Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adenotonsilitis
Uploaded by
AriSugihartoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adenotonsilitis
Uploaded by
AriSugihartoCopyright:
Available Formats
1
ADENO-TONSILITIS
Dr. Tolkha Amaruddin, M.Kes., SpTHT Dr. Tolkha Amaruddin, M.Kes., SpTHT
RSUD SARAS HUSADA
PURWOREJO 2008
2
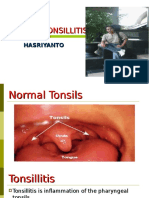
ADENOID
A triangular shape mass of lymphoid tissue
located on the posterior aspect of the box like
nasopharynx (Bailey, 1998)
TONSIL
A paired, in general ovoid shaped masses
located on the lateral walls of the oropharynx.
(Bailey, 1998)
3
4
5
Vascularisation - innervation the
adenoids:
The pharyngeal branches of the external
carotid artery.
Sensory the glossopharyngeal &
vagus nerves.
Referred pain from the adenoids (as
well as the tonsils) in both the ears
and throat.
6
Vascularisation and innervation
The tonsils :
ascending pharyngeal
ascending palatine
lingual & facial arteries
The lymphatic drainage superior deep
cervical & jugular lymph nodes
inflammatory cervical adenitis/abscess in
children.
7
8
9
Diagram skematis tonsil palatine & komposisi sel
10
11
Distribusi kelas-kelas sel T (CD 3+), sel B ( CD 20+),
sel T helper (CD4+) dan sel T sitotoksik (CD 8+).
12
Bacteria
Aerobic :
Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus, H.
influenza, S. pneumonia, Moraxella
cattaralis, S. aureus, H. parainflueza,
Neiseria sp, Mycobacteria sp
Anaerobic :
Bacteriodes sp, Peptococcus sp,
Peptostreptococcus sp, Actinomycosis sp.
13
Virus : Epstein Barr, Adenovirus, Influenza A
and B, Herpes simplex,parainfluenza
Others : Mycobacterium (atypical
nontuberculous)
14
PATOGENESIS OF ADENOTONSILAR DISEASE
Anatomic location organs of imunity
processing infection material a
focus of infection / inflamation loss
integrity of the crypt epithelium
chronic cryptitis & crypt obstruction
stasis of crypt debris & persistence
antigen
15
CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION OF THE ADENOIDS &
TONSILS
Adenoids :
Acute adenoiditis
Recurrent acute adenoiditis
Chronic adenoiditis
Tonsils
Acute tonsillitis
Recurrent tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis
16
CLINICAL FEATURES ADENOID
Symptoms & signs due to hypertrophy :
1. Nasal obstruction
2. Mouth breathing
3. Difficulty in eating
4. Noisy breathing snoring toneless voice
5. Adenoid facies
Eustachian obstruction:
1. Deafness
2. The presence of fluid in the middle ear
17
Symptom & sign due to inflamation
1.Nasal discharge
2.Postnasal drip
3.Cough
4.Otitis media
5.Rhinitis & sinusitis
6.Cervical adenitis
Generalized disturbances
Mental dullness, apathy, poor breathing, bad posture,
deafness, nocturnal enuresis
18
DIAGNOSIS ADENOID (Gray, 1992):
1. Rhinos copy posterior
2. The lateral soft tissue view
19
Differential diagnosis adenoid
1. Other causes of nasal obstruction
Vasomotor rhinitis, foreign bodies, hypertropied
posterior ends of inferior turbinates, deflected nasal
septum, congenital choanal atresia
2. Orthodontic abnormalities
High arch palates, wedge shaped faces, narrow
upper jaws, crowded teeth.
3. Thornwaldts disease in which there is cystic
persistence of the median furrow of the
nasopharyngeal tonsil
20
TREATMENT ADENOID
Conservative
The symptom are not marked:
Non irritan decongestants nasal drop, fresh
air, sensible diet, breathing and postural
exercise.
Surgical (Adenoidectomy)
Nasal obstruction
Deafness
Chronic otorhhoea
Recurrent otitis media
Sinusitis
21
INDICATION FOR ADENOIDECTOMY
Obstruction:
chronic nasal obstruction
obligate mouth breathing
Sleep apnea and/or sleep disturbances.
