Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Head Trauma - Case
Uploaded by
Sardito PhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Head Trauma - Case
Uploaded by
Sardito PhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Lamhot Asnir L. Tobing, M.D.
Neurosurgeon
Presentant:
Sardito (2012.061.069)
Deiby P S (2013.061.015)
Identity
Name : Mr. A Y
Gender : Male
Age : 30 y.o.
Occupation : Construction worker
Religion : Moslem
Address : Gong Bay
Date of hospitalization : July 11
th
2014
Anamnesis
Chief complaint : loss of consciousness
History of present illness :
Patient came with chief complaint of loss of
consciousness approximately for a 30-minute period
after trauma
Patient fell from a 5-metre height while he was
working on a building construction around 40
minutes before hosptalization.
According to the witnesses, the patients right leg hit
an iron rod before finally fell onto the road (ashpalt)
with the left side of the head hitting the road first.
Along the journey to the hospital, the patient
received no medication at all.
Meanwhile during in the Emergency Room, the
patient vomited 4 times with the total of +600mL
fluid being discharged containing gastric juice and
blood.
Patient also felt pain throughout the body
including severe headache
The patient denied the existence of blood
discharge from the nose and ears
History of past illness:
History of hypertension denied
History of stroke denied
History of allergy denied
History of Diabetes Melitus denied
History of past trauma denied
History of chronic cough denied
History of regular drug consumption denied
Habits:
Patient has been smoking cigarette since 15
years ago 12 cigars per day
Patient also occasionally counsumed alcoholic
beverages but not on a regular basis and not sure
about the amount consumed
Development :
Patient experienced no problem in during
developing stage of life
Primary Survey
A : good articulation, obstruction (-)
B : RR: 26 tpm
C : BP : 160/100 mmHg; HR : 120 bpm
D : Compos Mentis (GCS 14 E
3
M
6
V
5
)
E : Temp : 36,5
o
C
Allergy : -
Medication : -
Past Illness : -
Last Meal : unkown
Environment : 5-metre height fell
Physical examination
General condition : severely ill
Head :
Calvarium : hematoma
a
/
r
frontalis sinistra o
+ 3cm
Face : asymmetrical
Eyes : edema palpebra sinistra
Nose : nasal septal in the middle
Mouth : oral mucose wet
Ear : MAE +/+
Neck :
JVP : not assessable
Carotid Artery : +
Thyroid : not palpable
Thorax :
Cor : cardiomegaly -; Heart Sound I & II regular;
Murmur -; Gallop -
Pulmo : symmetrical; VBS +/+; Wheezing -/-;
Rales -/-
Abdomen :
Liver : hepatomegaly
Spleen : splenomegaly
Bladder : not palpable
Extremities :
Warm, CRT <2s, edema dorsal pedis sinistra
Muscle and tendon : spasticity
Neurological examination
Meningeal stimulation
Not assessable
Signs of intracranial pressure increase
Headache +
Blurry vision
Bradycardia
Papiledema
Cranial nerve examination is between
normal limits
Motoric :
Upper arms : 5555/xxxx
Lower arms : 55/55
Hands : 55/55
Fingers : 5555/5555
Upper legs : xxxx/5555
Lower legs : xx/55
Feet : 55/55
Toes : 55/55
Physiological reflexes :
Biceps : +/+
Triceps : +/+
Patella : x/+
Achilles : -/-
Pathological reflexes : all are negative
Clonus : patella -; feet
Tonus : normotonus, spasticity -; rigidity-
