Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Computer CPU Executes Programs
Uploaded by
Mohit GanigerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Computer CPU Executes Programs
Uploaded by
Mohit GanigerCopyright:
Available Formats
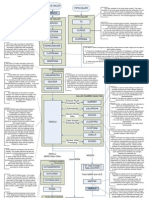
01 How does Computer
Execute a Program?
By
Darshit Shah
Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University
Index
System
Architecture of CPU
Basic Tasks Performed By CU
RAM
Types of RAM
ROM
Types of ROM
Motherboard
Components of Motherboard.
Exit
System
We are part of different Systems.
Every systems have few things in common.
Input
Process
Output
Example: Our Human Body
Input: Food
Process: at stomach
Output: Energy to Body/Blood/etc.
Computer System
INPUT PROCESS OUTPUT
KEYBOARD
C.P.U. MONITOR
C.P.U.
KEYBOARD
MONITOR
C.U.
A.L.U.
Cache
Memory
Primary Memory
ROM
RAM
Auxiliary Memory
Floppy Disks
Hard Disk
CD/Pen Drive
C.P.U.
KEYBOARD
MONITOR
C.U.
A.L.U.
Cache
Memory
Auxiliary Memory
Floppy Disks
Hard Disk
CD/Pen Drive
RAM
OS Programs
Program Area
INPUT A,B
C = A + B
PRINT C
Data Area
A B C
10 20 30
Basic Tasks Performed By CU
Fetch the instruction (from RAM)
Check for Errors:
Syntax Error: Grammatical Error
e.g. IPUT A,B
Semantic Error: Incomplete Statement
e.g. INPUT
Execute the Instruction(if no error found)
And Many More.
Cache Memory
Inside CPU
Works at the speed of CPU
And hence the fastest memory
CPU searches for the data in Cache Memory first. If
not found, then it will extract that data from RAM.
Two types of Cache Memory:
L1 Level 1within CPU. (Fixed)
L2 Level 2 On the Mother Board. (Size can
be increased or decreased)
In terms of Speed: L1 > L2 > RAM > Hard
Disk
In terms of Storage: L1 < L2 < RAM < Hard
Disk
ROM
It stands for Read Only Memory.
It is a non-volatile memory i.e. contents of ROM are
not lost even when we switch off the computer.
A backup UPS is not required.
The programs (micro codes) are written for once in
ROM during manufacturing.
These programs are not available to normal
programmers directly.
It is used to hold programs, which are needed
frequently e.g. Code Conversion, Character
Generation, Function Generation (sin(),
cos(),etc)etc.
Types of ROM: PROM, EPROM, EEPROM
Types of ROM
PROM: It stands for Programmable Read Only Memory.
It can be programmed only once with a PROM-Writer,
thereafter it cant be altered.
EPROM: It stands for Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory.
It can be electrically programmed multiple times.
Erasure is performed by exposing the chip to Ultra-Violet light
(Sunrays).
It is useful for experimental projects & prototypes in which the
data may have to be changed after the chips have been
programmed.
EEPROM: It stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable
Read Only Memory.
Now the data can be erased, and reprogrammed by applying
appropriate electrical charges.
It is useful for data that needs to be read frequently but
changed only occasionally, such as a price list stored in an
electronic cash register.
RAM
It stands for Random Access Memory.
It is a volatile memory i.e. the contents of RAM are
lost when the computers power is shut off.
A backup UPS is desirable in order not to lose the data.
It is constructed with Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor.
It retains the program & data that are currently being
executed.
It is called RAM because access time in RAM is
independent of the address of the word i.e. each
storage location inside the memory is as easy to reach
as any other location & it takes the same amount of
time.
Any Program that we want to run in a computer
must be loaded in the program area of RAM.
Types of RAM: Dynamic RAM, Static RAM.
Types of RAM
DRAM: It stands for Dynamic Random Access
Memory.
Each memory cell quickly loses its charge. So it
must be refreshed hundreds of times every
seconds to prevent data from being lost.
The computer does this refreshing process itself,
taking time out from other chores every few
milliseconds.
It will read all RAM memory positions while they are
still readable and put appropriate new charge on each
capacitor.
Some DRAM memory circuits include built-in
refresh circuit to relieve the computer.
It consumes lesser power than Static Ram.
Types of RAM
Static RAM: Static RAM is also faster,
larger & more expensive than DRAM.
It is Static because it doesnt need to be
continually refreshed.
It is used in a special area of memory
called a cache.
What is Motherboard?
It is the main circuit board on the
computer.
Motherboard acts as a direct channel for
the various components to interact &
communicate with each other.
If the CPU is compared to the human
brain, then the motherboard can be
compared to the nerve system.
Components of Motherboard
CPU - Through the use of Socket-7 or Slot-1.
Memory Chips (RAM, ROM, Cache, BIOS, CMOS etc).
