Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ray Optics1
Uploaded by
Park MinkukOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ray Optics1
Uploaded by
Park MinkukCopyright:
Available Formats
Contents
2
The field of optics
Ray optics
Wave optics
Electromagnetic optics
Quantum optics
Ray optics is the limit of
wave optics when the
wavelength is very short.
3
Introduction to Photonics
1.1. Postulates of Ray Optics
Fermats Principle
BC
x d
AB
x
b x d
x d
a x
x
dx
b x d d
dx
a x d
dx
b x d d
dx
a x d
dx
dS
dx
dS
b x d a x BC AB S
b x d BC
a x AB
=
+
+
=
+
+
+
=
+
+
+
=
=
+ + + = + =
+ =
+ =
2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2
) (
) (
0
) (
0
) (
) (
'
' sin sin
' sin
sin
u u
u u
u
u
=
=
=
=
BC
x d
AB
x
Shortest path!
d
x
d - x
4
The path length of the ray (S)
,
1.1. Postulates of Ray Optics
Snells Law
2 2 1 1
1
2
2
1
2
1
2
1
sin sin
sin
sin
u u
u
u
n n
n
n
v
v
d
d
=
= = =
S`
S
O
S
5
da
d
a = d - a
1.1. Postulates of Ray Optics
Exercise 1.1-1
6
1.2. Simple Optical Components
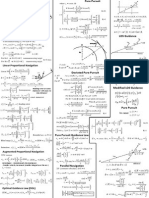
Mirrors
7
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Mirrors
0 1 2
2u u u = +
2
2
1
1 0
, ,
z
y
z
y
R
y
~ ~
~ u u u
R
y
z
y
z
y
~ +
2
2 1
f R z z
1 2 1 1
2 1
=
~ +
2 0 0 1
u u u u u u = + = +
8
[Conventions]
Concave surface: R < 0
Convex surface: R > 0
Upward ray: u > 0
Downward ray: u < 0
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Exercise 1.2-1
9
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Planar Boundaries
1
2
1
2 2 1
1 2
sin
2
sin sin
90
n
n
n n n
c
c
c
=
= =
= =
u
t
u
u u u
2 1
n n >
2 1
n n <
10
( )
1
2 45
c
n u > <
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Planar Boundaries - Prisms
3
2 3
1
3 2
1
1
1
1 1
1 2
1 1
1 2
2
( )
sin sin
sin ( sin )
sin { sin( )}
sin { (sin cos cos sin )}
sin { (sin 1 sin cos sin )}
1 1
sin { (sin 1 sin cos sin )}
u u o u
u u
u u
o u
o u o u
o u o u
o u o u
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
d
n
n
n
n
n
n
n n
( )
1 2
1
2
2 2
si
n (s
sin (sin sin cos sin )
( ) ,
in sin cos sin )
1 ( 1)
u u o o
o u o u
u o o u o u
u
o
u o
= +
=
~ + =
d
n
n
n
n
1 2
u o u =
u u
u
u
sin
1
sin
' sin
sin
1
1
n
n
n
n
=
= =
1
u
2
u
3
u
o
'
11
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Planar Boundaries - Prisms
12
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Planar Boundaries Beam Splitters
13
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Spherical Boundaries and Lenses
( )
1 1 2 2
1 1 2 2
1
2 1
2
1 1
1
2 2
1 1
1
2 2
sin( ) sin( ( ))
( ) ( ( ))
1
1
n n
n n
n
n
n n
n n
n n y
n n R
u o o u
u o o u
u u o o
u o
u
+ =
+ ~
= +
| |
= +
|
\ .
| |
= +
|
\ .
o
o
R y
R y
~
= sin
1 1 2 2
1 1 1 2 2 2
1 1 2 2 2 1
1 2 2 1
1 2
1 2 2 1
1 2
( ) ( ( ))
( )
( )
n n
n n n n
n n n n
y y y
n n n n
z z R
n n n n
z z R
u o o u
u o o u
u u o
+ ~
+ = +
=
+ =
+ =
o
o
1
z
2
z
R
y
z
y
z
y
~ ~
~ ~
~ ~
o o
u u
u u
tan
) tan(
tan
2
2 2
1
1 1
14
1 1
2 1
2 2
1
n n y
n n R
u u
| |
= +
|
\ .
