Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sludge
Uploaded by
AbdulSalamathOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sludge
Uploaded by
AbdulSalamathCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVATED SLUDGE
&
ITS PROCESS
MODIFICATION
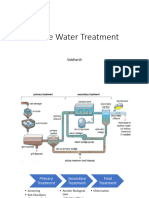
INTRODUCTION TO THE ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS
Historical Development
a) Developed around 1913 in Manchester
b) It is a Biological, secondary treatment
Activated sludge:
Settled Biomass
Activated micro-organism
Function of activated sludge:
1. Biodegradation of the influent organic material
2. To formation of floc particles
BASIC PRINCIPLE:
COHNS + O2 + bacteria CO2 + H2O+NH3
+ Energy + other end products
Synthesis:
COHNS + O2 + bacteria + energy C5H7NO2
( new cell tissue )
Chemoheterotrophic bacteria
Micro-organisms grow and form particles that clamp
together
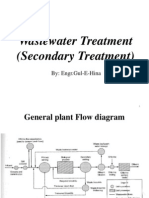
ACTIVATED SLUDGE PLANT
INVOLVES:
1. Wastewater aeration in the presence
of a microbial suspension,
2. Solid-liquid separation following
aeration,
3. Discharge of clarified effluent,
4. Wasting of excess biomass, and
5. Return of remaining biomass to the
aeration tank.
ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS
VARIABLES
MIXING REGIME :
LOADING RATE :
A) Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT)
B) Sludge Retention Time (SRT)
C) Volumetric Organic Loading
D) Food To Microorganism Ratio ( F/ M )
FLOW SCHEME :
The pattern of sewage addition
The pattern of sludge return to the aeration tank and
The pattern of aeration
Activated Sludge Process &
Modification :-
CONVENTIONAL ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS
STEP FEED SYSTEM
EXTENDED AERATION ASP
OXIDATION DITCH ACTIVATED SLUDGE PROCESS
CONTACT STABILIZATION ACTIVATED SLUDGE
HIGH PURITY OXYGEN ACTIVATED SLUDGE
CONVENTIONAL ACTIVATED SLUDGE
PROCESS
Advantages :
Allows smaller volume
Flexible operation & zone aeration.
Less aeration
Better settling characteristics
Disadvantages
High oxygen demand in inlet zone
May not buffer peak loads as well, although less likely in
activated sludge with high biomass
Less efficiency due to uniform aeration through out the
length of aeration tank but demand is less.
Step Feed System
nptel.iitm.ac.in
ADVANTAGES :
Suitable for high Bod wastewaters. Eg;
food processing industry wastewater
Lower the peak oxygen demand
Better equalization of waste load ( within
aeration tank )
Better distribution of oxygen demand over
entire length of A.T.
Smaller aeration tank volume compared to
conventional activated sludge unit
Extended Aeration System
External substrate is completely removed.
Auto oxidation (internal substrate is used).
Net growth =0
If Q, So, Se & X are the same
Volume required in extended aeration system = 30 times that
of conventional ASP
Advantages :
Sludge production minimum
Stabilized sludge no digesters are required
Nutrient requirement minimal
Disadvantages :
High power requirement
Large volume of aeration tank
Suitable for small communities
Oxidation ditch
nptel.iitm.ac.in
Secondary
clarifier
Influent
Sludge
return
Effluent
Brush-type
aerators
Working on the principle of extended
aeration.
Compact unit ( sedimentation, aeration &
sludge stabilization in one)
Used for small communities
Q < 3,800 cum m/day
- This unit is preferred
Advantages :
Typically small systems
Flexible operation with placement and use of
aerators can be used for nutrient removal
Very stable process
No primary clarifier simpler sludge handling
Good settling characteristics
Disadvantages :
Long aeration time, larger reactor.
Higher aeration requirement.
Mechanical aeration equipment (rotors, large
turbines)required to move water around the
channel as well as aerate. Can create zones of
high oxygen and add maintenance costs. More
recent designs use diffusers for aeration and
reduce mechanical requirement.
Contact Stabilization Process
Wastewater rich in colloidal organic solids
besides soluble BOD
Eg: Dairy industry, meat processing industry
www.webapps.cee.vt.edu
CONTACT TANK
Design is based on separation time.
Separation of colloidal and soluble substrate
based on MLSS.
