Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design and Analysis of Aircraft Propulsion Systems
Uploaded by
SandeepRajOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design and Analysis of Aircraft Propulsion Systems
Uploaded by
SandeepRajCopyright:
Available Formats
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF
PROPULSION(POWER
PLANT)
By:
Sandeep raj
Contents :
Propulsion
Aircraft engine
Types of Aircraft engine
Aero piston engine
Gas turbine engine
Brayton cycle
Other engines
Electronic Fuel Injection
Propulsion
Propulsion is an energy which creates force from
the engine to make the aircraft move forward.
On airplanes, thrust is usually generated through
some application of Newton's third law of action
and reaction. A gas, or working fluid, is
accelerated by the engine, and the reaction to
this acceleration produces a force on the engine.
Aircraft engine
An aircraft engine is the propulsion unit(power
plant) which generates thrust and pushes the
aircraft to move forward direction to reach
higher level.
Most of the aircraft engines are either run by
the piston engine and gas turbines.
The aircrafts which are powered by piston
engines comes under (Light civil aviation).
Reciprocating engine or IC engine
Most of the piston engines
consists of reciprocating
engines.
It consists of cylinders ,
piston , sparkplug ,crank case
, connecting rod , valves.
Reciprocating engines
operate on a four-stroke
cycle, where each piston
travels from one end of its
stroke to the other four times
.
The cycle is composed of four
operations:
-Intake,
-Compression,
-Expansion (or power),
-Exhaust.
With ignition taking place late
in the compression stroke
and combustion of the fuel-
air charge occurring early in
the expansion.
The reciprocating engines
work on the Otto power
cycle.
Otto Cycle:
Process 1-2 is an adiabatic
compression.
Process 2-3 is a heat
addition at constant
volume(isochoric).
Process 3-4 is an adiabatic
expansion.
Process 4-1 is a heat
rejection at constant
volume.
Types of reciprocating engines
In 1903 after the wright brothers first
successful flight ,the making aircraft engine
has been started.
Basically there are three types of reciprocating
engines.
Rotary engine
In 1918 in world war I where aircrafts were first
being used for military purposes.
It is an early type of IC engine.
It is designed with no. of cylinders per row,
crankshaft remains stationary, entire cylinder
block rotates around it the entire engine rotates
with the propeller which drives plenty of air inside
for cooling purpose.
It can generate up to 80 HP and gave good power
to weight ratio .
Major disadvantage was it became difficult to fly
as it consumed large amount of castor oil .
V shaped
The cylinders were aligned in
two separate planes from each
other tilted at an angle of 30-60
degree, where the crank shaft
holds the both pistons .
Rolls Royce was first to design
the V shaped engines for
aircraft .
V shaped designs gives high
power to weight ratio and high
reciprocating torque or mass .
The famous V12 engine played a
major role in world war II.
Radial
It is similar to the rotary engine where it has
one more set of rows of rotating cylinders
attached to the main crank case .
It gave a favorable power to weight ratio and
smooth running and radials also tends to
cool down the engine evenly.
But the lower cylinders under the crankcase
collected more oil when the engine is
stopped and due its large frontal area ( blunt
shaped ) nose it gave a insufficient
aerodynamics efficiency.
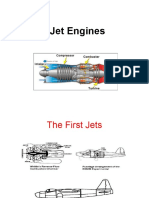
Gas Turbine engines
After world war II
designers dreamed to
invent an engine which
can break the sound
barrier (speed of sound) ,
which led to the discovery
of gas turbine engines
which was called as Jet
engine.
Gas turbine engines work
on Brayton power cycle.
The air enters the compressor gets compressed
and the compressed air enters in to the
combustion chamber,where the fuel and air are
mixed and burnt and passes through the turbine,
exit through nozzle with high acceleration.
Brayton Cycle
Since fresh air enters the compressor at the
beginning and exhaust are thrown out at the end,
this cycle is an open cycle.
By replacing the combustion process by a constant
pressure heat addition process, and replacing the
exhaust discharging process by a constant pressure
heat rejection process, the open cycle described
above can be modified as a closed cycle, called ideal
Brayton cycle. The ideal Brayton cycle is made up of
four internally reversible processes.
1-2 Isentropic compression (in a compressor)
2-3 Constant pressure heat addition
3-4 Isentropic expansion (in a turbine)
4-1 Constant pressure heat rejection
How propulsion takes place?
Aircraft propellers convert rotary motion from piston
engines or turboprops to provide propulsive force.
