Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Bello Nelson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views39 pagesRespiratory System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRespiratory System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views39 pagesRespiratory System
Uploaded by
Bello NelsonRespiratory System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 39
Respiratory System
A system in our body which
is responsible for gas
exchange.
Parts
A. Lungs
B. Air passages
Functions
Takes in oxygen
Removes carbon dioxide
Body has 4-6 minute supply of oxygen
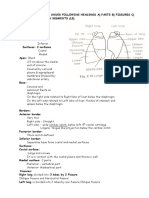
Air Passages
1. Nose
2 nostrils or nares
Nasal septum
Divides nose into 2 nasal cavities
Lined
With mucous membrane with a rich blood supply
Functions
Warms
Moistens
Filters
Cilia
Tiny hair-like structures
that help move dirt
trapped in mucous to the
esophagus
Olfactory Receptor
Receptors for sense of
smell
Lacrimal Ducts
Tear ducts
Drain tears from the eye
into the nose
Olfactory Receptors
Sinuses
Cavities in the skull that
surround the nasal area
Connected to nasal cavities
by short ducts
Function
Warms and moistens air
Lined with mucous
membrane
Provides resonance for the
voice
2. Pharynx
Throat
Lies behind the nasal
passages
3 sections
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
3. Larynx
Voice box
Layers of cartilage
Largest is the thyroid cartilage
commonly called the Adam's apple
Contains
Vocal chords
Vibrate on exhaled air to produce
sound
The tongue and lips act on the
sound to produce speech
Epiglottis
Flap of cartilage that closes the
larynx during swallowing and
prevents food and liquids from
entering the trachea
4. Trachea
Windpipe
Series of C shaped
cartilage to keep the tube
open to the back
Divide into the right and left
5. bronchi
Continues to divide into
smaller 6. bronchioles
End in the alveoli
Air sacs
7. Alveoli
- One cell thick and
surrounded by
capillaries
- Look like a cluster of
grapes
- Allow the exchange of
oxygen and carbon
dioxide
Surfactant
- Surfactant
- Reduces surface
pressure and
prevents alveoli
from collapsing
Exchange of Gases
Lungs
Right lung 3 lobes
Left lung 2 lobes due to
the heart
Pleura
Covered by a
double layer sac
called the pleura
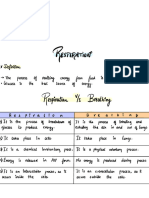
Ventilation
Process of breathing
Diaphragm
Muscle of
respiration
Assisted by the
intercostal muscles
Phases of respiration
Inspiration
Inhale
Expiration
Exhale
Diaphragm
Dome-shaped
muscle that
separates the
thoracic cavity
from the
abdominal
cavity
Process of Respiration
Controlled by the
medulla oblongata in
the brain
An increase in amount
of CO
2
in the blood ,
increases the rate of
respiration
Both involuntary and
voluntary process
Stages of Respiration
External
Respiration
Exchange of
gases
between air
in the lung
and the
blood
Internal Respiration
Exchange of
gases
between
the blood
and the
cells
Cellular Respiration
Use of
gases to
make
energy,
water
and CO
2
Summary of air flow
Nasal cavity
Pharynx
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Primary Bronchi
Secondary Bronchi
Tertiary Bronchi
Broncheoles
Terminal Broncheoles
Respiratory Broncheoles
Alveoli is the only site of gas exchange
Diseases
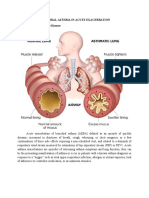
Asthma
Inflammation of
airways with
increased mucous
production and
muscle constriction
Cause allergen,
exercise, stress,
chemical
S/S - wheezing,
coughing, dyspnea,
shortness of breath
Tx -
bronchodilators,
steroids
Nebulizer Inhaler
Bronchitis
Inflammation of the
bronchi and bronchial
tubes
Acute infection
Chronic longtime
exposure to smoking
S/S productive cough,
dyspnea, fever, chest
pain
Tx antibiotics,
bronchodilators, oxygen
Emphysema
Emphysema
Non infectious, chronic
respiratory condition when
walls of alveoli deteriorate
and loss elasticity
CO
2
remains trapped in the
alveoli
Poor exchange of gases
S/S dypnea, feeling of
suffocation, barrel chest
TX No cure
Epistaxis
Nosebleed
Congested capillaries
bleed
Due to injury, blowing
too hard, hypertension
TX pinch nostrils lean
forward slightly
Influenza
Flu
