Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Critical Thinking1
Uploaded by
Dheeraj SrinathCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Critical Thinking1
Uploaded by
Dheeraj SrinathCopyright:
Available Formats
Critical
Thinking
What is critical thinking?
It is thinking that is purposeful, reasoned, and goal directed
It is searching, plotting, making associations, explaining,
analyzing, probing for multiple angles, justifying, scrutinizing,
making decisions, solving problems, and investigating
It is literally thinking about something from many angles.
Critical thinking is about making informed, enlightened,
educated, open-minded decisions in college in relationships in
finances and decisions in life in general.
Critical Thinking
To think critically, we must ask questions about the
information or data we have collected.
Is it important?
Is it relevant?
Is it applicable?
Is it significant?
But thats not enough. We must also ask questions about
the conclusion weve drawn from the information weve
collected
Is the conclusion fair?
Is it logical?
Is it reasonable?
Is it consistent with all the information collected?
Techniques of critical
thinking
Mind Mapping
Map whatever yours
mind thinks.
6 Thinking Hats
Using 6 different
mindsets to solve a
problem.
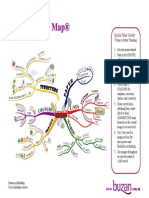
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a diagram used to visually outline
information.
A mind map is often created around a single word
or text, placed in the center, to which associated
ideas, words and concepts are added.
Major categories radiate from a central node, and
lesser categories are sub-branches of larger
branches.
Categories can represent words, ideas, tasks, or
other items related to a central key word or idea.
Guidelines
Start in the center with an image of the topic, using
at least 3 colors.
Use images, symbols, codes, and dimensions
throughout your mind map.
Select key words and print using upper or lower
case letters.
Each word/image is best alone and sitting on its
own line.
The lines should be connected, starting from the
central image. The central lines are thicker, organic
and thinner as they radiate out from the center.
Make the lines the same length as the word/image
they support.
Use multiple colours throughout the mind map, for
visual stimulation and also to encode or group.
Develop your own personal style of mind mapping.
Use emphasis and show associations in your mind
map.
Keep the mind map clear by using radial hierarchy,
numerical order or outlines to embrace your
branches.
Six Thinking Hats
There are six different imaginary hats that you
can put on or take off.
Think of the hats as thinking icons.
Each hat is a different color and represents a
different type or mode of thinking.
We all wear the same hat (do the same type of
thinking) at the same time.
When we change hats - we change our
thinking.
The Blue Hat Role
Only one blue hat in a group.
Control the thinking & the process
Begin & end session with blue hat
Role of Blue Hat:
o open, sequence, close
o Focus: what should we be thinking about
o Asking the right questions
o Defining & clarifying the problem
o Setting the thinking tasks
April 2009
Anne Egros- International Business
Coach-Zest and Zen
13
Thinking Process
Why we are here
what we are thinking about
Definition of the situation or problem
Alternative definitions
what we want to achieve
where we want to end up
The background to the thinking
White Hat Thinking
1. Neutral, objective information
2. Facts & figures
3. Questions: what do we know, what dont we
know, what do we need to know
4. Excludes opinions, judgments
5. Removes feelings & impressions
Green Hat Thinking
1. New ideas, concepts, perceptions
2. Deliberate creation of new ideas
3. Alternatives and more alternatives
4. New approaches to problems
5. Creative & lateral thinking
Yellow Hat Thinking
1. Positive & speculative
2. Positive thinking, optimism, opportunity
3. Benefits
4. Best-case scenarios
5. Exploration
Black Hat Thinking
1. Cautious and careful
2. Logical negative why it wont work
3. Critical judgement, pessimistic view
4. Separates logical negative from emotional
5. Focus on errors, evidence, conclusions
6. Logical & truthful, but not necessarily fair
Red Hat Thinking
1. Emotions & feelings
2. Intuitions, impressions
3. Doesnt have to be logical or consistent
4. No justifications, reasons or basis
5. All decisions are emotional in the end
Hats sequence in meetings
1. Facilitator (Blue Hat) Open Clarifying the problem
2. Present the facts of the case (White Hat).
3. Generate ideas, how the case could be handled (Green Hat).
4. Evaluate the merits of the ideas, List benefits (Yellow Hat).
5. List drawbacks (Black Hat).
6. Get everybody's gut feeling about the alternatives (Red Hat).
7. Summarize (Blue Hat).
You might also like
- Critical Thinking: 8 Surprisingly Effective Ways To Improve Critical Thinking Skills. Think Fast, Smart and Clear (Improve Logic and Analytical Skills)From EverandCritical Thinking: 8 Surprisingly Effective Ways To Improve Critical Thinking Skills. Think Fast, Smart and Clear (Improve Logic and Analytical Skills)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Six Thinking HatsDocument34 pagesSix Thinking HatsNishanthan100% (1)
- Six Thinking HatsDocument14 pagesSix Thinking HatsShruthi ManoharanNo ratings yet
- SixThinking Hats OverviewDocument17 pagesSixThinking Hats OverviewGeetha RajappaNo ratings yet
- 26.10six Thinking Hats - Efficient Decision Making TechniqueDocument51 pages26.10six Thinking Hats - Efficient Decision Making TechniqueRamesh Chandra DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 709 7Document45 pagesLecture 7 709 7Izzatullah JanNo ratings yet
- De Bono 6 Thinking Hats PPDocument20 pagesDe Bono 6 Thinking Hats PPDela Cruz GenesisNo ratings yet
- Six Thinking Hats: How To Use Edward Debono'S Parallel Thinking in Problem SolvingDocument14 pagesSix Thinking Hats: How To Use Edward Debono'S Parallel Thinking in Problem SolvingKaustavNo ratings yet
- 6 Thinking HatsDocument53 pages6 Thinking HatsAastha Arora100% (1)
- Change Management 6 Thinking HatsDocument22 pagesChange Management 6 Thinking Hatsswishrick18No ratings yet
- Creative Problem Solving With: Six Thinking HatsDocument11 pagesCreative Problem Solving With: Six Thinking Hatssaini420420No ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Ch4Document19 pagesCritical Thinking Ch4Wael Omran AlyNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Binal Gala Divisha Khera Komal Ganatra Meenakshi Guar Rashmi Sareen Suamya KapurDocument20 pagesPresented By:: Binal Gala Divisha Khera Komal Ganatra Meenakshi Guar Rashmi Sareen Suamya KapurBinal Gala100% (1)
- Six Thinking Hats: Edward Debono'S Parallel ThinkingDocument16 pagesSix Thinking Hats: Edward Debono'S Parallel ThinkingMyriam Vidi AstariNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps and Thinking Hats: Prof. Lakshman Madurasinghe, PHD Consultant Psychologist AttorneyDocument42 pagesMind Maps and Thinking Hats: Prof. Lakshman Madurasinghe, PHD Consultant Psychologist AttorneyAhmad Muhmad GhazaalNo ratings yet
- Edward de Bono's 6 Thinking HatsDocument29 pagesEdward de Bono's 6 Thinking HatsRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Six Thinking HatsDocument23 pagesSix Thinking HatsnoolanagarajuNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyDarshikasanghaniNo ratings yet
