Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seguin - Chapter 2
Uploaded by
noer818Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Seguin - Chapter 2
Uploaded by
noer818Copyright:
Available Formats
Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
Computer Concepts
2
Topics
Topics Computer Concepts
3
Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
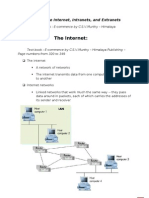
2.1 Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web
2.2 Connecting to the Internet
2.3 Popular Web Browsers
2.4 Understanding Internet and Web Addresses and Navigating Web Pages
2.5 Searching the Web
2.6 Evaluating Web Content
2.7 Popular Web Plug-ins and Players for Multimedia Content
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet Telephone and Conferencing Options
Chapter Summary
Computer Concepts
4
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.1 Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide
Web
Network: two or more devices that
are linked together to share
resources and communicate with
each other
Internet (Net): a global network
that links together other networks
Internet Service Provider (ISP):
a company that provides access to
the Internets infrastructure for a fee
Computer Concepts
5
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.1 Networks, the Internet, and the World
Wide Webcontinued
World Wide Web (Web or WWW): the
global collection of web pages circulated
on the Internet
web page: a document that contains text and
multimedia content
web browser: a software program used to
view web pages
website: a collection of related web pages for
one organization or individual
web server: where all of the web pages and
resources that make a website work are stored
Computer Concepts
6
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.1 Networks, the Internet, and the World
Wide Webcontinued
Web 2.0: websites that encourage and facilitate collaboration
and sharing and allow users to add or edit content
Web 3.0 or the Semantic Web: meaningful connections
between data and Web pages will exist, allowing you to find
more complex information more easily and quickly
Computer Concepts
7
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internet
Components needed for Internet access:
network interface card (NIC), often referred to in computer ads as
an Ethernet port: hardware where you plug one end of an Ethernet
cable into the notebook and the other end into a device that connects
to the Internet
wireless interface card: allows you to connect to a network using
wireless technology
Bluetooth: connectivity which offers the ability to connect to another
Bluetooth-enabled device
Computer Concepts
8
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
You will also need:
an account with an Internet Service Provider (ISP)
networking equipment (usually provided by your ISP) such as a cable
modem, DSL modem, wireless modem, or satellite modem
a router may be needed if you will be connecting multiple devices
(newer modems integrate a wireless router within the same
equipment)
a web browser such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, or Safari
Computer Concepts
9
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
ISPs are companies that provide the equipment and servers
that allow your PC or mobile device to connect to the Internet
backbone
fees for Internet access vary and are usually based on the connection
speed
deciding on the connection speed is generally based on your
anticipated usage
you may also receive multiple email accounts and security tools to
keep your PC or mobile device virus- and spam-free
Computer Concepts
10
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
Broadband: any always-on
connection capable of carrying
a large amount of data at a
fast speed
Megabits per second
(Mbps): how speed for
broadband connectivity is
expressed; data transfers at
the rate of 1 million bits per
second
Computer Concepts
11
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
Computer Concepts
12
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
Cable Internet access: provided by the
same cable company with which you
subscribe for television service
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL): provided
by your telephone company
Computer Concepts
13
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
Fiber-to-the-Premises (FTTP) also
referred to as Fiber-to-the-Home
(FTTH) or Fiber-Optic-Service (FiOS):
involves the ISP running a fiber-optic
cable directly to your home or business
Satellite Internet access: an option in
rural areas where cable or DSL is not
available
Computer Concepts
14
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
Fixed wireless Internet access: involves
installing an antenna outside your home to
send and receive radio signals
Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) network:
wireless access points and radio signals are
used to transmit data
Mobile broadband sticks: portable
modems that plug into a USB port on your
mobile device and connect via a cellular
network
Computer Concepts
15
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.2 Connecting to the Internetcontinued
3G (third generation) or 4G (fourth
generation): devices that provide
Internet access through cell towers
4G LTE network: fastest network for
mobile devices
Dial-up: connect your PC to your
telephone system via a modem built
into your PC
Computer Concepts
16
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING 1
1. The collection of networks that provides the
pathway for data to travel is the ______.
a. Web
b. Internet
c. Internet4
d. Superhighway
3. High-speed Internet access is referred to by
this term.
a. Broadband
b. Megabits per second (Mbps)
c. Superhighway
d. Baseband
4. Which of the following connections is NOT
high speed?
a. Cable
b. DSL
c. FTTP
d. Dial-up
2. This refers to the global collection of web
pages circulated on the Internet.
