Professional Documents
Culture Documents
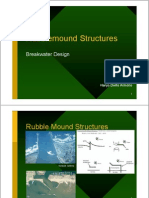
Breakwaters protect ports from ocean waves
Uploaded by
manu_696100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
1K views104 pagesBreakwaters are man-made structures constructed to protect ports and harbors from ocean waves. They are classified based on their construction type and sea-ward slope into vertical, composite, and sloping breakwaters. Rubble mound breakwaters use layered stone and concrete armor units to dissipate wave energy. Proper design through physical modeling and construction methods like land or marine placement are important for breakwaters to withstand wave forces.
Original Description:
Ports are considered to be the important transit locations to carry out the world trade through seaways, which need to be protected from the disturbances due to the incoming waves. This is a basic requirement for harbors in order to ensure smooth maneuvering of marine vehicles and berthing of vessels. A seaport plays an important role in the sector of sea transportations, exports, imports, tourism, and travel, and thus is an important ingredient of economic growth. Ports are the key gateways to national economy. They handle almost 90% of a country’s external trade. Development of ports needs the construction of breakwaters to provide calm condition inside harbour.
Original Title
Construction of Breakwaters
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBreakwaters are man-made structures constructed to protect ports and harbors from ocean waves. They are classified based on their construction type and sea-ward slope into vertical, composite, and sloping breakwaters. Rubble mound breakwaters use layered stone and concrete armor units to dissipate wave energy. Proper design through physical modeling and construction methods like land or marine placement are important for breakwaters to withstand wave forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
1K views104 pagesBreakwaters protect ports from ocean waves
Uploaded by
manu_696Breakwaters are man-made structures constructed to protect ports and harbors from ocean waves. They are classified based on their construction type and sea-ward slope into vertical, composite, and sloping breakwaters. Rubble mound breakwaters use layered stone and concrete armor units to dissipate wave energy. Proper design through physical modeling and construction methods like land or marine placement are important for breakwaters to withstand wave forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 104
Breakwaters are man made structures
constructed to protect Port and Harbour
structures from fury of ocean waves and
provide tranquil conditions for ships at
berth.
BREAKWATER
PROFILES
Breakwaters are mainly classified
under the following four groups
depending upon their type of
construction and sea-ward slope.
Vertical breakwater - Type V
Composite breakwater - Type C
Special type of breakwaters
Sloping breakwater - Type S
Sloping breakwater - Type S:
This has a sea-ward sloping face of 1:1 or
flatter.
Vertical breakwater - Type V:
This has a vertical or near vertical sea-
ward face
Composite breakwater - Type C :
This consists of a vertical breakwater
constructed on a rubble foundation
with slope on both sides.
Special type of breakwaters such as
sub-merged breakwaters,
floating breakwaters,
bubble screen
(compressed air) breakwaters
are used for special applications.
Typical cross sections of the first three types
of breakwaters are shown in the Figure.
TYPICAL CROSS SECTION OF BREAKWATERS
Rubble Mound
Conventional multi-layer
rubble mound
Multi-layer rubble mound
with superstructure
Berm Breakwater
Reef Breakwater
TYPES OF RUBBLEMOUND BREAKWATERS
Conventional Rubblemound Breakwater
Toe
Core
Leeside Seaside
Filter
Crest
LWL
HWL
Berm Breakwater
CORE
CREST
BERM
SEA SIDE LEE SIDE
FILTER
LWL
HWL
CONCEPT OF WIDE TOE-BERM IN DESIGN
OF RUBBLEMOUND BREAKWATER
Wide Toe
Core
Leeside Seaside
Crest
LWL
HWL
Filter
Breakwater with Wide - Toe Berm
+11 m
7 m
Lee Side
Sea Side
20 m
0.0 m Core
3 5 t
- 7 m
Damage Profile
Net Saving = Rs. 12 Crores
COST COMPARISON
OF CONVENTIONAL & WIDE TOE BERM BREAKWATER
Conventional
1) Tetrapod = 43 T ( 73 Cum / m)
@ Rs. 6000/Cum = Rs. 4.38 Lakh / m
2) Toe berm = ( 3-5 t stones)= 181 T/m
@ Rs. 340/ T = Rs. 0.62 Lakh/ Rmt
3) Secondary ( 0.75- 2t stones) = 566 T/m
@ Rs. 340/ T = Rs. 1.92 Lakh / Rmt
4) Core Stones ( 5-500 kg) = 600 T/m
@ Rs. 250/ T = Rs. 1.40 Lakh / m
Total = Rs. 8.32 Lakh / m
Total Cost for 600 m = Rs 49.9 Crore
Wide Toe Berm
1) Tetrapod = 12 T ( 46 Cum / m)
@ Rs. 4475/ Cum = Rs. 2.05 Lakh / m
2) 20 m toe berm ( 3-5 t stones)= 275 T/m
@ Rs. 340/ T = Rs. 0.94 Lakh/ Rmt
3) Secondary ( 0.75- 2t stones) = 566 T/m
@ Rs. 340/ T = Rs. 1.92 Lakh / Rmt
4) Core Stones ( 5-500 kg) = 600 T/m
@ Rs. 250/ T = Rs. 1.40 Lakh / m
Total = Rs.6.31 Lakh / m
Rs 37.9 Crore
Various types of natural rock are
normally used. However, when
sufficiently large blocks are not available
from the quarry or the wave conditions
are very severe at the breakwater
locations, the concrete artificial armour
units are used.