Viral infection of the
lungs
Spread by respiratory
droplet
S/S - fever, malaise,
chills, cough, sore
throat, muscle pain
Tx - symptomatic
Lung Cancer
Leading cause of death of
men and women
S/S no symptoms in early
stages, later cough
hemoptysis
Tx surgical removal,
radiation, chemotherapy
Pneumonia
Inflammation or
infection of the lungs
Build up of exudates
(fluid) in the alveoli
S/S cough, chest pain,
fever, dyspnea
Tx antibiotics, bed
rest, fluids, respiratory
therapy, pain
medication
Rhinitis, Laryngitis, Sinusitis
Tuberculosis
Infectious lung disease
caused by the bacteria
Mycobacterium
tuberculosis
Can be walled off in a
tubercle and become
dormant
New strains are drug
resistant
S/S fatigue, fever, night
sweats, hemoptysis weight
loss, chest pain
Tx - several drugs over a
period of two years
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Session 7Document29 pagesSession 7Bello NelsonNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- RQ TEST - Supplemental For Session 1Document2 pagesRQ TEST - Supplemental For Session 1Bello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Session 6Document64 pagesSession 6Bello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Session 5 Resiliency Training PresentationDocument34 pagesSession 5 Resiliency Training PresentationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Resiliency Training Presentation 1Document26 pagesResiliency Training Presentation 1Bello NelsonNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- DCEL - My Presentation-EditedDocument13 pagesDCEL - My Presentation-EditedBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Session 4 Resiliency Training PresentationDocument37 pagesSession 4 Resiliency Training PresentationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- SESSION 3 Resiliency Training PresentationDocument43 pagesSESSION 3 Resiliency Training PresentationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- DulvaDocument2 pagesDulvaBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Department of Education: Bureau of Curriculum Development Process Observation GuideDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Bureau of Curriculum Development Process Observation GuideBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- RO8 - RM - s2019 - 480 - Workshop On Policy FormulationDocument3 pagesRO8 - RM - s2019 - 480 - Workshop On Policy FormulationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- One With The PresidentDocument16 pagesOne With The PresidentBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- ACR - Action Research WorkshopDocument3 pagesACR - Action Research WorkshopBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DxDiag Sample GeneratedDocument33 pagesDxDiag Sample GeneratedBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- UNICEF ClimateChange ResourceManual Lores CDocument228 pagesUNICEF ClimateChange ResourceManual Lores CBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- PS PRD 18 115BDocument8 pagesPS PRD 18 115BBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- PotentialsDocument1 pagePotentialsBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum - Final Research ConsultationDocument8 pagesCorrigendum - Final Research ConsultationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Corrigendum - Final Research ConsultationDocument8 pagesCorrigendum - Final Research ConsultationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- ERF FormDocument1 pageERF FormJoseph Nobleza100% (1)
- BP 344 Accessibility LawDocument22 pagesBP 344 Accessibility Lawmoonstardolphins100% (2)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- 1335tongadisaster Management StrategyDocument88 pages1335tongadisaster Management StrategyBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ObservationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan ObservationBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Continuous Improvement AllanDocument8 pagesPresentation-Continuous Improvement AllanBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Property ManualDocument116 pagesProperty Manualkristinebondoc100% (1)
