Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uvea
Uploaded by
guestar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views43 pagesIris Is a diaphragm that dividing ocular chamber into two parts: - Anterior - Posterior Building a hole at the center called as pupil Anterior part ---> origins from corneal endothelia posterior part - origins from retinal endothelium Root of the iris are thin ---> tear easily pupil reaction anomaly are depend on : - afferent - efferent Argyle Robert
Original Description:
Original Title
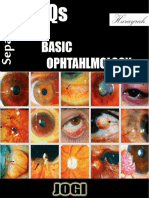
11. Uvea
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIris Is a diaphragm that dividing ocular chamber into two parts: - Anterior - Posterior Building a hole at the center called as pupil Anterior part ---> origins from corneal endothelia posterior part - origins from retinal endothelium Root of the iris are thin ---> tear easily pupil reaction anomaly are depend on : - afferent - efferent Argyle Robert
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views43 pagesUvea
Uploaded by
guestarIris Is a diaphragm that dividing ocular chamber into two parts: - Anterior - Posterior Building a hole at the center called as pupil Anterior part ---> origins from corneal endothelia posterior part - origins from retinal endothelium Root of the iris are thin ---> tear easily pupil reaction anomaly are depend on : - afferent - efferent Argyle Robert
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 43
Uveal Tract
Dr. Bambang Setiohadji, SpM
Anatomy
Is a vascular layer that consists of :
Iris
Cilliary body
Choroid
Function :
Nutrition supply
Iris
Is a diaphragm that dividing ocular chamber into
two parts:
Anterior
Posterior
Building a hole at the center called as pupil
Anterior part ---> origins from corneal endothelia
Posterior part --> origins from retinal endothelia
Muscles :
M. Spchiter pupil ---> circular, N III
(parasympatic), myosis
M. dilator pupil ---> radier, sympatic,
midriatics
Root of the Iris are thin ---> tear easily
Vascularization :
From A. ciliaris posterior longus
Pupil
As a aperture that can found in an ordinary
photographic camera
Normal : round, central, isokor
If > 1 : Polikoria, if not central : korektopia
Pupil reaction :
toward to the direct and indirect light
toward to the close point
toward to the drugs
Toward to the light :
retina N II Chiasma optic
Optical tract Brachium Coliculus sup.
Nc. Eidinger Westphal Parasymphatic fiber
N III Pupil
Afferent
Efferent
Toward to the close distance :
Trias :
convergence
miosis
accommodation
Toward to the drugs :
Miotic : esserine, pilocarpine
Midriatic : atropine, homatropine, cocaine,
adrenaline
Pupil reaction anomaly are depend on :
afferent
efferent
Argyle Robertson Pupil :
efferent damage, direct and indirect light
reaction (-)
irregular miosis
anisokor
Horner syndrome :
miosis, ptosis, enofthalmus, anhydrous,
paralysis of M. dilatator pupil
Cilliary body :
triangle form, the basis is at the front which the
iris attached spreads until the Choroid
consist of :
M. ciliaris for accommodation (longitudinal,
circular, radier)
Ciliar processus :
inside part divided into:
pars plana
pars corona
originating zonula zinii fibers : suspending the lens, for
accommodation process
On severe inflammation --> damage of ciliary body
---> atrophy ---> secretion ---> ptisis bulbi
perforating injuries can occurring SO
Congenital Iris Anomalies
Pupil membrane persistency
Fetus : pupil closed ---> 7 - 8 pregnancy
If absorption
altered
Fine cotton in front of
the lens
---> born : open pupil
Iris coloboma
Two forms :
Congenital : anomalies of formation
Acquired : after glaucoma operation, optical
iridectomy
Usually followed with Choroid coloboma
Iris heterochromia
bilateral ; unilateral
differences colors between different area of the iris
Two forms :
Congenital : glaucoma congenital
Acquired : iris atrophy after iridocyclitis/glaucoma
Traumatic Iris Disturbances
Iridoplegi
if affected by blunt injury, because of parese
N. III temporary (2 - 3 weeks)
permanent
Th/
Using of black eye glasses