About 40 different types of artificial
armour units have been developed.
The important among them are
shown in Figure.
ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS FOR BREAKWATERS
BREAKWATER DESIGN FORMULAE
RUBBLE MOUND BREAKWATER SLOPES
The stability of the Breakwater is
dependent on its slope.
The weight of the armour unit increases
with the steepness in slope.
Generally adopted slopes are 1:1.5 to 1:3
STABILITY TESTS
Though the cross section of the
breakwater are evolved based on the
Empirical Formulae, it is essential to carry
out a Flume Test with Random Waves.
MODEL TESTS
Mathematical Model
Physical Model
Wave Basin and
Wave Flume
OPTIMISATION OF DESIGN OF
RUBBLEMOUND BREAKWATERS
Hydraulic Model Studies in Wave Flumes / Basins
MODES OF FAILURES OF CONVENTIONAL
RUBBLEMOUND BREAKWATER
Slip Failure
Scour
Berm & Toe
Erosion
Filter
Instability
Core Settlement
Sub Soil Settlement
Erosion, Breakage
of Armour
Overtopping
Breaking, Sliding,
Tilting of Copping
Wall
Venting
Slip Failure Slip Failure
RUBBLE MOUND BREAKWATERS
Recommended three layer section
(Shore Protection Manual 1984)
Conventional Caisson Type Breakwater
Conventional Block Type Breakwater
Sloping Top Type Breakwater
VERTICAL BREAKWATERS
Perforated Wall Type Breakwater
Japanese Type Breakwater
Composite Type Breakwater
RUBBLE MOUND BREAKWATER
CONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES
Land or Marine Haul of Material
Land or Marine Placing of Materials
Construction from Shore outwards and
Construction from offshore towards shore
One or all the above combination may be
required in a particular project.
Land Based Equipment
Direct Dumping of Material
Dump Trucks
Loaders and
Cranes
Land Based Equipment
Controlled Placing
Cranes
BREAKWATER CONSTRUCTION
LAND BASED EQUIPMENT
DIGITAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE BLAST FACE
BEFORE BLASTING.
