
Difficult to cure
remote areas
Should not be
used in patients
allergic to
methacrylates
Light cured polyether
It has excellent elasticity
It has infinite working time and short setting time
The impression can be stored upto two weeks
Disinfection
Most manufacturers recommend a specific
disinfectant,such as iodophor,bleach,or glutaldehyde,for disinfection.
Certain disinfectants may result in gypsum casts that have a lower surface
hardness or diminished surface detail.
The current protocol for disinfecting hydrocolloid impressions recommended
by the centre for disease control is to use house hold bleach(1 to 10
dilutions),iodophor or synthetic phenols as disinfectants
An alternate disinfection method is by immersion,but this should not exceed 10
min.
Duplicating is required for two reasons:-
1, The cast on which the wax pattern of the metal frame work is to be
formed must be made from refractory investment because it must
withstand the casting temperatures required for gold or base metal
alloys
2, The original cast is needed for checking the accuracy of the metal
frame work and for processing the denture base portion of the
partial denture
The most common duplicating materials are agar hydrocolloid
compounds, The primary advantage of agar is their set is
reversible.the disadvantage is it is subject to dimensional
change.The best storage condition is 100% humidity.
Duplicating materials
Tissue conditoners are soft elastomers used to treat an
irritated mucosa supporting a denture.it is used to
provide time for healing of soft tissues
Tissue conditioners are composed of powder containing
poly(ethyl methacrylate)and a liquid containing an
aromatic ester ethyl alcohol.
The properties that make tissue conditioners effective are-
1,viscous behavior which allows adaptation to irritated
denture bearing mucosa
2,viscoelastic behavior which cushions the cyclic forces of
mastication and bruxism
Tissue conditioners
Zardiackas.L.D , Dental materials,Dentla clinics of morth
america,July 2007,vol 51,pg 629-643 .
OBrien.W.J, Dental materials and their selection, 3
rd
edition, Quintessence publications.
Craig.R.G, Dental Materials, 12th edition, Elsevier
publications.
Anusavice, Phillips Science of Dental Materials, 11
th
edition, Saunders publications. Impression materials.
References
You might also like
- Impression MaterialsDocument60 pagesImpression Materialsمحمد احمد محمدNo ratings yet
- Physical Science (Specialization) Reviewer 494 Items With Rationalization PDFDocument118 pagesPhysical Science (Specialization) Reviewer 494 Items With Rationalization PDFKaren DellatanNo ratings yet
- RCC DomesDocument3 pagesRCC Domesvaibhavamore0% (1)
- CRODA Surfactants and Alkoxylated Polyols Overview FEB 2013Document8 pagesCRODA Surfactants and Alkoxylated Polyols Overview FEB 2013Maria Eugenia CiveiraNo ratings yet
- Impression Compounds and AlginatesDocument13 pagesImpression Compounds and Alginatessourav dasNo ratings yet
- Data Sheets - UpdatedDocument267 pagesData Sheets - Updateddurgesh82338114100% (1)
- Modelling and Simulation of The Three-Phase Induction Motor Using SimulinkDocument10 pagesModelling and Simulation of The Three-Phase Induction Motor Using SimulinkÁron FehérNo ratings yet
- BASF - Prefabricated ProductsDocument4 pagesBASF - Prefabricated ProductsPamela Villanueva0% (1)
- 95 731 01 SilanesSelectorGuideDocument4 pages95 731 01 SilanesSelectorGuideAelya SanNo ratings yet
- Softener, Textile FinishingDocument4 pagesSoftener, Textile FinishingArif NursyabaniNo ratings yet
- MOMENTIVE Silicone in Coating Textile BrochureDocument12 pagesMOMENTIVE Silicone in Coating Textile Brochureoverlord5555100% (1)
- X-Ray Sources Diffraction: Bragg's Law Crystal Structure DeterminationDocument62 pagesX-Ray Sources Diffraction: Bragg's Law Crystal Structure DeterminationSrimanthula SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Cention N PDFDocument15 pagesCention N PDFFabio RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Dr - Jyoti Tripathi PG First Year Department of ProsthodonticsDocument48 pagesPresented By-Dr - Jyoti Tripathi PG First Year Department of ProsthodonticsJyoti TripathiNo ratings yet
- Bahan Cetak Elastomer: Etny Dyah HarniatiDocument30 pagesBahan Cetak Elastomer: Etny Dyah HarniatiRenata HazelwayNo ratings yet
- HS PDFDocument15 pagesHS PDFSawa Zayia MichaelNo ratings yet