No increase in biomass concentration (during
separation process no energy generated )
STABILIZATION TANK
Stabilization of colloidal and soluble BOD by
microbes.
Increase in biomass
Detention time in stabilization tank is 3 to 4 hrs.
Advantages
Reduced aeration requirement with short
contact tank residence time
Reportedly better settling sludge
Disadvantages
Complex operation
Possible reduced treatment for soluble
contaminants in contact tank
HIGH PURITY OXYGEN ACTIVATED
SLUDGE
Oxygen added under pressure to keeps dissolved oxygen level
high
Advantages:
Five times oxygen transfer rate over air
Smaller volume
Higher biomass concentration possible, but limited by
secondary settler capacity
Disadvantages :
Very expensive: covered tanks, high energy cost for O2
generation, gas recirculation equipment
No flexibility (all aerobic processes)
Settling problems have been reported
THANK
YOU
You might also like
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Activated SludgeDocument27 pagesActivated SludgeMukesh JagaNo ratings yet
- Activated SludgeDocument27 pagesActivated Sludgemostafagalal22No ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment: Municipal & Industrial WWTPDocument26 pagesWaste Water Treatment: Municipal & Industrial WWTPSiti Farhanah Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- MidsemDocument30 pagesMidsemSowmya TuragaNo ratings yet
- Suspended Growth Biological TreatmentDocument21 pagesSuspended Growth Biological Treatmentsaiful islamNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge Process: Waste Water TreatmentDocument16 pagesActivated Sludge Process: Waste Water TreatmentGarfield SmithNo ratings yet
- Extended AerationDocument17 pagesExtended AerationMorris Angelo NievaNo ratings yet
- Group 08 - Bio TowersDocument18 pagesGroup 08 - Bio TowersMeenu MariyamNo ratings yet
- PIAS-Sistem Lumpur AktifDocument32 pagesPIAS-Sistem Lumpur AktifTeknik Pdam Kota KupangNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Powerpoint - Technical Presentation On Bio-TowersDocument19 pagesMicrosoft Powerpoint - Technical Presentation On Bio-TowersbathalapalliNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment Process: By, Adarsh SDocument60 pagesBiological Treatment Process: By, Adarsh Sadarsh sNo ratings yet
- Module - 9 Secondary Treatment AS, EAAS, SBRDocument39 pagesModule - 9 Secondary Treatment AS, EAAS, SBRFaran Masood100% (1)
- WMT PPT 4Document15 pagesWMT PPT 4SamNo ratings yet
- The Following Slides Are Provided by Dr. Vincent O'FlahertyDocument47 pagesThe Following Slides Are Provided by Dr. Vincent O'FlahertyBalaji LamboNo ratings yet
- Ecostar - Compact Aer STP Using LevaporDocument5 pagesEcostar - Compact Aer STP Using LevaporAmit ChristianNo ratings yet
- ASML - Techincal Proposal For Grey Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesASML - Techincal Proposal For Grey Water TreatmentChachi TerijanNo ratings yet
- MBBR OM Manual-250Document42 pagesMBBR OM Manual-250senthil2002100% (3)
- Effluent Treatment: Dr. Mayank Chaudhary Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology MMEC, MM (DU), Mullana-AmbalaDocument13 pagesEffluent Treatment: Dr. Mayank Chaudhary Assistant Professor Department of Biotechnology MMEC, MM (DU), Mullana-AmbalaDr. Mayank ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (Uasb) - En-04Document11 pagesUpflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (Uasb) - En-04Engr Shakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge 1Document6 pagesActivated Sludge 1franz villafuerteNo ratings yet
- Biotower 001 PDFDocument3 pagesBiotower 001 PDFIsmael KhalilNo ratings yet
- 100 CMD DWWT MBBRDocument13 pages100 CMD DWWT MBBRAquasoul Co100% (1)
- Extended Aeration SystemDocument5 pagesExtended Aeration SystemTajTajNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic TreatmentDocument6 pagesAnaerobic TreatmentChandra JyotiNo ratings yet
- Construction Manual LUPO Digester Ethiopia GTZ 2002Document30 pagesConstruction Manual LUPO Digester Ethiopia GTZ 2002Micah Allen100% (4)
- 5.1 UASB REACTOR (5 Files Merged)Document115 pages5.1 UASB REACTOR (5 Files Merged)Krishnaprabha K TNo ratings yet
