Professional Documents
Culture Documents
"7 Habits of Highly Effective People" Summary
Uploaded by
Raj Kumar SharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
"7 Habits of Highly Effective People" Summary
Uploaded by
Raj Kumar SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTE:
To change the
image on this
slide, select
the picture and
delete it. Then
click the
Pictures icon in
the placeholder
to insert your
own image.
THE 7 HABITS OF
HIGHLY EFFECTIVE
PEOPLE
Power Lessons in Personal Change
By Stephen R Covey
About the Author
Stephen Richards Covey (October 24, 1932
July 16, 2012)
American educator, author, businessman, and
keynote speaker.
His most popular book ,The Seven Habits of
Highly Effective People , has sold more than 25
million copies worldwide.
Education:
Bachelor of Science degree in business
administration from the University of Utah,
MBA from Harvard University,
Doctor of Religious Education (DRE)
from Brigham Young University.
Ten honorary doctorates.
Personality Ethics vs. Character Ethics
Personality Ethics
The success literature of the last
half of the 20th century largely
attributed success to personality
traits, like
public image,
attitudes and behaviors,
skills and techniques that
lubricate the processes of
human interaction,
PMA, etc.
This philosophy can be referred
to as the Personality Ethic.
Character Ethics
However, 150 years prior, the literature on
success was character oriented. It emphasized
the deeper principles and foundations of
success.
This philosophy is known as the Character Ethic,
under which success is attributed more to such
as:
Humility
fidelity
courage,
justice,
patience,
simplicity,
modesty etc.
Personality Ethics vs. Character Ethics
According to Covey,
Both are important for Long term success. But
Personality Ethics Secondary Traits (Only Short term Success)
Character Ethics Primary Traits
What we are communicates far more eloquently than anything we say or do.
We all know it. There are people we trust absolutely because we know their
character. Whether they're eloquent or not, whether they have the human relations
techniques or not, we trust them, and we work successfully with them.
Paradigm
It's the way we "see" the world -- not in terms of our visual sense of sight, but in
terms of perceiving, understanding, and interpreting.
The basic problem with failure is not our behavior or attitude , it is our
understanding of the situation. It can be called as MENTAL MAP OF LIFE.
Two types of Mental Maps:
maps of the way things are, or realities, and
maps of the way things should be, or values.
We interpret everything we experience through these mental maps. We seldom
question their accuracy; we're usually even unaware that we have them. We simply
assume that the way we see things is the way they really are or the way they should
be. And our attitudes and behaviors grow out of those assumptions. The way we
see things is the source of the way we think and the way we act.
Paradigm Shift and Inside Out
Paradigm Shifts move us from one way of seeing the world to another.
We can only achieve quantum improvements in our lives if we
quit hacking at the leaves of attitude and behavior
get to work on the root, the paradigms from which our attitudes and behaviors flow.
But how ????
Answer given by Covey : We need a new level, a deeper level of thinking. A dramatic paradigm, shift
called the Inside-Out approach
"Inside-Out" means to start first with self; even more fundamentally, to start with the most inside part
of self -- with your paradigms, your character, and your motives.
The Inside-Out approach says that Private Victories precede Public Victories, that making and keeping
promises to ourselves precedes making and keeping promises to others.
It is futile to put personality ahead of character, to try to improve relationships with others before
improving ourselves.
Habits - Defined
Knowledge
(What to and
Why?)
Desire
(Want to)
Skills
(How to)
Habit
The Maturity Continuum
The Seven Habits are not a set of separate
formulas, but
incremental, sequential, highly integrated
approach to the development of personal and
interpersonal effectiveness.
Follows natural laws of growth
Dependence is the paradigm of you -- you take
care of me; you come
through for me; you didn't come through; I blame
you for the results.
Independence is the paradigm of I -- I can do it; I
am responsible; I am self-reliant; I can choose.
Interdependence is the paradigm of we -- we can
do it: we can cooperate; we can combine our
talents and abilities and create something greater
together.
HABIT 1
BE PROACTIVE
Habit 1 : Be Proactive
The term "proactive" as coined by Victor Frankl.