Coordination and cerebelar function :
not assessable
Sensibilities are between normal limits
Autonomic system
Miction : + (catheter)
Defecation : -
Sweating : + above shoulder
Noble function :
Motoric aphasia : -
Sensoric aphasia : -
No signs of regression
Peripheral nerve are not palpable
Lab test - July 12, 2014
Parameter Value
HEMATOLOGY
IV Routine
Hemoglobin 14.9
Hematocrit 41
WBC 20.9
Thrombocyte 308
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 10
DIFFERENTIAL COUNT
Basophils 0
Eosinophils 0
Band neutrophils 0
Segmented neutrophils 83
Lymphocytes 12
Monocytes 5
Bleeding Time 3
Clotting Time 5
Lab test July 12, 2014
BLOOD CHEMISTRY Value
SGOT/AST 36
SGPT/ALT 54
Renal Function
Ureum 20
Creatinine 0.8
CARBOHYDRATE
Random blood glucose 173
Lab test - July 13, 2014
Parameter Value
BLOOD CHEMISTRY
ELECTROLYTE
Sodium 159
Pottasium 4.47
Calcium 1.21
Chloride 128
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS
Temperature 37.4
Hemoglobin 12.7
Result
pH 7.35
pCO2 47
pO2 211
HCO3act 25
Base excess 1
ctCO2 60
O2Sat 100
O2CT 18
Lab test July 16th, 2014
BLOOD CHEMISTRY Value
CARBOHYDRATE
Random blood glucose 136
Parameter Value
BLOOD CHEMISTRY
ELECTROLYTE
Sodium 175
Pottasium 2.71
Calcium 1.4
Chloride 141
BLOOD CHEMISTRY Value
SGOT/AST 101
SGPT/ALT 164
Renal Function
Ureum 52
Creatinine 1.4
Parameter Value
URINE
COMPLETE
Glucose (-)
Protein One (+)
Bilirubin (-)
Urobilinogen One (+)
Ph 6
Density 1015
Smear blood Three (+++)
Keton (-)
Nitrit (-)
Leucocyte (-)
Sediment
Leucocyte 0-1
Erythrocyte 7-10
Epithel (+)
Silinder (-)
Crystal (-)
Bacteri (-)
Interpretation July 11th, 2014
Cereberal edema with subarrachnoid
hemmorrhage and mild cereberal
contussion at frontal sinistra
Multiple fracture at os. Frontalis with
minumum depressed fragment, cranial
base fracture, left temporal
Left retro orbital no fracture fragment seen
Bilateral maxillary, ethmoidal, frontal, and
sphenoid hematosinus
Left hematomastoid
Facial CT Scan 3D July 15th, 2014
Multiple fracture at os frontal with minimum
depressed fragment, fracture line that
elongates from left frontal to left orbital rim
direction until left maxillary sinus anterior wall
and left lamina cribiformis, no fracture
fragment seen in left retro orbita.
Bilateral maxillary, ethmoidal, frontal, and
sphenoid hematosinus
Basis cranii fracture
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Left hematomastoid
No fracture seen in cervical CV 1-6
EKG
Resume
A patient, male, 30 y.o., came with chief complaint of
loss of consciousness for 30 minutes after he fell
from a 5-meter height building construction. Patient
experienced severe headache and during in the ER,
the patient vomited 4 times with total + 600mL
gastric juice with blood discharged.
The patient denied any history of past illness,
smokes cigarette regularly and drinks alcohol
occasionally.
From the physical examination there is hematoma
a/r frontalis sinistra, headache as a sign of
intracranial pressure increase. From lab test, the
patient has leucocytosis, increased liver enzyme,
hyperglycemia, hypernatremia, hyperchloremia, and
anemia.
From the CT-scan were found Subarachnoid
haemorrhage with cerebral edema. Bilateral
maxillary, ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid
sinuses fractures with haematosinus.