a. Internet
b. Superhighway
c. World Wide Web
d. Web server
Computer Concepts
17
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.3 Popular Web Browsers
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): a markup language
used to create web pages
uses tags to describe page content
Computer Concepts
18
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.3 Popular Web Browserscontinued
Internet Explorer (IE): the web browser included with
Microsoft Windows
Computer Concepts
19
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.3 Popular Web Browserscontinued
Chrome: Googles free web browser that runs on Windows-
compatible PCs
Computer Concepts
20
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.3 Popular Web Browserscontinued
Firefox: a free web browser available at mozilla.org by the
Mozilla Foundation
Computer Concepts
21
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.3 Popular Web Browserscontinued
Safari: Apples browser used on Mac and Apple mobile devices
Computer Concepts
22
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.3 Popular Web Browserscontinued
Mobile web browsers:
designed to quickly display web
pages optimized for the smaller
screens on devices such as
tablets and smartphones
Computer Concepts
23
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.4 Understanding Internet and Web Addresses
and Navigating Web Pages
Internet Protocol (IP) address: a unique address assigned
to a computing device that is connected to the Internet
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and
Numbers): a nonprofit organization that is in charge of
keeping track of the Internet addresses and names all around
the world
Computer Concepts
24
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.4 Understanding Internet and Web Addresses
and Navigating Web Pagescontinued
Computer Concepts
25
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.4 Understanding Internet and Web Addresses
and Navigating Web Pagescontinued
Web address: a text-based address, to navigate to a website
also called a uniform resource locator (URL)
Domain Name System (DNS) server: a server that holds
the directory and is owned by a business or ISP
Computer Concepts
26
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.4 Understanding Internet and Web Addresses
and Navigating Web Pagescontinued
Computer Concepts
27
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.4 Understanding Internet and Web Addresses
and Navigating Web Pagescontinued
Most people browse the Web in one of two ways:
1. by typing the web address of a company or organization to go
directly to a website
2. by typing a search phrase into a search engine website
Home page: the first page of a website that displays when
the web address is requested
Hyperlinks (links): when clicked or tapped on a touchscreen
take you to a related web page
Computer Concepts
28
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING 2
1. This is the web browser included with
Microsoft Windows.
a. Internet Explorer
b. Chrome
c. Safari
d. Firefox
3. This is the nonprofit organization that keeps
track of Internet addresses for the world.
a. IPv6
b. IPv4
c. ICANN
d. IPANN
4. A Web address is called a(n) _________.
a. IP address
b. URL
c. DNS
d. Hyperlink
2. This browser allows you to type search
phrases directly in the Address bar.
a. Chrome
b. Internet Explorer
c. Firefox
d. Safari
Computer Concepts
29
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.5 Searching the Web
Search engine: a company that
searches web pages and indexes
the pages by keywords or by
subject
Spiders or crawlers: programs
used by search engines that read
web pages and other information
to generate index entries
Computer Concepts
30
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.5 Searching the Webcontinued
Computer Concepts
31
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.5 Searching the Webcontinued
Following are some guidelines for fine-tuning a search:
Place a search phrase in quotations
Type a minus symbol in front of a keyword
Consider using a search engines category
Check out a search engines advanced search tools
Restrict searches to a specific time frame
Look for Help at the search engines website
Metasearch search engines: send your search phrase to
other search engines and then compile the results in one list
Computer Concepts
32
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.5 Searching the Webcontinued
Content aggregator: an organization
that searches the Web for new content
and collects and organizes the content in
one place
Really Simple Syndication (RSS): a
specification used by content
aggregators to distribute updates to
subscribers
Computer Concepts
33
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.6 Evaluating Web Content
Start at the web address: look at domain names for publishers
of content in the print-based world with which you are familiar
Computer Concepts
34
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.6 Evaluating Web Contentcontinued
Look for an author and the authors affiliation: check for an
authors name at the page
Computer Concepts
35
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.6 Evaluating Web Contentcontinued
Check the publication date: in
most cases you want to find the
most recent information about a
topic
a clue to the date of publication
may appear in the linked web
address
Computer Concepts
36
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.6 Evaluating Web Contentcontinued
Purpose and design of the site: consider the purpose and
design of the page you are reading
Computer Concepts
37
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING 3
1. A search engine uses this type of program to
search the Web for keywords to index.
a. Hyperlinks
b. HTTP
c. Metaindex
d. Spider
3. Which of the following is NOT a strategy to
help you evaluate a web pages credibility?
a. Look at the domain name for an organization
you recognize.
b. Check for an authors name and affiliation.
c. Evaluate the page design.
d. Look for the same page at a different search
engine.