You can either be proactive or reactive when it comes to how you respond to things.
When you are reactive, you blame other people and circumstances for obstacles or
problems.
Being proactive means taking responsibility for every aspect of your life.
Between stimulus and response, we have the power of free will to choose our response.
FREEDOM OF RESPONSE (Response-Ability):
Self-awareness: choose to become angry or not
Conscience: what you principles suggest
Creativity: envision other responses
Independent will
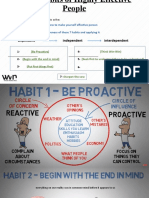
Habit 1: Be Proactive Continued
Circle of Concern: A circle depicting all the things we
are concerned about. Example: our health, our children,
problems at work, the national debt, nuclear war
Circle of Influence: A circle depicting all the things we
can do something about.
PROACTIVE people focus their efforts in the Circle of
Influence. They work on the things they can do something
about. The nature of their energy is positive, enlarging and
magnifying, causing their Circle of Influence to increase.
REACTIVE people, on the other hand, focus their efforts
in the Circle of Concern. They focus on the weakness of
other people, the problems in the environment, and
circumstances over which they have no control. Their focus
results in blaming and accusing attitudes, reactive
language, and increased feelings of victimization
HABIT 2
TO BEGIN WITH END IN MIND
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
Principle : All the Things are Created Twice
Mental or First Creation
Physical or Second Creation
By Design or Default
Leadership & Management The Two Creations
Leadership deals with the top line
Management is a bottom-line focus
Management is doing things right
leadership is doing the right things
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
Rescripting : Becoming Your Own First Creator
The two additional unique human endowments that enable us to
expand our proactivity and to exercise personal leadership in our
lives are imagination and conscience.
You can act with integrity.
You can be truly proactive, value driven, because your values are
clear.
You can tie yourself to your limitless potential instead of your
limiting past.
You can become your own first creator.
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
Create your Mission Statement :
Focus : What you want to be (Character) and to do (Achievements)
According to Values & Principles of Individuals
Examples :
Do not Repeat Your Mistakes
Be Punctual
Think Twice Before You Speak
Plan Tomorrows Work Today
Try Try But Dont Cry
Time Is Money
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
At The Center
We deal with our Vision and our Values
Whatever is at the center of our life will be the source of our Security,
Guidance, Wisdom, and Power.
Security : Represents your sense of worth, your identity.
Guidance : Means your source of direction in life.
Wisdom : Your perspective on life.
Power : The faculty or capacity to act.
Examples : Money Oriented, Work Oriented, Friend Oriented
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
Writing & Using a Personal Missing Statement :
Habit 1 : You are programmer
Habit 2 : Write the program
Imagination & Conscience
According To :
Deep Thinking
Central Analysis
Thoughtful Expression
Left and Right Hemisphere of Brain :
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
Two ways to Tap Right Brain :
Expand Perspective
Visualization & Affirmation
A good affirmation has five basic ingredients: it's personal, positive,
present tense, visual and emotional.
Mission Statement :
"It is deeply satisfying (emotional) that I (personal) respond (present tense) with
wisdom, love, firmness, and self-control (positive) when my Friends misbehave."
Habit 2 : To Begin with End in Mind
Application Suggestion :
Find separate time from daily activities.
Begin to work on your personal mission statement.
Start to collect quotes, notes & ideas which are useful in writing
personal mission statement.
Share your principles with your family & group and suggest to make
family & group mission statements.
HABIT 3
PUT FIRST THINGS FIRST
Habit 3:Put First Things First
The Power of Independent Will: In addition to self awareness, imagination &
conscience, this quality of human ch. makes effective self-management possible. Ability to
make decisions & choices and act accordingly.
Four Generations of Time Management:
1
st
Generation: Notes & Checklists centred,recognizing & including many demands on
our time & energy.
2
nd
Generation: Calendar & Appointment based, main concern on scheduling events &
activities.
3
rd
Generation: Prioritization, setting goals.
4
th
Generation: Preserving & Enhancing relationships rather than focusing on things &
time. Maintain the P/PC balance. Can be well represented in Time
Management Matrix.
