Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buddhistarchitecturestupafinal 140203122849 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
Abhinil MathewOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Buddhistarchitecturestupafinal 140203122849 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
Abhinil MathewCopyright:
Available Formats
BUDDHIST ARCHITECTURE
BILAL KHAN
BHURA UMAIR
IQBAL ZAFAR
JYOTI YADAV
MOHD. RAGHIB
OMID PAKSIMA
TABISH IFTEKHAR
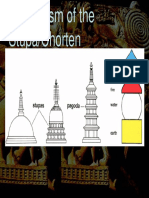
STUPA
INTRODUCTION
STUPA IS MOUND OF THE EARTH ENCLOSING A
RELICCAN BE COMPARED WITH THE MASSIVE FORM
OF THEGREAT PYRAMIDS OF EGYPT
THEY ALSO CALLED AS THUPPA IN PALI, DAGABA
INSIMBALI, TOPE IN ENGLISH & DHATUGRABH IN
SANSKRIT.(DHATUGRABH=RELICS PRESERVED IN
VESSEL
CLASSIFIED INTO THREE TYPES1.
SARIKA STUPA
PARIBHOJIKA STUPA
UDDESHIKA STUPA
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF STUPA
HARMIKA
ANDA
MEDHI
UPPER
PRADAKSHINA
PATH
LOWER
PRADAKSHINA
PATH
STUPA PLANNING
Sanchi Stupa is located 40 km north east of Bhopal, and 10 km from Besnagar and Vidisha in the
central part of the state of Madhya Pradesh.
Sanchi Stupa was built by Ashoka (273-236 B.C.)
Sanchi Stupas is located on the top of the Sanchi hill, which raise about 100M high above the plain.
The 'Great Stupa' at Sanchi is the oldest stone structure in India
SANCHI STUPA
LOCATION
Stupas were erected over the sacred relics of the monks and worshiped with great reverence.
They are therefore known as Relic-Shrines.
SITE PLANNING
The stupa more then a funeral mound was planned like a Vedic village
Great Stupa, Sanchi (Madhya Pradesh)
SITE PLANNING
The spherical dome symbolized the infinite
space of the sky, abode of God. The dome is
called as anda or egg or.
The dome is a solid brick work is 36.60M in
dia, and 16.46M high.
a large hemispherical dome which is flat at
the top, and crowned by a triple umbrella or
Chattra on a pedestal surrounded by a
square railing or Harmika.
a railing enclosed called Vedica which is
about 3.35 M high leaving an ambulatory
passage or pradikshina path with the
gateways.
At the base of the dome is a high circular
terrace probably meant for parikrama or
circumambulation and an encircling
balustrade.
The terrace (midi) 4.87M high from the
ground was added thus creating a separate
and upper ambulatory passage 1.8M wide.
There are four gateways known as Toronas
at the cardinal points of the campus.
Toronas built by ivory or metal worker.
Plan and elevation of Sanchi Stupa
Torona consist of 2 square upright columns with capitals or lion of elephant
heads denoting strength.
These columns support three separate horizontal panels between each of
which is row of ornamental balusters.
The panels have volutes at their terminal ends surmounting with animal
sculpture.
The top panels is crowned with Tri-Ratna symbol of the Buddhist trinity,
Buddha, the law (dharma) and monastic community (sangha) with wheels of justice
in the centre which rest on elephant shaped pedestal.
The total height of this erection is about 10. 36M with a width of 3M.
The Gateway Torona
Ashok
chakra
Steps leading to upper ambulatory
Lower Ambulatory 3.35 m. high
Harmika or triple umbrella
Upper Ambulatory
1.8m wide3.35m high
Stone vedica
Suchi 60 cm dia
Urdhava patas
45cm dia
60-90 cmc/c
Ushnisha
FEATURES
View of Torna from
upper ambulatory
Elephants and Yakshi of the Eastern Torana, Great
Stupa, Sanchi, mid-1st century BC - AD 1st century
Front View of sanchi stupa
Front View of Torna
Column of Torna
STUPA AT SARNATH-Dharmaksha stupa
built in 7
th
centaury
a commemorative Stupa,
situated 6.5KM to the north of
Benares.
built by Ashoka and later rebuilt in the
Gupta period.
The Stupa consist of large tower built
in stone masonry at the basement for a
height of 13M and in brick masonry
above for a height 34M.