The propellers are provided with several rows of
spinning blades called Rotors.
As the airflow goes through each row, the air is
accelerated and compressed.
The air after passing through the several rows of
rotors gets compressed. This stage of the engine is
called the Compressor.
The compressed gas enters a Combustion Chamber
where fuel is added an a spark ignites the fuel/air
mixture and this flame is self-sustaining.
The high pressure, high temperature gases exit
from the combustion chamber and expand in the
turbine to generate enough power .
The exhaust gases leave the turbine.
Gas turbine engines are more powerful
and efficient and produce more thrust.
All modern aircrafts do not use
reciprocating engines they use turbine
engines .
Basically there are three types of gas
turbine engines.
Types
1.Turbo jet - The turbojet
uses a series of fan-like
compressor blades to bring
air into the engine and
compress it.
It works with working
fluid(air) consists of inlet
compressor , combustion
chamber , turbine , nozzle.
Turbo jet gives good
efficiency at higher speeds
(800km/h) and high rate of
climb and un interrupted
power supply.
2.Turbo prop- It is a
combination of
propeller engine and
turbo jet engine.
It consists of a propeller
and reduction gear box
in the front to reduce
the speed of rpm.
Works same as turbo jet
it used by mostly
military and also civil
aviation.
3.Turbo fan - It has one or more rows
of compressor blades extend beyond
the normal compressor blades. The
result is that four times as much air is
pulled into the turbofan engine as in
the simple turbojet.
Most of this excess air is ducted
through by passing around the power
section and out the rear with the
exhaust gases.
The turbofan has greater thrust for
takeoff, climbing, and cruising on the
same amount of fuel than the
conventional turbojet engine.
It has the facility of thrust
augmentation like (afterburner, bleed
burner) turbofan engine has gained lot
more popularity then turbo jet.
4. Ram jet - After the achievement of
turbine engines ,designers, engineers
dreamed of building the engine which
could travel at high speeds and reach at
any point on earth in less time. These led
to the development of ramjet, scramjet
engines.
The ramjet engine is the simplest type of
the all-jet engines because it has no
moving parts.
And works by supersonic air flow at inlet.
The sharp edge acts as a diffuser and the
flow get further compressed inside and
reach the combustion chamber where the
fuel and air is mixed and ignited and exits
through converging nozzle.
It can work only at supersonic speeds not
suitable for less then (Mach no.1).
5.Scramjet Super sonic
combustion ramjet engine
works on oblique shock waves.
The shock waves pass through
inlet and get compressed
through deflections occurred
inside the walls and ignited
with fuel and exit through
nozzle.
It can travel more than Mach
no. 10, suitable for hyper sonic
speeds.
Mostly used in space launch
vehicles , supersonic missiles.
Thank You
You might also like
- Parts Manual NDR 030 AD, NR 035 AD, NR 040AD, NR 045 AD, NS 040 AE, NS 050 AE (B815)Document246 pagesParts Manual NDR 030 AD, NR 035 AD, NR 040AD, NR 045 AD, NS 040 AE, NS 050 AE (B815)Erisson60% (5)
- CNC Maintenance Guide for MachinesDocument206 pagesCNC Maintenance Guide for MachinesArjun M Betageri100% (1)
- Perkins M215C and M185C 1006 SeriesDocument2 pagesPerkins M215C and M185C 1006 SeriesDamian Cid Morales100% (1)
- Jet EnginesDocument32 pagesJet EnginesFelichi Dacumos Balajadia50% (2)
- Jet Engine - 1Document21 pagesJet Engine - 1MuhammedNayeemNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Engines: Reciprocating EngineDocument46 pagesAircraft Engines: Reciprocating EngineBadal Machchhar100% (1)
- Powerplant: Dimas Arango Emmauel Hincapie AMT 4 2019Document46 pagesPowerplant: Dimas Arango Emmauel Hincapie AMT 4 2019Emanuel Hincapie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Turbine Gas: Oil Nuclear ReactorDocument65 pagesTurbine Gas: Oil Nuclear ReactorDey TandirerungNo ratings yet
- TURBINE ENGINES HISTORY AND TECHNOLOGYDocument61 pagesTURBINE ENGINES HISTORY AND TECHNOLOGYRay-Ray Carino AraoNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine Propulsion in AircraftDocument43 pagesJet Engine Propulsion in AircraftfadyNo ratings yet
