Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pile Foundation
Uploaded by
ritam1991Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pile Foundation
Uploaded by
ritam1991Copyright:
Available Formats
Presentation by:
RITAM BAKSHI
B.C.E-IV,ROLL:000910401062
Under The Guidance of :
Dr. SANKAR CHAKRABARTI
PROFESSOR
CIVIL ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT
JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY
PILE FOUNDATIONS: WHEN IS IT REQUIRED
Top layers of soil are highly compressible for it to support
Structural loads through shallow foundations.
Rock level is shallow enough for end bearing pile Foundations
provide a more economical design.
Lateral forces are relatively prominent.
In presence of expansive and collapsible soils at the site.
Offshore structures
Strong uplift forces on shallow foundations due to shallow water
table can be partly transmitted to piles.
For structures near flowing water (bridge abutments, etc.)to avoid
the problems due to erosion.
TYPES OF PILES
1. POINT/END BEARING PILES
2. FRICTION PILES
3. TENSION/UPLIFT PILES
4. ANCHOR PILES
5. COMPACTION PILES
6. FENDER/DOLPHIN PILES
7. BATTER PILE
8. SHEET PILE
ON BASIS OF THEIR FUNCTION
OTHER CLASSIFICATIONS
(a)Material of Construction - timber, steel, concrete, composite piles.
(b)Cross-Section - circular, square, hexagonal, I-section-section, pipe,
etc.
(c)Shape - cylindrical, tapered, under reamed, etc.
(d)Mode Of Load Transfer - bearing, friction, tension etc.
(e)Method Of Forming - precast, prestressed, cast in situ, etc.
(f)Method Of Installation - driven, bored, vibrated, jetted, etc.
The selection of pile types to be used in a project depends on
several factors, these are:-
The type of structure and the load it carries.
Strata classification and soil characteristics
Durability
Economy
SELECTION OF PILE TYPES
Load Transfer Mechanism
Qu = Q
b
+ Q
f
= q
b
A
b
+f
s
A
s
Where Qu = ultimate load applied on
the top of the pile
q
b
= ultimate unit bearing capacity of
the pile at the base
A
b
= bearing area of the base of the
pile
A
s
= total surface area of pile
embedded below ground surface
f
s
= unit skin friction (ultimate)
SAFE LOAD CAPACITY & FACTOR OF SAFETY
2
..3
Q
a =
Q
u
F.O.S ........1
METHODS OF DETERMINING ULTIMATE LOAD BEARING
CAPACITY OF A SINGLE VERTICAL PILE
The ultimate bearing capacity, Qu, of a single vertical pile may
be determined by any of the following methods.
1. The use of static bearing capacity equations.
2. Dynamic method.
3. Field load tests.
4. The use of SPT and CPT values.
Point Load capacity of Pile: General Bearing
Capacity approach
Ultimate bearing capacity of soil considering general
bearing capacity equation. Shape, inclination, and depth
factors are included in bearing capacity factors
C=cohesion value of soil
q=effective overburden pressure
=unit weight of soil
D=dia. Of foundation
Nc,Nq,Nr=c- characteristics values of soil
LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY STATIC FORMULA
PILES IN GRANULAR SOILS
The ultimate bearing capacity ( Qu ) of piles in granular soils is given by :
Q
s
Q
B
D
D
f
Q
C,
Q
B
Q
S
K = coefficient of earth pressure;
P
Di
= effective overburden pressure in kg/cm
2
for the i
th
layer where i
varies from 1 to n;
= angle of wall friction between pile and soil, in degrees (may be
taken equal to ); and
A
si
= surface area of pile stem in cm
2
in the i
th
layer where i varies
from 1 to n.
Q
u
= A
p
(1/2.D.N
r
+ P
d
.N
c
) +
i=1
n
K.P
di
.tan.A
si
PILES IN COHESIVE SOILS
The ultimate bearing capacity of piles (Qu) in cohesive soil is given by the following:
Ap = cross sectional area of pile toe in cm
2
,
Nc = bearing capacity factor usually taken as 9,
C
p
= average cohesion at pile tip in kg/cm
2
,
= reduction factor,(generally taken between 0.3-0.5)
C = average cohesion throughout the length of pile in Kg/cm
2
, and
As = surface area of pile shaft in cm
2
.
Q
u
=A
p
.N
c
.C
p
+.C.A
s
PILE LOAD TEST
Static pile load test is the most reliable means of
determining the load capacity of a pile. The test
procedure consists of applying static load to the pile in
increments up to a designated level of load and
recording the vertical deflection of the pile. The load is
usually transmitted by means of a hydraulic jack placed
between the top of the pile and a beam supported by
two or more reaction piles. The vertical deflection of the
top of the pile is usually measured by mechanical
gauges attached to a beam, which span over the test
pile.