- Wastewatertreatment 130204082216 Phpapp02Document55 pagesWastewatertreatment 130204082216 Phpapp02CakEmUsNo ratings yet
- WastewaterDocument12 pagesWastewaterJerome JavierNo ratings yet
- Biogas Presentation PDFDocument44 pagesBiogas Presentation PDFAli Aamir100% (1)
- The Venturi Aeration Process:: Understanding Oxygen Transfer and Wastewater ConditioningDocument23 pagesThe Venturi Aeration Process:: Understanding Oxygen Transfer and Wastewater ConditioningKumarNo ratings yet
- 5 CMD DWWT MBBRDocument13 pages5 CMD DWWT MBBRAquasoul CoNo ratings yet
- Good1 - 25.08.2021 - Slot 1 - Dr. Deepak SharmaDocument34 pagesGood1 - 25.08.2021 - Slot 1 - Dr. Deepak SharmaDewin NeryNo ratings yet
- Comparing Technologies - Conventional ASP, SBR, MBBR, MBRDocument3 pagesComparing Technologies - Conventional ASP, SBR, MBBR, MBRJanakiram GoudNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterDocument118 pagesPhysical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterAseem Vivek Masih100% (1)
- 77 Two Stage Uasb Treatment of Industrial Wastewater With Internal CirculationDocument10 pages77 Two Stage Uasb Treatment of Industrial Wastewater With Internal CirculationngocdungmtNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument28 pagesActivated Sludge Processusmansherdin100% (2)
- ELMITVALLI 2005 Treatment of Municipal Wastewater in Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket UASB ReactorDocument32 pagesELMITVALLI 2005 Treatment of Municipal Wastewater in Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket UASB ReactorKuswandi AndiNo ratings yet
- D. WWTP SecondaryDocument37 pagesD. WWTP Secondaryzairulh7No ratings yet
- 120 MLD Sewage Treatment Plant: NCL/TMX/STP-VIKARABAD/BP-2244/R0/Tec OfferDocument39 pages120 MLD Sewage Treatment Plant: NCL/TMX/STP-VIKARABAD/BP-2244/R0/Tec OfferVķ MãħëšħNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Processes: Rate Systems. Thus One Can Have A Low-Rate, Suspended-Growth Anaerobic System WhichDocument6 pagesAnaerobic Processes: Rate Systems. Thus One Can Have A Low-Rate, Suspended-Growth Anaerobic System Whichnickao123No ratings yet
- Secondary Wastewater TreatmentDocument18 pagesSecondary Wastewater TreatmentSumaiya Rashid100% (1)
- Biogas Reactors: (Anaerobic Digester)Document24 pagesBiogas Reactors: (Anaerobic Digester)Maham AzamNo ratings yet
- Design Features of Stirred Tank BioreactorDocument60 pagesDesign Features of Stirred Tank BioreactorDhananjay KadamNo ratings yet
- Type of Reactor UsedDocument7 pagesType of Reactor UsedAzrul Sofi100% (1)
- STP Secondary Treatment Sept 27 2018Document26 pagesSTP Secondary Treatment Sept 27 2018Mulberry PlaceNo ratings yet
- Waste-To-Energy & Material Recovery: Chapter 5: Aerobic CompostingDocument32 pagesWaste-To-Energy & Material Recovery: Chapter 5: Aerobic CompostingMryam 'No ratings yet
- Anaerobic Digestion For Environmental ProcessesDocument5 pagesAnaerobic Digestion For Environmental ProcessesWONG TSNo ratings yet
- Wastewater ExamDocument9 pagesWastewater ExamSanti PoNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument17 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSOURABH GANGWARNo ratings yet
- Use of The Upflow Sludge Blanket (USB) ReactorDocument36 pagesUse of The Upflow Sludge Blanket (USB) ReactorinscNo ratings yet
- Week 9-CHEM4015-CIVE4140-2023-2024Document44 pagesWeek 9-CHEM4015-CIVE4140-2023-2024Nitin RautNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 33 and 34 - Group Discussion: BITS Pilani, Pilani CampusDocument45 pagesLecture - 33 and 34 - Group Discussion: BITS Pilani, Pilani CampussaisounyaNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge Treatment ProcessDocument7 pagesActivated Sludge Treatment ProcessMaizan Sofia100% (1)
- Lecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDocument41 pagesLecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsUsman KhalidNo ratings yet
- SOme InfoDocument7 pagesSOme InfoJITENDRA CARPENTERNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Plant Design ProjectDocument30 pagesSewage Treatment Plant Design Projectgk mNo ratings yet