1 2 2 1
1 2
n n n n
z z R
+ =
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Spherical Boundaries and Lenses
( )
( )
0.785, sin 0.707
4
0.314, sin 0.309
10
0.1745, sin 0.1736 Differenc
sin 1 0.1
e 0.51%
18
t
u u
t
u u
u
u u
t
u u
u
= ~ ~
= ~ ~
= ~ ~ <
~ <
15
Paraxial ray approximation
( )
( )
0.785, tan 1
4
0.314, tan 0.325
tan
10
0.1745, tan 0.1763 Difference 1.03%
1
1
8
0.1
t
u u
t
u u
t
u
u u u u
u
= ~ ~
= ~ ~
= ~ ~ <
~ <
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Spherical Boundaries and Lenses
1 1 1
3 1
2 2 1
1 1 2
3 2
2 2 2
1 (A)
1 (B)
n n y
n n R
n n y
n n R
u u
u u
| |
= +
|
\ .
| |
= +
|
\ .
16
2 3 1 2
2 3 1 2
1 1 1
3 2 2
2 2 2
1 1 2 1 1 2
2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
sin( ) sin( ( ))
( ) ( )
( ) (1 )
(1 ) 1
n n
n n
n n n
n n n
n n y n n y
n n R n n R
u o o u
u o o u
u o u o u o
u u
+ = +
+ ~
= + = +
| | | |
~ + = +
| |
\ . \ .
2
2
2 2
1 2
1
1 1
1 1 2
1
1
2
2 1 2
( )( )
1 ( )
n
n y y
n R
n
n
R
n y y
n R R
u u
u
| |
|
\
=
=
3
u
2
u
o
R
1
u
3
u
2
u
y
1
y
2
A B
n
1
n
1
n
2
R
1
R
2
A thick lens
(Exercise 1.2-4)
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Spherical Boundaries and Lenses
17
( )
( ) ( )
( )
1
2 1 2
1
1 1 2
1 2
1
1 2
1
2 1
2 1 2 1
2
1
1
2
1 2 2
1
1
1
1
1 1 1
ta
1
1
1 1
n & t n
1
a
1
n
R
n y y
n R R
y y n
R R
y
y y y y y
z z f z
R
y
f
n
f R R z z f
z
u
u
u
u u
u
u
| || |
=
| |
\ .\ .
| |
| |
=
| |
\ .
\ .
=
=
| |
= = =
|
+ =
\ .
| |
|
\ .
| |
=
|
\ .
| |
|
|
\ .
1 1 n
A thin lens
( )
2
1
1
1
2
2
1
1 1 1
1
1 1
y
f
z z f
n
f R R
u u
| |
=
|
| |
|
|
\
=
.
=
.
+
\
1 2
y y y = =
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Spherical Boundaries and Lenses
18
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
2
2
2 1 1 1
1 2
1 1
1
1
1 2
2
2
1
1 1
1
0
an
1
t
y
y y
f f f
n
y y
z
y y
z f f
y
R R
u u u u
u u
| |
=
= = =
+
= ~
| |
=
|
\
|
.
.
\
|
1
2
Minus sign means that a
focused image is inverted !
( )
( )
( )
1 1
1 2
1
2 1 2 2
1 2
2 2
2
1 2 1
2
1 1
0
ta
1
1
n
y y y
f f f
y y
z
y y y
z f
n
f R R
u u u u
u u
= = =
+
= ~
| |
| |
= =
|
\
\ .