Buses (wires connecting devices attached to the
motherboard)
Expansion Slots (where other expansion cards are
inserted. (SIMM (Single Inline Memory Module)/DIMM (Dual
Inline Memory Module) Slots, PCI Slots, AGP Slots )
Power Supply Connectors.(SMPS)
Ports (Parallel, Serial)
Connectors (IDE-Integrated Drive Electronics for Hard disk
and floppy drive connectors)
USB (Universal Serial Bus), PS/2 (Personal System/2)
connectors
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CH01 COA10e StallingsDocument57 pagesCH01 COA10e Stallingsfalconau100% (1)
- Complaint Management System AbstractDocument5 pagesComplaint Management System AbstractTelika Ramu67% (12)
- Project Report On Search EngineDocument9 pagesProject Report On Search EngineRahul Sharma100% (2)
- Performance Testing ResumeDocument4 pagesPerformance Testing ResumeSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Fifo Method of Process CostingDocument17 pagesFifo Method of Process CostingPrateek DubeyNo ratings yet
- Managerial CommunicationDocument225 pagesManagerial CommunicationSatheesh Ezhumalai100% (3)
- Clause 31 WithPanGRP31!12!2018Document8 pagesClause 31 WithPanGRP31!12!2018Mohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- Rera Report 4672 PDFDocument21 pagesRera Report 4672 PDFMohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- Managerial CommunicationDocument225 pagesManagerial CommunicationSatheesh Ezhumalai100% (3)
- Is India A Democratic System But Not ADocument13 pagesIs India A Democratic System But Not AMohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- Mint March 23 2016Document1 pageMint March 23 2016Mohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- FDI Guidelines For E-Commerce 0Document5 pagesFDI Guidelines For E-Commerce 0Mohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument22 pagesEconomicspolaris25No ratings yet
- WAT PI Kit 2018Document90 pagesWAT PI Kit 2018Mohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- End of The WorldDocument1 pageEnd of The WorldMohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- Hey! Guys :DDocument1 pageHey! Guys :DMohit GanigerNo ratings yet
- Friend FunctionDocument6 pagesFriend Functionmail.sushilk8403No ratings yet
- Market Survey of Quick Heal in NepalDocument5 pagesMarket Survey of Quick Heal in Nepalakusmarty2014No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document21 pagesChapter 10Prudhvinadh Kopparapu100% (2)
- To Restore Older Aging Snapshots When A Full ETL Is RunDocument28 pagesTo Restore Older Aging Snapshots When A Full ETL Is RunSuhel DayerNo ratings yet
- Software Testing - Goals, Principles, and LimitationsDocument4 pagesSoftware Testing - Goals, Principles, and LimitationsTederNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 PointersDocument20 pagesChapter7 PointersMuhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- SENTIMENT ANALYSIS ON TWEETSDocument2 pagesSENTIMENT ANALYSIS ON TWEETSvikibytesNo ratings yet
- 3 Typescript m3 SlidesDocument27 pages3 Typescript m3 SlidesAdnan OmanovicNo ratings yet
- GSM Security Overview: COMP128 Algorithm AttacksDocument38 pagesGSM Security Overview: COMP128 Algorithm AttacksEric TraoreNo ratings yet
- Sequence Detector Finite State Machine DesignDocument2 pagesSequence Detector Finite State Machine Designasic_masterNo ratings yet
- Minimum Mode and Maximum MOdeDocument35 pagesMinimum Mode and Maximum MOdechandrakanthNo ratings yet
- Cisco Ios DMVPN: February 2008Document46 pagesCisco Ios DMVPN: February 2008hadi_khan100% (1)
- 010 Informed Search 2 - A StarDocument20 pages010 Informed Search 2 - A StarRashdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Install STEDS Navigator and manualsDocument13 pagesInstall STEDS Navigator and manualsVũ Nguyễn MinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Two Dimensional System: 1. Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)Document11 pagesChapter 2 - Two Dimensional System: 1. Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)Gorakh Raj JoshiNo ratings yet
- DS Lab Manual-1Document63 pagesDS Lab Manual-1Amogh SkNo ratings yet
- Test SpecificationDocument2 pagesTest SpecificationYathestha SiddhNo ratings yet
- OS 180-94 Assignment 3Document3 pagesOS 180-94 Assignment 3Imran HayderNo ratings yet
- Multi-threaded prime number generatorDocument17 pagesMulti-threaded prime number generatorravi192005143No ratings yet
- PART I Chap 1 ADocument27 pagesPART I Chap 1 Akt8815No ratings yet
- Actual Copy PrjoectGuidelinesDocument92 pagesActual Copy PrjoectGuidelinesMohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Deployment Guide App Template Oracle EBSDocument16 pagesDeployment Guide App Template Oracle EBSSudhakar GanjikuntaNo ratings yet
- Develop Android Apps Using AndroidDocument1 pageDevelop Android Apps Using AndroidHaseeb MogralNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Conceptual Aside Javascript and UndefinedDocument2 pagesLecture 16 - Conceptual Aside Javascript and UndefinedTim PronNo ratings yet
- Number AnalysisDocument4 pagesNumber AnalysisaphadaniNo ratings yet
- Automated Testing and Performance Management - AXUG Upper Midwest Chapter MeetingDocument23 pagesAutomated Testing and Performance Management - AXUG Upper Midwest Chapter MeetingGajendraNo ratings yet