- De Bono PowerpointDocument32 pagesDe Bono PowerpointandromterNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving With: Six Thinking HatsDocument16 pagesProblem Solving With: Six Thinking HatsTIWARI priyanshuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Thinking SkillsDocument55 pagesChapter 1 Thinking SkillsnurulnabilahshaaraniNo ratings yet
- 4thweek-Designthinking-GEP0314 5 2020Document21 pages4thweek-Designthinking-GEP0314 5 2020Çağlar SivriNo ratings yet
- Creative Problem Solving With: Six Thinking HatsDocument20 pagesCreative Problem Solving With: Six Thinking Hatszaya sarwarNo ratings yet
- 6 Hat Thinking Techniques PDFDocument20 pages6 Hat Thinking Techniques PDFKishor LamdandeNo ratings yet
- 6 Hats ThinkingDocument4 pages6 Hats ThinkingPrabhpreet Singh100% (1)
- Dr. Gunjan Mathur: Six Thinking HatsDocument32 pagesDr. Gunjan Mathur: Six Thinking HatsGunjan Mathur100% (1)
- Six Thinking HatsDocument10 pagesSix Thinking HatsLee JianNo ratings yet
- Six Thinking Hats SummaryDocument8 pagesSix Thinking Hats SummaryPeter AtkinsonNo ratings yet
- DeBono - S Six Thinking HatsDocument12 pagesDeBono - S Six Thinking HatsMansingh jainNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Brain Model+Hats+Mind Map OBHRMDocument5 pagesModule 2 - Brain Model+Hats+Mind Map OBHRMriyanshi.natani398No ratings yet
- Topic 5 Creative Problem SolvingDocument44 pagesTopic 5 Creative Problem SolvingPREMIUM2023No ratings yet
- De Bonos Six Thinking HatsDocument7 pagesDe Bonos Six Thinking HatsBrian100% (2)
- Topic 4 Tourism Management Tourism Product DevelopmentDocument5 pagesTopic 4 Tourism Management Tourism Product DevelopmentAntonette SayconNo ratings yet
- 2 - Lec 3 Critical ThinkingDocument37 pages2 - Lec 3 Critical Thinkingmohanadhussein536No ratings yet
- Six Thinking Hats ExerciseDocument2 pagesSix Thinking Hats ExerciseAdina PopescuNo ratings yet
- Six Thinking Hats: An Edward de Bono ConceptDocument11 pagesSix Thinking Hats: An Edward de Bono ConceptVandana DesaiNo ratings yet
- Six HatsDocument1 pageSix HatsShareeLeongNo ratings yet
- 6 Thinking HatsDocument2 pages6 Thinking HatsSolomon Ezekiel OlajideNo ratings yet
- Critical and Creative ThinkingDocument12 pagesCritical and Creative Thinkingnavina yogeshNo ratings yet
- Brainstorming and Mind MapDocument17 pagesBrainstorming and Mind MapSimiso NdlovuNo ratings yet
- 6 Thinking Hats: Edward de BonoDocument16 pages6 Thinking Hats: Edward de BonoSivarama Krishna SNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making: Mahesh K PrasadDocument36 pagesDecision-Making: Mahesh K PrasadSwathi GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- PPT01 - Creativity and InnovationDocument30 pagesPPT01 - Creativity and Innovationadelia zahraNo ratings yet
- Six HatsDocument85 pagesSix Hatsanna39No ratings yet
- Generating Options and Alternatives: Brainstorming, Mind Mapping and Lateral ThinkingDocument26 pagesGenerating Options and Alternatives: Brainstorming, Mind Mapping and Lateral ThinkingEmi YunzalNo ratings yet
- Creativity WorkshopDocument42 pagesCreativity WorkshopRamyaa RameshNo ratings yet
- 6 Thinking HatsDocument32 pages6 Thinking HatsAakriti Patwari100% (1)
- Thinking SkillsDocument8 pagesThinking SkillsmchonvicNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument27 pagesCritical ThinkingWaheeda AltafNo ratings yet
- 6 Hats by MovasalatDocument16 pages6 Hats by MovasalatVrajesh ShahNo ratings yet
- SixthinkinghatsDocument10 pagesSixthinkinghatsapi-248496621No ratings yet
- Six Thinking HatsDocument18 pagesSix Thinking HatsjyotibudhrajaNo ratings yet
- How To Apply 6 Hats ThinkingDocument19 pagesHow To Apply 6 Hats ThinkingAnonymous qPt2MHzXT100% (3)
- Lateral Thinking: The Concept of "Six Thinking Hats" Developed by Ed de BonoDocument9 pagesLateral Thinking: The Concept of "Six Thinking Hats" Developed by Ed de BonoMonisha ParekhNo ratings yet
- 8D - Problem SolvingDocument43 pages8D - Problem Solvingkhairolanuarmasuan100% (1)
- Six Thinking Hats - Learn More: HereDocument2 pagesSix Thinking Hats - Learn More: Hereashstu88No ratings yet
- Thinking in Hats (Edward de Bono)Document23 pagesThinking in Hats (Edward de Bono)Rahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Six Thinking HatsDocument11 pagesSix Thinking Hatsssg7111No ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: Improve Your Academic Standards and ObjectivityFrom EverandCritical Thinking: Improve Your Academic Standards and ObjectivityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- A Study On Customer's Brand Loyalty Towards OralDocument12 pagesA Study On Customer's Brand Loyalty Towards OralDheeraj SrinathNo ratings yet