THE TIME MANAGEMENT MATRIX
URGENT NOT URGENT
IMPORTANT I.
Immediate attention.
Crisis Manager, Problem-minded
People, Deadline-driven Producer.
Stress,Burnout,Crisis Management
etc.
II.
Deals with important but not
urgent. Building relationship, long
range planning, preventive
control, preparation etc.
Ideal for being personal
management effective.
NOT IMPORTANT
III.
Focus on Urgent Work Only.
Short Term Focus, Shallow or
Broken Relationships.
IV.
Most Irresponsible Life.
SOME BASIC LESSONS:-
1)Learn to say NO to the unwanted things but in a proper way. Needed a strong YES
burning inside.
2)For effective time & life management we have to work upon some basic areas, like:
i)ability to prioritize,
ii)ability to organize around these priorities &
iii)having executed in a disciplinary manner.
MOVING INTO QUADRANT II:-
1
s
t
G
e
n
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
p
e
o
p
l
e
No prioritization,
only
accomplishments,
Little productive,
little sense of
control & self
esteem.
Undependable &
irresponsible.
2
n
d
G
e
n
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
P
e
o
p
l
e
A little bit control is
there, plan in
advance &
schedule things
but again no
priority is there
depending on
deeper values and
goals of life. Few
significant
achievements.
3
r
d
G
e
n
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
P
e
o
p
l
e
Clarify their goals,
plan every day &
prioritize tasks.
But lack of vision,
only short term
goal.
No provision for
managing roles in
a balanced way.
QUADRANT II TOOL:-
Main Objective: Balance of life, focusing on important as well as urgent tasks,
Increase in production & production capability.
6 Areas of Concern:
1.Concern: harmony, Unity & Integrity between mission & vision, roles & goles,Priorities &
Plans.
2.balance:Maintaining balance for health, personal life, professional preparation & personal
development.
3.Quadrant II Focus:Organising lives in weekly basis, leading to better balance & context than
daily planning.
4.A People Dimension: Dealing with people not just schedule.Principle-centred value
oriented. Not only creation but also implementation of guilt when a schedule is not followed.
5.Flexibility: Use your planning tool as per your needs,style,keep provision for flexibility.
6.Portability: Portable tool to get it available whenever you need it.
BECOMING A QUADRANT II SELF MANAGER:-
Identify you key roles. Define your roles based on your upcoming week routine.
Selection of sort term goals based on your week activity but try to link it with your
long-term mission goal.
Scheduling :After identification & setting of goals we have to schedule our goals as
per prioprity & we should monitor the progress & concern to those unattained
areas.
After weekly organizing try to attach daily adaptation as a part of your life. Daily
concentrate on your schedulation of work which will bring proper value-based
decision. Be principle centred & make other lives different.
HABIT 4
Think Win-Win TM -- Principles of
Interpersonal Leadership
WHETHER YOU ARE THE PRESIDENT OF A COMPANY OR THE JANITOR, THE MOMENT YOU
STEP FROM INDEPENDENCE INTO INTERDEPENDENCE IN ANY CAPACITY, YOU STEP INTO A
LEADERSHIP ROLE.
YOU ARE IN A POSITION OF INFLUENCING OTHER PEOPLE.
As with many, many problems between people:
in business,
in family, and
in other relationships.
You are expecting much more from your work and it is obvious:
But you can't change the fruit without changing the root.
So we can focus instead on producing personal and organizational
excellence in an entirely different way by developing information
and reward systems which reinforced the value of cooperation.
SO HERE WIN WIN IS
Win-win is not a technique; it's a total philosophy of human interaction. In fact, it is one of six
paradigms of interaction.
Win-Win.
Win-win is a frame of mind and heart that constantly seeks mutual benefit in all human interactions.
Win-win means that agreements or solutions are mutually beneficial, mutually satisfying.
With a win-win solution, all parties feel good about the decision and feel committed to the action plan.
Win-win sees life as a cooperative, not a competitive arena.
The alternative paradigms are :
win-lose, lose-win, lose-lose, win, and Win-Win or No Deal TM
IT'S NOT YOUR WAY OR MY WAY; IT'S A
BETTER WAY,
A HIGHER
WAY.