Do not read (can not accommodate)
R/ pilocarpine ---> for myotics
Iridodialisis
E/ : injuries ---> tearing of iris root --> pupil
excentric
Th/
Midriatics
banded
diplopia (+) ---> iris reposition
Hifema
E/ : injury --> rupture of blood vessels --> blood in the
anterior chamber (hifem)
There is two types :
Primary : straight after injuries
Secondary :
fifth days after injuries
> severe
if immediately reabsorption of the clot & regeneration not
occurred
Complication :
IOP elevated
Corneal hemosiderosis
Uveitis
Muddying of vitreous body
Th/
totally bed rest
IOP observation & condition of hifema
IOP high --> diamox, glycerin
--> 24 hours still high ---> parasintesa
--> if normal & hifema still >>> --> parasintesa
Iris Neoplasm
Iris Tumor
Nevus Pigmentosus Iridis --> benign melanoma
clear border
brown spotted
not progressive
no disturbances
Malignant
deep brown spotted
rough surface
not clear border
Metastasis to preaulicular glands
Therapy :
Metastasis (-) : Iridectomy
Metastasis (+) : Enucleation
Inflammation of The Iris
Inflammation of the Iris : Iritis
Usually followed by inflammation of the ciliary
body : Iridocyclitis
E/ :
Systemic disease :
lues, TBC, gout, GO, focal infection, tooth, ENT, urinary tract,
infection (virus, fungal, worm), DM
Secondary iridocyclitis around eye region
Perforating trauma
SO
Idiopathic ----> Immune reaction
Clinical Finding
Subjective :
Spontaneous pain of the eye ball, headache reference to
temporal regions
Photophobia
Decreasing visual acuity
Objective :
Palpebra : edema
CB : ciliar injection
C : muddying, KP in endothel
COA : Flare (+), Hipopion +/-, mild
---> narrow if iris bombe is present
P : Irregular --> sinechia post.
Pupil : seclusion & oclusion
Complication :
muddiness of vitreous
cataract
IOP low or high
Sequels :
pupil seclusion
pupil occlusion
posterior synechia
Iris bombe
glaucoma
Uveitis anterior clinically divided into :
Granulomatous
Non-granulomatous
Mixed
Uveitis Granulomatous
Non acute
Cellular reaction >>> vascular
Blurred iris surface
KP in thick endothel
deep COA
muddying vitreous
Uveitis Non Granulomatous
E/ allergy ?
Acute reaction >>> cellular
Fine KP
Vitreous not so muddy
COA : Hipopion +/-
Mixed : all of signs above
Iridocylitis caused by virus :
Bechet syndrome, uveitis, stomatitis, genital ulcer
Vogt. Kyanagi syndrome : uveitis, tinnitus, alopecia, vitiligo
Th/ :
Midriatics :
SA 0,5 % ed/eo
for lowering blood vessel congestion/inflammation
resting the eye (relaxation of M. spinchter pupil & M ciliaris)
If IOP high ----> diamox 3 x I tablets
Contra Indications :
kidney disturbances
diamox allergy
signs :
stomach uncomfort
lips dryness
Analgesic ---> to relieve the pain
Causative & symptomatic therapy
Local & systemic corticosteroid
Local : e.d. sub conjungtival 2 X 1/week
Systemic high dose, short terms 1 X 12 tablets ---> tapering off
Contra Indication :
Pulmonary TBC, Hypertension, DM, Coronary disturbances,
Physiological disease, peptic ulcer
Continuing observation (important):
Blood glucose
Blood pressure
Weight body
Water retention
The eye should be bandaged
Choroid
Consists of several layer :
Epithelium
Bruch membrane
Chorio capillaries
Blood vessels (medium and large size)
Suprachoroid
Artery : origins from A. ciliaris breves
Vein : 4 V. Vortikalis from 4 posterior quadrant --
-> V. ophthalmic --> cavernous sinus
Non-inflammation
Choroid Anomalies
Coloboma
Degenerative :
Choroid Bodies Drusen
Myoris Degenerative
Blunt trauma
Macular tearing ---> white sclera
Th/ : SA --> relaxation of the eye
Tumor
Benign : melanoma, white spotted below retinal
blood vessel ---> visual disturbances
malignant :
secondary glands melano sarcoma
Th/ :
Metastasis (-) : Enucleation
Metastasis (+): Excenteration
Inflammation of The Choroid
Choroiditis : Posterior Uveitis
Disturbances near the Retina ---> usually
followed by retinal infection : Chorioretinitis
Dividing into two forms :
Exudative Choroiditis : Non purulent
Purulent Choroiditis : Supurative
Exudative Choroiditis
Clinical manifestation depend on location of the