- Starch Industry Effluent Treatment PlantDocument30 pagesStarch Industry Effluent Treatment PlantBSridhar50% (2)
- Xylem Introduction To Sanitaire AerationDocument46 pagesXylem Introduction To Sanitaire AerationOscar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Next Generation of MBBR Technology PDFDocument48 pagesNext Generation of MBBR Technology PDFAbhisek BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Hydro-Mechanical Equipment Gates Module-VDocument119 pagesDesign of Hydro-Mechanical Equipment Gates Module-VBalkrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Gate GA Prep ScheduleDocument3 pagesGate GA Prep ScheduleMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Gate GA Prep ScheduleDocument3 pagesGate GA Prep ScheduleMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- GatesDocument49 pagesGatesPrem Singh RawatNo ratings yet
- Gate Maths Prep ScheduleDocument6 pagesGate Maths Prep ScheduleMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Guide Lines For Erection of Verticallift GatesDocument46 pagesGuide Lines For Erection of Verticallift GatesMahipal Reddy100% (1)
- Guidelines For Preparing O&M Manuals For DamsDocument104 pagesGuidelines For Preparing O&M Manuals For DamsMuhammadGani0% (1)
- Gate Prep ScheduleDocument15 pagesGate Prep ScheduleMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Vision IAS Prelims 2020 Test 17 Solutions PDFDocument36 pagesVision IAS Prelims 2020 Test 17 Solutions PDFankithdayanandaNo ratings yet
- A 2020 VisionIAS Test 16 PDFDocument36 pagesA 2020 VisionIAS Test 16 PDFMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Annexure VII Conversion FactorsDocument6 pagesAnnexure VII Conversion FactorsMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Vision IAS Prelims 2020 Test 14 SolutionsDocument35 pagesVision IAS Prelims 2020 Test 14 SolutionsDhanesh DeokarNo ratings yet
- Gate Maths Prep ScheduleDocument6 pagesGate Maths Prep ScheduleMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ebooks On The GooDocument38 pagesEbooks On The GoodghNo ratings yet
- 4th To 8th Order CD Proposals I.B.sub Division Singoor 27.04.2019Document4 pages4th To 8th Order CD Proposals I.B.sub Division Singoor 27.04.2019Mahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- A 2020 VisionIAS Test 15 PDFDocument32 pagesA 2020 VisionIAS Test 15 PDFMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- A 2020 VisionIAS Test 11 PDFDocument46 pagesA 2020 VisionIAS Test 11 PDFMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- 10 A Vision IAS Prelims 2020 (Freeupscmaterials - Org)Document37 pages10 A Vision IAS Prelims 2020 (Freeupscmaterials - Org)Monu KumarNo ratings yet
- L.a.o.p.63 of 2006Document11 pagesL.a.o.p.63 of 2006Mahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- A 2020 VisionIAS Test 13 PDFDocument41 pagesA 2020 VisionIAS Test 13 PDFMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- 247081ce PDFDocument138 pages247081ce PDFMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Individual Tanks Proforma: CertificateDocument6 pagesIndividual Tanks Proforma: CertificateMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Statistical Year Book 2015Document466 pagesStatistical Year Book 2015Kranti KumarNo ratings yet
- Circ 1389Document5 pagesCirc 1389Mahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- All About Grand Slam!!: English Medium Telugu Medium Practice Tests Current AffairsDocument2 pagesAll About Grand Slam!!: English Medium Telugu Medium Practice Tests Current AffairsMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument16 pagesIntroductionMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Commands 1 PDFDocument6 pagesAutoCAD Commands 1 PDFAlvin YanglayNo ratings yet
- 8.264 UT-Model 2Document1 page8.264 UT-Model 2Mahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler IrrigationDocument23 pagesSprinkler IrrigationMahipal ReddyNo ratings yet
- Barangay Tanods and The Barangay Peace and OrderDocument25 pagesBarangay Tanods and The Barangay Peace and OrderKarla Mir74% (42)