The facing of stone basement has 8
niches,
a line of sculptured ornaments.run
below it
these niches were mostly provided to
erect Buddhas statue. Delicately carved
with beautiful floral and geometrical
patterns.
Site Map
STUPA AT SARNATH
Stupa at Sarnath of Present days
Stupa at Sarnath at 1843
Ornamentation
STUPA AT SARNATH
CHAITYAS
THE PRAYER HALL OR BUDDHIST TEMPLE & USUALLY
REFFERED TO AS THE CHAITYA HALL
CHAITYAS ARE THE HALLS ENCLOSING THE STUPAS.
A CHAITYA-GRIHA BUDDHIST CAVE (STUPA HALL) IS A
MEETING OR ASSEMBLY CHAMBER OFTEN USED FOR
PURPOSES SIMILAR TOA STUPA.
ARCHITECTURALLY THEY SHOW SIMILARITIES TO
ROMAN DESIGN CONCEPTS OF COLUMN AND ARCH.
FEATURES OF CHAITYYAS
A LARGE HORSESHOE-SHAPEDWINDOW, THE CHAITYA-
WINDOW, WAS SET ABOVE THE ARCHED DOOR WAY.
THE WHOLE PORTICO-AREA WAS CARVED TO IMITATE A
MULTI-STOREYED BUILDING WITH BALCONIES AND
WINDOWS.
THE COLUMNS SLOPED INWARDSIN THE IMITATION OF
WOODENCOLUMNS THAT WOULD HAVEBEEN STRUCTU
RALLY NECESSARY TO KEEP A ROOF UP
HORSESHOE-SHAPED WINDOW
You might also like
- Buddhist ArchitectureDocument26 pagesBuddhist ArchitectureMomitha_MohanNo ratings yet
- Bhudhist Archiecture FinalDocument38 pagesBhudhist Archiecture FinalUtsavNo ratings yet
- Indian Most SculptureDocument62 pagesIndian Most SculptureKumaran ThanthondiNo ratings yet
- Stupas in Different Parts of The WorldDocument41 pagesStupas in Different Parts of The WorldSwapnil DahaleNo ratings yet
- Stupas 100211074024 Phpapp01Document17 pagesStupas 100211074024 Phpapp01AADIL AHMED ANo ratings yet
- Stupas AND ViharasDocument17 pagesStupas AND ViharasAADIL AHMED ANo ratings yet
- Hindu ArchitectureDocument30 pagesHindu ArchitecturedeepakdodeNo ratings yet
- Buddhist ArchitectureDocument26 pagesBuddhist ArchitectureArjun BishoyiNo ratings yet
- The Great StupaDocument14 pagesThe Great Stupanikita100% (1)
- Stupas Abhishekabhinavsagar 150220015148 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument30 pagesStupas Abhishekabhinavsagar 150220015148 Conversion Gate02 PDFVishnu BhusalNo ratings yet
- Class 6 - Buddhist ArchitectureDocument44 pagesClass 6 - Buddhist ArchitectureRithas Mohammad PKNo ratings yet
- BuddhistDocument40 pagesBuddhistNavdeep ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Dravidian - Chola ArchitectureDocument27 pagesDravidian - Chola ArchitectureSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- L4 - The Sunga & Andhras Period-4Document48 pagesL4 - The Sunga & Andhras Period-4crazy 4No ratings yet
- Carle Cave Architecture: Patna University, PatnaDocument3 pagesCarle Cave Architecture: Patna University, PatnaTanishq SinghNo ratings yet
- Carle Cave Architecture: Patna University, PatnaDocument3 pagesCarle Cave Architecture: Patna University, PatnaTanishq SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian Temple Architecture - Buddhist-1Document80 pagesIndian Temple Architecture - Buddhist-1Harshitha VNo ratings yet
- Chaityas and ViharasDocument14 pagesChaityas and ViharasAswani BhupathiNo ratings yet
- Buddhist ArchitectureDocument16 pagesBuddhist Architecturesandhya bandhuNo ratings yet
- Buddhist ArchitectureDocument10 pagesBuddhist ArchitectureBhagyashri BadigerNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Architecture in IndiaDocument41 pagesBuddhist Architecture in IndiaAditi Shaw100% (2)
- StupaDocument15 pagesStupanyana varaNo ratings yet
- Temple ArchitectureDocument17 pagesTemple ArchitectureSanjana GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- BuddhistDocument20 pagesBuddhistKranthiNo ratings yet
- Buddhist-Jain - Vedic ArchitectureDocument33 pagesBuddhist-Jain - Vedic ArchitecturelatikaNo ratings yet
- Brihadeshvara TempleDocument7 pagesBrihadeshvara TempleSandra MosesNo ratings yet
- History OrissaDocument14 pagesHistory OrissaAdrish NaskarNo ratings yet