Win-Lose
One alternative to win-win is win-lose, the paradigm of the race. It says "If I win, you lose. In
leadership style, win-lose is the authoritarian approach: "I get my way; you don't get yours."
Win-lose people are prone to use position, power, credentials, possessions, or
personality to get their way.
Most people have been deeply scripted in the win-lose mentality since birth. First
and most important of the powerful forces at work is the family. When one child is
compared with another --when patience, understanding or love is given or
withdrawn on the basis of such comparisons people are into win-lose thinking.
It's in comparison with somebody else or against some expectation.
Lose-Win
Some people are programmed the other way -- lose-win.
"I lose, you win."
"Go ahead. Have your way with me."
"Step on me again. Everyone does.
Lose-win is worse than win-lose because it has no standards -- no demands, no
expectations, no vision.
People who think lose-win are usually quick to please or appease. They seek
strength from popularity or acceptance.
They have little courage to express their own feelings and convictions and are easily
intimidated by the ego strength of others.
Lose-Lose
When two win-lose people get together -- that is, when two determined, stubborn,
ego-invested individuals interact -- the result will be lose-lose. Both will lose.
Some people become so centered on an enemy, so totally obsessed with the
behavior of another person that they become blind to everything except their desire
for that person to lose, even if it mean losing themselves.
Win
Another common alternative is simply to think win. People with the win mentality
don't necessarily want someone else to lose.
What matters is that they get what they want.
A person with the win mentality thinks in terms of securing his own ends --and
leaving it to others to secure theirs.
Which Option Is Best?
Of these five philosophies discussed so far -- win-win, win-lose, lose-win, lose-lose, and
win --which is the most effective?
The answer is, "It depends.
If you work in a regional office that is miles away from another regional office, and you
don't have any functional relationship between the offices, you may want to compete in
a win-lose situation to stimulate business.
However, you would not want to set up a win-lose situation like the contest within a
company or in a situation where you need cooperation among people or groups of
people to achieve maximum success.
If you value a relationship and the issue isn't really that important, you may want to go
for lose-win in some circumstances to genuinely affirm the other person. "What I want
isn't as important to me as my relationship with you. Let's do it your way this time."
THE BEST CHOICE, THEN, DEPENDS ON REALITY.
THE CHALLENGE IS TO READ THAT REALITY
ACCURATELY AND NOT TO
TRANSLATE WIN-LOSE OR OTHER SCRIPTING INTO
EVERY SITUATION.
CHARACTER
Character is the foundation of win-win, and everything else builds on that foundation. There are
three character traits essential to the win-win paradigm.
INTEGRITY. integrity as the value we place on ourselves.
As we clearly identify our values and proactively organize and execute around those values on a daily basis,
we develop self-awareness.
MATURITY. Maturity is the balance between courage and consideration.
If a person can express his feelings and convictions with courage balanced with consideration for the feelings
and convictions of another person, he is mature, particularly if the issue is very important to both parties.
ABUNDANCE MENTALITY. They see life as having only so much, as though there were only one pie out
there.
RELATIONSHIPS
From the foundation of character, we build and maintain win-win relationships.
The trust, the Emotional Bank Account, is the essence of win-win.
The trust, the Emotional Bank Account, is the essence of win-win. Without trust, the best we can
do is compromise.
Because we trust each other, we're open. We put our cards on the table.
A relationship where bank accounts are high and both parties are deeply committed to win-win
WIN-WIN PERFORMANCE
AGREEMENTS
Win-Win Agreement is the central activity of management. With an agreement in place, employees can
manage themselves within the framework of that agreement.
Win-win puts the responsibility on the individual for accomplishing specified results within clear guidelines
and available resources.
It makes a person accountable to perform and evaluate the results and provides consequences as a natural
result of performance.
HABIT 5
SEEKING FIRST TO UNDERSTAND, THEN
TO BE UNDERSTOOD
HABIT 5 : Seek first to understand , then to be understood
Powerful habit of effective interdependence.
Primary focus on Listening part of communication.
