Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation
Uploaded by
Chandan Gowda GCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation
Uploaded by
Chandan Gowda GCopyright:
Available Formats
Floors and Roofs
G.CHANDAN
K.B.PRAKASH
P.VIGNESH
S.VIGNESH
FLOORS
INTRODUCTION
Floors are horizontal elements of building structures which support live
loads such as people, furnishings, and movable equipment and dead loads
(the weight of the floor itself, any non-movable, built-in components on the
floor).
It divides building into different levels for the purpose of creating more
accommodation with in the restricted space.
FACTORS CONSIDERED FOR SELECTION OF
FLOORING
Durability and wear factors.
Free from dampness.
Appearance.
Fire Resistant.
Low Maintenance cost.
METHODS OF FLOORING
1.Concrete block/ inner wall
2. Outside wall
3. Hardcore infill
4. Damp-proof membrane
5. Sand blinding
6. Min 100mm concrete
a) Solid Concrete
b) Suspended Concrete
1. Concrete block
2. Outside wall
3. Concrete block/ inner wall
4. Sleeper wall
5. Concrete beam
Types ,Method of Construction and
Advantages and Disadvantages
TYPES OF FLOORING
Cement Concrete Flooring.
Tile Flooring.
Mosaic Flooring.
Cement Concrete Floor
The floor having its topping consisting of cement concrete is called
Cement Concrete Floor or Conglomerate
CLASSIFICATION:
1. Non-monolithic or bonded floor finish concrete floor
2. Monolithic floor finish concrete floor.
1. Non-monolithic or Bonded floor finish concrete Floor
It is a flooring where topping is not laid monolithically with the base
concrete.
METHOD:
The earth is consolidated and 10cm thick layer of clean sand is spread.
10cm thick Lime Concrete (1:4:8) or Lean Cement Concrete (1:8:16) is
laid thus forming base concrete.
The topping (1:2:4) is laid on the third day of laying base cement
concrete, thus forming Non-monolithic construction.
2. Monolithic floor finish concrete Floor
It is a flooring where topping of 2cm thick concrete is laid monolithically
with the base concrete.
METHOD:
The surface of earth filling is levelled, well watered and rammed, 10cm
layer of clean and dry sand is spread over.
When the sub soil conditions are not favourable, then 5cm to 10cm thick
hard core of dry brick or rubble filling is laid.
10 cm of Base concrete is laid followed by topping concrete 2cm after
45 min to 4 hrs
Durable and wearing surface
Sustain Impact loads hence
adopted in industrial buildings
Base layer for other type of
flooring
Cause injuries if fallen
Causes nerve numb in cold
weather as since it does not
retain heat in bare foot.
Due to hardness makes it
uncomfortable to stand for
long time
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Tile Floor
The floor having its topping consisting of tiles is called tile floor.
METHOD:
The earth filling is properly consolidated, 10cm thick layer of dry sand is evenly laid.
10cm thick layer of Lime Concrete (1:4:8) is laid , compacted and cured to form a base
concrete
A thin layer of lime or cement mortar is spread with the help of screed battens.
Then the screed battens are properly levelled and fixed at the correct height.
When the surface mortar is hardened, 6mm thick bed of wet cement (1:5) is laid
and then over this the specified tiles are laid.
Tile Floor
The surplus mortar which comes out of the joints is cleaned off.
After 3 days, the joints are well rubbed with a corborundum stone to chip
off all the projecting edges.
Durable
Difficult to crack
Maintenance is easy and
so adopted in all residential
buildings .
Available in different varieties.
Does not hold heat so causes
blood clotting in bare foot
during winter
Expensive
Ceramic tiles are quite heavy
so not adopted in high rise
buildings
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Mosaic Floor
The floors having its topping consisting of mosaic tiles or small regular cubes,
square or hexagons, embedded into a cementing mixture.
METHOD:
The earth is consolidated, 10cm thick layer of clean sand is spread.
10cm thick Lime Concrete (1:4:8) or Lean Cement Concrete (1:8:16) is laid forming
base concrete.
Over this 5cm thick Lime Mortar or Cement Mortar or Lime and Surkhi mortar (1:2)
is laid.
3mm thick cementing mixture is spread, The cementing mixture consists of one part
of pozzolana, one part of marble chips and two parts of slacked lime.
Now the tiles of regular shaped marble cubes are hammered in the mortar along
the outline of the pattern.
The inner spaces are then filled with colored pieces of marble and a roller is passed
over the surface.
The surface is rubbed with pumice stone fixed to a wooden handle about 1.5m long.
The surface is then allowed to dry up for 2 weeks.
Aesthetic
In Luxury Buildings
Proper grip and traction for
the people using it
Very expensive and high cost
of maintenance
Rehabilitaion is difficult
and time consuming
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Roofs
What is a Roof ?
A roof is part of a building envelope, both the covering on the
uppermost part of a building or shelter which provides protection
from animals and weather, notably rain, but also heat, wind
and sunlight; and the framing or structure which supports the
covering.