lesion --> macula ---> visual acuity decreased,
even the inflammation is not severe
Divided into :
Disseminate
Diffuse
Sircumscripted :
Centralized/Macular
Paracentralized/paramacular
Juxta Papillary
Periphery
Sircumsripted Choroiditis :
limited exudat area, solitaire :
PD : TBC, Lues, toxoplasma, focal infection
Disseminated Choroiditis
small exudat in just one area or all around the
fundus
PD : miliary TBC
Diffuse Choroiditis
Exudat are spreading to healthy area
Supurative Choroiditis
E/ :
Pyogenic bacteria, which exogenous acquired --
--> ocular bulb perforating
Endogenous --> hematogen metastasis
percontinuitatum
Main clinical sign :
Pus in the Vitreous
Supurative Endophthalmitis
Looks like without clinical sign manifestation if
observed outside the eye
Signs :
subjective : fast loss of visual acuity
objective : yellow vitreous, fundus is not clearly
seen
Inflammation is not reach the ciliary body
Septic Endophthalmitis
The inflammation reaching the ciliary body
Clinical sign :
Cilar injection (+), hipopion, choroid abscess &
ciliary body
Loosing fast of visual acuity, not reversible
Th/ :
Antibiotics
Corticosteroid
Analgesic
Roborantia
If severe pain present ---> evisceration, not
enuclation
Panophthalmitis
All of eye tissue are infected including the adnexa
Clinical signs :
bulb protorsio, difficulty to move the eye, palpebral edema,
conjugtival chemosis, muddying of cornea, perforating, visus 0,
headache
Th/ :
bulbar evisceration
Local & systemic antibiotics
Periphery --> even severe inflammation occurred, visual
acuity good --> scotoma occur
(+) : blind spot
(-) : blind spot with perimeter examination
Clinical signs :
Objective with ophthalmoscopy :
yellow spotted, clear border with retinal blood vessel
above
Blood vessels (-) : if the inflammation reach the retina
Vitreous are muddy if inflammation cells are present
Subjective :
Visual acuity disturbances : metamorphosis --> macropsi
& micropsi
If exudat + infiltrate pressing the retina --> visual cell
stacking
Hemeralopia/nyctalopia --> if chronic
Scotoma
Fotopsi
Photophobia
Symphatic Ophthlamia
Unique granulomatous iridocyclitis
bilateral
leading from wound of one eye --->
infection ---> iridocyclitis (exiting eye)
followed by other eye ( sympathizing eye)
Etiology :
Wound :
Injury ---> wounding of ciliary body
Operation --> ciliary body ; iris ; capsule lentis are
trauma
Corpus Alineum in Intra Ocular space
Perforating of Corneal ulcer
Corneal ulcer
Incubation
3 - 8 weeks after the eye wounding
can also happen after 20 years
Beware :
Wounding eye --> recurrent iridocyclitis for more
than 3 weeks
Observe the other eye if iritasio simpatica occur :
photophobia
lacrimation
blurred vision
pain
flare (+)
Enucleating wounding eye as soon as possible
If neglected/doubtfully ---> iritatio oftalmia -->
symphatic ophthalmia
Stadium I (Iritation)
Signs of Symphatic ophthalmic :
Muddying of cornea
small pupil
greeny muddy vitreous body
Therapy :
Same as iridocyclitis
Stadium II
(stadium
simpatica)
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Best Aid To OphthalmologyDocument501 pagesBest Aid To OphthalmologyMilthon Catacora Contreras67% (3)
- 1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesDocument124 pages1 Anatomy & Physiology of Eye For Ophthalmic NursesSMEY204100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Anti-Anemia DrugsDocument25 pagesAnti-Anemia DrugsAdrul FauzanNo ratings yet
- Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesSensory OrgansCurex QANo ratings yet
- A Project On " Human Eye": Submitted To-Submitted byDocument13 pagesA Project On " Human Eye": Submitted To-Submitted byaman1990100% (1)
- The EyeDocument252 pagesThe EyeMp Neela86% (7)
- Sensory SystemDocument51 pagesSensory SystemsureshdassNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument96 pagesEye and Ear HistologyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- Jogi. Mcqs-1Document47 pagesJogi. Mcqs-1Fazan Gem100% (3)
- Ophthalmic Preparations 1435Document97 pagesOphthalmic Preparations 1435zayedaliNo ratings yet