- Algisium C: ExsymolDocument3 pagesAlgisium C: ExsymolEvelyn Vasquez VasquezNo ratings yet
- Catalogo San NopcoDocument12 pagesCatalogo San NopcopedroNo ratings yet
- Leistritz Compounding ENGDocument9 pagesLeistritz Compounding ENGGustavoNo ratings yet
- Collection For Impression MaterialsDocument3 pagesCollection For Impression Materialselsayed barhomeNo ratings yet
- Impression MaterialsDocument11 pagesImpression Materials050023No ratings yet
- Static RecommendGradeDocument1 pageStatic RecommendGradeJohn BansahNo ratings yet
- TrueDocument12 pagesTrueThree AuNo ratings yet
- Adhesive Classification and Properties: Chapter TwoDocument46 pagesAdhesive Classification and Properties: Chapter TwoFrancisco Javier Salamanca BorreroNo ratings yet
- Clearfil SE BondDocument2 pagesClearfil SE BondSupriya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- AdhesivesDocument22 pagesAdhesivesTanzeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Permabond Flyer Crystal Clear Plastic BondingDocument1 pagePermabond Flyer Crystal Clear Plastic BondingM2 APNo ratings yet
- HeliobondDocument36 pagesHeliobondNg JunnNo ratings yet
- Origin and Early Development of Rubber-Toughened Plastics: I ÎatureDocument11 pagesOrigin and Early Development of Rubber-Toughened Plastics: I ÎatureAsheesh shipra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Belami NYLO Gemini Surfactant CatalogueDocument7 pagesBelami NYLO Gemini Surfactant CatalogueNihar Mango VakilNo ratings yet
- Waterborne PVAc Quick Tack AdhesiveDocument1 pageWaterborne PVAc Quick Tack AdhesiveFacundo SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- ImpressionDocument71 pagesImpressionArpit HalaniNo ratings yet
- Elastic Impression MaterialDocument53 pagesElastic Impression MaterialAriba AsifNo ratings yet
- Galata Fomrez Product GuideDocument1 pageGalata Fomrez Product Guideparijat patelNo ratings yet
- Anti Blocking AdditiveDocument5 pagesAnti Blocking AdditiveSergey TrifonovNo ratings yet
- Natural RubberDocument2 pagesNatural RubbertanuNo ratings yet
- 15ifiziegftenioneers Standard Specification For Surface Preparation and Protective Coating 6-79-0020 Rev. 0Document3 pages15ifiziegftenioneers Standard Specification For Surface Preparation and Protective Coating 6-79-0020 Rev. 0Chinmay DaveNo ratings yet
- BROCHURE Product Range - I&I and Home Care Solutions Europe-BASF-09-18Document19 pagesBROCHURE Product Range - I&I and Home Care Solutions Europe-BASF-09-18Francesco RicciNo ratings yet
- Water-Based Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives For Screen PrintingDocument12 pagesWater-Based Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives For Screen PrintingfaizNo ratings yet
- Chapter I-Impressions (2021)Document15 pagesChapter I-Impressions (2021)Hany NassifNo ratings yet
- Solutions For The Thermoset Composites Industry Flipbook PDF - CompressDocument12 pagesSolutions For The Thermoset Composites Industry Flipbook PDF - Compressmarcela walterosNo ratings yet
- Coupling: SilaneDocument5 pagesCoupling: SilaneAkash YadavNo ratings yet
- Journal of Adhesion Science and TechnologyDocument7 pagesJournal of Adhesion Science and TechnologyDaniel L. FrandsenNo ratings yet
- Construction Solutions: Polymer Emulsions & Specialty ChemicalsDocument9 pagesConstruction Solutions: Polymer Emulsions & Specialty ChemicalsLong An DoNo ratings yet
- Coatosil : Additives For High Performance Coatings and InksDocument8 pagesCoatosil : Additives For High Performance Coatings and InksLong An ĐỗNo ratings yet
- RelyX Ultimate Step by StepDocument16 pagesRelyX Ultimate Step by StepTaylorNo ratings yet
- PUMA RSL V - 06 - 14 Final PDFDocument2 pagesPUMA RSL V - 06 - 14 Final PDFTrinhTruongNo ratings yet
- Plastic RecyclingDocument1 pagePlastic RecyclingkerenpkpNo ratings yet
- PigmentsDocument6 pagesPigmentsAbhinav TayadeNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials - Introduction and Impression Compound - Dr. AnandDocument61 pagesImpression Materials - Introduction and Impression Compound - Dr. AnandDr Anand RajapurNo ratings yet
- Additives For Specialty PolymersDocument8 pagesAdditives For Specialty Polymers吉启周No ratings yet
- Kosmos 19 TdsDocument1 pageKosmos 19 TdsjahdaNo ratings yet
- Spec10 Bitumen RubbersDocument1 pageSpec10 Bitumen RubbersashrafelkhalawyNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials For The Polyurea Industry - Global - EN - May2021Document6 pagesRaw Materials For The Polyurea Industry - Global - EN - May2021Jella NurohmahNo ratings yet