- Coursework For ResumeDocument7 pagesCoursework For Resumeafjwdxrctmsmwf100% (2)
- Software Testing Notes Prepared by Mrs. R. Swetha M.E Unit I - Introduction at The End of This Unit, The Student Will Be Able ToDocument30 pagesSoftware Testing Notes Prepared by Mrs. R. Swetha M.E Unit I - Introduction at The End of This Unit, The Student Will Be Able ToKabilan NarashimhanNo ratings yet
- A.2 de - La - Victoria - v. - Commission - On - Elections20210424-12-18iwrdDocument6 pagesA.2 de - La - Victoria - v. - Commission - On - Elections20210424-12-18iwrdCharisse SarateNo ratings yet
- D6a - D8a PDFDocument168 pagesD6a - D8a PDFduongpn63% (8)
- Brother Fax 100, 570, 615, 625, 635, 675, 575m, 715m, 725m, 590dt, 590mc, 825mc, 875mc Service ManualDocument123 pagesBrother Fax 100, 570, 615, 625, 635, 675, 575m, 715m, 725m, 590dt, 590mc, 825mc, 875mc Service ManualDuplessisNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Mutual Fund SchemesDocument29 pagesComparative Analysis of Mutual Fund SchemesAvinash JamiNo ratings yet
- Learner Guide HDB Resale Procedure and Financial Plan - V2Document0 pagesLearner Guide HDB Resale Procedure and Financial Plan - V2wangks1980No ratings yet
- Design of Open Channels US Department of Agriculture SCSDocument293 pagesDesign of Open Channels US Department of Agriculture SCSMiguelGuavitaRojasNo ratings yet
- For Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesFor Exam ReviewerGelyn Cruz67% (3)
- CNS Manual Vol III Version 2.0Document54 pagesCNS Manual Vol III Version 2.0rono9796No ratings yet
- Business Occupancy ChecklistDocument5 pagesBusiness Occupancy ChecklistRozel Laigo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Simplified Concrete Modeling: Mat - Concrete - Damage - Rel3Document14 pagesSimplified Concrete Modeling: Mat - Concrete - Damage - Rel3amarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0304389421026054 MainDocument24 pages1 s2.0 S0304389421026054 MainFarah TalibNo ratings yet
- Gowtham Kumar Chitturi - HRMS Technical - 6 YrsDocument4 pagesGowtham Kumar Chitturi - HRMS Technical - 6 YrsAnuNo ratings yet
- Si KaDocument12 pagesSi KanasmineNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Risk Management: Resilience and Business ContinuityDocument27 pagesSupply Chain Risk Management: Resilience and Business ContinuityHope VillonNo ratings yet
- S SSB29 - Alternator Cables PM: WARNING: This Equipment Contains Hazardous VoltagesDocument3 pagesS SSB29 - Alternator Cables PM: WARNING: This Equipment Contains Hazardous VoltagesMohan PreethNo ratings yet
- MP 221 Tanael PLUMBING CODE Definition of Terms 2Document3 pagesMP 221 Tanael PLUMBING CODE Definition of Terms 2Louie BarredoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Troubleshooting For Biomedical Technicians 2edDocument239 pagesBasic Electronic Troubleshooting For Biomedical Technicians 2edClovis Justiniano100% (22)
- It14 Belotti PDFDocument37 pagesIt14 Belotti PDFHolis AdeNo ratings yet
- Karmex 80df Diuron MsdsDocument9 pagesKarmex 80df Diuron MsdsSouth Santee Aquaculture100% (1)
- Revenue Management Session 1: Introduction To Pricing OptimizationDocument55 pagesRevenue Management Session 1: Introduction To Pricing OptimizationDuc NguyenNo ratings yet
- MNO Manuale Centrifughe IngleseDocument52 pagesMNO Manuale Centrifughe IngleseChrist Rodney MAKANANo ratings yet
- Tank Emission Calculation FormDocument12 pagesTank Emission Calculation FormOmarTraficanteDelacasitosNo ratings yet
- Minas-A6 Manu e PDFDocument560 pagesMinas-A6 Manu e PDFJecson OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Medical Devices RegulationsDocument59 pagesMedical Devices RegulationsPablo CzNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Financial Accounting and Reporting PART 1Document3 pagesReview Questions Financial Accounting and Reporting PART 1Claire BarbaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management ModelsDocument4 pagesStrategic Management ModelsBarno NicholusNo ratings yet
- T&B Detailed Plan: Ceiling LineDocument1 pageT&B Detailed Plan: Ceiling LineKuthbert NoceteNo ratings yet