4. If a publication date is not on the web page,
a clue may appear in this linked address.
a. IP address
b. Web address
c. Mailing address for the organization
d. DNS
2. A search engine that compiles results from
other search engines is called a _______
search engine.
a. category
b. hypertext
c. metasearch
d. cybersearch
Computer Concepts
38
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.7 Popular Web Plug-ins and Players for
Multimedia Content
Plug-in (add-on) or player: a software program that allows
the browser to display enhanced content that it cannot display
on its own
Computer Concepts
39
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.7 Popular Web Plug-ins and Players for
Multimedia Contentcontinued
Computer Concepts
40
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet
Telephone and Conferencing Options
E-commerce: the abbreviation for electronic commerce,
which involves buying or selling over the Internet
Computer Concepts
41
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet
Telephone and Conferencing Optionscontinued
Computer Concepts
42
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet
Telephone and Conferencing Optionscontinued
Email (electronic mail): the sending and receiving of digital
messages using the Internet, sometimes with documents or
photos attached
Email address: used to connect to your email account at the
ISP server and is generated in the format
username@mailserver.com or username@mailserver.net
Email client: a program such as Microsofts Outlook or
Apples Mail to send and receive messages
Computer Concepts
43
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet
Telephone and Conferencing Optionscontinued
Text messages: short text exchanges,
referred to as texting, that you send to
another mobile device using a service
called Short Message Service (SMS)
Instant messaging: exchanging text
messages in real time between other
users of similar devices
Computer Concepts
44
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet
Telephone and Conferencing Optionscontinued
Voice over Internet Protocol
(VoIP): the ability to call
someone using the Internet and
engage in a voice conversation
Computer Concepts
45
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
2.8 E-Commerce, Messaging, and Internet
Telephone and Conferencing Optionscontinued
Web conferencing: a program that allows a group of
individuals to connect online to engage in a meeting
Computer Concepts
46
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING 4
1. This player allows you to read PDF
documents.
a. Adobe Reader
b. Adobe Flash Player
c. Shockwave Player
d. Real Player
3. E-tailers are primarily involved in this
category of e-commerce.
a. B2C
b. B2B
c. B2W
d. C2C
4. This type of software allows a group of
individuals to collaborate online in a meeting.
a. VoIP
b. Email
c. Instant messaging
d. Web conferencing
2. This player is a programming language used
on web pages.
a. QuickTime
b. Real Player
c. Silverlight
d. Java
Computer Concepts
47
Topics Paradigm Publishing, Inc.
Chapter Summary
After successfully completing this chapter, you are now able to:
Describe the Internet and the World Wide Web
Identify the hardware, software, and service you need to connect to the
Internet
List and explain the various types of Internet connectivity options
Recognize four popular web browsers used to view content
Distinguish parts of a URL and search, browse, and evaluate online content
Recognize plug-ins and players used on web pages to enrich content
Explain online services such as e-commerce, email, and VoIP
You might also like
- Internet, Intranets, and Extranets by T.R. VaidyanathanDocument65 pagesInternet, Intranets, and Extranets by T.R. VaidyanathanPrachi Rungta AnvekarNo ratings yet
- Web Dev & Design Foundations with XHTML Chapter 1Document43 pagesWeb Dev & Design Foundations with XHTML Chapter 1Kalani PittsNo ratings yet
- Internet and The World Wide WebDocument14 pagesInternet and The World Wide WebOloka George OkwirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - The Web and InternetDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - The Web and InternetTin EupenaNo ratings yet
- IIT Lecturer 3 & 4Document60 pagesIIT Lecturer 3 & 4awais mehmoodNo ratings yet
- 3 Slkm-css-7 - 8 5 Using Www-Browser To Locate Information (No Answer Key)Document29 pages3 Slkm-css-7 - 8 5 Using Www-Browser To Locate Information (No Answer Key)Lyssa BasNo ratings yet