- Stupa and Caves in IndiaDocument15 pagesStupa and Caves in IndiaGautam JainNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture - Module 1.1Document15 pagesHistory of Architecture - Module 1.1Noori Dhillon0% (1)
- Nagara StyleDocument42 pagesNagara StylePooja PAdhy50% (2)
- The Sunga & Andhras Period-4Document50 pagesThe Sunga & Andhras Period-4SHristi ShaRmaNo ratings yet
- The Temples of Osian & MT - Abu - Architecture of RajputanaDocument28 pagesThe Temples of Osian & MT - Abu - Architecture of RajputanakomalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 FinalDocument11 pagesChapter 3 FinalEkta ThakurNo ratings yet
- Rastrakuta Architecture: The Rastrakutas of Kanauj and Western Ghats (6Th To 10Th C)Document32 pagesRastrakuta Architecture: The Rastrakutas of Kanauj and Western Ghats (6Th To 10Th C)Varsha KadapattiNo ratings yet
- StupaDocument13 pagesStupaJayant SuriNo ratings yet
- Maurya Art and Sunga ArtDocument5 pagesMaurya Art and Sunga Arts.acharya100% (1)
- Lda253 Chapter 6 The Eastern CivilisattionDocument46 pagesLda253 Chapter 6 The Eastern CivilisattionNURUL NADRAH ROSLINo ratings yet
- StupaDocument15 pagesStupaPurba MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 03 Buddhist Architecture ShaharDocument46 pages03 Buddhist Architecture Shaharalbatroos earlybirdNo ratings yet
- Buddhist ArtDocument22 pagesBuddhist ArtHarish LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Srirangam TempleDocument25 pagesSrirangam TempleChristySindhujaNo ratings yet
- The Buddhist PartDocument14 pagesThe Buddhist PartYeasfi ArafNo ratings yet
- Temple Architecture of OrissaDocument31 pagesTemple Architecture of OrissaJai Belpathak Shejwalkar100% (1)
- E-Book On Buddhist ArchitectureDocument28 pagesE-Book On Buddhist ArchitectureChaarvee BevaraNo ratings yet
- The Wonders of IndiaDocument8 pagesThe Wonders of IndiaKala DeviNo ratings yet
- BuddhistDocument94 pagesBuddhistIsaa JatuNo ratings yet
- Sanchi Stupa in IndiaDocument30 pagesSanchi Stupa in Indiaraja vijjayNo ratings yet
- Monumental Principles of The Buddhist EraDocument40 pagesMonumental Principles of The Buddhist EraRiddhi ShrivastwaNo ratings yet
- Gujrat Temple ArchitectureDocument22 pagesGujrat Temple ArchitectureAdrish NaskarNo ratings yet
- CholasDocument40 pagesCholasTalha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 DravidianDocument27 pagesModule 3 DravidianAswathy Mullakkal Ravindran100% (2)
- 11 Chapter 3Document51 pages11 Chapter 3Kranthi Kumar Chowdary ManamNo ratings yet
- Cultural and Religious Aspects of Sculptures Discovered From Somapura Vihara, Naogaon: A Case Study of Sculptures Displayed at Paharpur Site MuseumDocument37 pagesCultural and Religious Aspects of Sculptures Discovered From Somapura Vihara, Naogaon: A Case Study of Sculptures Displayed at Paharpur Site MuseumrhinemineNo ratings yet
- Meenakshi TempleDocument26 pagesMeenakshi Templeshivani lohiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On PaharpurmahaviharaDocument19 pagesAssignment On PaharpurmahaviharaSaima Binte IkramNo ratings yet
- Dravidian Temple and Indo-Aryan TempleDocument34 pagesDravidian Temple and Indo-Aryan TempleShivani Snigdha100% (1)
- KanganhalliDocument6 pagesKanganhalliGradin JoseNo ratings yet
- The Tämpiṭavihras of Sri Lanka: Elevated Image-Houses in Buddhist ArchitectureFrom EverandThe Tämpiṭavihras of Sri Lanka: Elevated Image-Houses in Buddhist ArchitectureNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument16 pagesInternshipAbhinil MathewNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Sections EditedDocument32 pagesAluminium Sections EditedAbhinil MathewNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics SlidesDocument205 pagesAerodynamics SlidesAbhinil MathewNo ratings yet