Empathic Listening :
Listening with an intent to understand.
You see through the person, you see the world the way they see and understand
how they feel.
You understand a person emotionally and intellectually.
Words, sound and body language function as a unit.
It's deeply therapeutic and healing because it gives a person psychological air.
When you listen with empathy to another person, you give that person
psychological air.
HABIT 5 : Seek first to understand , then to be understood
If you don't have confidence in the diagnosis, you won't have confidence in the
prescription. Example: A good engineer will understand the forces, the stresses at work,
before designing the bridge.
Because we listen autobiographically, we tend to respond in one of four ways, which
need to be avoided: We evaluate; we probe; we advise or we interpret.
The skills, the tip of the iceberg of empathic listening, involve four developmental stages:
1. The first and least effective is to mimic content. This is the skill taught in "active" or
"reflective" listening.
2. The second stage of empathic listening is to rephrase the content. You've put
meaning into other persons words.
3. The third stage brings your right brain into operation. You reflect feeling.
4. The fourth stage includes both the second and the third. You rephrase the content
and reflect the feeling, thus giving him psychological air. You also help him work
through his own thoughts and feelings.
HABIT 5 : Seek first to understand , then to be understood
Emphatic listening converts a transactional opportunity into a transformational
opportunity.
The key is to genuinely seek the welfare of the individual, to listen with empathy, to let
the person get to the problem and the solution at his own pace and time.
Seek First to Understand, Then to be Understood. Knowing how to be understood is the
other half of Habit 5, and is equally critical in reaching win-win solutions.
Seeking to understand requires consideration; seeking to be understood takes courage.
Win-win requires a high degree of both.
The Greeks gave the philosophy of three sequentially arranged words: ethos, pathos,
and logos. Ethos represents your personal credibility, the faith people have in your
integrity and competency. Pathos is the empathic side -- it's includes feeling and
relationships. Logos is the logic, the reasoning part of the presentation. All three need
to be implemented while performing a task.
Habit 5 is something you can practice right now. The next time you communicate with
anyone, you can put aside your own autobiography and genuinely seek to understand.
HABIT 6
SYNERGY
HABIT 6 : Synergy
At the business level, people move from mutual respect and understanding to
creative synergistic communication(collective free association, spontaneous
piggybacking of ideas).
Different levels of communication:
The lowest level of communication is characterized by defensiveness,
protectiveness, and often legalistic language. It produces only win-lose or lose-lose.
The middle position is respectful communication where fairly mature people
interact. They have respect for each other, but they want to avoid the possibility of
ugly confrontations, so they communicate politely but not empathically. It produces
a low form of win-win.
The highest level is synergistic communication.
Third Alternative: A solution that is mutually beneficial and is better than what either
of them originally proposed. The aim is to find an optimum solution that satisfies all
the parties involved.
HABIT 6 : Synergy
Negative Synergy: Highly dependent people trying to succeed in an interdependent
reality. They may talk win-win technique, but they don't really want to listen; they
want to manipulate.
The key to interpersonal synergy is intrapersonal synergy, that is synergy within
ourselves.
When a person has access to both the intuitive, creative, and visual right brain, and
the analytical, logical, verbal left brain, then the whole brain is working which is
highly synergistic.
Force Field Analysis: A model in which describes any current level of performance or
being as a state of equilibrium between the driving forces that encourage upward
movement and the restraining forces that discourage it.
Driving forces generally are positive, reasonable, logical, conscious, and economic.
Restraining forces are often negative, emotional, illogical, unconscious, and
social/psychological. You unfreeze the restraining forces, loosen them up, and
create new insights that actually transform those restraining forces into driving ones.
Habit 7: Sharpen the saw
The Spiritual Dimension
Renewing the spiritual dimension provides leadership to your life
Your core, your center
Commitments to your value system
Private are and supremely important
The Physical Dimension :
Caring effectively for your body
Eating right kind of food
Getting sufficient rest
Exercise on regular bases
Habit 7: Sharpen the saw
The Mental Dimension :
Educating yourself
Reading
Planning
Writing
Social and emotional dimension :
Talks about the Public victory necessary for habit 4,5,6.