- Propulsion Ancillary System and Gas Turbine (PASGT) : 3AE Julie Mar AyumanDocument74 pagesPropulsion Ancillary System and Gas Turbine (PASGT) : 3AE Julie Mar AyumanColeen BattungNo ratings yet
- Turbine System: Indiana Aerospace UniversityDocument29 pagesTurbine System: Indiana Aerospace UniversityKirito kunNo ratings yet
- Powerplant 2 Module 1 Part 1Document19 pagesPowerplant 2 Module 1 Part 1Santos MaineNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine - 1Document21 pagesJet Engine - 1MuhammedNayeemNo ratings yet
- 4-Stroke Petrol Engine History & DesignDocument19 pages4-Stroke Petrol Engine History & Designvivek8194No ratings yet
- Wankel EngineDocument8 pagesWankel EngineMuhammad Qasim JameelNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Jet Engine: Presented by Deepak Kumar ROLL NO-1120854 Section-M7Document27 pagesSeminar On Jet Engine: Presented by Deepak Kumar ROLL NO-1120854 Section-M7an anNo ratings yet
- 6-Aircraft PropulsionDocument32 pages6-Aircraft PropulsionNeeraj K GahlotNo ratings yet
- Diesel PPDocument58 pagesDiesel PPManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht100% (1)
- Chapter 1 and 2 Lecture Notes - IRISDocument111 pagesChapter 1 and 2 Lecture Notes - IRISSsh keys JoshNo ratings yet
- KeshavDocument23 pagesKeshavDhruv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prop - Unit IDocument64 pagesProp - Unit IsahithiNo ratings yet
- Engine and Motors: Presented by Muhammad Ulul Azmi 10001 Septian Lindhar Listio 10002Document10 pagesEngine and Motors: Presented by Muhammad Ulul Azmi 10001 Septian Lindhar Listio 10002dwi adi santosoNo ratings yet
- Aircraftpropulsion 170811074437 PDFDocument31 pagesAircraftpropulsion 170811074437 PDFHUGO MORANo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoHannah AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Thermal 1unit3Document178 pagesThermal 1unit3NAGU2009No ratings yet
- Presentation Internal Combustion EngineDocument25 pagesPresentation Internal Combustion EngineAbderrazak ZahirNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 - Turbin Gas (2016)Document53 pagesPertemuan 4 - Turbin Gas (2016)Prabowo WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Air PropulsionDocument32 pagesAir PropulsionPramodPradhanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Best PPT On Jet EnginesDocument25 pagesLec 2 Best PPT On Jet Enginesahmet yıldızNo ratings yet
- Propulsion 2 NotesDocument84 pagesPropulsion 2 NotesTAMILSELVAM NALLUSAMY50% (2)
- Jet Aircraft PropulsionDocument133 pagesJet Aircraft PropulsionShubham Jain100% (2)
- Engine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Document27 pagesEngine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Bias PanduNo ratings yet
- Jet Engines: BY:-Karan Prabhakar Aryabhatta CollegeDocument23 pagesJet Engines: BY:-Karan Prabhakar Aryabhatta Collegeمحمد القدوميNo ratings yet
- Jet Engines Explained: Parts, Types & Working PrinciplesDocument3 pagesJet Engines Explained: Parts, Types & Working PrinciplesYemaneDibetaNo ratings yet
- Lecture.6. Агрегаты продувки и наддуваDocument49 pagesLecture.6. Агрегаты продувки и наддуваSea Man MktNo ratings yet
- Aircraft PowerplantsDocument18 pagesAircraft PowerplantsSridhar KanagarajNo ratings yet
- Practical #11: To Study Cutaway Models of Petrol and Diesel Engine Heat EngineDocument9 pagesPractical #11: To Study Cutaway Models of Petrol and Diesel Engine Heat EngineMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Aircraft and Jet Propulsion Systems: Ratan Kumar Rout Regd No.:-1221225081 Mechanical Engg. College:-BCETDocument32 pagesAircraft and Jet Propulsion Systems: Ratan Kumar Rout Regd No.:-1221225081 Mechanical Engg. College:-BCETPramodPradhanNo ratings yet
- LEC# 14. I.C EngineDocument43 pagesLEC# 14. I.C EngineAli Murad JokhioNo ratings yet
- Pplant ReviewerDocument7 pagesPplant ReviewerMikaelarae GermanNo ratings yet
- Jet PropulsionDocument45 pagesJet PropulsionPranay SahuNo ratings yet
- Marine Propulsion Systems GuideDocument63 pagesMarine Propulsion Systems GuidetoshugoNo ratings yet
- Ice CH1 2022-2023Document36 pagesIce CH1 2022-2023AS GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Jet EnginesDocument33 pagesJet EnginesntfaNo ratings yet