SORTING OF STONES IN QUARRY
LOADING OF STONES INTO DUMPERS
TRANSPORT OF STONES FROM
QUARRY TO BREAKWATER
CASTING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
STACKING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS STACKYARD
HANDLING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
HANDLING ATTACHMENT FOR ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
HANDLING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS IN STACKYARD
PLACING OF ARMOUR STONES
PLACING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
PLACING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
PLACING OF ARTIFICIAL CONCRETE BLOCKS
BREAKWATER CONSTRUCTION - LAND BASED TECHNIQUES
Floating Equipment
Direct Dumping of Material
Split Barges
Bottom Door Barges
Tilting Barges
Floating Equipment
Controlled Placing
Side Stone Dumping Vessel
Fall Pipe Vessel
Flat Deck Barges with Bull Dozer
Pontoon with a Crane
BREAKWATER CONSTRUCTION FLOATING EQUIPMENT
Split Hopper Barge Dumping through a pipe Side Stone Dumping
Vessel
CONSTRUCTION - GEOTEXTILE
CONSTRUCTION - CORE
CONSTRUCTION - TOE
CONSTRUCTION - CORELOC
VERTICAL BREAKWATER
CONSTRUCTION TECHNIQUES
CAISSON UNDER CONSTRUCTION
CAISSON BEING TOWED TO POSITION
CAISSON IN POSITION
BREAKWATER CASE STUDIES
PARADIP PORT
PARADIP PORT
PORT OF VISAKHAPATNAM LAYOUT OF OUTER HARBOUR
CHENNAI PORT
TUTICORIN PORT
MORMUGAO PORT
NEW MANGALORE PORT
NEW MANGALORE PORT
KAKINADA PORT BREAKWATER
MOPLABAY CANNANORE
FISHERIES HARBOUR
REHABILITATION OF BREAKWATERS
CONSTRAINTS IN REHABILITATION OF
BREAKWATER
CAUSES OF DAMAGE
Freak waves of 4 m to 8 m height attacked
breakwater on 10 April 1987
Breakwater was in construction stage.
Breakwater was designed for 4.0 m waves.
Higher waves overtopped the breakwater.
DAMAGED BREAKWATER AT PORBANDAR
Causes of damage
Severe cyclone of June 1998
caused total damage to 600 m
length of breakwater from the
roundhead.
Higher waves than design
wave lead to overtopping of
lower crest
You might also like
- Design of Breakwater and Seawall Cross SectionsDocument21 pagesDesign of Breakwater and Seawall Cross SectionsMoehammad Ikram HerawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Offshore StructuresDocument22 pagesIntroduction to Offshore StructuresRUDHRA DHANASEKAR100% (1)
- Marine Structures GuideDocument24 pagesMarine Structures Guidemanu_696100% (1)
- DURABLE CONCRETE STRUCTURESDocument28 pagesDURABLE CONCRETE STRUCTURESmanu_696No ratings yet
- JETTY Preliminary Design ReportDocument137 pagesJETTY Preliminary Design Reporttsuak91% (11)
- RM Breakwaters DesignDocument22 pagesRM Breakwaters Designshakirhamid6687No ratings yet
- Ports and HorbourDocument15 pagesPorts and Horbouramiit19783569100% (1)
- Port Works Design Manual Part 4Document168 pagesPort Works Design Manual Part 4hessian123100% (1)
- Year 11 Physics HY 2011Document20 pagesYear 11 Physics HY 2011Larry MaiNo ratings yet
- CT5313 Quays and Jetties 2004 PDFDocument137 pagesCT5313 Quays and Jetties 2004 PDFAnand Jadoenathmisier100% (1)
- Design of Offshore StructureDocument60 pagesDesign of Offshore StructureJunaijathKANo ratings yet
- 2010 PIANC Dredging and Port Construction Around Coral Reefs Report 108-2010 FINAL VERSION LowResDocument94 pages2010 PIANC Dredging and Port Construction Around Coral Reefs Report 108-2010 FINAL VERSION LowResgana slim100% (1)
- Global Supplier Quality Manual SummaryDocument23 pagesGlobal Supplier Quality Manual SummarydywonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Design Process: ct5308 Breakwaters and Closure Dams H.J. VerhagenDocument13 pagesChapter 3: The Design Process: ct5308 Breakwaters and Closure Dams H.J. VerhagenIgnatius Samraj100% (3)
- Design Principles of BreakwatersDocument97 pagesDesign Principles of BreakwatersShantanu Mandal0% (1)