Communication
Listening and understanding
Coming with common solution(Win Win)
Habit 7: Sharpen the saw
Scripting Others
1)Act as social mirror
2)Script by opinions and perceptions
3)Positive script
Balance in renewal
If any one dimension is neglected it may affect other dimensions too.
In organization we can relate these dimensions as
1)Physical:- economic
2)mental:-recognition and development.
3)Social/emotional:-Human relations
4)Spiritual:-finding meaning through purpose or contribution.
Synergy in renewal
Habit 7: Sharpen the saw
The Upward Spiral :
Conclusion
In this book Author presents principle centric approach for solving
personal and professional problems.
He reveals step by step pathway for living with fairness, integrity,
honesty and human dignity principles.
GROUP MEMBERS:
RAJ KUMAR SHARMA (14030241122)
PRIYANK PATEL (14030241120)
HIMANSHU GUPTA (14030241120)
SOURADYUTI CHATTERJEE (14030241130)
RUTUJA TEMBHURNE (14030241120)
AJINKYA WAGH (14030241120)
You might also like
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective People PPT - Covey StephenDocument142 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective People PPT - Covey StephenVijay Kumar100% (10)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument38 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeoplePayal Malik100% (1)
- Summary: The 7 Habits Of Highly Effective People … In 15 Minutes The Super-Human Summary of Stephen Covey’s Best Selling BookFrom EverandSummary: The 7 Habits Of Highly Effective People … In 15 Minutes The Super-Human Summary of Stephen Covey’s Best Selling BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument20 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleHR Syscore100% (8)
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument9 pagesThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleRomy Wacas100% (7)
- 7habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument249 pages7habits of Highly Effective PeopleVisesh95% (20)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People ComboDocument33 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People ComboPassionate_to_Learn67% (6)
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument204 pagesThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective Peopletvalleys80% (10)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument34 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleLucu100% (2)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People - Snapshots Edn - Stephen R. Covey (2014)Document45 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People - Snapshots Edn - Stephen R. Covey (2014)Nashwa Saad85% (26)
- 7 Habits SummaryDocument34 pages7 Habits Summarydeo1532100% (1)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument32 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective Peopleswetha1210862223100% (5)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument12 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleHazem Mostafa100% (1)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument41 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective Peopleneelam_hotmaleNo ratings yet
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument93 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleImran Malik88% (25)
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective TeensDocument27 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective Teensluckieman100% (6)
- The 7 Habbits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument12 pagesThe 7 Habbits of Highly Effective PeopleVinay Pandey100% (1)
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument125 pagesThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleKhairil Azni100% (3)
- Principal Centred Leadership - Covey.ebsDocument6 pagesPrincipal Centred Leadership - Covey.ebsAbebe MenedoNo ratings yet
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective FamiliesDocument7 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective Familiesalimehdi110100% (2)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument7 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleANUPAM83% (6)
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective People by Stephen R. CoveyDocument172 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective People by Stephen R. CoveyRadhika81% (42)
- Atomic HabitsDocument31 pagesAtomic HabitsRafaelOliveira100% (23)
- Principle-Centered Leadership Key TakeawaysDocument32 pagesPrinciple-Centered Leadership Key TakeawaysypraviNo ratings yet