Infection
Adenoid hyperplasis with Recurrent /chronic
adenoiditis
Recurrent/chronic otitis media with effusion
Chronic otitis media
Neoplasia
22
23
CHRONIC TONSILLITIS
1. Chronic parenchymatous tonsillitis
2. Chronic follicular tonsillitis
24
CHRONIC PARENCHYMATOUS
TONSILLITIS (Gray, 1992)
More common in children (between 4 and
15 years)
A chronic inflammatory hypertrophy
Associated with enlargement of the
nasopharengeal tonsil
25
CLINICAL FEATURE
1. Persistent or recurrent sore throats
2. Persistent cervical adenitis
3. Marked tonsillar enlargement
4. Injected anterior faucial pillars
5. Irritation cough
26
TREATMENT :
1. Conservative
Attention to general health and diet
2. Tonsillectomy
27
CHRONIC FOLLICULAR TONSILLITIS
Most commonly in adults
Follow repeated attacks of acute follicular tonsillitis
Clinical feature :
1. Chronic irritation or repeated sore throat
2. Cervical adenitis
3. Cough
4. Bad taste and halitosis
Treatment : 1. Conservative
2. Tonsillectomy
28
29
I. Seven or more episodes of tonsillitis in one
year
II. Five or more episodes of tonsillitis each year
over a period of two years
III. Three or more episodes of tonsillitis a year for
a period of three years
IV. Tonsillitis that recurs despite treatment with
antibiotics
V. Airway or swallowing obstruction due swollen
tonsils
Patient may be candidate for tonsillectomy
if patient meets one of the following criteria:
30
31
32
33
34
35
You might also like
- Adenotonsillitis NewDocument100 pagesAdenotonsillitis NewDrravikumar Bhandari100% (1)
- 1.acute PharyngitisDocument88 pages1.acute PharyngitisIhsan Hanif0% (1)
- Chapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPeej Reyes100% (2)
- TonsilitisDocument23 pagesTonsilitisatai-phin-4632100% (4)
- TonsilDocument60 pagesTonsilShabiela Mafazah100% (1)
- Online Learning ModuleDocument38 pagesOnline Learning ModuleMani SainiNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases of PharynxDocument72 pagesCommon Diseases of PharynxPinak DeNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Tonsilitis KronisDocument49 pagesLaporan Kasus Tonsilitis KronisTabita P SNo ratings yet
- Adenotonsillar Diseases DrbugnahDocument37 pagesAdenotonsillar Diseases DrbugnahDr.Sherif Bugnah100% (8)
- Krishna Reddy Inflammations of NasopharynxDocument18 pagesKrishna Reddy Inflammations of NasopharynxSiva ramaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Children With Respiratory System DysfunctionsDocument27 pagesNursing Management of Children With Respiratory System DysfunctionsDody ZainNo ratings yet
- AdenotonsilitisDocument42 pagesAdenotonsilitisELIA RICHARDNo ratings yet
- Mbbs Feb11Document22 pagesMbbs Feb11Dr. T. Balasubramanian100% (2)
- Adenotonsillar DiseasesDocument36 pagesAdenotonsillar DiseasesKIBET ERNEST MUTAINo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Tonsillectomy: Aau-Chs School of AnesthesiaDocument54 pagesAnesthesia For Tonsillectomy: Aau-Chs School of AnesthesiaagatakassaNo ratings yet
- Serous Otitis MediaDocument21 pagesSerous Otitis Mediagiri00767098No ratings yet
- 18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)Document7 pages18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)osamaeNo ratings yet
- ON TONSILITIS (Autosaved)Document31 pagesON TONSILITIS (Autosaved)kiran kumari yadav0% (1)
- Adenotonsillar Diseases: Becky ChepngenoDocument37 pagesAdenotonsillar Diseases: Becky ChepngenoKIBET ERNEST MUTAINo ratings yet
- Adenoiditis With Tonsillitis (H)Document6 pagesAdenoiditis With Tonsillitis (H)Ilyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- بعد التعديل 2Document16 pagesبعد التعديل 2Sima SaeedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorder: BY Hidayat Khan MSN, MPH, BSN, & Chpe, Ip&C, Rn. DPHNDocument89 pagesRespiratory Disorder: BY Hidayat Khan MSN, MPH, BSN, & Chpe, Ip&C, Rn. DPHNSyed MaazNo ratings yet
- PHARYNGITISDocument25 pagesPHARYNGITISWesam TayaNo ratings yet
- IVRSDocument61 pagesIVRSAndrew ChinchillaNo ratings yet
- Parts: Nose Throat Pharynx LarynxDocument47 pagesParts: Nose Throat Pharynx LarynxRANJIT GOGOINo ratings yet
- Maxillary SinusDocument43 pagesMaxillary SinusAli FalihNo ratings yet
- Disorder of ThroatDocument21 pagesDisorder of ThroatSumit YadavNo ratings yet
- Polip Nasi 1Document19 pagesPolip Nasi 1Adli RifkiNo ratings yet
- SinusitisDocument23 pagesSinusitisMumin Alamin AllaminNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and Peritonsillar AbscessDocument19 pagesTonsillitis and Peritonsillar AbscesszayNo ratings yet
- Ent Med RevisionDocument41 pagesEnt Med RevisionswamysamsonNo ratings yet
- Common Disorde Rs in ChildrenDocument172 pagesCommon Disorde Rs in Childrenblacklilha100% (1)
- By (PG in ENT) : DR B.SowmyaDocument87 pagesBy (PG in ENT) : DR B.Sowmyadrchinna100% (1)
- اسايمنت بالغين ٢Document12 pagesاسايمنت بالغين ٢Sima SaeedNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis BK (LR)Document57 pagesTonsillitis BK (LR)Tiffany NurzamanNo ratings yet