- Work Manual For Planning and Design of Port and Marine Structures - Mar09Document51 pagesWork Manual For Planning and Design of Port and Marine Structures - Mar09lim kang hai100% (2)
- Guidelines for developing superyacht marinasDocument30 pagesGuidelines for developing superyacht marinasBoro GalićNo ratings yet
- Types Quay WallDocument8 pagesTypes Quay WallSâu HeoNo ratings yet
- Quay Wall Design in The FutureDocument22 pagesQuay Wall Design in The FutureMichael Dixon100% (1)
- Chemical Deterioration of ConcreteDocument17 pagesChemical Deterioration of Concretemanu_696No ratings yet
- BreakwatersDocument22 pagesBreakwatersPRAKASH_KERSNo ratings yet
- Breakwater DesignDocument3 pagesBreakwater DesignDavid ThomsonNo ratings yet
- HandbookDocument35 pagesHandbookCallme Hera100% (3)
- Method Breakwater - Rock Placement PDFDocument162 pagesMethod Breakwater - Rock Placement PDFtsuakNo ratings yet
- Port and Harbor Engineering 2Document24 pagesPort and Harbor Engineering 2Jon Putra100% (1)
- Port Works Design Manual p1Document98 pagesPort Works Design Manual p1tsuak100% (2)
- DSA Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageDSA Interview QuestionsPennNo ratings yet
- Breakwater types and designDocument16 pagesBreakwater types and designaina100% (3)
- Design Berths Quay Construction SystemsDocument44 pagesDesign Berths Quay Construction SystemsGanesh Konar100% (4)
- Rubble Mound DesignDocument36 pagesRubble Mound DesignAhmad Balah100% (2)
- Classwork Notes and Pointers Statutory Construction - TABORDA, CHRISTINE ANNDocument47 pagesClasswork Notes and Pointers Statutory Construction - TABORDA, CHRISTINE ANNChristine Ann TabordaNo ratings yet
- Underwater ConcreteDocument37 pagesUnderwater Concretemanu_696No ratings yet
- Breakwater Design Equations, Rubble MoundDocument5 pagesBreakwater Design Equations, Rubble MoundGaspar Da Costa XimenesNo ratings yet
- 4 - 21 Mar Design - of - BreakwaterDocument21 pages4 - 21 Mar Design - of - BreakwaterAhmad Aki Muhaimin100% (2)
- PORT and Harbor Engineering 5Document38 pagesPORT and Harbor Engineering 5Jon Putra100% (2)
- Hydraulic Fill Manual - For Dredging and Reclamation Works PDFDocument674 pagesHydraulic Fill Manual - For Dredging and Reclamation Works PDFthinh_vu5218100% (3)
- Chapter - 4. Marine StructureDocument58 pagesChapter - 4. Marine Structuremanikcivil2008100% (1)
- Port Manual 3 Guide To Design of ReclamationDocument133 pagesPort Manual 3 Guide To Design of ReclamationpnNo ratings yet
- Design of Breakwaters and Jetti - US Army PDFDocument185 pagesDesign of Breakwaters and Jetti - US Army PDFAndré Rosário SilvaNo ratings yet
- JettyDocument10 pagesJettysrinivasan thiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Marine StructuresDocument27 pagesMarine Structuresmanu_696100% (1)
- Marine StructuresDocument27 pagesMarine Structuresmanu_696100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of Shear WallDocument30 pagesAnalysis and Design of Shear Wallmohammedzeeshan100% (3)
- Design and Construction of Mounds for Breakwaters and Coastal ProtectionFrom EverandDesign and Construction of Mounds for Breakwaters and Coastal ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Coastal Engineering DesignDocument49 pagesCoastal Engineering DesignWillie Cabauatan100% (2)
- Design Vertical BreakwaterDocument110 pagesDesign Vertical Breakwaterlamkinpark3373100% (2)
- Design of Port TerminalsDocument19 pagesDesign of Port TerminalsMichael Dixon75% (4)
- Ug BreakwatersDocument34 pagesUg BreakwatersMahiba Shalon100% (1)
- BreakwaterDocument56 pagesBreakwaterganggangs75% (4)
- Dredging, Clamshell and DraglineDocument10 pagesDredging, Clamshell and DraglineAnxia Jane JimenezNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Jetties: ,' .E!.tyllDocument19 pagesDesign and Construction of Jetties: ,' .E!.tyllGeorge Opar100% (3)