- Cention NDocument14 pagesCention NGiTa TAriganNo ratings yet
- Byk Le-G 1 enDocument11 pagesByk Le-G 1 enHelene Di marcantonioNo ratings yet
- Hasan 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 213 012048Document10 pagesHasan 2017 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 213 012048yombexNo ratings yet
- Bituthene 3000 Elastomeric Sheet Tanking and Waterproo NG MembraneDocument1 pageBituthene 3000 Elastomeric Sheet Tanking and Waterproo NG MembraneHen8No ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide Product TreeDocument1 pageSodium Hydroxide Product TreeFawait KasyafaniNo ratings yet
- BASF - Sports Flooring 2020Document12 pagesBASF - Sports Flooring 2020Carlitos PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitDocument4 pagesChemical Inventory Sheet: Name of Company/Production UnitNur E Alam NuruNo ratings yet
- Function Mit18086Document3 pagesFunction Mit18086Ria Dwi IzahyantiNo ratings yet
- Notification APSWREIS Teacher PostsDocument14 pagesNotification APSWREIS Teacher PostsRuthvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- I.S.I. C.M.I EntranceDocument6 pagesI.S.I. C.M.I Entrancegaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- New Oscillation Criteria For Second Order Nonlinear Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesNew Oscillation Criteria For Second Order Nonlinear Differential EquationsresearchinventyNo ratings yet
- Simulation Analysis of Compression Refrigeration Cycle With Different RefrigerantsDocument5 pagesSimulation Analysis of Compression Refrigeration Cycle With Different RefrigerantsSpicyNo ratings yet
- Comments Resolution Discharge Filter Coalescer Skid - Foundation - Anchor - CVL ReplyDocument1 pageComments Resolution Discharge Filter Coalescer Skid - Foundation - Anchor - CVL ReplySana UllahNo ratings yet
- Phy131h1 Final Exam Review Questions 3Document6 pagesPhy131h1 Final Exam Review Questions 3hanujahNo ratings yet
- Water DistillerDocument13 pagesWater DistillerjordanrmaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Verbs Compounded With Aus, Ein, Etc., As Contrasted With Those Compounded With Heraus, Hinaus, Herain, Hinein, EtcDocument152 pagesA Study of Verbs Compounded With Aus, Ein, Etc., As Contrasted With Those Compounded With Heraus, Hinaus, Herain, Hinein, EtcEnkindooNo ratings yet
- A Solar Chimney Power Plant TULJAPURDocument16 pagesA Solar Chimney Power Plant TULJAPURDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (3)
- Design GuideDocument30 pagesDesign Guiderapidindustries100% (6)
- Statistical Mechanics and Out-of-Equilibrium Systems!Document15 pagesStatistical Mechanics and Out-of-Equilibrium Systems!hrastburg100% (1)
- GEOTECH 1 Module 8Document12 pagesGEOTECH 1 Module 8Earl averzosaNo ratings yet
- Load and Stress Distribution in Screw Threads With Modified WashersDocument11 pagesLoad and Stress Distribution in Screw Threads With Modified WashersminakirolosNo ratings yet
- 1 Force and MotionDocument27 pages1 Force and Motion5kfwvjk68bNo ratings yet
- US 0702-3A Design and Execution-F3Document42 pagesUS 0702-3A Design and Execution-F3almirante_andreNo ratings yet
- Ramzan Timetable Grade IX-ADocument1 pageRamzan Timetable Grade IX-AMBJNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws: By: Armaan NooraniDocument10 pagesNewtons Laws: By: Armaan NooraniArmaan NooraniNo ratings yet
- List of Institutes Engineering (Gujcet)Document20 pagesList of Institutes Engineering (Gujcet)Kumar ManglamNo ratings yet
- Rr211402 Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesRr211402 Mechanics of SolidsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument1 pageQuestion PaperDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Multiphoton PolymerizationDocument9 pagesMultiphoton PolymerizationMircavid HeydəroğluNo ratings yet
- SBF BK A07025 Accelerating Admixtures For ConcreteDocument53 pagesSBF BK A07025 Accelerating Admixtures For ConcreteSandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Notes 2Document65 pagesNotes 2Aamir khanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 1Document2 pagesProblem Set No. 1Zukato DesuNo ratings yet
- FS-l6S: Instruction ManualDocument25 pagesFS-l6S: Instruction ManualFazrulNo ratings yet