.
|
|
1 2
( )
1 2 1
2
2
1 2 2
2 1
1
1 2 2
1
1
&
y y y y y y
z
y y
z
z f z f
z y
z y
=
=
=
=
A thin lens
Lens aberration
1. Non-paraboloidal surface
- Lens boundary: refraction angle
- Lens center: refraction angle
2. Chromatic dispersion
- Refractive index that is a function
of wavelength: n()
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Spherical Boundaries and Lenses
19
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Light Guides
1 2
n n <
20
1.2. Simple Optical Components
Exercise 1.2-5
21
You might also like
- Fizika Formule 1. KolokvijDocument1 pageFizika Formule 1. Kolokvijkosto1234No ratings yet
- Determination of Refractive Indices For A Prism Material and A Given Transparent LiquidDocument9 pagesDetermination of Refractive Indices For A Prism Material and A Given Transparent LiquidAsa mathew100% (8)
- Lame Thick Cylinder EquationsDocument17 pagesLame Thick Cylinder Equationsbeegmac100% (2)
- P1 Ray OpticsDocument76 pagesP1 Ray OpticsfraiefNo ratings yet
- Slepý Tahák: Přehled Vzorců Pro Beztrestné Použití U Výpočtové Části Zkoušky Ze Statistiky BDocument2 pagesSlepý Tahák: Přehled Vzorců Pro Beztrestné Použití U Výpočtové Části Zkoušky Ze Statistiky BMartin Spyyd PřidalNo ratings yet
- (2012) MEIII (Midterm) PDFDocument8 pages(2012) MEIII (Midterm) PDFTai-Yuan HsuNo ratings yet
- OC Chapter II 110215Document48 pagesOC Chapter II 110215Ruben LopezNo ratings yet
- Guidance Law OptimizationDocument2 pagesGuidance Law OptimizationeliavvNo ratings yet
- ECSE 353 FormulasDocument6 pagesECSE 353 FormulasEileen FuNo ratings yet
- Finite Differencing Method for Numerical Solution of PDEsDocument30 pagesFinite Differencing Method for Numerical Solution of PDEsQasim AliNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry: Computer Vision #8Document49 pagesDifferential Geometry: Computer Vision #8aerogem618No ratings yet
- Quadrapole - Parmisse DURRANI-2006Document36 pagesQuadrapole - Parmisse DURRANI-2006parmisd84No ratings yet
- Multipl As Camada SDocument30 pagesMultipl As Camada SWilliam BaileyNo ratings yet
- Optimize Aberration Theory DocumentDocument44 pagesOptimize Aberration Theory DocumentKatic TeodorNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Optics Lecture 6Document16 pagesNonlinear Optics Lecture 6t8enedNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio 2014Document2 pagesFormula Rio 2014Alberto García WatsonNo ratings yet
- Natural or Intrinsic CoordinatesDocument38 pagesNatural or Intrinsic CoordinatesDeepak ChachraNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet CSUNDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet CSUNKyle WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Regression MethodsDocument73 pagesNon-Linear Regression MethodsDNo ratings yet
- FORMULAE Formulas for Algebra, Calculus, Statistics, Geometry and TrigonometryDocument3 pagesFORMULAE Formulas for Algebra, Calculus, Statistics, Geometry and TrigonometryKama AzizNo ratings yet
- Plate Theory - 1 PDFDocument1 pagePlate Theory - 1 PDFkumaras1No ratings yet
- Appendix 16: Equation Sheet Chapter 1: Review of Modern PhysicsDocument14 pagesAppendix 16: Equation Sheet Chapter 1: Review of Modern PhysicsDragan SokolovskiNo ratings yet
- Teorija Električnih KolaDocument14 pagesTeorija Električnih KolaLuka NikitovicNo ratings yet
- 12 Nonreciprocal CircuitDocument14 pages12 Nonreciprocal CircuitTeerachot SiriburanonNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Analysis and Allowable Vibration Determination For The Piping SystemsDocument31 pagesDynamical Analysis and Allowable Vibration Determination For The Piping SystemsChirag ShahNo ratings yet
- Scattering Theory: P. ThangaduraiDocument23 pagesScattering Theory: P. ThangaduraiMohammad RameezNo ratings yet
- INTEGRALSDocument6 pagesINTEGRALSsaketgolyanNo ratings yet
- Info Sheet t2 2012Document4 pagesInfo Sheet t2 2012Luthando PuzaNo ratings yet