- Jet EngineDocument50 pagesJet EngineAnand HariNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine Power Point PresentationDocument15 pagesJet Engine Power Point PresentationHarsh GautamNo ratings yet
- Che422: Fuels and Combustion: Dr. Taqi Mehran Scme, NustDocument53 pagesChe422: Fuels and Combustion: Dr. Taqi Mehran Scme, NustKhizAr Hayat KhizArNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine Chapter 1Document31 pagesInternal Combustion Engine Chapter 1norazwanizaNo ratings yet
- How Does An Internal Combustion Engine Work?Document5 pagesHow Does An Internal Combustion Engine Work?AsraNo ratings yet
- Engines ExplainedDocument64 pagesEngines ExplainedSujithNo ratings yet
- Engines ExplainedDocument40 pagesEngines ExplainedSujithNo ratings yet
- Lecture Jet EngineDocument36 pagesLecture Jet EngineHibbaNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Unit 4 - TDDocument43 pagesIC Engines Unit 4 - TDchincha chuNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument44 pagesIC EnginesIbrahim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Ibrahim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- 4-Valve Engine Guide: Types, Design & Benefits Over 2-Valves/TITLEDocument37 pages4-Valve Engine Guide: Types, Design & Benefits Over 2-Valves/TITLEtarunskumarNo ratings yet
- How A Turbofan Engine Works: By: Matthew ChmielDocument10 pagesHow A Turbofan Engine Works: By: Matthew ChmielPouryaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine ClassificationDocument43 pagesInternal Combustion Engine ClassificationAhmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document33 pagesChapter 7kuma alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Q 1Document34 pagesQ 1SandeepRajNo ratings yet
- 117.218.49.227 DGCIL Conclusion RohitDocument4 pages117.218.49.227 DGCIL Conclusion RohitSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Frigate Flyer Dribble ConveyorDocument1 pageFrigate Flyer Dribble ConveyorSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - MA - QPDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Word - MA - QPSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Drawing1 ModelDocument1 pageDrawing1 ModelSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Marksheet 4th YrDocument1 pageMarksheet 4th YrSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurements andDocument29 pagesMechanical Measurements andsrajapratyNo ratings yet
- DMEDocument52 pagesDMESathya KidduNo ratings yet
- Ankit Final RMP ReportDocument3 pagesAnkit Final RMP ReportSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Drawing1 ModelDocument1 pageDrawing1 ModelSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Online Application - NSPCL 2015 PDFDocument2 pagesOnline Application - NSPCL 2015 PDFSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- RMP TempleteDocument17 pagesRMP TempleteSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2Document6 pagesExperiment No.2SandeepRajNo ratings yet
- B 384 K 94 ApplicationformDocument1 pageB 384 K 94 ApplicationformSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- 5 Lathe PDFDocument74 pages5 Lathe PDFPrakash PednekarNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Manufacturing Using Rapid Prototyping FDMDocument8 pagesFeasibility Study of Manufacturing Using Rapid Prototyping FDMSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Blis-I Semester (Paper B-103 - Library Classification (Practical) ) DuDocument3 pagesBlis-I Semester (Paper B-103 - Library Classification (Practical) ) DuSandeepRaj100% (1)
- Journal of MFGDocument16 pagesJournal of MFGSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- L6 3dtrans PDFDocument12 pagesL6 3dtrans PDFKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- Turn Tapers with Compound Rest, Form Tools, Tailstock OffsetDocument4 pagesTurn Tapers with Compound Rest, Form Tools, Tailstock OffsetSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- 3) 3D TransformationsDocument13 pages3) 3D TransformationsSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Laser Rapid MFG On Vertical SurfacesDocument11 pagesLaser Rapid MFG On Vertical SurfacesSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- (Firstname) (Middle/Initial) (Lastname)Document3 pages(Firstname) (Middle/Initial) (Lastname)SandeepRajNo ratings yet