Diagnosis
Clinical : Headache
Topis : Subarachnoid
Etiology : Trauma
Pathology : Haemorrhage
Os patella dextra fracture
Bilateral maxillary, ethmoid, frontal,
sphenoid sinus fracture
Assessment
A patient, male, 30 y.o., capitis trauma,
anhydrosis, multiple vulnus laceratum
and os patella dextra fracture
Treatment
Collar neck
IVFD RL 1000cc/24hours
Omeprazole 2x40mg IV
Ceftriaxone 2x2 g IV
Vit C 1x400mg IV
Mannitol 250cc 4x125cc
Tramadol 2x50mg/drip
Metilprednisolon 2x125mg
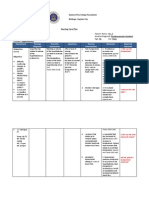
Follow up
12/07/14 13/07/14 14/07/14 15/07/14 16/07/14 17/07/14
Vomits
300cc,
dizzy, pain
fullout the
body
Left shoulder
pain, dizzy,
post
operation
wound pain
110/70;116;
34;37
150/100;140
;22;37
157/104;138;
22;38
160/99;108
;24;38
147/93;106
;25;38.2
125/83;161;
43;39.7
GCS 14
E
3
V
5
M
6
GCS 15
E
4
V
5
M
6
GCS 14
E
3
V
5
M
6
GCS 14
E
3
V
5
M
6
GCS 14
E
3
V
5
M
6
GCS 14
E
3
V
5
M
6
NGT 300cc
dark brown
NGT 425cc
cloudy
Motoric
weakness in
all
extremities
Introduction
Primary goal prevention of secondary
brain injury
Adequate O2 and BP good perfusion
= limiting brain damage
ABCDE + identify mass lesion CT
Scan
CT Scan Should Not Delay Referal!
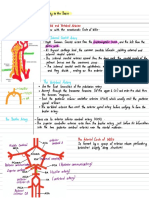
SCALP
Skin
Connective Tissue
Aponeurosis (galea aponeurotika)
Loose areolar Tissue
Subgaleal haematom blood loss in infants
and child
Pericranium
Bleeding of the Scalp
The Cranium
The Meninges
The Brain
Frontal executive,
emotions, motor, speech
Parietal - sensory function
and spatial orientation
Temporal - memory
functions
Occipital - vision
Brainstem
Midbrain - RAS
Pons - RAS
Medulla Cardiorespiratory
Cerebellum coordination
and balance
Tentorium
Supratentorial
Fossa cranii anterio and media
Infratentorial
Fossa cranii posterior
Midbrain
Tentorial hiatus
Connects brain hemisphere pons and medulla
N.III along tentorium edge
Medial Temporal lobe (Uncus) herniation
dilated pupil
Tentorium
Monro-Kellie Doctrine
Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF)
Decreased in comatose patients
Cerebral Perfusion Pressure
= MAP ICP
50 150 mmHg constant CBF
Autoregulated by vasoconstriction-dilation PaO2 and PaCO2
Effort should be done:
Enhance CPP
Reduce elevated ICP
Maintain intravascular volume
Maintain MAP
Normal O2 and CO2
Hematoma and other lesions evacuated early
Failure = secondary brain injury
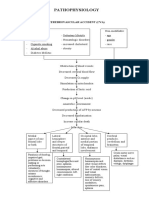
Epidemiology
In USA, 1,5 million cases/year
50.000 +, 80.000-90.000 longterm
neurologic impairment
Head trauma is the main cause of death
in traumatic patients
Main cause of head trauma : fall and
traffic accident (80%)
Types of Injury
Injuries on head trauma is classified into 2 :
Primary injury anatomy and physiology
disorder caused directly by trauma
Secondary injury extention of primary
injury swelling, hypoperfusion, hypoxemia,
ICP increase)
Acute phase management : to prevent
secondary injury
Recucitation priority
Hypotension caused twice the death
compared to hypoxemia Goal: sistole
90
Classification of Head Injury
Based on mechanism of injury: blunt (automobile
collisions, fall, blunt weapon) or penetrating
(gunshot, stab)
Basal Skull Fracture
Sign:
Racoon eyes (periorbital ecchymosis)
Battle sign (retroauricular ecchymosis)
Rhinorrhea & otorrhea (CSF leakage)
N. VII and N. VIII dysfunction N. VII
recovery prognosis better than N. VIII
Management of Minor Brain
Injury (GCS 13)
Management of Moderate Brain
Injury
(GCS 9-12)
Management of Severe Brain
Injury
(GCS 8)
Summary of Management
Minor: Neuro PE & CT (if needed)
Moderate: Minor + CT, Close
Observation,baseline blood work, CT
follow up
Severe: Moderate + Therapeutic agent
Therapeutic Agent
IV fluid isotonic
Prevent Hypovolemia
Hyperventilation
As indicated, normocapnia preferred
Anticonvulsant (fenitoin)
Inhibit brain recovery
Prolong seizure = secondary brain injury
Manitol (ICP in acute phase)
Barbiturat (ICP in chronic phase)