- The Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument12 pagesThe Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleHiten BishtNo ratings yet
- Press KitDocument36 pagesPress KitHerson Mata100% (2)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument25 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleSheraz Khan100% (1)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument78 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleIslam AdelNo ratings yet
- 7 Habits CompetenciesDocument2 pages7 Habits Competenciesrahulkalia50% (2)
- 7habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument30 pages7habits of Highly Effective PeopleumaNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument10 pagesA Critical Review of The 7 Habits of Highly Effective Peopledniolet60% (5)
- Tools of Titans PDF Summary FromDocument43 pagesTools of Titans PDF Summary Fromgallardos10100% (9)
- Brief Summary of Atomic HabitsDocument16 pagesBrief Summary of Atomic Habitsgeorgemlima100% (4)
- 12 Rules For Life - An Antidote To ChaosDocument1 page12 Rules For Life - An Antidote To ChaosPrashanth Bangalore83% (12)
- 12 Rules for Life Book SummaryDocument8 pages12 Rules for Life Book SummaryGaurav Chauhan75% (4)
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective People SummaryDocument27 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective People Summarymukesh427No ratings yet
- 75 How To Stop Worrying and Start Living PDFDocument6 pages75 How To Stop Worrying and Start Living PDFFelimon Megerssa100% (2)
- Drive Book SummaryDocument2 pagesDrive Book SummaryTarheel668100% (2)
- The Golden BookDocument7 pagesThe Golden Bookalcastillom100% (4)
- Book Review: Pooja Sanjeev Jagtap Roll No.20 MHRDM (2015-2018)Document25 pagesBook Review: Pooja Sanjeev Jagtap Roll No.20 MHRDM (2015-2018)Pooja100% (3)
- 4 Disciplines of ExecutionDocument65 pages4 Disciplines of ExecutionEunice ManayagNo ratings yet
- 4 Disciplines of ExecutionDocument44 pages4 Disciplines of Executiondjdeeablo100% (12)
- Covey Stephen - The Seven Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument172 pagesCovey Stephen - The Seven Habits of Highly Effective Peoplemikyboy777100% (6)
- Atomic Habits - Text SummaryDocument14 pagesAtomic Habits - Text Summaryapi-48921266495% (38)
- The 4 Disciplines of Execution (4DX)Document24 pagesThe 4 Disciplines of Execution (4DX)svredkar100% (5)
- Atomic Habits 1KAD Multi MM Content PlanDocument1 pageAtomic Habits 1KAD Multi MM Content PlanSarah Nurraysa10% (10)
- Emotional Intelligence 2.0Document7 pagesEmotional Intelligence 2.0easy_astronaut100% (4)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument4 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleMahwish Zia100% (1)
- "How To Win Friends and Influence People" Cheat SheetDocument2 pages"How To Win Friends and Influence People" Cheat Sheetthe_schmave95% (21)
- Steven R. Covey’s The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change | SummaryFrom EverandSteven R. Covey’s The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change | SummaryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary of Tiny Habits: The Small Changes That Change Everything by BJ Fogg PhD (Fireside Reads)From EverandSummary of Tiny Habits: The Small Changes That Change Everything by BJ Fogg PhD (Fireside Reads)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Summary of Radical Candor: Be a Kick-Ass Boss Without Losing Your HumanityFrom EverandSummary of Radical Candor: Be a Kick-Ass Boss Without Losing Your HumanityRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Actionable Summary Part 2 of The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People by Stephen R. CoveyFrom EverandActionable Summary Part 2 of The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People by Stephen R. CoveyNo ratings yet
- Seven Habits of Highly Effective People TEXTDocument10 pagesSeven Habits of Highly Effective People TEXTFahrettin OnderNo ratings yet
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People PDFDocument23 pagesThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People PDFSuchat KotcheapNo ratings yet
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument9 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective Peopleneha galaNo ratings yet
- 7 Habit of Highly Effective People - WordDocument5 pages7 Habit of Highly Effective People - WordHR Syscore100% (1)
- The Key to Successful LivingDocument142 pagesThe Key to Successful Livingfajrialbantani9886100% (3)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDocument15 pages7 Habits of Highly Effective PeoplePhượng LêNo ratings yet