- Ronald Deskin, 2002Document60 pagesRonald Deskin, 2002Ratna Puspa RahayuNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation TonsilectomyDocument46 pagesClinical Presentation TonsilectomySREEDEVI T SURESH100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Disorders Respiratory in ClientDocument101 pagesChapter 6 Disorders Respiratory in Clientanisa ahmedNo ratings yet
- Diseases - of - The - Tonsil 2023Document41 pagesDiseases - of - The - Tonsil 2023dr MohammedNo ratings yet
- Assignment Adults SimaDocument19 pagesAssignment Adults SimaSima SaeedNo ratings yet
- Uworld ENT NotesDocument4 pagesUworld ENT Notes808kailuaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument45 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionNatasha Abdulla100% (2)
- TonsilitisDocument32 pagesTonsilitisFitriNajibahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 73Document88 pagesChapter 73Julian TaneNo ratings yet
- Who Gets Tonsillitis?Document3 pagesWho Gets Tonsillitis?Mounir ChadliNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 INFLAMMATORY CONDITION OF NOSE & PNSDocument38 pagesChapter10 INFLAMMATORY CONDITION OF NOSE & PNSSULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Acute Tonsillitis: Zhong Shixun PH.DDocument43 pagesAcute Tonsillitis: Zhong Shixun PH.DEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- Acute SinusitisDocument11 pagesAcute Sinusitisعبدالله فائز غلامNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Tonsilitis Kronis Dengan Eksaserbasi AkutDocument30 pagesCase Report: Tonsilitis Kronis Dengan Eksaserbasi AkutRara SudibyoNo ratings yet
- Chronic RhinosinusitisDocument8 pagesChronic RhinosinusitisYunardi Singgo100% (1)
- PRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalDocument33 pagesPRACTICE TEACHING On Otitis Media FinalAjit ThangeNo ratings yet
- 5+6. Nasal Polyp & DNS PDFDocument43 pages5+6. Nasal Polyp & DNS PDFJames StiltonNo ratings yet
- Otitis Media: Prepared By: - Priyanka ThapaDocument38 pagesOtitis Media: Prepared By: - Priyanka ThapaKalo kajiNo ratings yet
- Pharygitis AND TonsillitisDocument29 pagesPharygitis AND Tonsillitisstara123No ratings yet
- Tonsillitis FACT SheetDocument3 pagesTonsillitis FACT SheetSiska SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Upper Respiratory System (URTI) : DR Sarwar Hussain, Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, NBUDocument36 pagesDiseases of Upper Respiratory System (URTI) : DR Sarwar Hussain, Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, NBUخالد مطرNo ratings yet
- Casea Omsk W Fas N PalDocument28 pagesCasea Omsk W Fas N PalMegan ShanzuNo ratings yet
- 3-Pharynx. Diseases of OropharynxDocument79 pages3-Pharynx. Diseases of OropharynxislamNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal Abscesses, Tonsillar and Adenoid InfectionsDocument36 pagesPharyngeal Abscesses, Tonsillar and Adenoid InfectionsRon Christian Neil RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chronic AdenoiditisDocument8 pagesChronic AdenoiditisVinoster ProductionNo ratings yet
- AdenoidsDocument6 pagesAdenoidsIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- MSN Ii - 24.6.2020 An-Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisDocument41 pagesMSN Ii - 24.6.2020 An-Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Throat Pharynx Adenoids ENT LecturesDocument33 pagesThroat Pharynx Adenoids ENT LecturesRaju GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathy in Adenoiditis - A Review Nagendra SisiodiaDocument4 pagesHomoeopathy in Adenoiditis - A Review Nagendra SisiodiaDr nagendra kumar sisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis, Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy: - Literature ReadingDocument52 pagesTonsillitis, Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy: - Literature ReadingdestiNo ratings yet
- Ent Case Sheet ProformaDocument8 pagesEnt Case Sheet ProformaDebzz Pradhan100% (3)
- AdenotonsilitisDocument35 pagesAdenotonsilitisAriSugiharto100% (2)
- Surgical Nursing (III)Document32 pagesSurgical Nursing (III)Opio MosesNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and Adenoiditis: Islamic University Nursing CollegeDocument15 pagesTonsillitis and Adenoiditis: Islamic University Nursing CollegeNinaNo ratings yet
- Indications For Tonsillectomy and AdenoidectomyDocument13 pagesIndications For Tonsillectomy and AdenoidectomyAntonius Verdy Tedjosantoso100% (1)
- Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisDocument12 pagesTonsillitis and AdenoiditisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Adenoid Hypertrophy FixDocument7 pagesAdenoid Hypertrophy FixWidi Yuli HariantoNo ratings yet
- Tonsilectomy and AdenoidectomyDocument7 pagesTonsilectomy and AdenoidectomySabella Gustika VernandaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillectomy, and AdenoidectomyDocument38 pagesTonsillectomy, and AdenoidectomyAlbert MatakenaNo ratings yet
- Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy - Pediatric Clinics of North AmericaDocument13 pagesTonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy - Pediatric Clinics of North AmericayosefNo ratings yet