Surgical Management
Indications:
Scalp wounds - Wound Toilet, Hecting
Depressed Skull Fracture operative
elevation
Intracranial Mass Lesion craniotomy
Penetrating Brain Injury neurosurgical
removal
Partially exteriorized object SHOULD NOT
BE REMOVE!! vascular injury, intracranial
hemorrhage
You might also like
- Background: Viral Mumps InfectionDocument5 pagesBackground: Viral Mumps InfectionAgustin UyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- SEPTICARTHRITISDocument2 pagesSEPTICARTHRITISapi-3822433No ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Acute Tonsil Lo PharyngitisDocument27 pagesAcute Tonsil Lo PharyngitisCheysser Alagao50% (2)
- Cerebral Concussion (Mini Case Study)Document8 pagesCerebral Concussion (Mini Case Study)Airalyn Chavez AlaroNo ratings yet
- Seizure PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesSeizure PathophysiologyqwertyuiopNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HydrocephalusDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan HydrocephalusFarnii MarquezNo ratings yet
- Febrile SeizuresDocument4 pagesFebrile Seizuresmgonzalez_29No ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument8 pagesGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Case StudyDocument11 pagesMental Health Case Studyapi-453449063No ratings yet
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument39 pagesAcute TonsillopharyngitisCin AtianzarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367No ratings yet
- Addison'sDocument4 pagesAddison'sKoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- HNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDocument2 pagesHNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Clinical Worksheet for Stroke PatientDocument6 pagesClinical Worksheet for Stroke PatientJackie GriffisNo ratings yet
- GE BasavaDocument21 pagesGE BasavaAmalin PrãdhãñNo ratings yet
- Case Study PP - AdhdDocument21 pagesCase Study PP - Adhdapi-482726932100% (1)
- Knowledge DeficitDocument5 pagesKnowledge DeficitteamstrocaNo ratings yet
- Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesFluid Volumecoldfire28No ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Document34 pagesOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Head TraumaDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Head TraumaMohammad ZianuddinNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningoceleDocument1 pageSpina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningocelesmilingstarsNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Group B1 (Cholera)Document66 pagesGroup B1 (Cholera)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Case StudyDocument10 pagesHead Injury Case StudyJayd Lorenz Vicente ChuanNo ratings yet
- PPPDocument3 pagesPPPJack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- What Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistDocument12 pagesWhat Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistLidiaAMonroyRNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation OsteomylitisDocument64 pagesCase Presentation OsteomylitisDemi Rose Bolivar100% (1)
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument41 pagesIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Choledolithiasis Cs 103 1Document34 pagesCholedolithiasis Cs 103 1Merlene Sarmiento SalungaNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Intracranial (Inside The Skull) Hemorrhage (Bleeding)Document41 pagesIntracranial (Inside The Skull) Hemorrhage (Bleeding)MASIINo ratings yet
- Epilepsy CaseDocument17 pagesEpilepsy CaseSuresh ThanneruNo ratings yet
- Brain and Spinal Cord Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesBrain and Spinal Cord Anatomy and PhysiologyynecesityNo ratings yet
- Case Study in KidneyDocument3 pagesCase Study in KidneyVenice VelascoNo ratings yet