- PhononsDocument25 pagesPhononsPeter Đình-Khôi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Wave PropagationDocument23 pagesWave PropagationvichuNo ratings yet
- 3 - G Optics 3Document23 pages3 - G Optics 3Beauponte Pouky MezonlinNo ratings yet
- Formulario CalculoDocument2 pagesFormulario CalculoAntonio UuhNo ratings yet
- Integrale Nedefinite Si DerivateDocument2 pagesIntegrale Nedefinite Si DerivatemirelamanteamirelaNo ratings yet
- System Identification TechniquesDocument243 pagesSystem Identification TechniquesfonsverbiestNo ratings yet
- 17 InterferometersDocument84 pages17 InterferometersAnirban PaulNo ratings yet
- iNTERFERENCEDocument36 pagesiNTERFERENCEAditya [Sem 1&2]No ratings yet
- Formulario de Evaluación de Datos Y Calibración: X FX Z Z F X ZDocument4 pagesFormulario de Evaluación de Datos Y Calibración: X FX Z Z F X Zsaranya1919No ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Flyback ConverterDocument31 pagesLesson 9 - Flyback ConverterJhana Kimberly S. AquinoNo ratings yet
- 6., 7. Mintavétel, Statisztikai Becslés: Sokasági Várható Érték BecsléseDocument9 pages6., 7. Mintavétel, Statisztikai Becslés: Sokasági Várható Érték BecsléseRéka HunyadNo ratings yet
- FEM Higher Order ElementsDocument28 pagesFEM Higher Order Elementsjoshibec100% (1)
- Elektronika 2-Usmeni Ispit - VedekDocument12 pagesElektronika 2-Usmeni Ispit - Vedekpancaro93No ratings yet
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDocument56 pagesChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Charotar University of Science and TechnologyDocument7 pagesCharotar University of Science and TechnologyDarshan SoniNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Week 13 LecturesDocument8 pagesMechanics of Solids Week 13 LecturesFlynn GouldNo ratings yet
- Static Economy Functional FormDocument5 pagesStatic Economy Functional Formbobo411No ratings yet
- Rotational Motion 2009 7Document85 pagesRotational Motion 2009 7Julian BermudezNo ratings yet
- Table of derivative formulasDocument1 pageTable of derivative formulasaddamo13No ratings yet
- Determining Wavelength of Light Using Newton's RingsDocument8 pagesDetermining Wavelength of Light Using Newton's RingsVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- S. V. Bulanov-Extreme Light - Matter Interactionthrough The Lensesof The Relativistic Flying Mirror ConceptDocument67 pagesS. V. Bulanov-Extreme Light - Matter Interactionthrough The Lensesof The Relativistic Flying Mirror ConceptELI BeamlinesNo ratings yet
- PPS W0R Estimation TechniquesDocument1 pagePPS W0R Estimation TechniquesAhmad JailaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Filter Analysis & Design FundamentalsDocument37 pagesDigital Filter Analysis & Design FundamentalsSamhithaNo ratings yet
- P, SV, SH Waves Boundary Conditions, Snell’s Law, and Ray ParameterDocument4 pagesP, SV, SH Waves Boundary Conditions, Snell’s Law, and Ray ParameterIbnu RusydyNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question PaperDocument12 pagesAIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question Papermohit24031986No ratings yet
- Solar CellDocument38 pagesSolar CellBhargav ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Arithmetic: Implementations and Applications: A TutorialDocument30 pagesDistributed Arithmetic: Implementations and Applications: A Tutorialmurlak37No ratings yet
- Exam1 F02Document2 pagesExam1 F02fuenincNo ratings yet
- Ux VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoDocument2 pagesUx VX : Função Derivada Da Função Fórmulas de IntegraçãoJosierBaiottoNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- 02-Ray Optics IIDocument29 pages02-Ray Optics IIPark MinkukNo ratings yet
- Fluke111 ManualDocument18 pagesFluke111 ManualPark MinkukNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 121Document2 pagesSyllabus 121Park MinkukNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 121Document2 pagesSyllabus 121Park MinkukNo ratings yet