- Access and Use Internet Lo1Document34 pagesAccess and Use Internet Lo1Cherinet dubaleNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian TVET-System: Based On May 2011 Occupational StandardsDocument73 pagesEthiopian TVET-System: Based On May 2011 Occupational StandardsendashawNo ratings yet
- Access Internet L-IIDocument13 pagesAccess Internet L-IILetaNo ratings yet
- Internet Communication PDFDocument20 pagesInternet Communication PDFRishaana Sarangan100% (1)
- 12-IP NotesDocument3 pages12-IP NotesParasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudDocument40 pagesChapter 1 Studshazy7No ratings yet
- Internet Concepts Inter Refers To International I.E. Global and Net Is Network Which Is ADocument9 pagesInternet Concepts Inter Refers To International I.E. Global and Net Is Network Which Is ARicky Ryan AndasNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim El-Sherif 5Document13 pagesIbrahim El-Sherif 5amal attiaNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document44 pagesCH 7Agnes AuroraNo ratings yet
- AIT Unit1 InternetDocument44 pagesAIT Unit1 InternetNaina_Dwivedi_6514No ratings yet
- The Internet in 40 charactersDocument7 pagesThe Internet in 40 characterslilboss2010No ratings yet
- DCSA 1201 Full PDFDocument50 pagesDCSA 1201 Full PDFআলিফ বিন আকতারNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computers and Information TechnologyDocument45 pagesIntroduction to Computers and Information TechnologyOsaigbovo TimothyNo ratings yet
- Topic VII - The Internet, Intranets, and ExtranetsDocument61 pagesTopic VII - The Internet, Intranets, and ExtranetsIsabel BernardoNo ratings yet
- Internet ApplicationsDocument3 pagesInternet Applicationsbalaji bysaniNo ratings yet
- Web Browsers and Internet ConnectionsDocument17 pagesWeb Browsers and Internet ConnectionssreejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document29 pagesUnit 5drgurungr18No ratings yet
- WT R19 Unit 1Document33 pagesWT R19 Unit 1SivaNo ratings yet
- Vry Imp.Document16 pagesVry Imp.Heena TalwarNo ratings yet
- Ch02 The Internet and The World Wide WebDocument11 pagesCh02 The Internet and The World Wide Webcdavila55No ratings yet
- Internet ConceptDocument36 pagesInternet ConceptDorisday Caballes EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Web Programming NotesDocument5 pagesWeb Programming NotesArchana ARCHANANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Technology Week-11Document22 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology Week-11Agus SudaryantoNo ratings yet
- Configuring and Using InternetDocument29 pagesConfiguring and Using Internetm.tsedey2013100% (1)
- Internet and Web Development FundamentalsDocument9 pagesInternet and Web Development FundamentalsAyele MitkuNo ratings yet
- The Internet and The WWWDocument52 pagesThe Internet and The WWWCollins MainaNo ratings yet
- ITC Lec 6Document22 pagesITC Lec 6Zubair FazalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Internet and WebDocument48 pagesIntroduction To The Internet and WebLoiDa FloresNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: Aim: To Understand, Describe and Identify The Following Web TerminologyDocument8 pagesPractical 1: Aim: To Understand, Describe and Identify The Following Web TerminologyBijalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2seulgi kangNo ratings yet
- Internet Chap 1Document50 pagesInternet Chap 1Hussen MossaNo ratings yet
- IT Applications in ET: Session 6 Dr. Devendra Kumar PuniaDocument45 pagesIT Applications in ET: Session 6 Dr. Devendra Kumar PuniaNidhi SinghNo ratings yet
- A%UISDocument22 pagesA%UISderejeNo ratings yet
- Aligarh Muslim UniversityDocument28 pagesAligarh Muslim UniversityMd AMsh MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer Applications: Information and CommunicationDocument100 pagesMicrocomputer Applications: Information and Communicationjohn onesmoNo ratings yet
- TIK - Chapter 2 Exploring CyberspaceDocument7 pagesTIK - Chapter 2 Exploring CyberspaceAska NoveliaNo ratings yet
- The Internet, The Web and Electronic CommerceDocument16 pagesThe Internet, The Web and Electronic CommerceBea BonitaNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet & ExtranetDocument17 pagesInternet, Intranet & ExtranetSony ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Internet - Unit PDFDocument11 pagesInternet - Unit PDFJanelle CuiNo ratings yet
- Access and Use the Internet in 40 CharactersDocument26 pagesAccess and Use the Internet in 40 CharactersXOG OGAALNo ratings yet
- Simple Questions About Internet For KidsDocument11 pagesSimple Questions About Internet For KidsJanelle Cui0% (1)