- Management of patients with meningitis and encephalitisDocument71 pagesManagement of patients with meningitis and encephalitisSachin DwivediNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument61 pagesNephrotic SyndromeRanah Julia Garchitorena AyoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- NCP AgnDocument2 pagesNCP Agnj3nann3No ratings yet
- Long Case PresentationDocument3 pagesLong Case PresentationAkshat WaranNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis Case StudyDocument3 pagesLeptospirosis Case StudyMarie Jennifer ParilNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Case PresentationDocument12 pagesPediatric Case PresentationMohammed jouhra100% (1)
- Brain Tumor DiagnosisDocument65 pagesBrain Tumor DiagnosisMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologynitlihpNo ratings yet
- Human Diseases Case Study 18 ADocument4 pagesHuman Diseases Case Study 18 Aairickann100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument50 pagesPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis GRAND CASE PRESDocument52 pagesCholelithiasis GRAND CASE PRESKyle Cholo CholoNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Congenital Hydrocephalus RevisedDocument20 pagesCongenital Hydrocephalus RevisedDave Noel AytinNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaDhonabelleVanessaFetalinoAdona100% (1)
- Maintaining Eye Tissue Integrity Through Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageMaintaining Eye Tissue Integrity Through Nursing Interventionsjanine marie oraizNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument12 pagesGoutEarle Jimenez Niervo RN100% (1)
- Pathophysiology HeadinjuryDocument1 pagePathophysiology HeadinjuryK.b. Dequiña100% (1)
- Case Study 1 (Pneumonia)Document13 pagesCase Study 1 (Pneumonia)Kate EscotonNo ratings yet
- Concomitant PAD and CADDocument96 pagesConcomitant PAD and CADric_vir_014No ratings yet
- Juni Blunt Thoracic InjuryDocument17 pagesJuni Blunt Thoracic InjuryibnusinaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism CHF NYHA IV HHD PH SevereDocument31 pagesPulmonary Embolism CHF NYHA IV HHD PH SevereNurfitrianti ArfahNo ratings yet
- Case IlustrationDocument15 pagesCase IlustrationRobbi OcktadinataNo ratings yet
- No Seminar Tanggal KeteranganDocument4 pagesNo Seminar Tanggal KeteranganSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Litter FormDocument1 pageLitter FormSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Single DogDocument1 pageSingle DogSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Effectiveness of Bepotastine BesilateDocument11 pagesProlonged Effectiveness of Bepotastine BesilateSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- JURDING Otitis Externa Akut - Aafp 2012Document7 pagesJURDING Otitis Externa Akut - Aafp 2012Sardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Incidence and Progression of Diabetic RetinopathyDocument8 pagesIncidence and Progression of Diabetic RetinopathySardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Uveitis Presenting For The First Time inDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Uveitis Presenting For The First Time inSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- CCB 61Document78 pagesCCB 61Sardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Total Tear IgE and Severity of AcuteDocument7 pagesRelation Between Total Tear IgE and Severity of AcuteSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Case DR OscarDocument19 pagesCase DR OscarSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Grafik CDCDocument10 pagesGrafik CDCArief Budi LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Nonpharmacologic Treatments For Childhood Constipation: Systematic ReviewDocument9 pagesNonpharmacologic Treatments For Childhood Constipation: Systematic ReviewSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Case Dr. OscarDocument25 pagesCase Dr. OscarSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Feeding of Preterm Infants: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument4 pagesFeeding of Preterm Infants: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualSedaka DonaldsonNo ratings yet
- Journal 1Document8 pagesJournal 1Sardito PhanNo ratings yet
- TB in PregnancyDocument7 pagesTB in PregnancySardito PhanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ObgynDocument4 pagesJurnal ObgynSardito PhanNo ratings yet
- OMM Fellows ReviewDocument178 pagesOMM Fellows ReviewTony Ziherl100% (1)
- Manual Bicicleta Eliptica Nordictrack e 110Document32 pagesManual Bicicleta Eliptica Nordictrack e 110Emil StanimirNo ratings yet
- Fire Disaster GroupDocument17 pagesFire Disaster GroupChristian NyiNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder and The Overhead AthleteDocument373 pagesThe Shoulder and The Overhead AthleteChirvas VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Troubled Teen IndustryDocument5 pagesTroubled Teen IndustryBartek GłuszakNo ratings yet
- OphthoBook 1-6.0Document180 pagesOphthoBook 1-6.0David Cheng100% (1)
- SOFT TISSUE INJURIES AND TOLERANCE LEVELSDocument12 pagesSOFT TISSUE INJURIES AND TOLERANCE LEVELSDeepsNo ratings yet
- Pembagian PPK Elektif OrthoDocument4 pagesPembagian PPK Elektif OrthoIbnu ImadudinNo ratings yet
- CEPHALOCAUDAL ASSESSMENT Krissha-1Document4 pagesCEPHALOCAUDAL ASSESSMENT Krissha-1Vhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- Patient - Carpal Tunnel ReleaseDocument2 pagesPatient - Carpal Tunnel Releaseapi-277825138No ratings yet
- 5 - Patient Assessment LatestDocument112 pages5 - Patient Assessment LatestRose Ann Leah ChanNo ratings yet
- Pittman Mechanical Contractors, Incorporated v. Director, Office of Workers' Compensation Programs, United States Department of Labor Michael T. Simonds, 35 F.3d 122, 4th Cir. (1994)Document8 pagesPittman Mechanical Contractors, Incorporated v. Director, Office of Workers' Compensation Programs, United States Department of Labor Michael T. Simonds, 35 F.3d 122, 4th Cir. (1994)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete: Method: Pre TensioningDocument9 pagesPrestressed Concrete: Method: Pre TensioningmohdkhalidrazaNo ratings yet
- Ques NeboshDocument4 pagesQues Neboshanoop0% (1)
- ATRA Accessories OverviewDocument3 pagesATRA Accessories OverviewDiego FlórezNo ratings yet
- Lockwood Complaint & Jury DemandDocument12 pagesLockwood Complaint & Jury DemandMark KlekasNo ratings yet
- NaveedDocument18 pagesNaveednaveed aliNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF MANDIBULAR FRACTURES - Ghiffar Oka Prihardian - 18700062Document22 pagesMANAGEMENT OF MANDIBULAR FRACTURES - Ghiffar Oka Prihardian - 18700062fransiscaNo ratings yet
- A Core Syllabus in AnatomyDocument16 pagesA Core Syllabus in Anatomydod_nur100% (1)
- Hysteroscopic Limitations PDFDocument59 pagesHysteroscopic Limitations PDFV R100% (1)
- BLOK 1.3 Jaras PenglihatanDocument43 pagesBLOK 1.3 Jaras PenglihatanlenypsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 72. Case StudiesDocument40 pagesChapter 72. Case Studiesstawberry shortcake100% (1)
- Operacion y Mantenimiento Cargador Doosan dl320 02Document11 pagesOperacion y Mantenimiento Cargador Doosan dl320 02kzarate.crybNo ratings yet
- CP DiplegiaDocument3 pagesCP DiplegiaNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Assessment Sample PDFDocument11 pagesOrthopedic Assessment Sample PDFSyahrani SaidNo ratings yet
- ArsMagica5 BrokenCovenantOfCalebaisDocument96 pagesArsMagica5 BrokenCovenantOfCalebaisConstantin Bucur100% (1)
- Skin InjuryDocument4 pagesSkin InjuryNina SchutzmanNo ratings yet
- DIGEST - Juntilla V Fontanor GR L45637Document2 pagesDIGEST - Juntilla V Fontanor GR L45637norzeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document5 pagesLecture 10bibifamelaganieNo ratings yet