- HospitalDocument8 pagesHospitalAbhinil MathewNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Meditation CenterDocument11 pagesBuddhist Meditation CenterAbhinil Mathew100% (1)
- SkripsiDocument101 pagesSkripsiNurul Maharani PutriNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemDocument182 pagesIntroduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemValerie Suge-Michieka100% (1)
- The Discovery of The Tun Huang Library and Its Effect On Chinese StudiesDocument21 pagesThe Discovery of The Tun Huang Library and Its Effect On Chinese Studiesfabricatore_21639575No ratings yet
- WaveDocument5 pagesWaveArijitSherlockMudiNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS PretDocument4 pagesCASE ANALYSIS PretNate Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1955 Fujita - The Magnitude and Distribution of Residual StressDocument25 pages1955 Fujita - The Magnitude and Distribution of Residual StressAKNo ratings yet
- "The Sacrament of Confirmation": The Liturgical Institute S Hillenbrand Distinguished LectureDocument19 pages"The Sacrament of Confirmation": The Liturgical Institute S Hillenbrand Distinguished LectureVenitoNo ratings yet
- Spalding Application SampleDocument5 pagesSpalding Application Sampleapi-66670156No ratings yet
- Nift B.ftech Gat PaperDocument7 pagesNift B.ftech Gat PapergoelNo ratings yet
- Contoh Writing AdfelpsDocument1 pageContoh Writing Adfelpsmikael sunarwan100% (2)
- Growth PredictionDocument101 pagesGrowth PredictionVartika TripathiNo ratings yet
- The Oldest Man - Made Structures On EarthDocument5 pagesThe Oldest Man - Made Structures On EarthDoug Hoseck100% (1)
- Graph Theory and ApplicationsDocument45 pagesGraph Theory and Applicationssubramanyam62No ratings yet
- RCBC Capital Corporation Vs Banco de OroDocument18 pagesRCBC Capital Corporation Vs Banco de OroLove HatredNo ratings yet
- Content 1. Knowing Oneself: Leyte National High SchoolDocument6 pagesContent 1. Knowing Oneself: Leyte National High SchoolMaria Theresa Deluna MacairanNo ratings yet
- 13 19 PBDocument183 pages13 19 PBmaxim reinerNo ratings yet
- Simplified Analysis of 'Out, Out' - Robert FrostDocument3 pagesSimplified Analysis of 'Out, Out' - Robert FrostSANDREA RUTHNo ratings yet
- Knee Jerk Libertarianism by Frank Van DunnDocument9 pagesKnee Jerk Libertarianism by Frank Van DunnLuis Eduardo Mella GomezNo ratings yet
- Taylor Scientific ManagementDocument2 pagesTaylor Scientific ManagementworkingfolksNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Marketing 12th Edition LambDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Marketing 12th Edition Lambangelascottaxgeqwcnmy100% (39)
- Manila Jocky Club Vs CADocument20 pagesManila Jocky Club Vs CAryusuki takahashiNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Roces v. HRETDocument1 page4.5 Roces v. HRETZepht Badilla100% (1)
- MailEnable Standard GuideDocument53 pagesMailEnable Standard GuideHands OffNo ratings yet
- 04 HPGD1103 T1Document24 pages04 HPGD1103 T1aton hudaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Job Performance of Myanmar School TeachersDocument16 pagesThe Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Job Performance of Myanmar School TeachersAmadeus Fernando M. PagenteNo ratings yet
- Personal Entrepreneurial Competencies (Pecs) Self-Rating QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesPersonal Entrepreneurial Competencies (Pecs) Self-Rating QuestionnaireMESIE JEAN PARAL100% (3)
- Data ListDocument239 pagesData Listpriyanka chithran100% (1)
- STaD 01 C 4Document4 pagesSTaD 01 C 4rogeraccuraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Standards For Heart Disease 2010Document59 pagesClinical Standards For Heart Disease 2010Novita Dwi MardiningtyasNo ratings yet
- Neurovascular Holding PointsDocument8 pagesNeurovascular Holding PointsAlexandru Baciu100% (1)