- The Internet Websites and MediaDocument48 pagesThe Internet Websites and Mediafairuz hafizieNo ratings yet
- It Sivapadidapu PDFDocument130 pagesIt Sivapadidapu PDFAnonymous 0f4b6SNo ratings yet
- Basic Internet TerminologyDocument4 pagesBasic Internet TerminologyAbi Abinaya100% (1)
- Web DevelopmentDocument22 pagesWeb DevelopmentBeckieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The InternetDocument3 pagesLesson 2: The InternetZaira EdiomaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Information Systems Eighth Edition: The Internet, Intranets, and ExtranetsDocument31 pagesPrinciples of Information Systems Eighth Edition: The Internet, Intranets, and ExtranetsHope..!No ratings yet
- Intro InternetDocument29 pagesIntro InternetAaKash VastNo ratings yet
- Internet, Intranet, ExtranetDocument35 pagesInternet, Intranet, ExtranetFarah Atika Ar Azmi100% (1)
- LIVING IN ICT ERA ModulesDocument14 pagesLIVING IN ICT ERA ModulesRenz Daniel R. ElmidoNo ratings yet
- MODULE-01-Interduction To Web TechonolgyDocument110 pagesMODULE-01-Interduction To Web TechonolgySanthosh SgraoNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument34 pagesInternetapi-19998385No ratings yet
- Ip NotesDocument74 pagesIp NotesMunavalli Matt K S100% (5)
- 6th Iread G8 Google Nonfiction-Reading-TestDocument1 page6th Iread G8 Google Nonfiction-Reading-TestPauline Diane Presente0% (1)
- Boolean Search Strings PDFDocument100 pagesBoolean Search Strings PDFPriya80% (5)
- Physical Science Skill and Practice SheetsDocument164 pagesPhysical Science Skill and Practice SheetsjosieA_12383% (6)
- FTC Google Probe RecommendationDocument85 pagesFTC Google Probe RecommendationJason MickNo ratings yet
- 15 Google Search Tips and TricksDocument7 pages15 Google Search Tips and TricksvimpatNo ratings yet
- Market Leader Answer Keys 2Document21 pagesMarket Leader Answer Keys 2Ale GuzmÁn67% (6)
- Postmate 3: User's ManualDocument30 pagesPostmate 3: User's ManualPablo RfcNo ratings yet
- Twitter's S-1Document420 pagesTwitter's S-1USA TODAYNo ratings yet
- Baeza Yates 2003Document8 pagesBaeza Yates 2003api-3803202No ratings yet
- University of Calicut MCQ EcomDocument19 pagesUniversity of Calicut MCQ EcomAfad KhanNo ratings yet
- Sergey BrinDocument13 pagesSergey BrinEmad MansyNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument28 pagesBig DatasunilNo ratings yet
- Google Analytics Glossary Top 50 TermsDocument3 pagesGoogle Analytics Glossary Top 50 Termssrikar MessiNo ratings yet
- Internet.comDocument174 pagesInternet.comSandip LahiriNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Website Launch ChecklistDocument3 pagesThe Ultimate Website Launch ChecklistDan Zambonini100% (13)
- SEO Engineer ResumeDocument7 pagesSEO Engineer ResumeSelvamNo ratings yet
- Web Acappella User's GuideDocument100 pagesWeb Acappella User's GuidemaykonjhioneNo ratings yet
- 6251 Ecomm Site - UnknownDocument16 pages6251 Ecomm Site - UnknownstavyagNo ratings yet
- PDF UG WBS Hotel MultiSingleAvailability HOTEL MULTISINGLEAVAILABILITY 10.0 383 PDFDocument99 pagesPDF UG WBS Hotel MultiSingleAvailability HOTEL MULTISINGLEAVAILABILITY 10.0 383 PDFAndrei GoguNo ratings yet
- Better Searching Directions and Worksheet: D - SearchDocument3 pagesBetter Searching Directions and Worksheet: D - Searchapi-281741201No ratings yet
- ICT Module BTEC National Health & Social Care: Workbook 11Document6 pagesICT Module BTEC National Health & Social Care: Workbook 11desbestNo ratings yet
- Primary Sources in Teaching Critical Thinking Skills in World LiteratureDocument202 pagesPrimary Sources in Teaching Critical Thinking Skills in World LiteratureRaduMonicaLianaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Discrete StructuresDocument5 pagesDefinitions - Discrete StructuresYi Lin LimNo ratings yet
- 2012 Technology Use Survey QuestionsDocument24 pages2012 Technology Use Survey Questionsjeremy_riel75% (12)
- Search Engine Optimization: Abhilash Patel Ranklab Interactive, Recovery Brands, LLC @mistabhilashDocument31 pagesSearch Engine Optimization: Abhilash Patel Ranklab Interactive, Recovery Brands, LLC @mistabhilashapi-62303070No ratings yet
- Green City PlanDocument29 pagesGreen City Planyogi_patel90No ratings yet
- In5™ Help Documentation: © 2012-2017 Ajar Productions. All Rights ReservedDocument18 pagesIn5™ Help Documentation: © 2012-2017 Ajar Productions. All Rights ReservedzetaequisNo ratings yet
- Kundan Khatu ResumeDocument4 pagesKundan Khatu Resumekundan_khatu50% (4)
- Google Hacking TechniquesDocument12 pagesGoogle Hacking Techniquesnana100% (2)