Types of Roof construction :
1. Flat roof
2. Pitched Roof
Design elements
Design
elements
Durability
material
Constructio
n
1. Durability
2. Construction
3. Material
Roof Types
Roofing materials
The selection of roofing materials is based on the following factors.They are
1. Investment
2. Conditions
3. Energy Efficiency
Construction of Roof
Types of Roof Construction
A flat roof is generally defined as having a
pitch not greater than 15 to the horizontal
A pitched or sloping roof has a pitch
of at least 15 but often much more
Flat Roof Construction
Its constructed based on the conditions namely:
o Cold roof
o Warm roof
Pitched Roof Construction
Its constructed based on the conditions namely:
o Cold roof
o Warm roof
Thank you
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MF Ceiling Calculator: Primary Channel at 1200mm Centres, Furring Channel at 450mm CentresDocument2 pagesMF Ceiling Calculator: Primary Channel at 1200mm Centres, Furring Channel at 450mm CentresAngel JinHiroNo ratings yet
- Project progress report with construction delaysDocument29 pagesProject progress report with construction delaysHesham MohamedNo ratings yet
- 01 JSB551 Introduction To Design of Multi Storey BuildingsDocument34 pages01 JSB551 Introduction To Design of Multi Storey BuildingsBarongan BsgNo ratings yet
- Composite Construction MethodsDocument53 pagesComposite Construction MethodsChino PadolinaNo ratings yet
- Building Structure Terms ExplainedDocument4 pagesBuilding Structure Terms ExplainedViberlie PonterasNo ratings yet
- IEI Rules of Thumb Line Card 03012016Document2 pagesIEI Rules of Thumb Line Card 03012016Anonymous 4ItkiwINo ratings yet
- Indirect Heat Gain System:: Five Elements of A Thermal Storage Wall Can Be IdentifiedDocument20 pagesIndirect Heat Gain System:: Five Elements of A Thermal Storage Wall Can Be IdentifiedAbishaTeslinNo ratings yet
- Ieoh Ming PeiDocument12 pagesIeoh Ming Peiriddhima100% (1)
- QC Inspectors Tool Box Meeting ScheduleDocument1 pageQC Inspectors Tool Box Meeting ScheduleadnanNo ratings yet
- 2013 ALE Board ExamsDocument4 pages2013 ALE Board ExamsJonas MakiramdamNo ratings yet
- U Value ExplainedDocument3 pagesU Value ExplainedNidhi MehtaNo ratings yet
- RARP Admin Building-Design PDFDocument22 pagesRARP Admin Building-Design PDFravi kumarNo ratings yet
- A Study of Efficiency of Natural Ventilation Strategies in A Library BuildingDocument6 pagesA Study of Efficiency of Natural Ventilation Strategies in A Library BuildingAaron lisboaNo ratings yet
- Works of Antoni GaudíDocument13 pagesWorks of Antoni GaudíPaula LNo ratings yet
- Proposed Building of Service Apartment in Sri Rangam, TrichyDocument1 pageProposed Building of Service Apartment in Sri Rangam, TrichyGopal KrishNo ratings yet
- Standards and Tolerances GuideDocument74 pagesStandards and Tolerances GuideJoseph Cloyd L. LamberteNo ratings yet
- Assignment Portal FrameDocument3 pagesAssignment Portal FrameShakiraNo ratings yet
- Partition - Metal StudDocument27 pagesPartition - Metal StudJaiNo ratings yet
- Hollow-core Slab Systems Information ManualDocument36 pagesHollow-core Slab Systems Information ManualEng.wissam Safaa100% (1)
- Revit MEP PresentationDocument73 pagesRevit MEP PresentationShubham PuriNo ratings yet
- Arki ExamDocument29 pagesArki ExamAngela LaraNo ratings yet
- Posi Struts DetailsDocument15 pagesPosi Struts DetailsSuciul E ViuNo ratings yet
- A. Admixtures 1. Air Entraining AgentsDocument26 pagesA. Admixtures 1. Air Entraining AgentsShady RainNo ratings yet
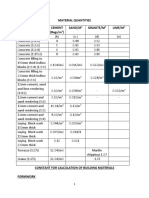
- Material Quantities MIX Cement (Bags/m) Sand/M Granite/M Lime/MDocument5 pagesMaterial Quantities MIX Cement (Bags/m) Sand/M Granite/M Lime/Mjmarkunongo_69397286No ratings yet
- School in GandoDocument6 pagesSchool in GandorenNo ratings yet
- A SmoothKitchenCabinetInstallationDocument142 pagesA SmoothKitchenCabinetInstallationEsteban Yepes0% (1)
- Fine Homebuilding - Framing A Cross-Gable RoofDocument5 pagesFine Homebuilding - Framing A Cross-Gable RoofSrcNo ratings yet
- HELIT015 Oct15 High Rise Facades DIGuide-2Document60 pagesHELIT015 Oct15 High Rise Facades DIGuide-2alfieNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialsDocument8 pagesBuilding MaterialsMagda Szymanska Piotrek SzymanskiNo ratings yet
- Camber GuidelineDocument1 pageCamber GuidelineShamsul IslamNo ratings yet