- Manual de Técnicas Qx. en Oftalmología 14-10-22Document115 pagesManual de Técnicas Qx. en Oftalmología 14-10-22YAZMIN DEL JESUS LARA HUCHINNo ratings yet
- DiverticulosisDocument8 pagesDiverticulosisguestarNo ratings yet
- Otosclerosis Causes Conductive Hearing LossDocument13 pagesOtosclerosis Causes Conductive Hearing LossguestarNo ratings yet
- M80e - 7 10 07Document36 pagesM80e - 7 10 07guestarNo ratings yet
- Acoustic NeuromaDocument21 pagesAcoustic NeuromaguestarNo ratings yet
- Obat-Obat AnthelmintikDocument46 pagesObat-Obat AnthelmintikguestarNo ratings yet
- Anti Virus Anti JamurDocument53 pagesAnti Virus Anti JamurguestarNo ratings yet
- Nephro Pharmacology: A Guide to Drug Prescribing in Renal DisordersDocument29 pagesNephro Pharmacology: A Guide to Drug Prescribing in Renal DisordersguestarNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument13 pagesInsulinguestarNo ratings yet
- Tym Pa No SclerosisDocument6 pagesTym Pa No SclerosisguestarNo ratings yet
- Bullous MyringitisDocument4 pagesBullous MyringitisguestarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A's Role in Vision & the Visual CycleDocument22 pagesVitamin A's Role in Vision & the Visual CycleguestarNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Neuritis: DR Ika Yuliartanti.,Sptht-Kl.,M.KesDocument5 pagesVestibular Neuritis: DR Ika Yuliartanti.,Sptht-Kl.,M.KesguestarNo ratings yet
- Sclera: Dr. Bambang Susetio, SPMDocument19 pagesSclera: Dr. Bambang Susetio, SPMmalim fairrulNo ratings yet
- Unjani – RS Dustira Cimahi 2008 Parkinson's Disease Signs and SymptomsDocument8 pagesUnjani – RS Dustira Cimahi 2008 Parkinson's Disease Signs and SymptomsAgniya Ali FahmiNo ratings yet
- Histology of The EyeDocument21 pagesHistology of The Eyeshmirtb100% (5)
- Atlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesDocument11 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesAndrijana StevancevicNo ratings yet
- Ocular AnatomyDocument96 pagesOcular AnatomyKawtar VetoamiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2022 B213298B OPTC201Document4 pagesAssignment 2022 B213298B OPTC201Kudzai RusereNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Biology Investigatory Project On Eye DiseasesDocument22 pagesFdocuments - in Biology Investigatory Project On Eye DiseasesSantosh SatputeNo ratings yet
- Waves Aranoco Ppt-Anatomy of The EyeDocument40 pagesWaves Aranoco Ppt-Anatomy of The EyeARNOLD ARANOCONo ratings yet
- OAP 2010 Practical 1 - Anatomy of Eye and AppendagesDocument14 pagesOAP 2010 Practical 1 - Anatomy of Eye and Appendagesslawren11No ratings yet
- Httpdocshare01 Docshare Tipsfiles28391283912279 PDFDocument572 pagesHttpdocshare01 Docshare Tipsfiles28391283912279 PDFAryati PutriNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Eyes and Ears: by B.Lokay, MD, PHD Institute of Nursing, TsmuDocument62 pagesAssessment of Eyes and Ears: by B.Lokay, MD, PHD Institute of Nursing, TsmuMamta KujurNo ratings yet
- 38 Lecture AnimationDocument33 pages38 Lecture AnimationGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- Dr. Padmaja PhadeDocument46 pagesDr. Padmaja PhadeElaine ChongNo ratings yet
- Sensory OrgansDocument72 pagesSensory OrgansHarshiya ChintuNo ratings yet
- Panca InderaDocument26 pagesPanca Inderakema_hiperkes100% (1)
- Ophtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007Document57 pagesOphtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007api-3856051100% (2)
- Viva Questions PharmacologyDocument6 pagesViva Questions Pharmacologymazhar abbas GhoriNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument54 pagesHuman EyeRadu VisanNo ratings yet
- 10 Neural Control N Coordination-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document5 pages10 Neural Control N Coordination-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Activity Number 1 in Eyes ConceptDocument4 pagesActivity Number 1 in Eyes ConceptWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument9 pagesThe Human Eyegiana 4e100% (1)
- Assessment of The EyeDocument4 pagesAssessment of The EyeAira Nicole ROMASNo ratings yet