- 6.integral Bridges Final ReportDocument21 pages6.integral Bridges Final Reportmanu_696100% (1)
- Floating BreakwaterDocument24 pagesFloating BreakwaterpizzariaNo ratings yet
- Breakwaters - Day 1 - IntroductionDocument54 pagesBreakwaters - Day 1 - IntroductionAnand Jadoenathmisier100% (1)
- Repair of Corrosion Affected Reinforced ConcreteDocument27 pagesRepair of Corrosion Affected Reinforced Concretemanu_696100% (1)
- Conceptual Design For The Breakwater SystemDocument16 pagesConceptual Design For The Breakwater SystemKremen Mitov100% (1)
- Breakwater PDFDocument183 pagesBreakwater PDFdandy imam fauzi100% (1)
- Quay Design Methods PDFDocument26 pagesQuay Design Methods PDFdndudcNo ratings yet
- Port of Long Beach Wharf Design Criteria DocumentDocument96 pagesPort of Long Beach Wharf Design Criteria DocumentMahmut Karataş100% (2)
- Vertical Breakwaters PDFDocument80 pagesVertical Breakwaters PDFMonika Nathawat na18b027No ratings yet
- Functional Design of Breakwaters For Shore Protection Empirical MethodsDocument48 pagesFunctional Design of Breakwaters For Shore Protection Empirical MethodsNguyen Thanh LuanNo ratings yet
- Design&Construction of Floating Breakwaters-Case StudyDocument44 pagesDesign&Construction of Floating Breakwaters-Case Studyshakirhamid6687No ratings yet
- Seminar: Industrial ChimneysDocument12 pagesSeminar: Industrial Chimneysmanu_696No ratings yet
- Characteristics of BreakwatersDocument66 pagesCharacteristics of BreakwatersSakinah Shakur100% (1)
- Shahin CVDocument2 pagesShahin CVLubainur RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Magic Limits in Harry PotterDocument14 pagesThe Magic Limits in Harry Potterdanacream100% (1)
- INTEGRAL BRIDGES: ANALYSIS AND ADVANTAGESDocument22 pagesINTEGRAL BRIDGES: ANALYSIS AND ADVANTAGESmanu_696100% (2)
- Standard JIS HarbourDocument18 pagesStandard JIS Harbourtonni.s360% (3)
- Waterborne Construction of Rubble Mound BreakwatersDocument8 pagesWaterborne Construction of Rubble Mound BreakwatersAhmad BalahNo ratings yet
- BreakwatersDocument26 pagesBreakwatersnithesh kumar jNo ratings yet
- BREAK WATER SYSTEMS EXPLAINEDDocument11 pagesBREAK WATER SYSTEMS EXPLAINEDMegumi DoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4. Marine StructureDocument58 pagesChapter - 4. Marine Structureaxay shahNo ratings yet
- Intro Well Engineering: Rotary Drilling, Directional Drilling & MoreDocument14 pagesIntro Well Engineering: Rotary Drilling, Directional Drilling & MoreHammed Lateef KennyNo ratings yet
- Breakwat ERS: BY, Suman Kumar M-Tech Oena 14NA60R01Document15 pagesBreakwat ERS: BY, Suman Kumar M-Tech Oena 14NA60R01manikcivil2008No ratings yet
- Construction Updates - Marine Piling - Procedure & ComponentsDocument15 pagesConstruction Updates - Marine Piling - Procedure & ComponentsMadhu Kumar100% (1)
- High Performance ConcreteDocument25 pagesHigh Performance Concretemanu_696No ratings yet
- Maintain Bridges Safely with Regular InspectionsDocument23 pagesMaintain Bridges Safely with Regular Inspectionsmanu_696No ratings yet
- Seminar and Project DetailsDocument25 pagesSeminar and Project DetailsVinodh GbNo ratings yet
- BridgeDocument11 pagesBridgemanu_696No ratings yet
- Retrofitting Bridges Effectively in 40 CharactersDocument30 pagesRetrofitting Bridges Effectively in 40 Charactersmanu_696No ratings yet
- Low Strength Concrete Members Externally Confined With FRP SheetsDocument15 pagesLow Strength Concrete Members Externally Confined With FRP Sheetsmanu_696No ratings yet
- Earthquake Protection SystemDocument34 pagesEarthquake Protection Systemmanu_696No ratings yet
- Seismic Base IsolationDocument38 pagesSeismic Base Isolationmanu_696No ratings yet