CONCLUSION
Generally pile foundation is provided for
high rise building or a super structure where the load coming from the
superstructure is high, and also the soil is weak and is unable to take the
load. But now a days in all kind of Industrial and General structures pile
foundation is provided due to the following main advantages:
Load carrying capacity is high
Pile foundation resists the wind load, seismic load and torsional moment
due to effects of wind and seismic action or both
Also piles can be provided in groups so that it can resist the load coming
for the superstructure and the soil volume inside the pile group can resist
the horizontal forces acting on the piles
REFERENCES
1.IS-2911(PART 1,PART 2,PART 3,PART 4).1979
2.FOUNDATION DESIGN THEORY AND PRACTICE ,N. S. V. Kameswara Rao
3.Principles and Practices of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering By
V N S Murthy
4.Theory and Practice of Foundation Design, Som & Das
You might also like
- 2Document8 pages2Eduardo Antonio Comaru Gouveia75% (4)
- Sla At&tDocument2 pagesSla At&tCésar Lainez Lozada TorattoNo ratings yet
- Volvo BL 71 ManualDocument280 pagesVolvo BL 71 ManualAlberto G.D.100% (2)
- Foundation Analysis: Ultimate Bearing Capacity: Shallow FoundationDocument21 pagesFoundation Analysis: Ultimate Bearing Capacity: Shallow FoundationShiela Marie Cruz100% (1)
- Lecture 11-1 Bases by H.J. MtyanaDocument29 pagesLecture 11-1 Bases by H.J. MtyanaHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (1)
- Steel Concrete Composite High Rise BuildingsDocument7 pagesSteel Concrete Composite High Rise Buildingsscchung50% (2)
- Civil Engineering Department: Government Engineering Colleg BilaspurDocument11 pagesCivil Engineering Department: Government Engineering Colleg Bilaspurtinu sahuNo ratings yet
- Bore Pile Design in Sand Rev ADocument2 pagesBore Pile Design in Sand Rev AOlanrewaju OkunolaNo ratings yet
- Ramset Specifiers Anchoring Resource Book ANZ - TruBolt Mechanical AnchoringDocument10 pagesRamset Specifiers Anchoring Resource Book ANZ - TruBolt Mechanical AnchoringjlolhnpNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Analysis of Frame StructuresDocument54 pagesTwo Dimensional Analysis of Frame StructuresFrank PuchiNo ratings yet
- Composite Columns IDocument15 pagesComposite Columns IHeng Kimseng100% (1)
- Finite Element Analysis of Soil Bearing Capacity Using PlaxisDocument5 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Soil Bearing Capacity Using PlaxisRehan HakroNo ratings yet
- Rock Socket Piles at Coventry Point, Market Way, CoventryDocument16 pagesRock Socket Piles at Coventry Point, Market Way, Coventrynagas440% (1)
- Ceng3143 Fge-III Ext Chapter5Document122 pagesCeng3143 Fge-III Ext Chapter5ABAMELANo ratings yet
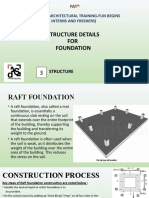
- Structure Details FOR Foundation: Practical Architectural Training-Fun Begins (For Interns and Freshers)Document37 pagesStructure Details FOR Foundation: Practical Architectural Training-Fun Begins (For Interns and Freshers)Divya Varshney100% (1)
- Chapter 8-Earth Retaining Structures-13Document23 pagesChapter 8-Earth Retaining Structures-13Alexander AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Mat (Raft) Foundations - BookDocument10 pagesDesign and Construction of Mat (Raft) Foundations - BookbatteekhNo ratings yet
- Optimize Positioning of Relief Shelf in Cantilever Retaining WallDocument3 pagesOptimize Positioning of Relief Shelf in Cantilever Retaining WallGRD Journals100% (1)
- LysmerDocument147 pagesLysmerHans OlmosNo ratings yet
- Optimal Deign of Pile FoundationDocument13 pagesOptimal Deign of Pile FoundationJustin Johnson100% (1)
- 1) Deep FoundationsDocument30 pages1) Deep FoundationsmehtabhumikaaNo ratings yet
- M. Tech. (Structural Engineering) SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONDocument26 pagesM. Tech. (Structural Engineering) SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONAjay AjaiNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete ElementsDocument62 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete ElementsGodwin AcquahNo ratings yet
- Development of Column Interaction Curves For Higher Grades of ConcreteDocument22 pagesDevelopment of Column Interaction Curves For Higher Grades of Concreteyedida v r aviswanadhNo ratings yet