- EO - 888-1983 - Disposal of Unserviceable FacDocument2 pagesEO - 888-1983 - Disposal of Unserviceable FacBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Revised IRR of RA 9184Document114 pagesRevised IRR of RA 9184zanpaktho100% (3)
- RevisedIRR RA9184Document114 pagesRevisedIRR RA9184Pearl AudeNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Activities Amount Replacement of Roof and Gutters 75,000.00 Repair of Ceilings 30,000.00 Repainting of Walls 355,000.00Document1 pageActivities Amount Replacement of Roof and Gutters 75,000.00 Repair of Ceilings 30,000.00 Repainting of Walls 355,000.00Bello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Organizational Research Management Performance MeasureDocument9 pagesOrganizational Research Management Performance MeasureBello NelsonNo ratings yet
- Wheezing Child...Document71 pagesWheezing Child...DawitNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument43 pagesAtelectasismulan557100% (1)
- Activity#1Document2 pagesActivity#1LINDA RAGUINDINNo ratings yet
- Case Study Pneumonia)Document20 pagesCase Study Pneumonia)Jai - Ho83% (6)
- 3.LUNGS Medo NotesDocument17 pages3.LUNGS Medo NotesChandrababu ANo ratings yet
- Antimonium TartaricumDocument21 pagesAntimonium TartaricumShah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy Learning Module Cat 1and2Document62 pagesOxygen Therapy Learning Module Cat 1and2Baha'aeddin HammadNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation Case StudyDocument43 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation Case Studyroseanne parkNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesUnit 7 - Respiratory SystemAbdullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Neurotherapy Study GuideDocument26 pagesNeurotherapy Study GuideWholebraintech100% (1)
- Feline Brochial DiseaseDocument7 pagesFeline Brochial DiseaseDimas SetiawanNo ratings yet
- USMLE Questions SummarizedDocument85 pagesUSMLE Questions SummarizedJamesIwu89% (19)
- Homeopathy Narayani Finder Thierry ClercDocument50 pagesHomeopathy Narayani Finder Thierry ClercSanjeev Agarwal100% (4)
- 6th Grade Body Systems Student Edition 1Document37 pages6th Grade Body Systems Student Edition 1Martha RincónNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH LESSONS FIRST GRADE.-pages-1-4Document4 pagesENGLISH LESSONS FIRST GRADE.-pages-1-4conchi gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Respiration (Life Processes) NotesDocument8 pagesPadhle 10th - Respiration (Life Processes) Notespharmacybanswara2019No ratings yet
- NCP Bronchila Ashma Dra.Document3 pagesNCP Bronchila Ashma Dra.ЯicaЯdo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Medicine PDFDocument58 pagesMedicine PDFIsabel Alvarez Garcia100% (1)
- Chapter 2 (Science Form 3)Document3 pagesChapter 2 (Science Form 3)Shatviga VisvalingamNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument257 pagesHuman PhysiologyAyushNo ratings yet
- Respiratory BSNMedsurgDocument27 pagesRespiratory BSNMedsurgLeobert Yancy SalosagcolNo ratings yet
- Biology GlossaryDocument6 pagesBiology GlossarySayam JhaveriNo ratings yet
- AI CT ThoraxDocument22 pagesAI CT ThoraxdanyaNo ratings yet
- Mouse Cell Culture Methods and Protocols - Ivan Bertoncello - 2019 PDFDocument311 pagesMouse Cell Culture Methods and Protocols - Ivan Bertoncello - 2019 PDFTristan PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument29 pagesLesson PlanJo anne Jo anneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory TractDocument49 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory TractshvnagaNo ratings yet
- What Is Emphysema?Document33 pagesWhat Is Emphysema?Lovina MeenaNo ratings yet
- Pneumo Tot MergedDocument103 pagesPneumo Tot MergedAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Ventilation Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: Ventilation Cellular RespirationSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Respiratory QuestionsDocument116 pagesRespiratory QuestionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)