- BARC Syllabus 2015 For (CSE, ECE, EEE, Civil, Mechanical Engineering) - Recruitment, Result, Application Form, Admit CardDocument4 pagesBARC Syllabus 2015 For (CSE, ECE, EEE, Civil, Mechanical Engineering) - Recruitment, Result, Application Form, Admit CardSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- After Gate Guide 2015Document100 pagesAfter Gate Guide 2015JaydeepRanipaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Service Examinationsdfgh For Government Job - RailElectricaDocument5 pagesEngineering Service Examinationsdfgh For Government Job - RailElectricaSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- CSIR-UGC NET EXAMDocument9 pagesCSIR-UGC NET EXAMVijay KakaniNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0960148107001103 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0960148107001103 MainResearcherzNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Graduate Seeks Entry-Level RoleDocument2 pagesComputer Science Graduate Seeks Entry-Level RoleSandeepRajNo ratings yet
- Victory Rig - LB50-3 ManualDocument75 pagesVictory Rig - LB50-3 ManualLuis CastelanNo ratings yet
- Grove-GMK5275 Product Guide PDFDocument24 pagesGrove-GMK5275 Product Guide PDFMarco Torres HenrriquezNo ratings yet
- Diccionario Mecanico Ingles-EspañolDocument64 pagesDiccionario Mecanico Ingles-EspañolJhon Fernandez67% (9)
- 55: Brakes Handbrake, Brake Shoes, Replacing: 55: Brakes V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D 25/5/2020Document5 pages55: Brakes Handbrake, Brake Shoes, Replacing: 55: Brakes V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D 25/5/2020E MakinenNo ratings yet
- PLTMG Prabumulih 18V34SG Rev.3 PendahuluanDocument39 pagesPLTMG Prabumulih 18V34SG Rev.3 PendahuluanOctavianus HarahapNo ratings yet
- Manuals TVS Star City PlusDocument69 pagesManuals TVS Star City PlusdavidNo ratings yet
- NAFEMS Auto Unified CAE Analysis For A Leaf Spring TypeDocument10 pagesNAFEMS Auto Unified CAE Analysis For A Leaf Spring TypeIndranil BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- AsideDocument16 pagesAsideStephanie JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MSD Ignition TechDocument132 pagesMSD Ignition Techthis oneNo ratings yet
- Supply and usage report for partsDocument8 pagesSupply and usage report for partsajayNo ratings yet
- Chevrolet Cruze BCMDocument4 pagesChevrolet Cruze BCMAndrés Caleb Blanco GuzmanNo ratings yet
- PC200-8 KomatsuDocument636 pagesPC200-8 Komatsujoao maria100% (1)
- MB W115Document183 pagesMB W115mnbvqwert0% (1)
- Engine All (4xWD, CAR, Light Transporter, Smart)Document7 pagesEngine All (4xWD, CAR, Light Transporter, Smart)Tomica TišljarićNo ratings yet
- 250HP 2T - 2004Document0 pages250HP 2T - 2004Ray Cepeda MenaNo ratings yet
- Valvetronic EngineDocument5 pagesValvetronic EngineHafis SayedNo ratings yet
- Maruti SuzukiDocument19 pagesMaruti Suzukianik jainNo ratings yet
- IRC 30D New Qualified Plug-In Electric Drive Motor Vehicle Credit Internal Revenue ServiceDocument1 pageIRC 30D New Qualified Plug-In Electric Drive Motor Vehicle Credit Internal Revenue ServiceJohnNo ratings yet
- Service and Repair Manual: Ao Avtovaz 2001Document214 pagesService and Repair Manual: Ao Avtovaz 2001Ivan73100% (11)
- Waukesha VHP Series EnginesDocument8 pagesWaukesha VHP Series EnginesJhon SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Axle Shafts RearDocument19 pagesAxle Shafts RearCarlos VelázquezNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin Trucks: 2140 05 02 03 Valves and Injectors, AdjustmentDocument19 pagesService Bulletin Trucks: 2140 05 02 03 Valves and Injectors, AdjustmentJ JNo ratings yet
- Oshkosh - SandcatDocument16 pagesOshkosh - SandcatUsNdaomanuNo ratings yet
- Dear Customer,: Combilift LTDDocument53 pagesDear Customer,: Combilift LTDВиталийNo ratings yet
- Seatboat Sample ArticleDocument31 pagesSeatboat Sample ArticleJoseph AlimNo ratings yet
- CDC - Heavy Equipment Daily Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesCDC - Heavy Equipment Daily Inspection ChecklistJonathan CambaNo ratings yet
- r15.v3 Monstar Indo 2020Document56 pagesr15.v3 Monstar Indo 2020Omar SahadatNo ratings yet
- Ge 41 Kva Eagle Pride Power: Power Your Future ZH4100ZDS Ricardo Generator LG30KFDocument3 pagesGe 41 Kva Eagle Pride Power: Power Your Future ZH4100ZDS Ricardo Generator LG30KFRaniaTortueNo ratings yet