- CE4070 Structural Modelling Yield Line Analysis of Slab IETDocument18 pagesCE4070 Structural Modelling Yield Line Analysis of Slab IETkartheepan100% (1)
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument6 pagesEarthquake Resistant StructuresAmith KeshvtakarNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Caissons and CofferdamsDocument9 pagesCH-2 Caissons and CofferdamsAsegid Bezabih100% (1)
- Indeterminate Structure AnalysisDocument17 pagesIndeterminate Structure Analysispranjal singhNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementDocument32 pagesShallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementPhanna MongNo ratings yet
- 4610 sl4Document73 pages4610 sl4Rodrigo de León100% (1)
- Continuous Beam For RCDocument44 pagesContinuous Beam For RCHammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Underground Water TankDocument18 pagesUnderground Water TankMohonAliNo ratings yet
- SoilTest ProjectDocument115 pagesSoilTest ProjectMd Shahimul HaqueNo ratings yet
- RCC54 Circular Column ChartingDocument13 pagesRCC54 Circular Column Chartingali billNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDocument46 pagesBearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationPranavaDart100% (1)
- River Training Works - Case Studies of Ganga Bridge No. 52: Project Report ONDocument72 pagesRiver Training Works - Case Studies of Ganga Bridge No. 52: Project Report ONRam NepaliNo ratings yet
- Lec (3) Part 2 Combined FootingDocument44 pagesLec (3) Part 2 Combined FootingDemse ZelelewNo ratings yet
- Design of Retaining WallDocument40 pagesDesign of Retaining WallVeera Vimallen100% (1)
- Gannon - Primary Firm Secant Pile Concrete Specification - April 2016Document11 pagesGannon - Primary Firm Secant Pile Concrete Specification - April 2016muhammad ismailNo ratings yet
- RCC Design TipsDocument9 pagesRCC Design Tipssatoni12No ratings yet
- SEEPW Engineering BookDocument412 pagesSEEPW Engineering BookTudor MilchisNo ratings yet
- Experimental Observations and Parametric Study of Piled Raft Foundation Using PlaxisDocument7 pagesExperimental Observations and Parametric Study of Piled Raft Foundation Using PlaxisAngelinSavioNo ratings yet
- Counterfort Retaining Wall MCN PDFDocument12 pagesCounterfort Retaining Wall MCN PDFHoshear BakrNo ratings yet
- SPREW Part 3 of 3 PDFDocument122 pagesSPREW Part 3 of 3 PDFhz135874No ratings yet
- 1.0 Cover Page of Tandrang - KholaDocument1 page1.0 Cover Page of Tandrang - KholaNepali KanchooNo ratings yet
- Some Geotechnical Properties of Tokai Clay PaperDocument6 pagesSome Geotechnical Properties of Tokai Clay PaperSen HuNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Seismic Response of Multi-Storied Structures With and Without Soil Structure InteractionDocument4 pagesComparison of Seismic Response of Multi-Storied Structures With and Without Soil Structure InteractionAkhil LamdadeNo ratings yet
- W3 Deep FoundationDocument42 pagesW3 Deep FoundationTeoh Zhi TongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Design For Serviceability PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Design For Serviceability PDFChee Fong MakeNo ratings yet
- Design PDFDocument260 pagesDesign PDFPrf El-SakhawyNo ratings yet
- 2-Bearing CapacityDocument107 pages2-Bearing CapacityZemen JMNo ratings yet
- King Post Wall Design-1Document10 pagesKing Post Wall Design-1Ibrahim MeharoofNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Grain Size Distribution: Sieve AnalysisDocument20 pages2.2 Grain Size Distribution: Sieve AnalysisYen Ling NgNo ratings yet
- Vertical Loads On Building Frames: Assumptions For The Analysis of Girders Using Approximate AnalysisDocument10 pagesVertical Loads On Building Frames: Assumptions For The Analysis of Girders Using Approximate AnalysisNeven Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- EC2 Ch03aDocument15 pagesEC2 Ch03asunilarunaNo ratings yet
- Sotney ColmDocument7 pagesSotney ColmrajNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 November 2014 TO Is 4326: 2013 Earthquake Resistant Design and Construction of Buildings - Code of PracticeDocument9 pagesAmendment No. 1 November 2014 TO Is 4326: 2013 Earthquake Resistant Design and Construction of Buildings - Code of PracticeAKSNo ratings yet