- PDF: Outsourcing Delivery Model For Avaiation Industry To IndiaDocument23 pagesPDF: Outsourcing Delivery Model For Avaiation Industry To IndiaRaj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Brand Personality Assignment For Nike and AmulDocument3 pagesBrand Personality Assignment For Nike and AmulRaj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- CAS 1-Classification of CostDocument27 pagesCAS 1-Classification of CostVivekanand100% (2)
- Itie Ass1 - Group 5 - Div C - FinalDocument6 pagesItie Ass1 - Group 5 - Div C - FinalRaj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Apriori Algorithm Explained in 40 CharactersDocument23 pagesApriori Algorithm Explained in 40 CharactersRamdhaniNo ratings yet
- Abm Trial Balance ActivityDocument3 pagesAbm Trial Balance ActivityRoxanne RoldanNo ratings yet
- Public Arrest Report For 22jan2016Document4 pagesPublic Arrest Report For 22jan2016api-214091549No ratings yet
- CV Program Coordinator NigeriaDocument8 pagesCV Program Coordinator NigeriaCV Program CoordinatorNo ratings yet
- Advance NewsletterDocument14 pagesAdvance Newsletterapi-206881299No ratings yet
- Jmeter Performance Testing Your Webapp 1203622239433273 3Document12 pagesJmeter Performance Testing Your Webapp 1203622239433273 3pallavi91No ratings yet
- Sp8300 Part CatalogoDocument111 pagesSp8300 Part CatalogoLeonard FreitasNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternMarc Johnuel HumangitNo ratings yet
- Bosley Declaration - FTC VemmaDocument69 pagesBosley Declaration - FTC VemmaThompson BurtonNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Chapter Six Human Resources Processes With ERPDocument39 pagesConcepts in Enterprise Resource Planning: Chapter Six Human Resources Processes With ERPasadnawazNo ratings yet
- Jabiru Inc S Senior Management Recently Obtained A New Decision Support DatabaseDocument1 pageJabiru Inc S Senior Management Recently Obtained A New Decision Support DatabaseDoreenNo ratings yet
- Aartv Industrial Training ReportDocument48 pagesAartv Industrial Training ReportRupal NaharNo ratings yet
- Revision Question 2023.11.21Document5 pagesRevision Question 2023.11.21rbaambaNo ratings yet
- Final Eligible Voters List North Zone 2017 118 1Document12 pagesFinal Eligible Voters List North Zone 2017 118 1Bilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- ABE College Manila. 2578 Legarda Avenue Sampaloc, ManilaDocument11 pagesABE College Manila. 2578 Legarda Avenue Sampaloc, ManilaRonalie SustuedoNo ratings yet
- Introducing Global PoliticsDocument8 pagesIntroducing Global PoliticsMeann Joy BaclayonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document28 pagesChapter 10ahmedNo ratings yet
- SafeCargo PDFDocument76 pagesSafeCargo PDFSyukry MaulidyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document30 pagesChapter 5فاطمه حسينNo ratings yet
- Prova ScrumDocument11 pagesProva ScrumJoanna de Cassia ValadaresNo ratings yet
- 4563Document58 pages4563nikosNo ratings yet
- Income from Business and Profession Section 28,29&30Document14 pagesIncome from Business and Profession Section 28,29&30imdadul haqueNo ratings yet
- E No Ad Release NotesDocument6 pagesE No Ad Release NotesKostyantinBondarenkoNo ratings yet
- Role of Commercial Banks in Developing The Economy of PakistanDocument40 pagesRole of Commercial Banks in Developing The Economy of PakistanIshtiaq Ahmed84% (25)
- Theory of Elinor OstromDocument5 pagesTheory of Elinor OstromSanjana KrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- The crucial step to a great careerDocument96 pagesThe crucial step to a great careerVinod ThukarulNo ratings yet
- United States v. James Lonzo Turner and Kevin Orlando Moore, 120 F.3d 271, 10th Cir. (1997)Document4 pagesUnited States v. James Lonzo Turner and Kevin Orlando Moore, 120 F.3d 271, 10th Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Specification For Temporary Electrical Supplies For Construction & Maintenance WorkDocument27 pagesSpecification For Temporary Electrical Supplies For Construction & Maintenance WorkvisakhgsNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Optimal Placement of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations A ReviewDocument5 pagesTechniques For Optimal Placement of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations A Reviewkumar_ranjit6555No ratings yet
- Neeraj Kumar: Nokia Siemens Networks (Global SDC Chennai)Document4 pagesNeeraj Kumar: Nokia Siemens Networks (Global SDC Chennai)Kuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Relocation Guide Version 5.6 - New BrandingDocument29 pagesRelocation Guide Version 5.6 - New BrandingEndika AbiaNo ratings yet