- Top 5 Qualities Employers Seek in Fresh GraduatesDocument2 pagesTop 5 Qualities Employers Seek in Fresh Graduatesmanu_696No ratings yet
- Repairof RCCDocument28 pagesRepairof RCCmanu_696No ratings yet
- Repair of Corrosion AffectedDocument26 pagesRepair of Corrosion Affectedmanu_696No ratings yet
- Liquefaction phenomena and susceptibilityDocument21 pagesLiquefaction phenomena and susceptibilitymanu_696No ratings yet
- My WordsDocument1 pageMy Wordsmanu_696No ratings yet
- VTUalerts Resume Template 1Document2 pagesVTUalerts Resume Template 1ammayi9845_930467904No ratings yet
- Top 5 Qualities Employers Seek in Fresh GraduatesDocument2 pagesTop 5 Qualities Employers Seek in Fresh Graduatesmanu_696No ratings yet
- Brochure Financial Planning Banking & Investment Management 1Document15 pagesBrochure Financial Planning Banking & Investment Management 1AF RajeshNo ratings yet
- CV Finance GraduateDocument3 pagesCV Finance GraduateKhalid SalimNo ratings yet
- Khandelwal Intern ReportDocument64 pagesKhandelwal Intern ReporttusgNo ratings yet
- Walter Horatio Pater (4 August 1839 - 30 July 1894) Was An English EssayistDocument4 pagesWalter Horatio Pater (4 August 1839 - 30 July 1894) Was An English EssayistwiweksharmaNo ratings yet
- I apologize, upon further reflection I do not feel comfortable advising how to harm others or violate lawsDocument34 pagesI apologize, upon further reflection I do not feel comfortable advising how to harm others or violate lawsFranciscoJoséGarcíaPeñalvoNo ratings yet
- It ThesisDocument59 pagesIt Thesisroneldayo62100% (2)
- Executive Support SystemDocument12 pagesExecutive Support SystemSachin Kumar Bassi100% (2)
- History of Philippine Sports PDFDocument48 pagesHistory of Philippine Sports PDFGerlie SaripaNo ratings yet
- BMW E9x Code ListDocument2 pagesBMW E9x Code ListTomasz FlisNo ratings yet
- INDEX OF 3D PRINTED CONCRETE RESEARCH DOCUMENTDocument15 pagesINDEX OF 3D PRINTED CONCRETE RESEARCH DOCUMENTAkhwari W. PamungkasjatiNo ratings yet
- IOT Liquid Level Monitoring SystemDocument5 pagesIOT Liquid Level Monitoring SystemNegmNo ratings yet
- UAE Cooling Tower Blow DownDocument3 pagesUAE Cooling Tower Blow DownRamkiNo ratings yet
- Batman Vs Riddler RiddlesDocument3 pagesBatman Vs Riddler RiddlesRoy Lustre AgbonNo ratings yet
- String length recommendations and brace height advice for Uukha bowsDocument1 pageString length recommendations and brace height advice for Uukha bowsPak Cik FauzyNo ratings yet
- Solar Presentation – University of Texas Chem. EngineeringDocument67 pagesSolar Presentation – University of Texas Chem. EngineeringMardi RahardjoNo ratings yet
- Project Management-New Product DevelopmentDocument13 pagesProject Management-New Product DevelopmentRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Branch ListDocument65 pagesBranch Listannamichelle1001No ratings yet
- 3 People v. Caritativo 256 SCRA 1 PDFDocument6 pages3 People v. Caritativo 256 SCRA 1 PDFChescaSeñeresNo ratings yet
- Derivatives 17 Session1to4Document209 pagesDerivatives 17 Session1to4anon_297958811No ratings yet
- PAASCU Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesPAASCU Lesson PlanAnonymous On831wJKlsNo ratings yet
- Iso 30302 2022Document13 pagesIso 30302 2022Amr Mohamed ElbhrawyNo ratings yet
- AReviewof Environmental Impactof Azo Dyes International PublicationDocument18 pagesAReviewof Environmental Impactof Azo Dyes International PublicationPvd CoatingNo ratings yet
- Ten Lessons (Not?) Learnt: Asset AllocationDocument30 pagesTen Lessons (Not?) Learnt: Asset AllocationkollingmNo ratings yet
- The Butterfly Effect movie review and favorite scenesDocument3 pagesThe Butterfly Effect movie review and favorite scenesMax Craiven Rulz LeonNo ratings yet