- Critical System ValidationDocument13 pagesCritical System ValidationDheeraj SrinathNo ratings yet
- Encryption and Case Study On Data Protection: BY: Dheeraj SrinathDocument15 pagesEncryption and Case Study On Data Protection: BY: Dheeraj SrinathDheeraj SrinathNo ratings yet
- Database Models: Presented by - Dheeraj Srinath 131GCMA035Document19 pagesDatabase Models: Presented by - Dheeraj Srinath 131GCMA035Dheeraj SrinathNo ratings yet
- Technology in Retail: By: Dheeraj Basavraj Maimom SriduttaDocument10 pagesTechnology in Retail: By: Dheeraj Basavraj Maimom SriduttaDheeraj SrinathNo ratings yet
- Health Care Industry1Document8 pagesHealth Care Industry1Dheeraj SrinathNo ratings yet
- Science Folio-Assessment Task 1aDocument6 pagesScience Folio-Assessment Task 1aapi-318070288No ratings yet
- ACTIVITY: Here Is The Quick and Simple Test (Simple Test For Dominant Learning Style) To FindDocument8 pagesACTIVITY: Here Is The Quick and Simple Test (Simple Test For Dominant Learning Style) To Findkaren grace salatan100% (1)
- ChatGPT Guide Use These Prompt Strategies To Maximize Your ResultsDocument12 pagesChatGPT Guide Use These Prompt Strategies To Maximize Your ResultsBirkimsaNo ratings yet
- Recycling Mind MapDocument2 pagesRecycling Mind Mapmsole124100% (1)
- GESE Grades 7-9 - Lesson Plan 1 - Choosing Topics (Final)Document6 pagesGESE Grades 7-9 - Lesson Plan 1 - Choosing Topics (Final)aquaman2001No ratings yet
- Freeplane Handbook Fullcircle Parts 1 14Document42 pagesFreeplane Handbook Fullcircle Parts 1 14Andrei Cuturela100% (1)
- LSA 3: Reading Skill: Part 2: Lesson PlanDocument18 pagesLSA 3: Reading Skill: Part 2: Lesson PlanRavi ManoharNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document8 pagesLesson Plan 1api-316778650No ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument8 pagesConcept PaperJani SoleilNo ratings yet
- Management Consulting Edison 3Document18 pagesManagement Consulting Edison 3Divyaprakash PandaNo ratings yet
- NATE Module 2 - Week 8 - 1 PDFDocument26 pagesNATE Module 2 - Week 8 - 1 PDFKoushik V PrasadNo ratings yet
- Efficient and Effective Academic Reading: Online ResourceDocument16 pagesEfficient and Effective Academic Reading: Online ResourceFahimul Hoque JisanNo ratings yet
- Seven Pillars of Creativity in The Primary Classroom PDFDocument8 pagesSeven Pillars of Creativity in The Primary Classroom PDFAnda RascanuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 06 - Personal DevelopmentDocument6 pagesLesson 06 - Personal DevelopmentJade Quezon SabioNo ratings yet
- BSBOPS503 Student GuideDocument30 pagesBSBOPS503 Student GuideBui AnNo ratings yet
- Language and Tools Silvia RomaDocument3 pagesLanguage and Tools Silvia RomablablaNo ratings yet
- Outcomes Pre-Int TB Unit 10Document13 pagesOutcomes Pre-Int TB Unit 10Haneen DalatyNo ratings yet
- 3.mindmap ToolDocument14 pages3.mindmap ToolArul JothiNo ratings yet
- Effective Engagement Book 2Document128 pagesEffective Engagement Book 2TheCPNo ratings yet
- NCPAG PAkilalaDocument19 pagesNCPAG PAkilalaJules GuiangNo ratings yet
- RPT English Form 1 KSSMDocument17 pagesRPT English Form 1 KSSMaqilahaiman67% (3)
- Overview of Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesOverview of Lesson PlanYui FauzianiNo ratings yet
- 13 The SQ3R Method of Reading and The 6 Stages of Accelerated LearningDocument20 pages13 The SQ3R Method of Reading and The 6 Stages of Accelerated LearningJames JohnsonNo ratings yet
- A Mind Map Laws PadDocument2 pagesA Mind Map Laws PadzskebapciNo ratings yet
- CIDAM EntrepDocument32 pagesCIDAM EntrepGenner Raz86% (7)
- Personal Development (1st) - Lesson 6 - The Powers of MindDocument24 pagesPersonal Development (1st) - Lesson 6 - The Powers of MindJohannaHernandez86% (14)
- Early Career English Teacher Identity ReportDocument28 pagesEarly Career English Teacher Identity ReportNguyễn LinhNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Concept PaperDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Concept PaperJigar ChavdaNo ratings yet
- ConceptDraw Samples - Management - SWOT and TOWS MatricesDocument8 pagesConceptDraw Samples - Management - SWOT and TOWS MatricesToto SubagyoNo ratings yet
- RW Lesson 1Document3 pagesRW Lesson 1isabella marieNo ratings yet