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985From EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985No ratings yet
- Piles IntroductionDocument39 pagesPiles IntroductionKhushboo PriyaNo ratings yet
- TCS Global Trend Study IoT Intel Case Study PDFDocument4 pagesTCS Global Trend Study IoT Intel Case Study PDFritam1991No ratings yet
- Cases 1Document5 pagesCases 1ritam1991No ratings yet
- Venue Choosing A Suitable Center For Training Activities Which Should Be Project & Training Management Resources Capital Requirement For The Following SchedulingDocument1 pageVenue Choosing A Suitable Center For Training Activities Which Should Be Project & Training Management Resources Capital Requirement For The Following Schedulingritam1991No ratings yet
- Water Problems For Kolkata Metropolitan RegionDocument8 pagesWater Problems For Kolkata Metropolitan Regionritam1991No ratings yet
- C31978612h1200a0712 SS12J2MMDocument1 pageC31978612h1200a0712 SS12J2MMritam1991No ratings yet
- The New Order of BarbariansDocument39 pagesThe New Order of Barbariansbadguy100% (1)
- Information Systems and Supply Chain ManagementDocument2 pagesInformation Systems and Supply Chain Managementvipinkandpal86No ratings yet
- CBC Heo (Wheel Loader) NC IIDocument58 pagesCBC Heo (Wheel Loader) NC IIJohn JamesNo ratings yet
- Debate ReportDocument15 pagesDebate Reportapi-435309716No ratings yet
- 02 Object Modeling TechniqueDocument50 pages02 Object Modeling TechniqueMuhammad Romadhon Batukarang EsdNo ratings yet
- Yale Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesYale Revision WorksheetYASHI AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- SilmaDocument12 pagesSilmanobleconsultantsNo ratings yet
- I M Com QT Final On16march2016Document166 pagesI M Com QT Final On16march2016Khandaker Sakib Farhad0% (1)
- PM Jobs Comp Ir RandDocument9 pagesPM Jobs Comp Ir Randandri putrantoNo ratings yet
- Noise and DB Calculations: Smart EDGE ECE Review SpecialistDocument2 pagesNoise and DB Calculations: Smart EDGE ECE Review SpecialistLM BecinaNo ratings yet
- CISF Manual Final OriginalDocument17 pagesCISF Manual Final OriginalVaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Derivational and Inflectional Morpheme in English LanguageDocument11 pagesDerivational and Inflectional Morpheme in English LanguageEdificator BroNo ratings yet
- A P P E N D I X Powers of Ten and Scientific NotationDocument5 pagesA P P E N D I X Powers of Ten and Scientific NotationAnthony BensonNo ratings yet
- Existentialism in CinemaDocument25 pagesExistentialism in CinemanormatthewNo ratings yet
- Img 20201010 0005Document1 pageImg 20201010 0005Tarek SalehNo ratings yet
- Financial Market - Bsa 2A Dr. Ben E. Bunyi: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument3 pagesFinancial Market - Bsa 2A Dr. Ben E. Bunyi: Imus Institute of Science and TechnologyAsh imoNo ratings yet
- Nutridiet-Enteral and Parenteral FeedingDocument3 pagesNutridiet-Enteral and Parenteral FeedingBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesChapter 13 CarbohydratesShanna Sophia PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Plan (JFJS-788)Document18 pagesProject Quality Plan (JFJS-788)mominNo ratings yet
- A.meaning and Scope of Education FinalDocument22 pagesA.meaning and Scope of Education FinalMelody CamcamNo ratings yet
- RARE Manual For Training Local Nature GuidesDocument91 pagesRARE Manual For Training Local Nature GuidesenoshaugustineNo ratings yet
- Python in Hidrology BookDocument153 pagesPython in Hidrology BookJuan david Gonzalez vasquez100% (1)
- Best Mutual Funds For 2023 & BeyondDocument17 pagesBest Mutual Funds For 2023 & BeyondPrateekNo ratings yet
- Praise and Worship Songs Volume 2 PDFDocument92 pagesPraise and Worship Songs Volume 2 PDFDaniel AnayaNo ratings yet
- IM1 Calculus 2 Revised 2024 PUPSMBDocument14 pagesIM1 Calculus 2 Revised 2024 PUPSMBEunice AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Livingston Seagull - Richard Bach - (SAW000) PDFDocument39 pagesJonathan Livingston Seagull - Richard Bach - (SAW000) PDFAdrià SonetNo ratings yet
- Subject OrientationDocument15 pagesSubject OrientationPearl OgayonNo ratings yet